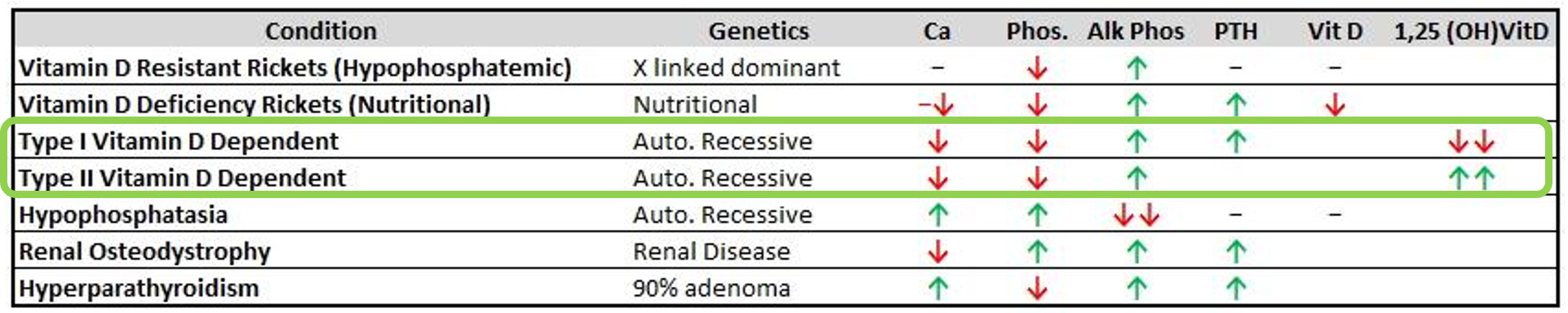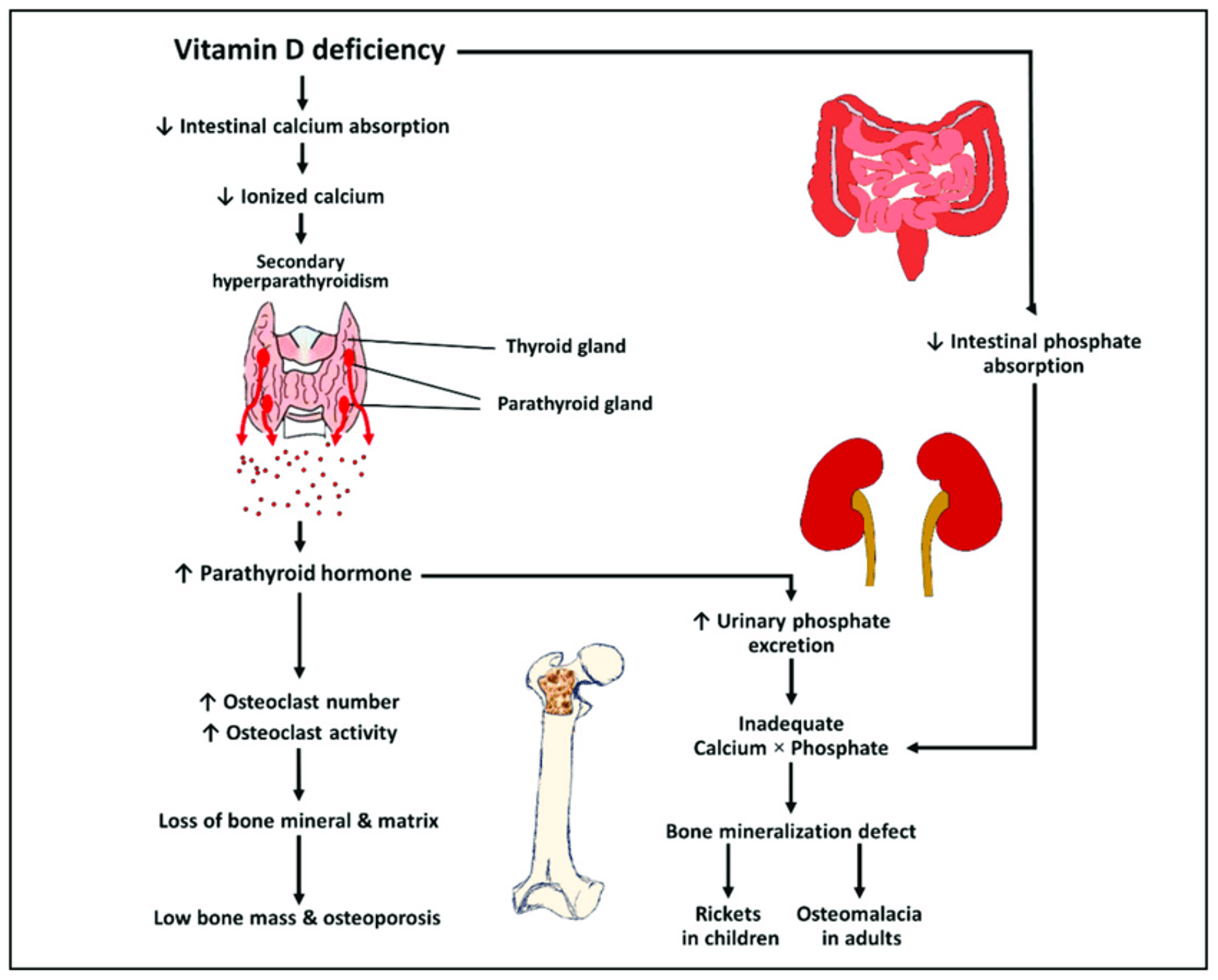
Vitamin D Deficient Rickets
Another term: nutritional Rickets
Risk Factors:
- Exclusively breastfed for 6 months
- Limited sun exposure
- Vitamin D deficient mothers
Sources of Vitamin D:
- Fortified milk, cheese, liver; sunlight
Clinical Presentation
Hypocalcemic Symptoms:
- Convulsions
- Stridor
- Laryngospasm
- Wide anterior fontanelle (three fingers width)
General Presentation:
- Irritability
- Weakness
- Frontal bossing
- Tooth malformation and abscess
Musculoskeletal Symptoms:
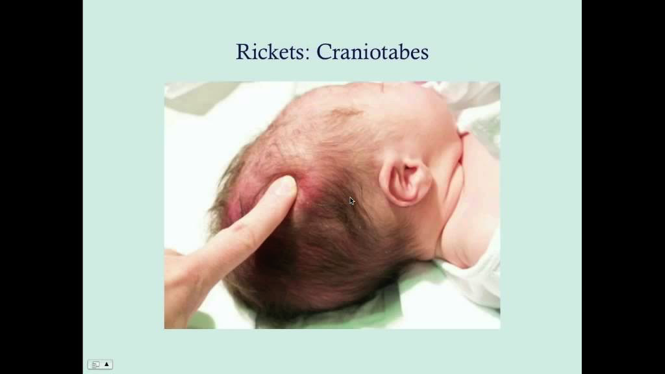
- Craniotabes
- Delayed dentition/enamel hypoplasia
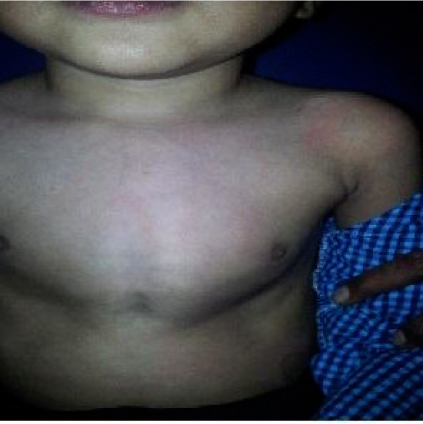
- Chest pigeon chest
- Rachitic rosary
- Harrison’s sulcus
- Long bones deformities
- Widened wrists and ankles
- Hypotonia/muscle weakness
- Bone pains
- Delayed motor development/hypotonia
- Short stature
- Bell-shaped chest
- Bowlegs (genu varus) or knock-knees (genu valgum)
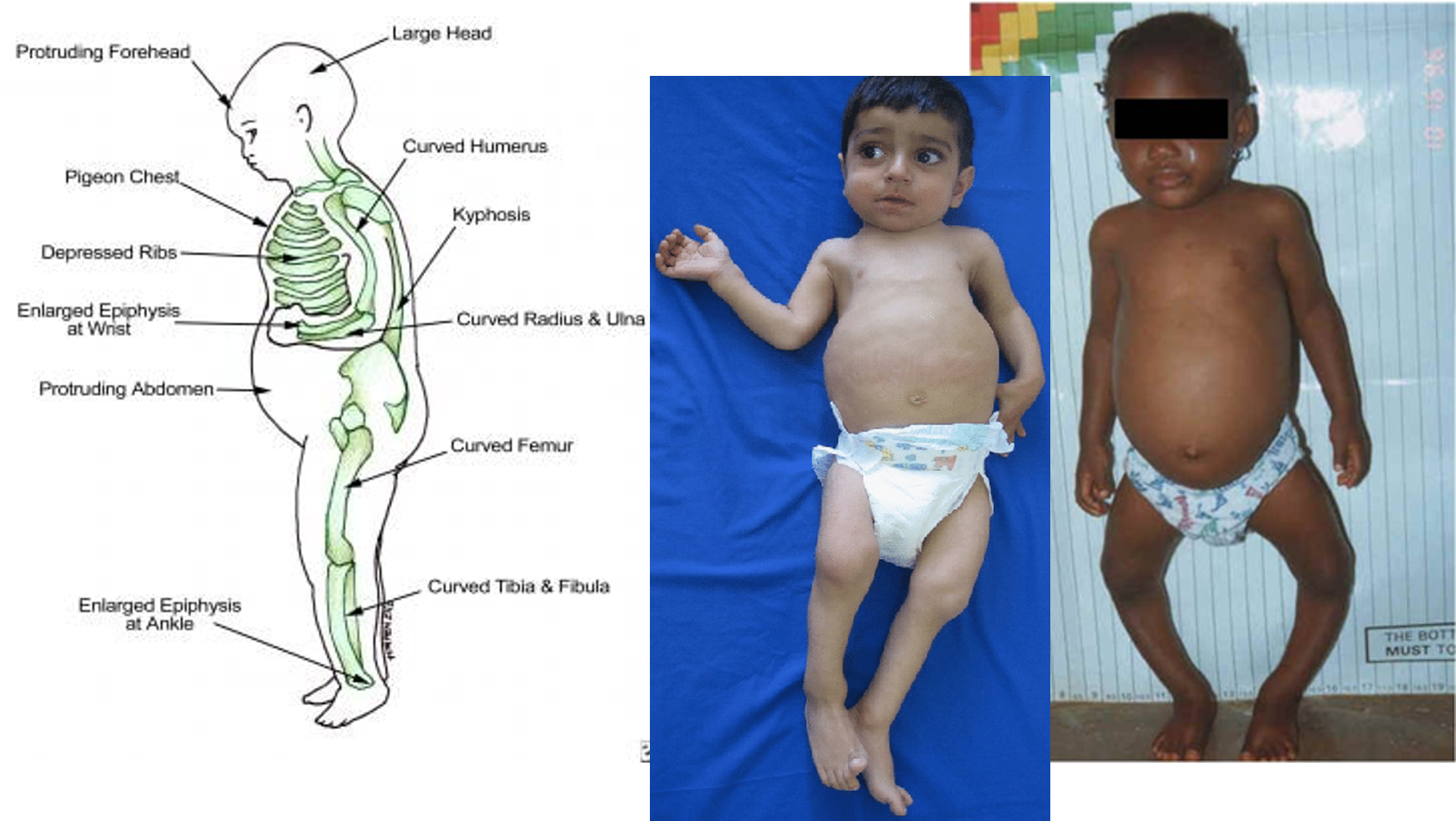
Rachitic Rosary
Enlargement of costochondral junction
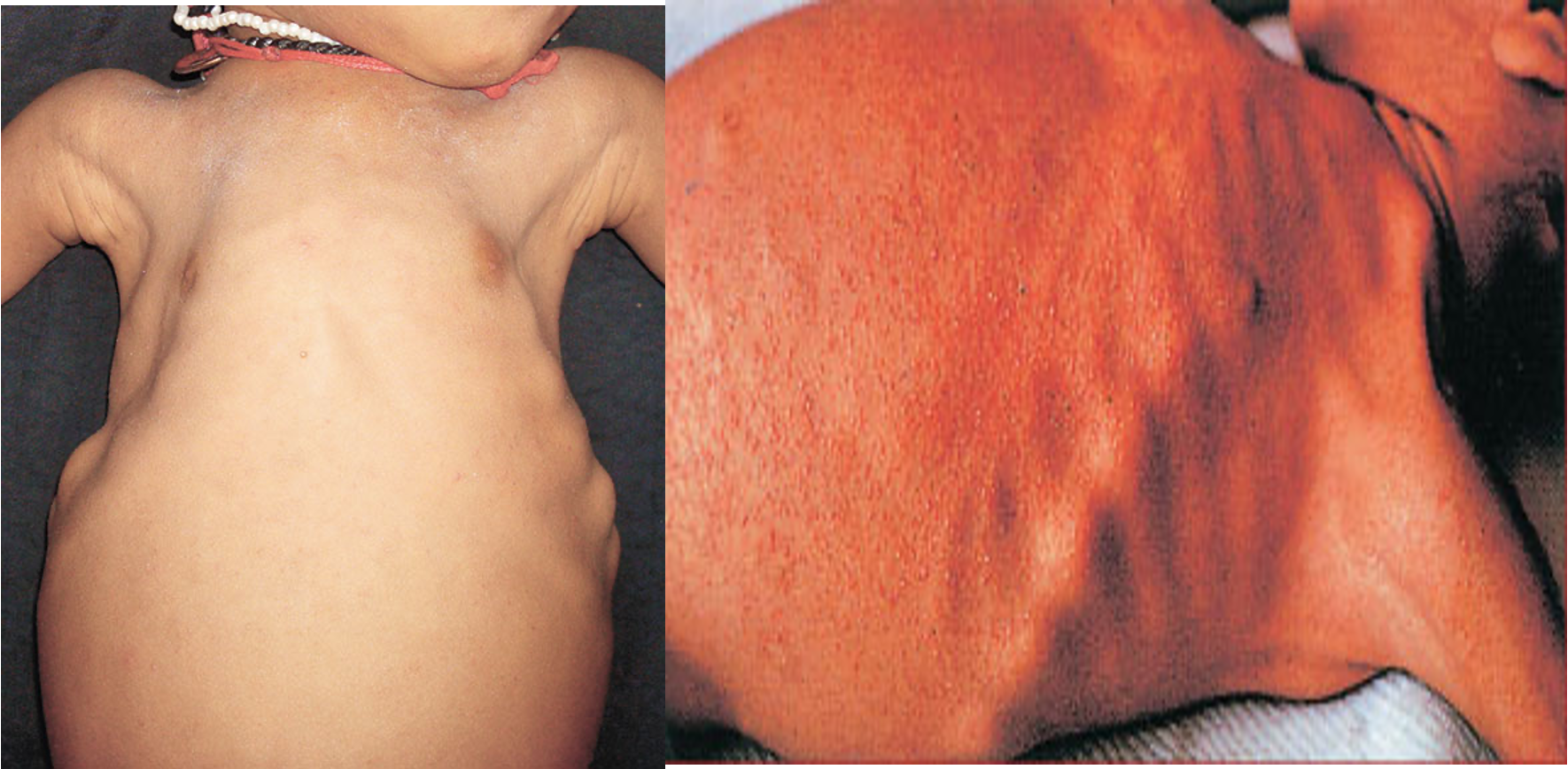
Harrison Sulcus
Inward pulling of diaphragmatic attachments
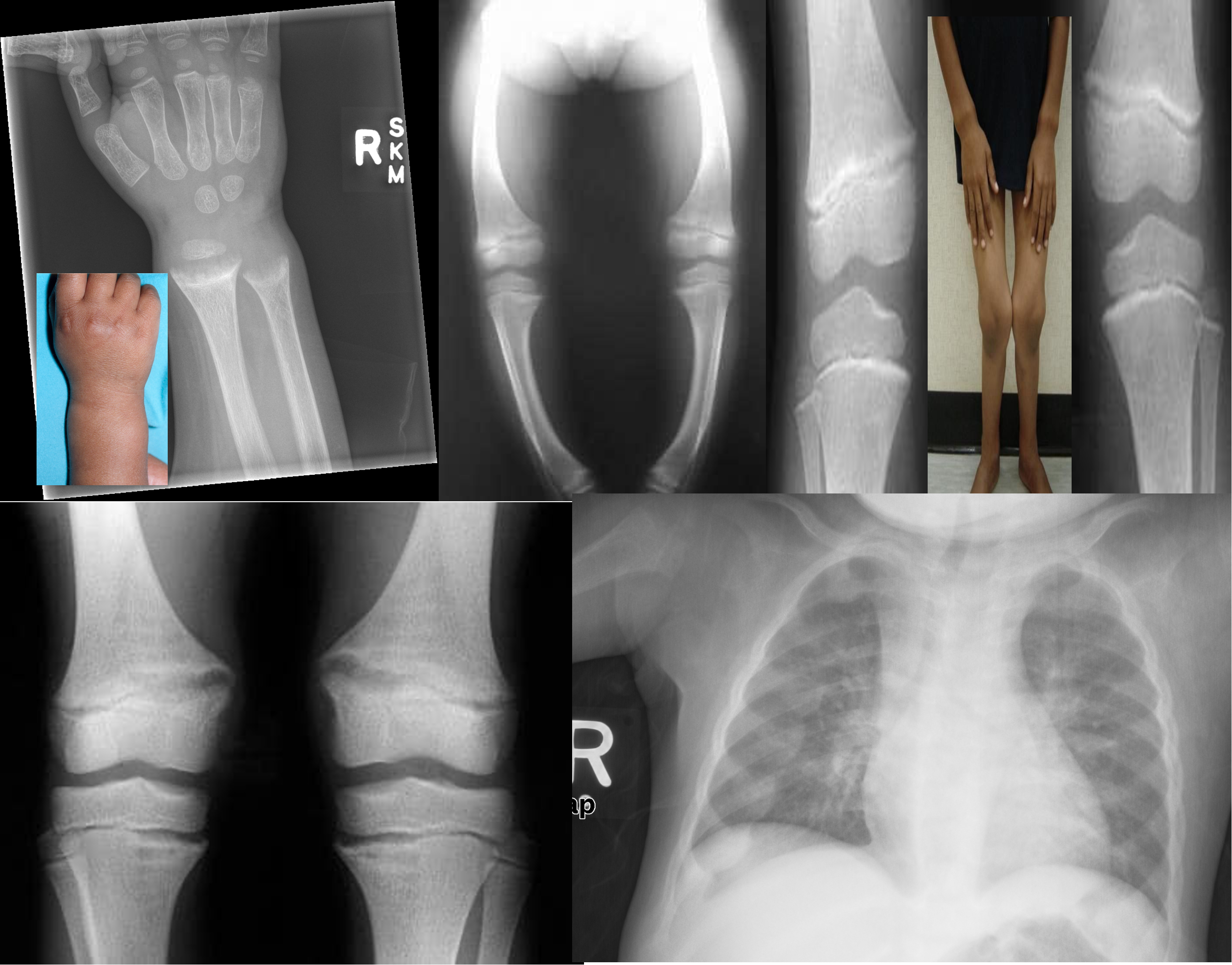
X-ray Findings
-
Fraying and widening of the growth plate
-
Cupping of the metaphysis
-
Bowing of the legs due to osteopenia (Genu varus)
-
Knock-knees (Genu Valgum)
-
Multiple growth arrest lines
-
Underdevelopment of the medial aspect of both the tibial plateau and the femoral condyle
-
Rachitic rosary (differential for child abuse also seen in proximal)
VDDR II (reversible)
Baldness is a common manifestation
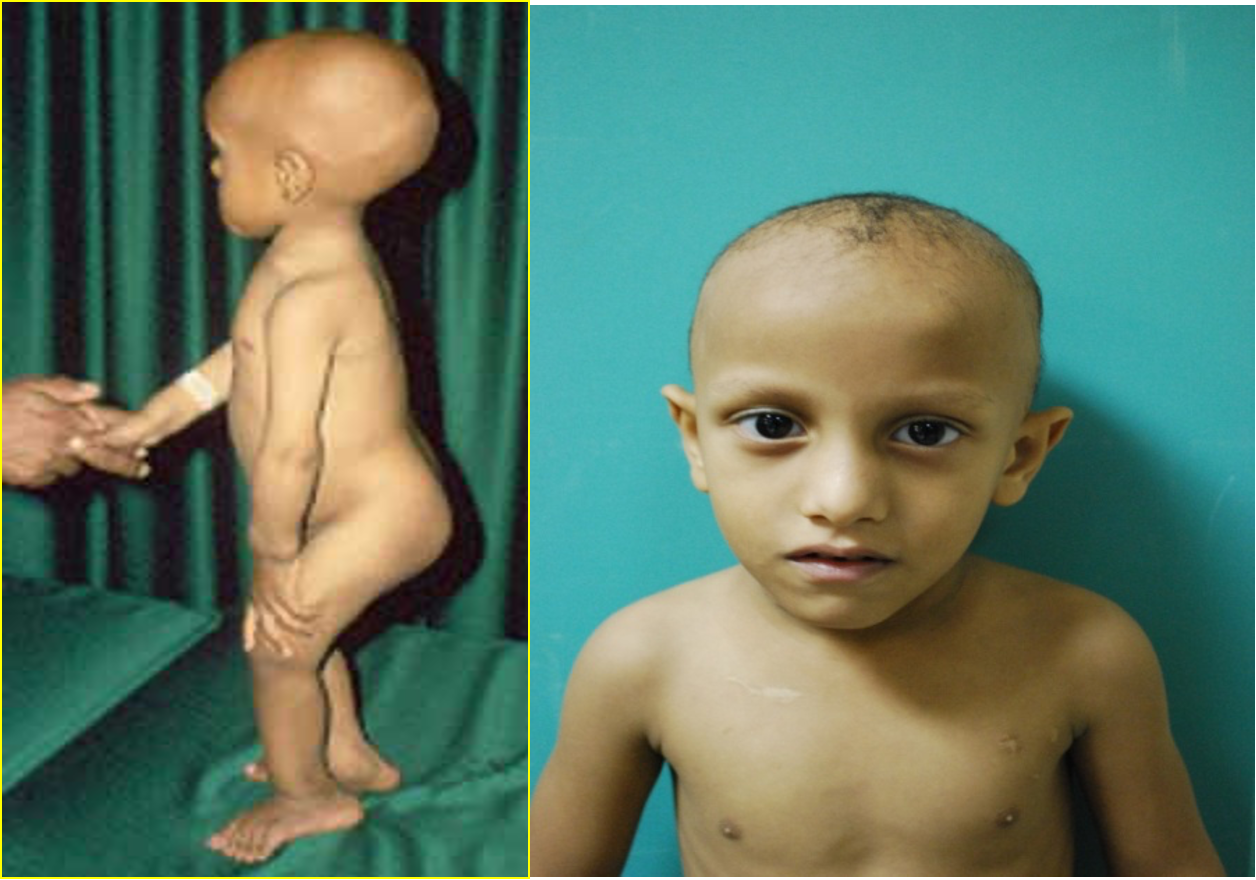
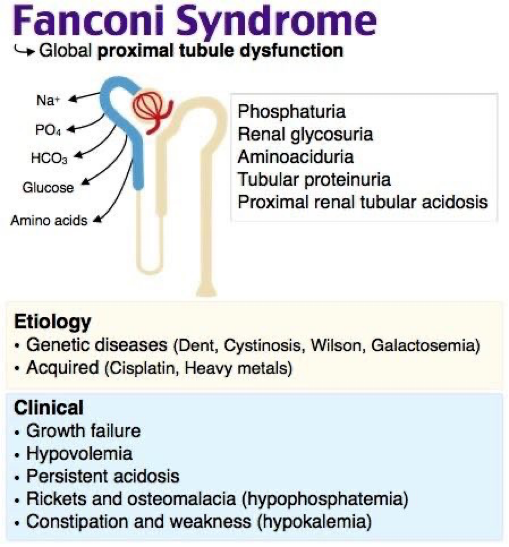 disturbed absorption of phosphate in Proximal tubule in fanconi syndrome
disturbed absorption of phosphate in Proximal tubule in fanconi syndrome
Approach
Lab Investigations:
- Ca level (corrected for any elevated albumin level)
- Albumin
- Phosphate (index of PTH activity when there is hypocalcemia: Low serum phosphate reflects increased PTH activity, high Ph reflects reduced PTH activity) / ALP
- PTH
- Magnesium (as hypomagnesemia inhibits PTH release)
- Alkaline phosphatase (level is raised when hypocalcemia is secondary to a disorder of vitamin D) & (level is in the normal range when hypocalcemia is secondary to hypoparathyroidism)
- 25-hydroxyvitamin D
- Creatinine and electrolyte will help in determining renal disease / renal failure
Radiological Workup:
- X-ray of left wrist and/or knees
Vitamin D Status Lab Variation
| Level (nmol/l) | Status |
|---|---|
| >50 | Sufficiency |
| 30-50 | Insufficiency |
| <30/20 | Deficiency |
| >250 | Toxicity |
Treatment Vitamin D Deficiency 1. Prevention: - Vitamin D for breastfed infants 400 IU daily - Daily sun exposure 2. Treatment: - Vitamin D2 2000-4000 IU daily for 6-8 weeks - Followed by maintenance dose 400 IU (0-12 months old) - 600 IU (over 12 months old) daily Note: Since vitamin D is fat-soluble, overdose Vitamin D will result in: - Hypercalciuria: monitor calcium/creatinine ratio - Nephrocalcinosis: periodic renal US
Note
In Type I, there will be no increase in vitamin D level after VD3 supplements