Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver, due to various causes, both infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic) and noninfectious (alcohol, drugs, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic diseases); Viral hepatitis is the most common type.
Causative Agents of Viral Hepatitis are: 1- Hepatitis viruses: Hepatitis A,B,C,D, E, F and G (HPgV-1). Non-A-G viruses. they have strong tropism to hepatocyte.
2- Other Viruses: Yellow fever viruses, EBV, CMV, adenovirus, Herpes simplex, and VZV.
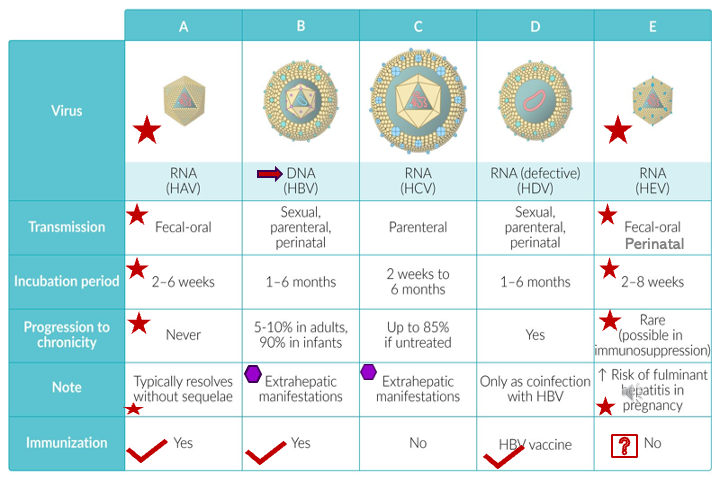 Hepatitis E contains vaccine, but not yet FDA approved as of 2024
Hepatitis E contains vaccine, but not yet FDA approved as of 2024
Clinical Features
Acute:
- Subclinical disease: HCV, HBV
- Symptomatic disease: fever, fatigue, myalgia, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, pruritus, dark urine & pale stool.
Recovery Fulminant: - Acute liver failure complicated by hepatic encephalopathy. - Mortality > 50% - HBV, pregnant ladies with HEV. Chronic: - HCV: RNA persists in the blood for* > 6 months*. - HBV: HBsAg, DNA persist in the serum for > 6 months. - HEV: immunocompromised
Extrahepatic manifestations:
- HBV, HCV due immunocomplexes.
- Skin rash, arthralgia, glomerulonephritis, serum sickness, ……