Neurons and Brain Structure
Neuron Structure
- Dendrites
- Axon
- Synapse
Neurotransmitter Mechanism
- Neurotransmitter molecules
- Receptor
Brain Lobes
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Cerebellum
- Motor cortex


Evolutionary Development
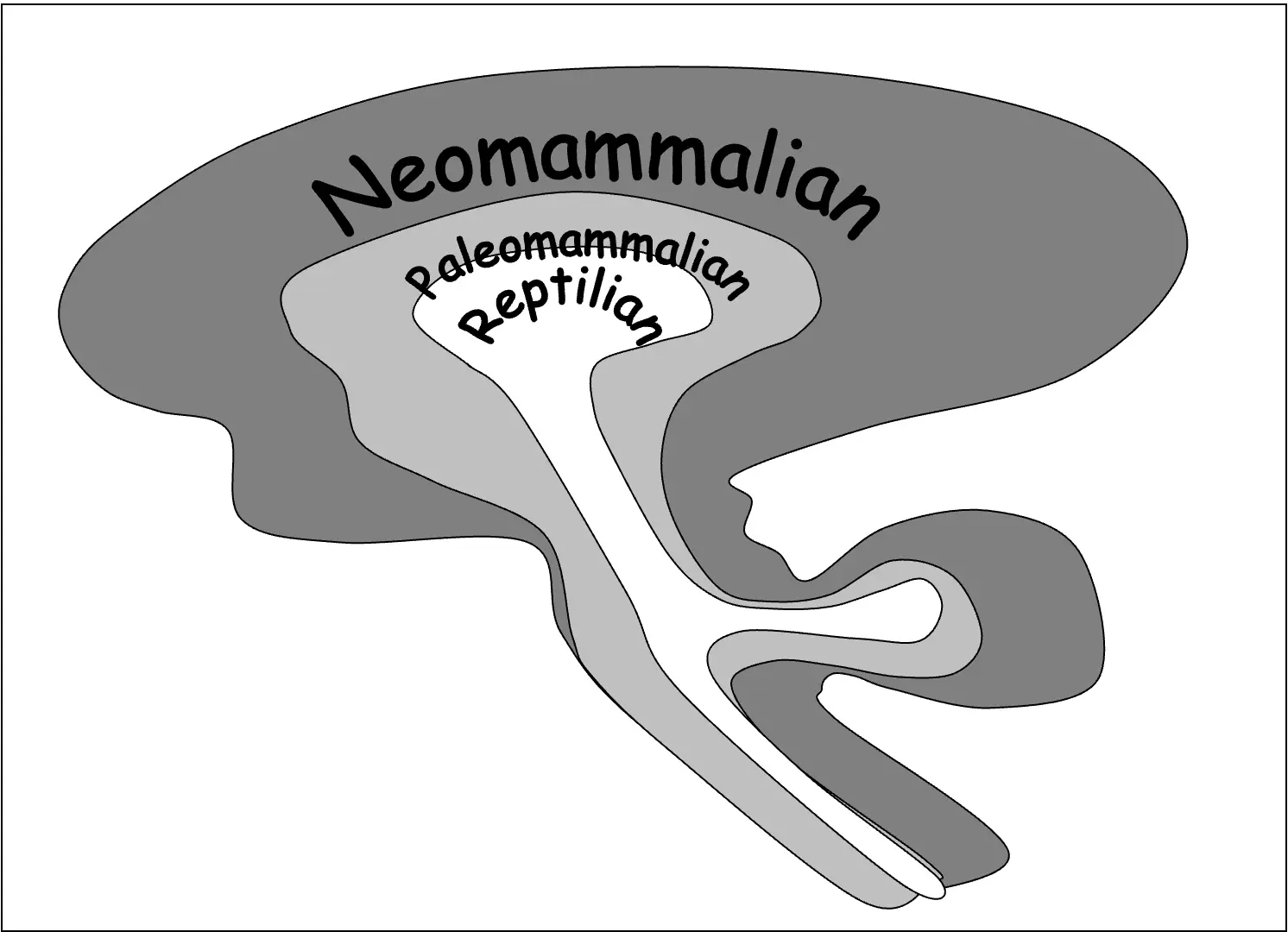
If you examine the brain from an evolutionary perspective, this can help to understand the interlinks between form and function. The brain can be divided anatomically and functionally into three basic components.
Reptilian Brain
- Corresponds to the brainstem
- Consists of the medulla, pons, midbrain, and basal ganglia
- Not only responsible for vegetative functions but also for many volitional behaviors directed towards individual preservation and propagation such as feeding, drinking, and sexual aggression.
Paleomammalian Brain
- The primitive cortex of the limbic lobe
- Subserves primitive (but distinctly mammalian) behaviors such as hoarding and parental care of offspring.
Neomammalian
- Paleomammalian
- Reptilian
Functional Organization of the Cerebrum
- Primary motor cortex (voluntary movement)
- Premotor cortex (coordinates voluntary movements)
- Central sulcus
- Primary somatosensory cortex (somesthetic sensations and proprioception)
- Sensory association areas (integration of sensory information)
- Visual association areas (higher vision processing)
- Primary visual cortex (vision)
- Wernicke’s area (language comprehension)
- Broca’s area (speech formation)
- Olfactory cortex (smell)
- Limbic association cortex (emotions, learning, and memory)
- Primary auditory cortex (hearing)
- Auditory association areas

The Limbic System
- Amygdala: response to fear
- Prefrontal cortex: integrates this emotion with conscious sources of information and plans our physiological and behavioral responses to the situation.
- Hippocampus: consolidation of conscious memories and cognitive navigation
- Cingulate gyrus: error detection, determining the focus of our attention, the personal sense of urgency, and social interactions
Basal Ganglia and Limbic System
- Cerebrum
- Corpus Callosum
- Basal Ganglia
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Amygdala
- Hippocampus
- Cerebellum

Hippocampus

Hippocampal Formation & Amygdala
- Hippocampal Formation
- Dentate gyrus + the hippocampus proper + Subiculum
- Memory, spatial navigation, and attention
- Amygdala
- Via hypothalamus activates the ANS
- Activation of Neurotransmitters
- Emotional Learning – Conditioning
- Memory modulation
- Kluver Bucy Syndrome – Docility: diminished fear responses, dietary changes, Hyperorality, Hypersexuality, Visual Agnosia
- Hypermetamorphosis: irresistible impulse to notice and react to everything, memory loss
Function of the Limbic System
- Affective Functions
- Playful moods
- Emotions and feelings,
- Like wrath, fright, passion,
- Love, hate, joy, and sadness
- Self-preservation
Prefrontal Cortex
- Dorsolateral cortex (DLC): Attention, planning, decision making, inhibition, and initiation of goal-directed behavior, working memory
- The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC): inhibits the emotional and autonomic reactivity of subcortical structures such as the amygdala.
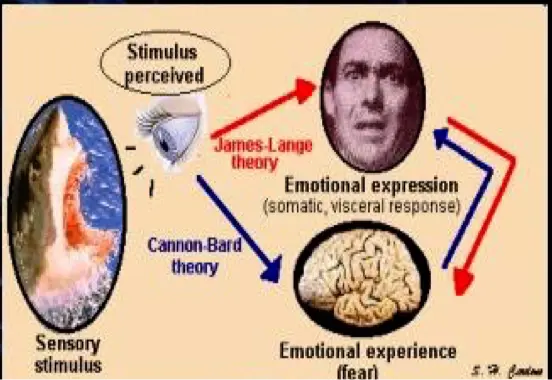
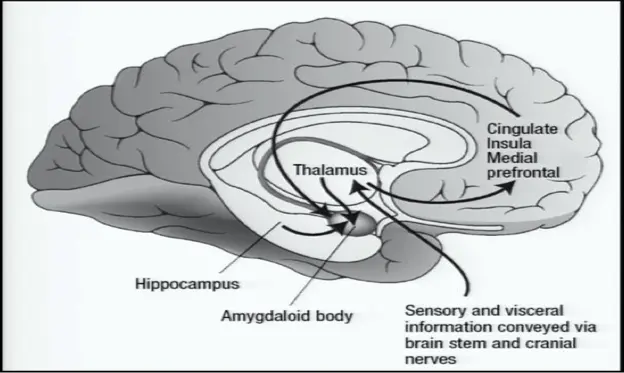
Fear Neurocircuitry
- Cingulate
- Insula
- Medial prefrontal
- Thalamus
- Hippocampus
- Amygdaloid body
Sensory and visceral information conveyed via brain stem and cranial nerves
Fear Extinction Circuitry
- Infralimbic mPFC
- Retrieval of extinction
- Amygdala
- Fear memory, Acquisition of extinction
- Hippocampus
- Contextual modulation of extinction
- Fear response
