Ortho
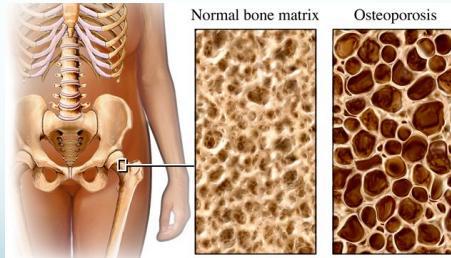
Osteoporosis
Definition
- Reduction of bone mass:
- Both bone minerals & matrix reduced
- Matrix present is mineralized normally
Gender Distribution
- More common in women, especially post-menopausal
- In men: occurs 15 years later than women
Types
- Generalized: Systemic disease affecting entire skeleton
- Localized: Due to disuse (e.g., immobilization in cast)
Risk Factors for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Caucasian (white) or Asiatic ethnicity
- Very slim body build
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Early onset menopause
- Low peak bone mass in third decade
- History of anorexia nervosa or amenorrhea
- Oophorectomy & early hysterectomy
Modifiable Risk Factors ✓
- Nutritional deficiency
- Chronic lack of exercise
- Cigarette smoking
- Alcohol consumption
Note: Some risk factors can be changed (modifiable), while others cannot (non-modifiable).
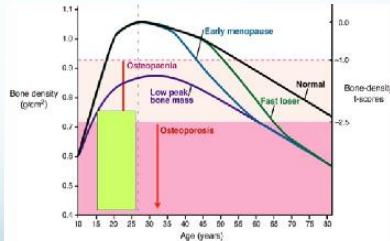
Variation in the bone density of women at different ages Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine © 1996 Cambridge University Press
Clinical Features
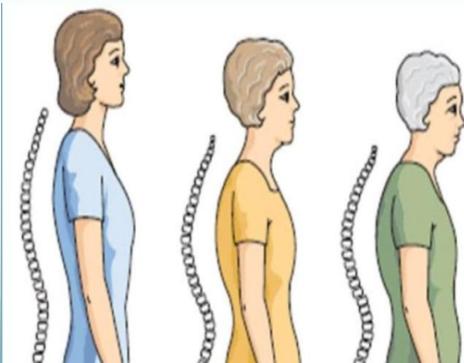
- Weak bones: generalized bony ache
- Backache and kyphosis (dowager’s hump)
 Source: www.rcuv.org/tag/health
Source: www.rcuv.org/tag/health
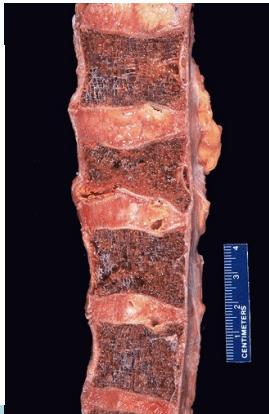 Source: http://library.med.utah.edu
Source: http://library.med.utah.edu
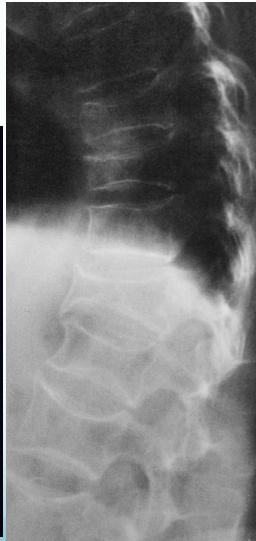
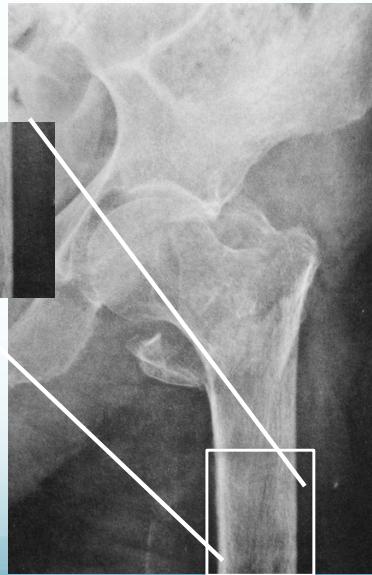
Radiological Features
X-ray Findings
- Loss of cortical thickness
- Osteopenic appearance
Common Fracture Sites ✓
- Vertebral compression fractures
- Colle’s fracture (distal radius)
- Neck of femur (has many complications)
- Proximal humerus
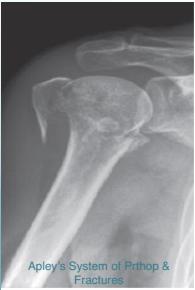
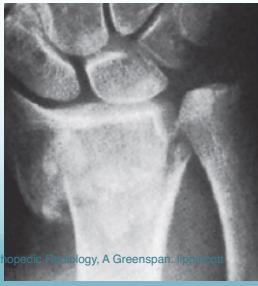
Prevention Strategies
- Adequate Calcium & Vitamin D intake
- Regular physical activity
- Sufficient sun exposure
- Avoid smoking
- Limit alcohol consumption

Treatment Approach
Acute Management
- Treat existing fractures appropriately
Conservative Measures
- Adequate Calcium & Vitamin D intake (may address associated Osteomalacia)
- Sufficient sun exposure
- Maintain good physical activity
- Lifestyle modifications: No smoking, no alcohol
Pharmacological Treatment
- Reduce rate of further bone loss:
- Bisphosphonates → anti-osteoclastic agents
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (estrogen)
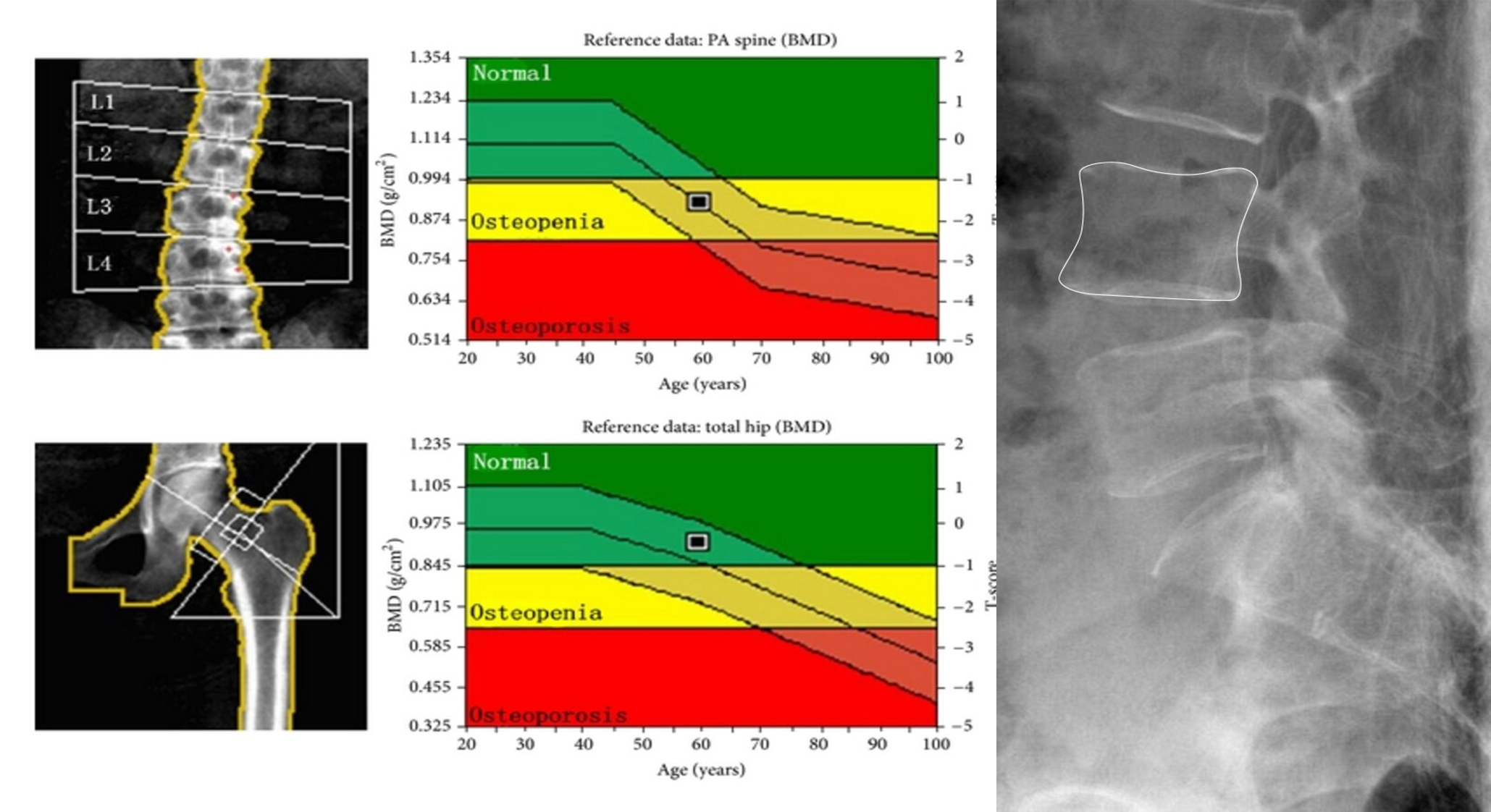
IMAGING
Osteoporosis is a skeletal condition in which the loss of bone mineral density (BMD) leads to decreased bone strength and increased susceptibility to fractures.
- Risk factors:
Postmenopausal women ,older adults (abrupt decrease in estrogen and age-related processes play a key role in the development of osteoporosis, physical inactivity, a diet low in calcium and vitamin D , smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Radiographic features:
The changes of osteoporosis are best seen in the spine (Lateral thoracic and lumbar spine x-ray )
- Decreased bone density
- Loss of normal bony trabecula Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is the gold standard technique for the diagnosis of osteoporosis
Decreased bone density in osteoporosis
X-ray lumbar spine (lateral view) of a patient with osteoporosis
The vertebrae have a low-density appearance as a result of the loss of trabecular bone, and the cortical outline of each vertebra appears accentuated. Z
Other potential findings on a spine radiograph in osteoporosis include an abnormal trabecular pattern and biconcave or compressed vertebral configuration.