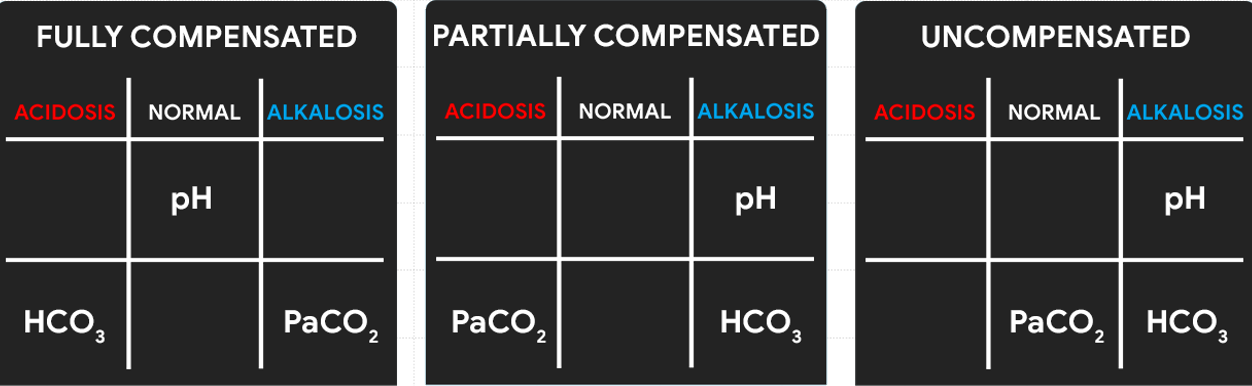
Compensation
Determine the compensation:
- It is FULLY COMPENSATED if pH is normal.
- It is PARTIALLY COMPENSATED if all three (3) values are abnormal.
- It is UNCOMPENSATED if PaCO2 or HCO3 is normal and the other is abnormal.
- Normal Range for pH: 7.35 to 7.45
- Normal Range for PaCO2: 35 to 45
- Normal Range for HCO3: 22 to 26
- Anion Gap: ([Na^+ + K^+] - [Cl^- + HCO_3^-]), normal value = 10–16 mmol/L.
Differential
Here’s a comprehensive table comparison between the variables found in your notes, formatted in Markdown:
| Condition | Description | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Acidosis | Metabolic acidosis may be with increased anion gap or with normal anion gap. An increase in anion gap is due to overproduction or decrease in excretion of acids. A normal anion gap signifies HCO3- loss rather than excess of acids. | With Elevated Anion Gap (MUDPILES): Methanol ingestion, Uremia, Diabetic/alcoholic/starvation ketoacidosis, Paraldehyde ingestion, Isoniazid/salicylate/iron poisoning, Lactic acidosis, Ethylene glycol ingestion. With Normal Anion Gap (HARD-UP): Hyperalimentation, Acetazolamide, Renal tubular acidosis, Diarrhea and diuretics, Uteroenterostomy, Pancreatic fistula. |
| Metabolic Alkalosis | A primary increase in plasma bicarbonate and an increase in plasma pH. | Gastrointestinal loss (e.g., pyloric stenosis), Congenital chloride diarrhea, Furosemide therapy, Cystic fibrosis, Bartter syndrome, Hyperaldosteronism, Excess intake of base (e.g., antacid medicine). |
| Respiratory Acidosis | CO2 is not properly removed by the lungs. | CNS depression (comatose, drug overdose, head injury), Thoracic injury (pneumothorax, flail chest), Airway obstruction (asthma, laryngospasm), Severe pneumonia, Pulmonary edema, Obesity hypoventilation syndrome, Neuromuscular weakness, Interstitial fibrosis. |
| Respiratory Alkalosis | Occurs when the lungs blow off excessive CO2. | Hyperventilation (anxiety, mechanical ventilation), Salicylate toxicity, Hepatic encephalopathy, Hyperthyroidism, Hypoxemia, High altitude, Sepsis (initially hypoventilation). |
Example 1
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.45
- PaCO2: 41
- HCO3: 25
Interpretation: Normal ABG
Example 2
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.30
- PaCO2: 66
- HCO3: 32
Interpretation: Respiratory acidosis partially compensated (HC03)
Example 3
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.26
- PaCO2: 32
- HCO3: 18
Interpretation: Metabolic acidosis partially compensated (PaCO2)
Example 4
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.79
- PaCO2: 24
- HCO3: 21
Interpretation: Respiratory alkalosis partially compensated
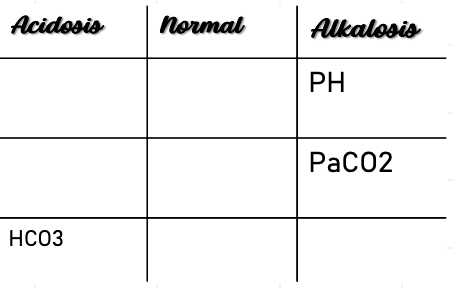
Example 5
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.17
- PaCO2: 35
- HCO3: 12
Interpretation: Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
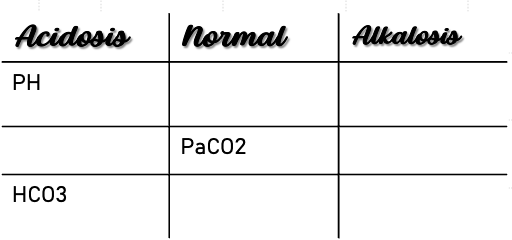
Example 6
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.54
- PaCO2: 24
- HCO3: 25
Interpretation: Uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
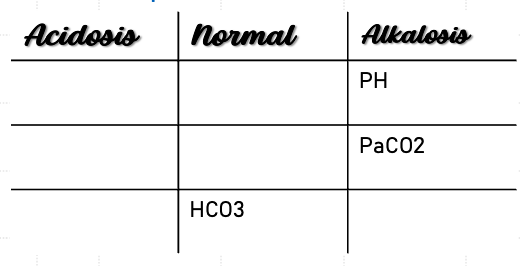
Example 7
ABG Values:
- pH: 7.17
- PaCO2: 50
- HCO3: 15
Interpretation: Mixed metabolic and respiratory acidosis

ABG Analysis
- pH = 7.202 (7.35 - 7.45)
- PaCO2 = 19.8 mmHg (38 - 42 mmHg)
- PaO2 = 86.6 mmHg (75 – 100 mmHg)
- HCO3 = 7.4 mmol/L (22 – 28 mmol/L)
- BE = -18 mmol/L (-2 to +2 mmol/L)
- Sat = 91.5 % (95 - 100%)
Questions
- Describe abnormal findings in the arterial blood gases test?
- Low pH
- Low PaCO2
- Low HCO3
- Low Sat
- What is the likely diagnosis?
- Metabolic acidosis
- Mention 2 possible causes?
- DKA
- Diarrhea
- Renal tubular acidosis
Respiratory Alkalosis
What are the blood gas findings? pH 7.48, pCO2 2.9 kPa, pO2 15.5 kPa, Cl- 100 mM, Na+ 142 mM, K+ 3.2 mM, HCO3- 17 mM.
What is the likely diagnosis? Respiratory alkalosis.
What are the possible causes? Early pneumonia, asthma, mechanical ventilation, psychogenic causes, and drugs like salicylate poisoning.
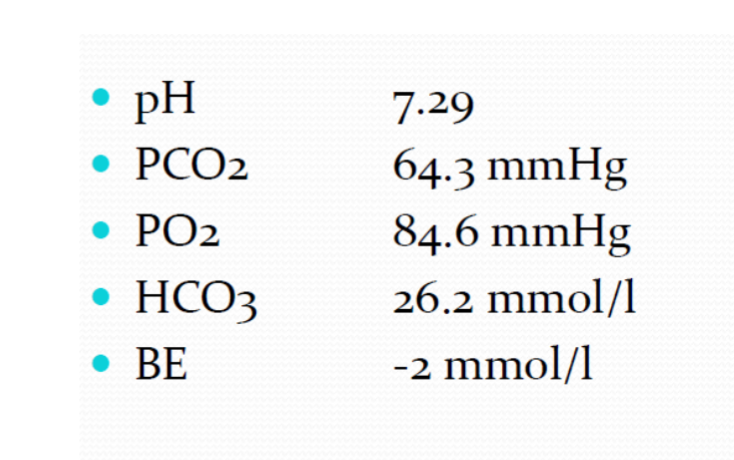
Case
pH abnormality ? Acute respiratory acidosis DDx? severe pneumonia, severe asthma, COPD

Case
pH abnormality ? Metabolic alkalosis DDx? Vomiting

Case
Q1. What is the cause of this baby’s jaundice? Hemolysis due to ABO incompatibility. Q2. What are the complications? Anemia, kernicterus . Q3. What is the treatment ? Blood transfusion, Phototherapy, Exchange transfusion.

Case
Describe 2 abnormalities in the results of serum electrolyte ? Hyponatremia and hyperkalaemia Mention the likely diagnosis? CAH Q3.What are other relevant investigations ? Cortisol level, ACTH level, karyotype Q4. What are the main outlines of treatment for such baby? Cortisol and mineralocorticoid
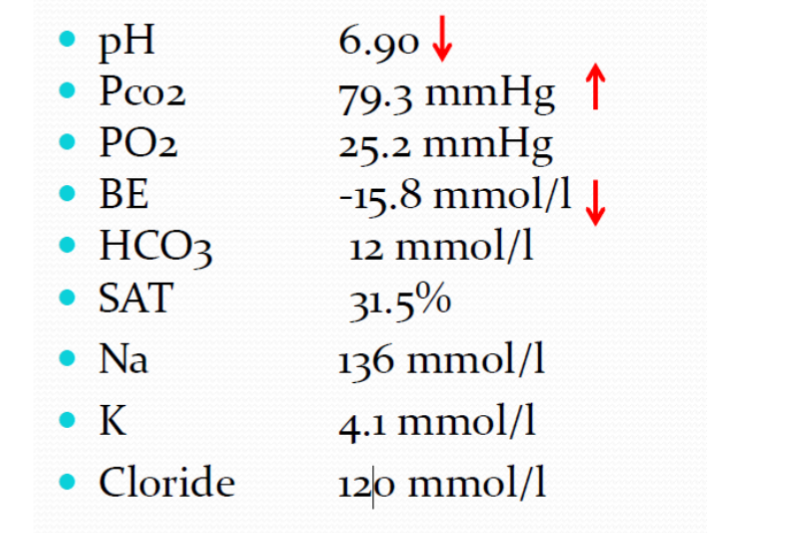
Case
Diagnosis ? Combined respiratory and Metabolic acidosis.