IM
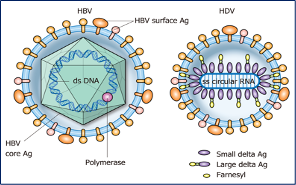
HEPATITIS D
- Hep D virus is unable to cause infection on its own. It requires the presence of the Hep B virus to replicate.
- Infection can occur together with Hep B (co-infection) or in a person who already has Hep B.
- Risk factors, mode of spread, and symptoms are similar to Hep B.
Thera
Clinical course
- Acute coinfection with HBV → Resolve.
- HDV superinfection with chronic hepatitis B increases the risk of liver cirrhosis and HCC. Rapid progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
Diagnostics:
- Detection of HBsAg.
- Anti-HDV antibodies
- Serum HDV RNA
Prevention:
- HBV vaccination.
Prognosis
Patients with superinfection have a poor prognosis. While most patients with acute coinfection successfully recover from both HBV and HDV infection, coinfection presents a greater risk of acute liver failure.