Hemotympanum
- Usually asymptomatic
- May cause conductive hearing loss
- Treated by observation as most cases resolve spontaneously
 type b
type b
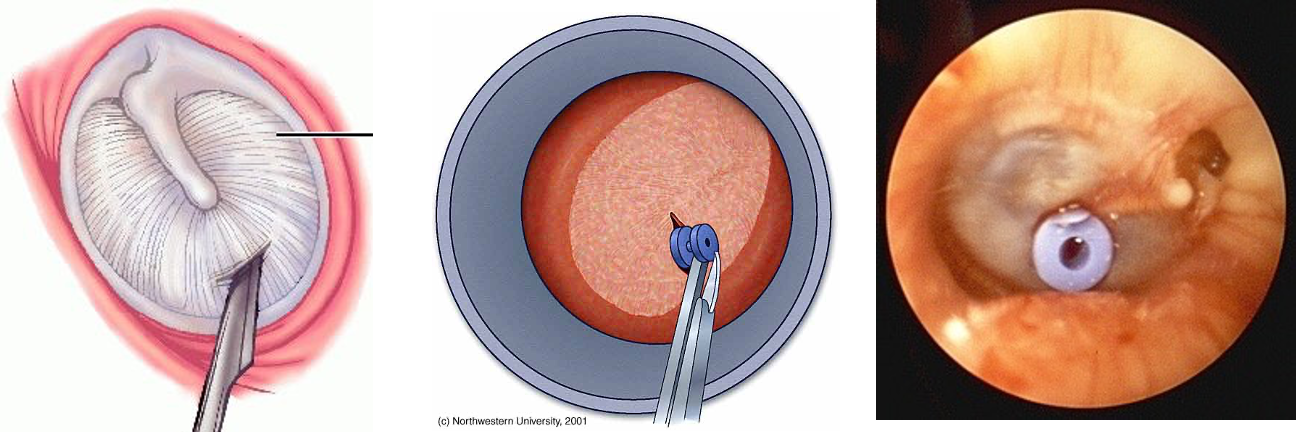
Traumatic Ossicular Disruption
- Suspected if trauma followed by CHL with intact TM
- Diagnosis confirmed by CT and/or surgical exploration (tympanotomy)
- Treatment by surgical repair
 conductive, osteoplasty
conductive, osteoplasty
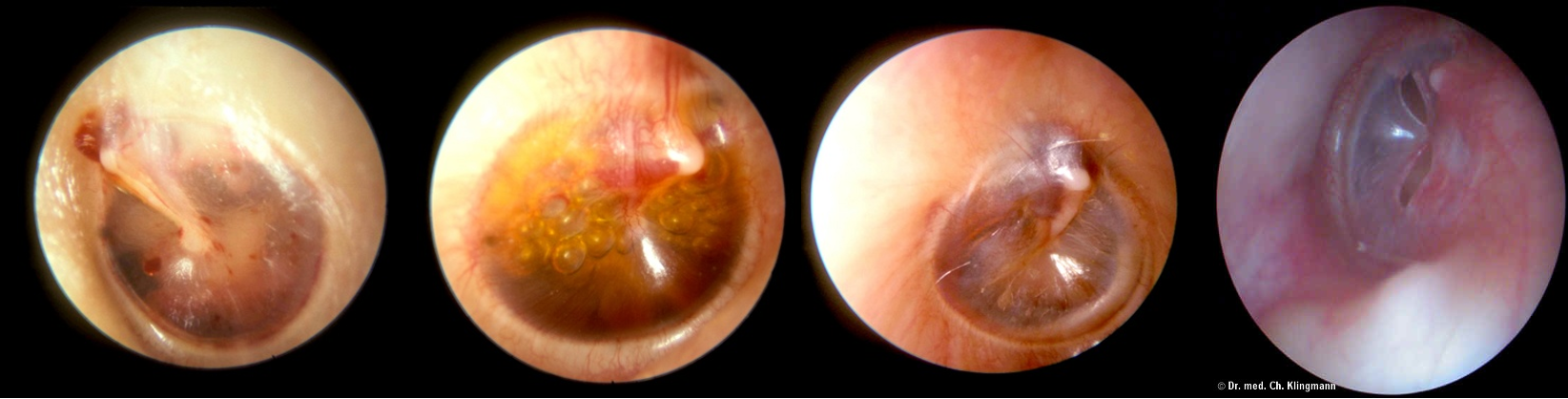
Otitic Barotrauma Y
- Pathological conditions of the ear induced by pressure changes
- Middle ear otitic barotrauma results from failure of the Eustachian tube to equalize increasing atmospheric pressure
- Occurs most commonly during descent from high altitudes in aircraft or during descent in underwater diving
- Pathology: negative middle ear pressures cause transudate in the middle ear, rupture of superficial vessels, retraction of TM, and may cause perforation
- Symptoms: discomfort, pain & deafness
Examination
Treatment
- Prophylactic
- Decongestant, analgesic, and auto inflation (Valsalva maneuver)
- Myringotomy ± VT insertion