Acute complications:
- Diabetic keto-acidosis (DKA)
- Hypoglycemic coma
Chronic Complications of diabetes mellitus
- Diabetic macroangiopathy
- Diabetic microangiopathy
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus
| diagnosis | fasting blood sugar | Glucose tolerance test (after 2 hours) | HbA1c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | ﹤100mg/dL | ﹤140mg/dl | ﹤5.7% |
| Prediabetic | 100-126 mg/dL | 140-199/dL | 5.7-6.4% |
| Diabetic | ﹥ 126mg/dL | ﹥200mg/dL | ﹥6.4 % |
Type 1 VS 2
| Type I diabetes | Type II diabetes | |
|---|---|---|
| 1.clinical | Onset:childhood. Normal weight or weight loss | Above 40 years. -obesity |
| 2. Etiology | 1. Hereditary as it linked to MHC class I&II 2.Autoimmune inflammation with destruction of the B.cells by circulating autoantibodies due to failure of tolerance to self antigens | 1. Not linked to MHC antigens. 2. No islet autoantibodies 3. There is prepheral resistance to insulin enhanced by cytokines released from adipose tissue that mask insulin receptors. |
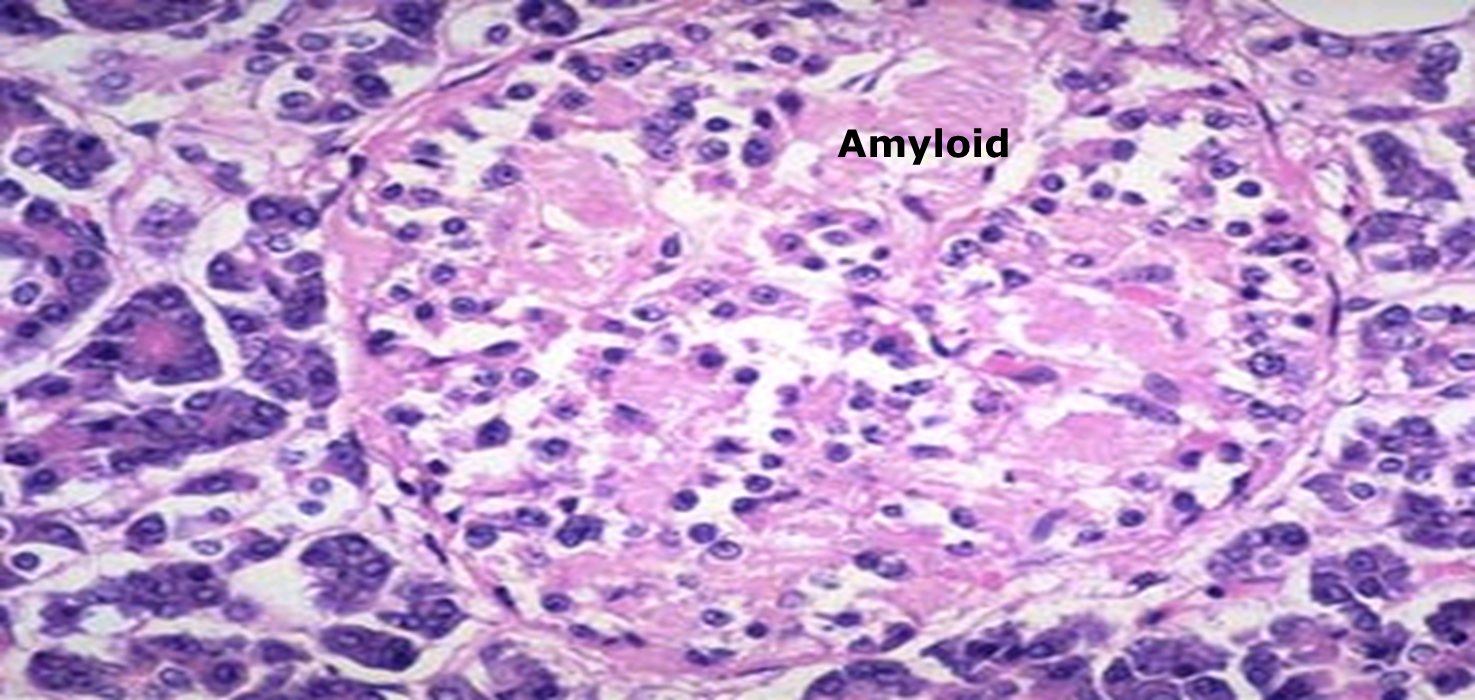
| 3. B. Cell mass. | Insulitis with lymphocytic infiltration causing early b cell depletion and atrophy of them leading to Progressive decrease in insulin level . | normal in early stage as no insulitis, later on shows amyloid deposition with mild B cell depletion. |
Pancreatic islets in type II DM - H &E stain(Islet shows extensive deposition of amyloid)
- Complications of diabetes mellitus: