Case 1 Z
-
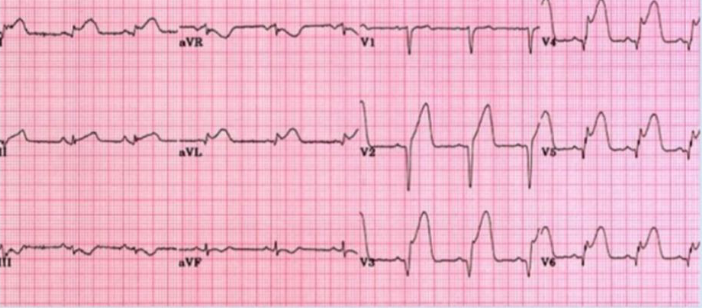
What abnormality do you see in this ECG? ST segment elevation in Lead 1, aVL, V2, V3, V4, V5 and V6
-
What is your clinical diagnosis? Anterolateral ST elevation Myocardial infarction (STEMI)
-
Mention 2 serum markers will you check to confirm your diagnosis? Troponin T and I, CK-MB
-
Mention 3 immediate treatment will you give to this patient? Supplemental O2, Morphine, Aspirin
-
Mention 3 risk factors for this condition? Hyperlipidemia, DM, Obesity, Smoking
Case 2
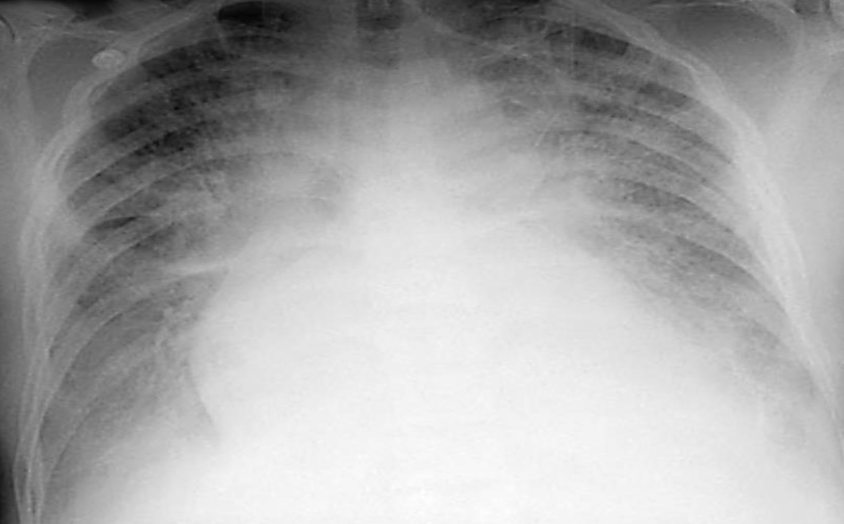 -Chest X ray of a 40 year old man
-HTN since 15 years
-Presents with acute dyspnea
-B.P. : 160/110
-Chest : Bilateral crepts on auscultation
-JVP: Raised
-Chest X ray of a 40 year old man
-HTN since 15 years
-Presents with acute dyspnea
-B.P. : 160/110
-Chest : Bilateral crepts on auscultation
-JVP: Raised
Q1: What’s your clinical diagnosis? Congestive heart failure.
Q2: name 2 abnormal findings in the chest x-ray? Cardiomegaly, pulmonary edema.
Q3: what investigation will give you more information about this cardiac condition? Echo.
Q4: What’s the cause of crepitation on auscultation? Pulmonary edema.
Q5: what immediate treatment will you give to this patient? Name any 2. Lasix, oxygen.
Q6: while this pt is in the ER, in what position should you put him? On 45 degree position.
Case 3
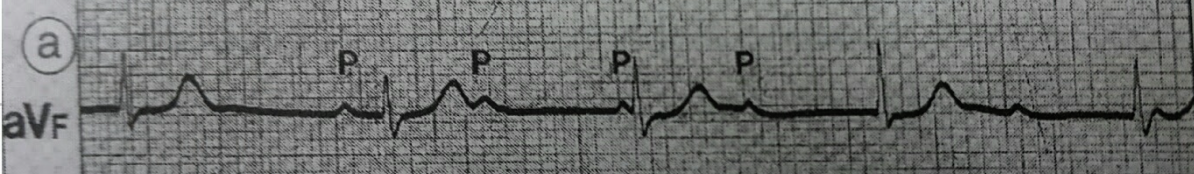 A) What is ur diagnosis?
A) What is ur diagnosis?
Complete heart Block.
B) Treatment? Pacemaker
Case 4
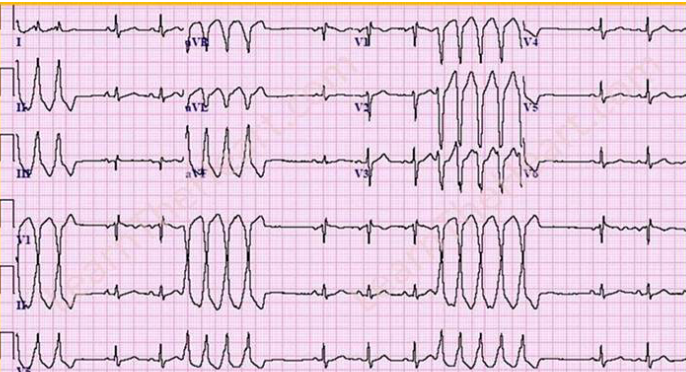 Ventricular Tachycardia - Abnormal QRS complex
Ventricular Tachycardia - Abnormal QRS complex
Case 5 Z
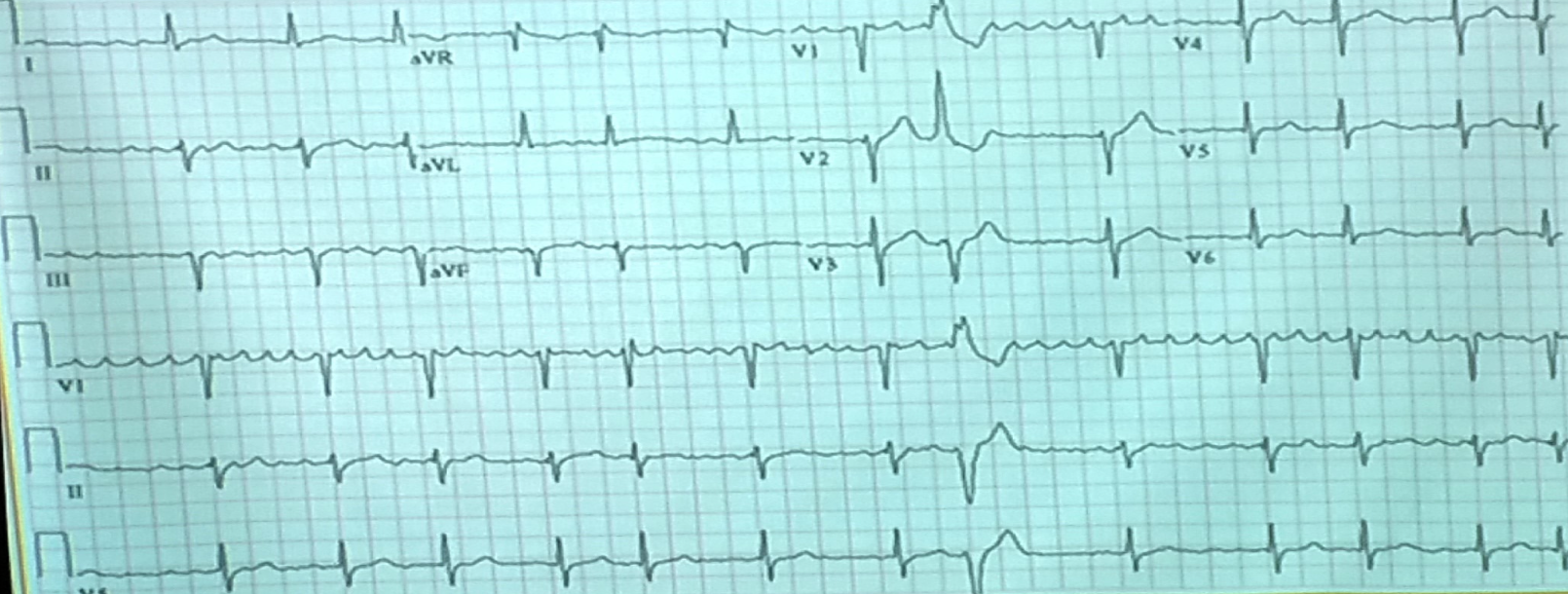
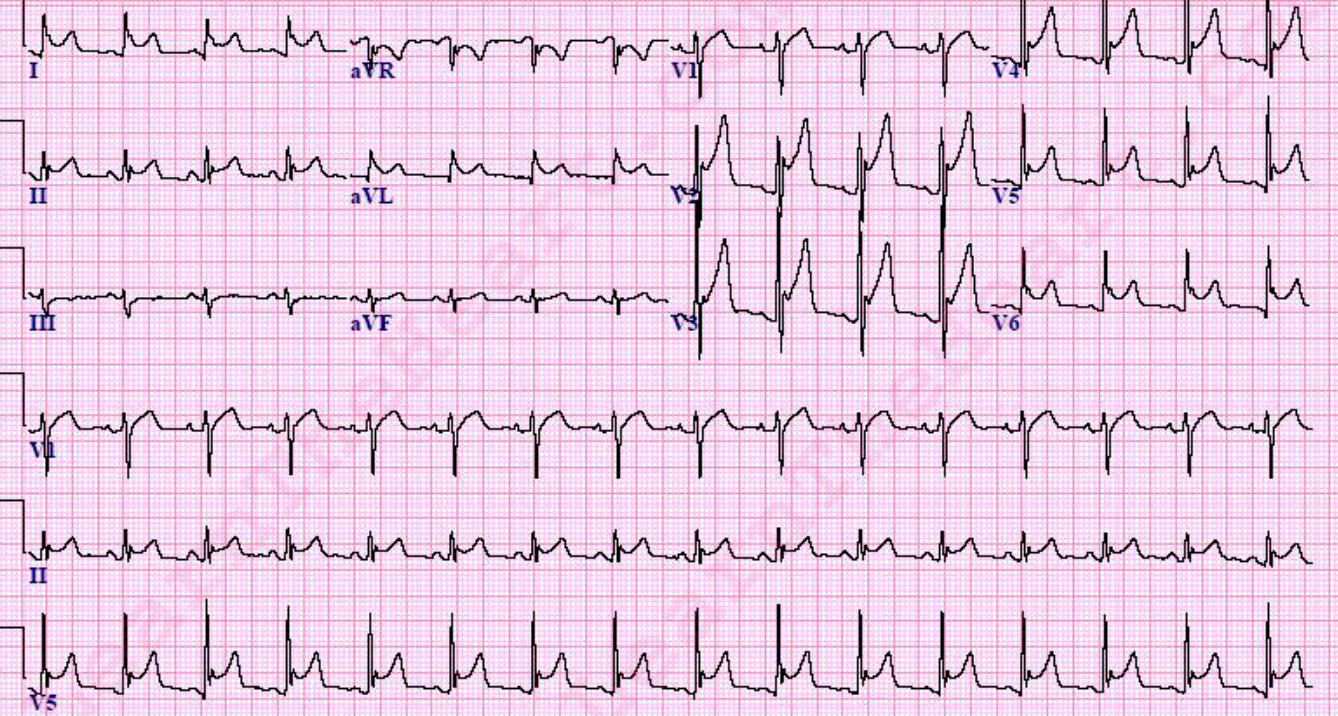
- Describe 2 abnormal features of the ECG?
a. ST elevation
b. Increase PR interval
PR segment depression and ST segment elevation in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF) and precordial leads (V2 V6), most prominent in leads V2 and V3, with reciprocal ST depression in aVL. There are also widespread T wave inversions.
Likely diagnosis is acute pericarditis.
- What is the ECG diagnosis?
a. Pericarditis
| Idiopathic Causes | Other Causes |
|---|---|
| Infectious conditions: - Viral - Bacterial - TB | Cardiovascular disorders: - Acute MI - Dressler syndrome - Aortic dissection |
| Inflammatory disorders: - RA - SLE - Scleroderma - Rheumatic fever | Miscellaneous causes: - Iatrogenic - Neoplasms - Drugs - Irradiation - Cardiovascular procedures - Trauma |
| Metabolic disorders: - Renal failure - Hypothyroidism - Hypercholesterolemia |
Case 6 Z
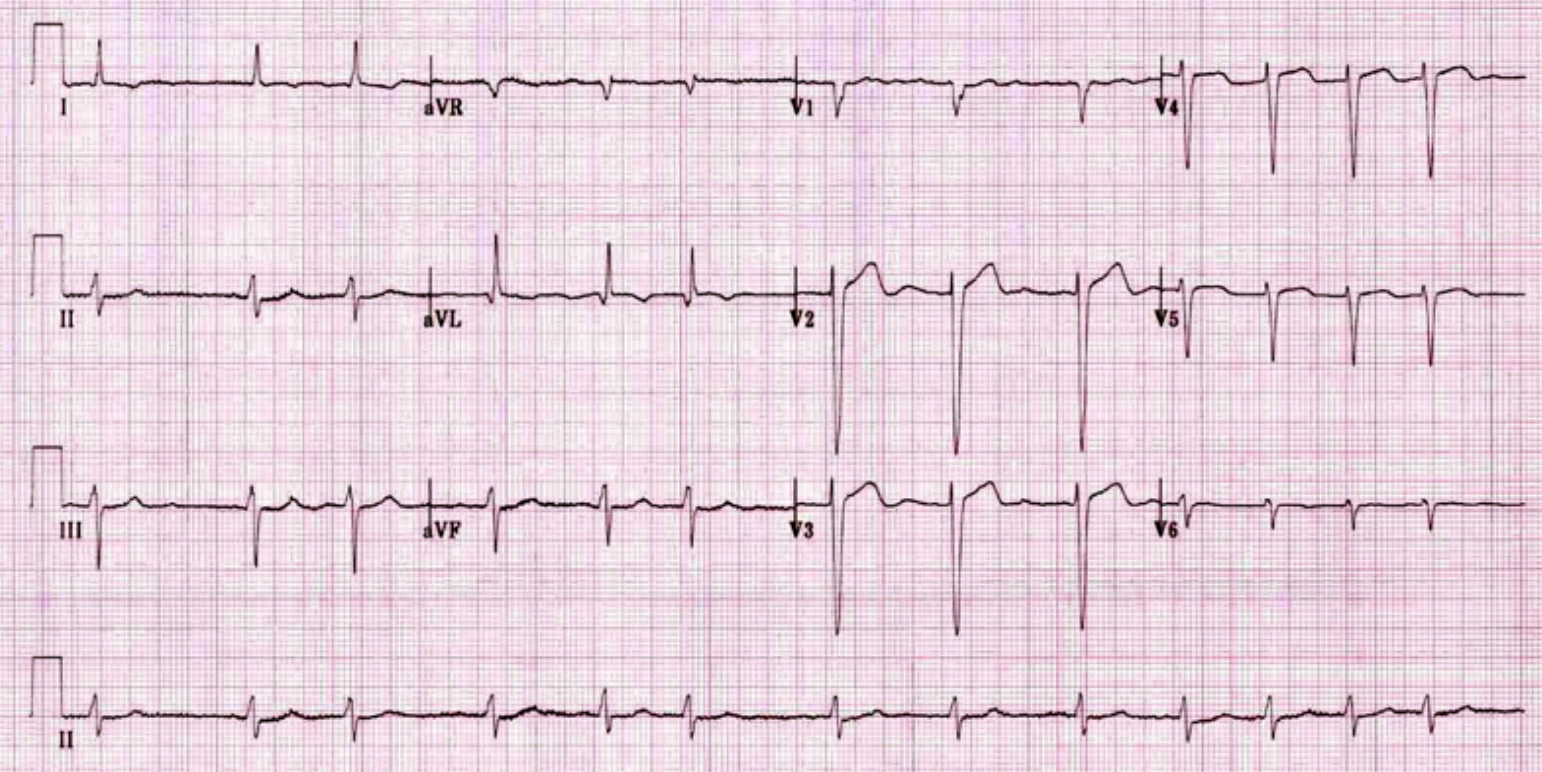
-
Describe the abnormal ECG finding?
p wave absent, irregular rhythm -
What is the diagnosis?
Atrial fibrillation
Case 7
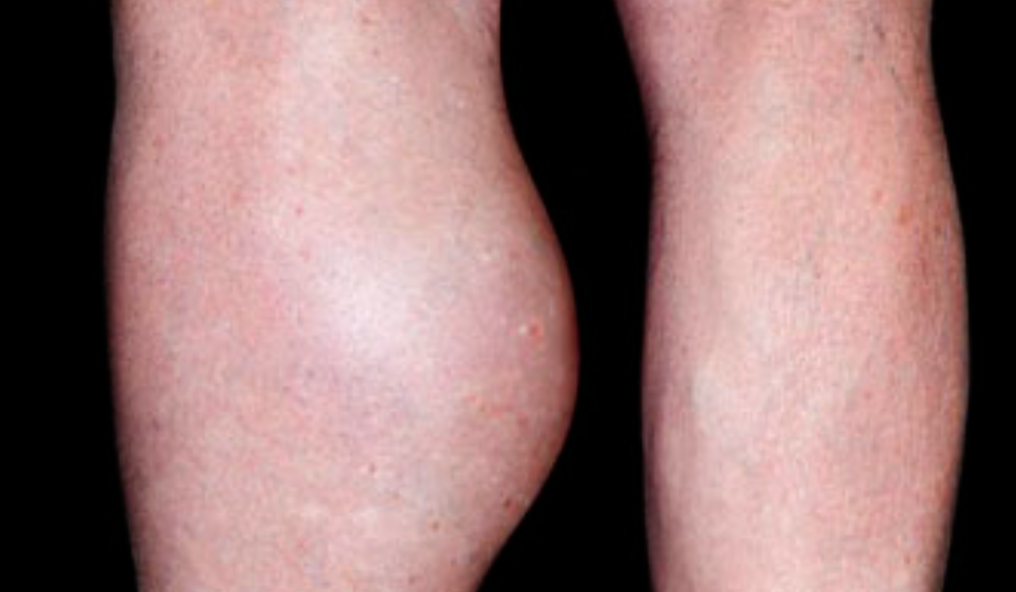
-
What is the likely diagnosis?
a. DVT -
Name 2 differential diagnosis?
a. Hematoma
b. Ruptured backer cyst -
What 2 steps are advised to confirm diagnosis?
a. Doppler UltraSound
b. D dimer test
60 Year old presented with recurrent attacks of syncope
-
What does ECG rhythm strip show?
This would depend on the cause of syncope. Possible findings include bradycardia, tachycardia, heart block, or signs of ischemia. -
What treatment is recommended?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, which needs to be determined through further investigation. It may include medication, pacemaker implantation, or lifestyle changes.
ECG of a man who has chest pain after 5 min of staircase climbing 1. abnormalities? a. Brady cardia (62-65 bpm) b. Prolonged PR interval (7 small squares)
2. Diagnosis? a. NSTEMI b. With Heart block first degree
3.2 further tests? a. Stress test b. Angiography c. echocardiography
STAGES OF HTN
-
Elevated BP: Systolic between 120-130
-
Stage 1 HTN: Systolic between 130-140 +/- diastolic b/w 80 & 90
-
Stage 2: Systolic 140 or more +/- diastolic 90 or more
-
Sometimes, you may need 24 hrs continuous BP monitoring at home ( ambulatory BP monitoring) to diagnose HTN.
Hypertensive Urgency:
- Very high BP. DBP usually >120, but NO acute end organ damage (encephalopathy, angina, papilloedema etc)
Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic usually more than 180 and diastolic more than 120
- Urgency
- Emergency
Hypertensive Emergency:
- Very high BP (SBP > 210, and DBP> 130) + end organ damage begins.
Complications of Hypertension:
- Hypertension is a risk factor
- TIA, stroke
- Retinopathy
- Peripheral vascular disease
- LVH, CHD, HF
- Renal failure
Rx contd.
- First, a trial of diet & exercise for about 2 months ( depending on the BP)
- low salt diet * wt. reduction * exercise
- eat more fruits & vegetables * stop smoking
- Add medicine if the above fails.
- Start with 1 medicine and gradually go to the max. dose
- Give at least 2-3 wks for a medicine to work fully. Then add another medicine if needed.
DRUGS FOR HTN
- Diuretics
- ACE inhibitors
- ARBs (angiotensin receptor blockers)
- Beta blockers
- Ca channel blockers
- Others