Presented by:
Nader ALDAjani
Otologist, KFMC
Definition:
- Misnomer; neither contains cholesterol crystals nor is a tumor.
- Skin in the wrong place.
Pathophysiology:
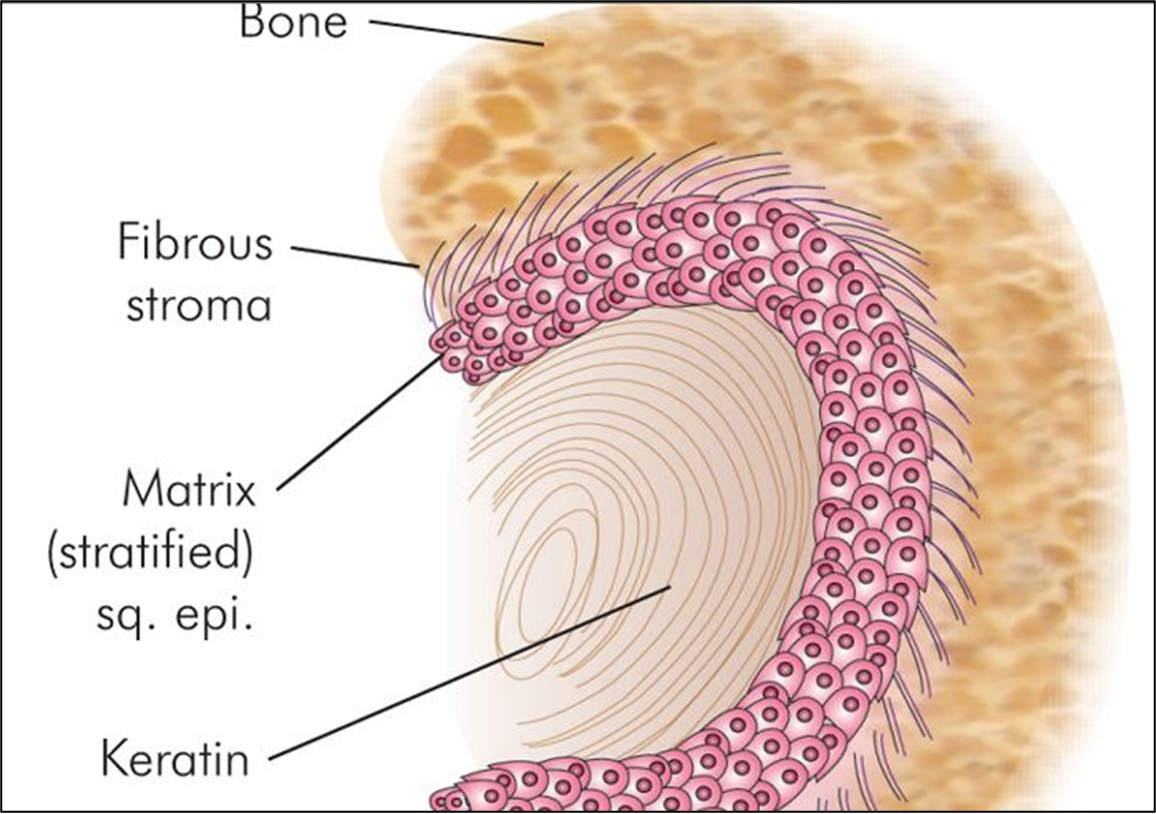
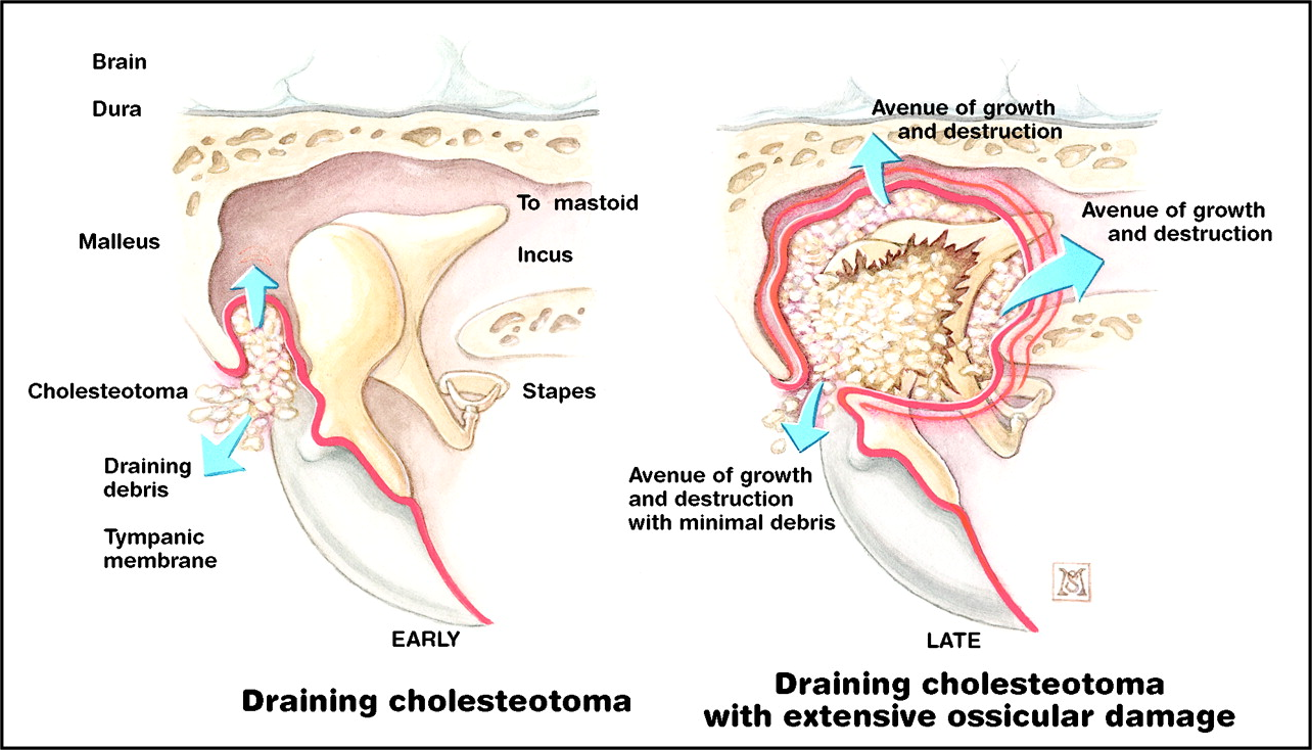
- Squamous epithelium in the middle ear or mastoid.
- Desquamation leads to keratin debris accumulation.
- Associated with bone and soft tissue erosion and recurrent infections.
Types:
-
Acquired:
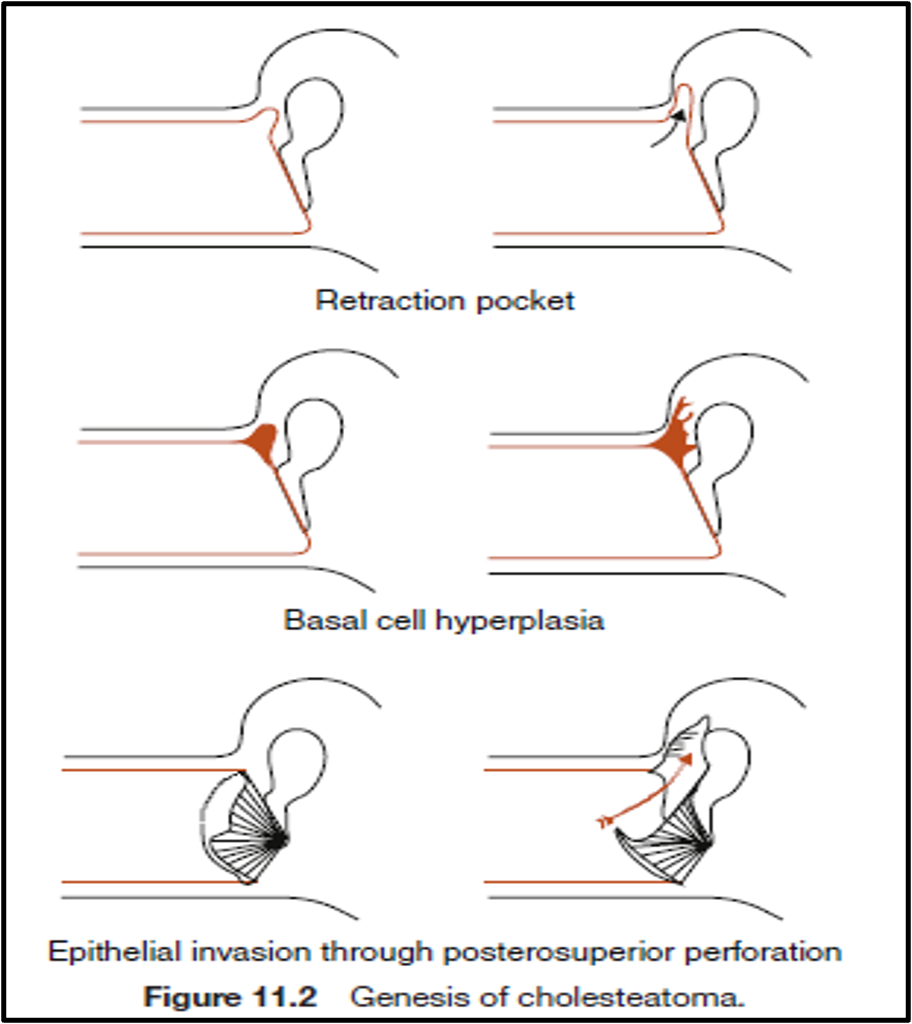
- Primary: Due to invagination of a retraction pocket. - associated with negative ear pressure (eustachian tube dysfunction).
- Secondary: Ingrowth of keratinizing epithelium into the middle ear space through a pre-existing TM perforation.
-
Congenital:
- Presents as a white mass generally in the anterosuperior middle ear with an intact TM.
- Presents as a white mass generally in the anterosuperior middle ear with an intact TM.
Presentation:
- Progressive conductive hearing loss (CHL), discharge. ((cholesteatoma can act as a sound conductor))
- OE: White “pearly” mass, perforation, discharge, polyps, destruction of attic area.
- Tests: CT, PTA, Tympanometry.
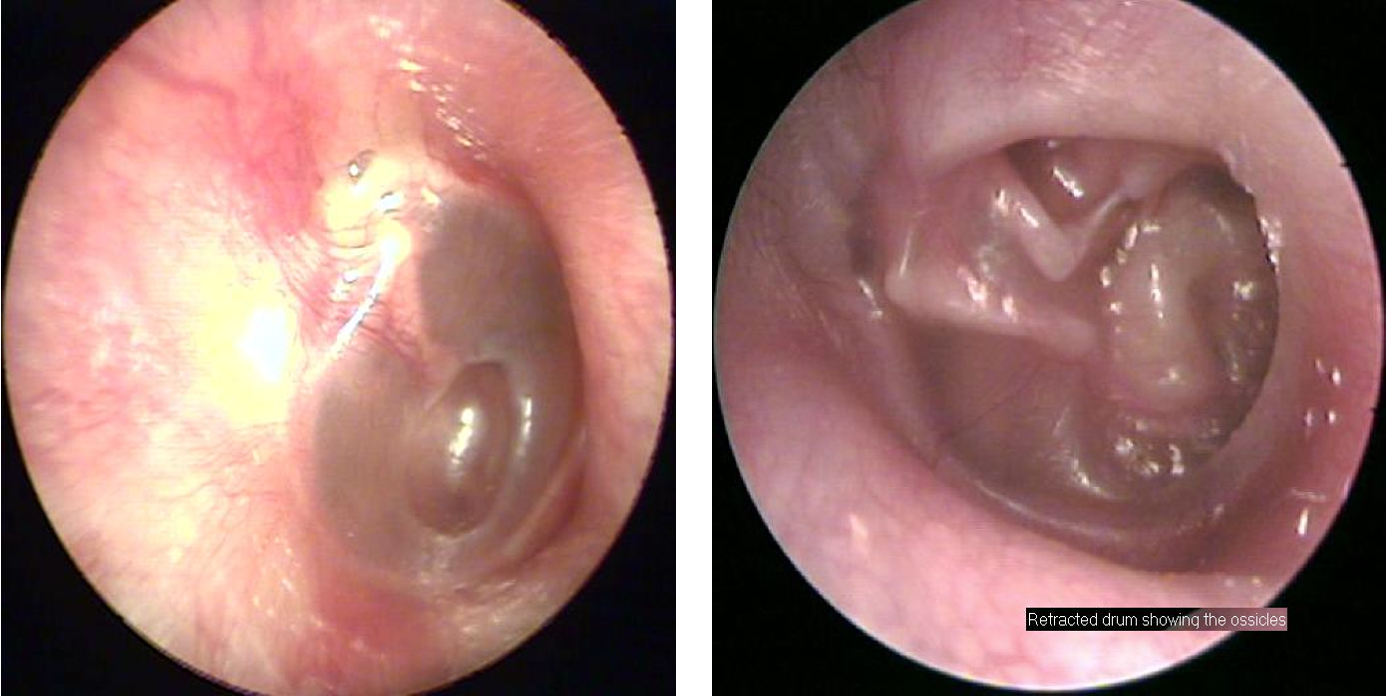
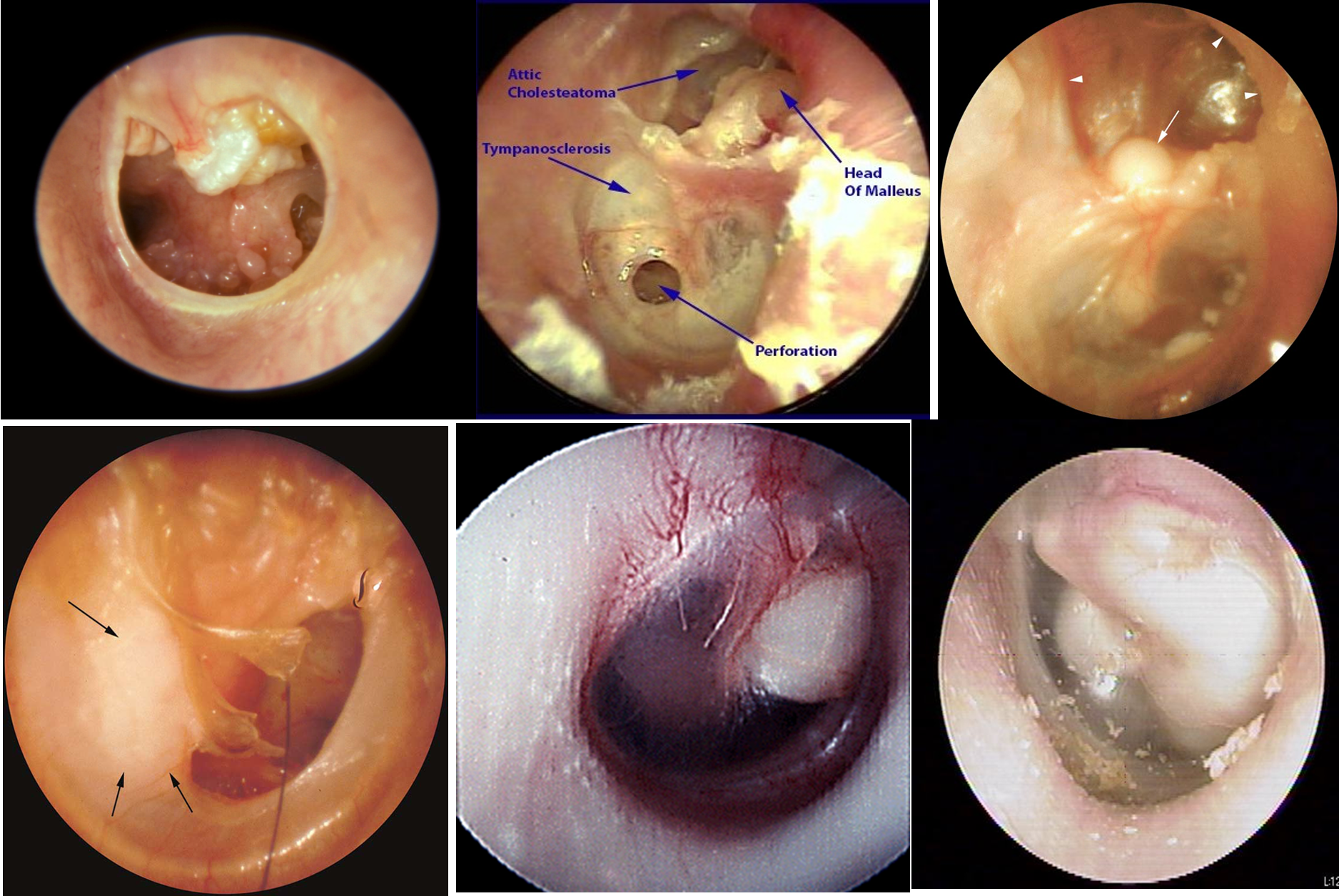 congenital if there are no perforations
congenital if there are no perforations
Complications:
- Destruction of the ossicular chain.
- Chronic otitis media.
- Labyrinthine fistula.
- Intracranial complications.
- Facial nerve paralysis.
Management:
Antibiotics.
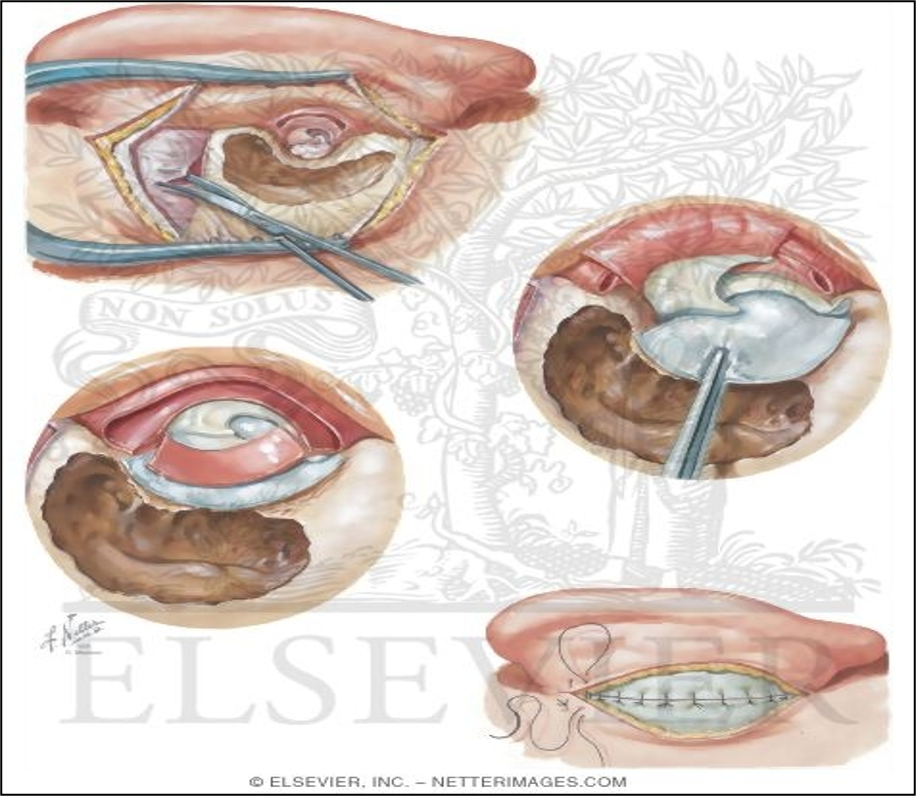
Surgery.
- Aim: to remove the disease, restore the function.
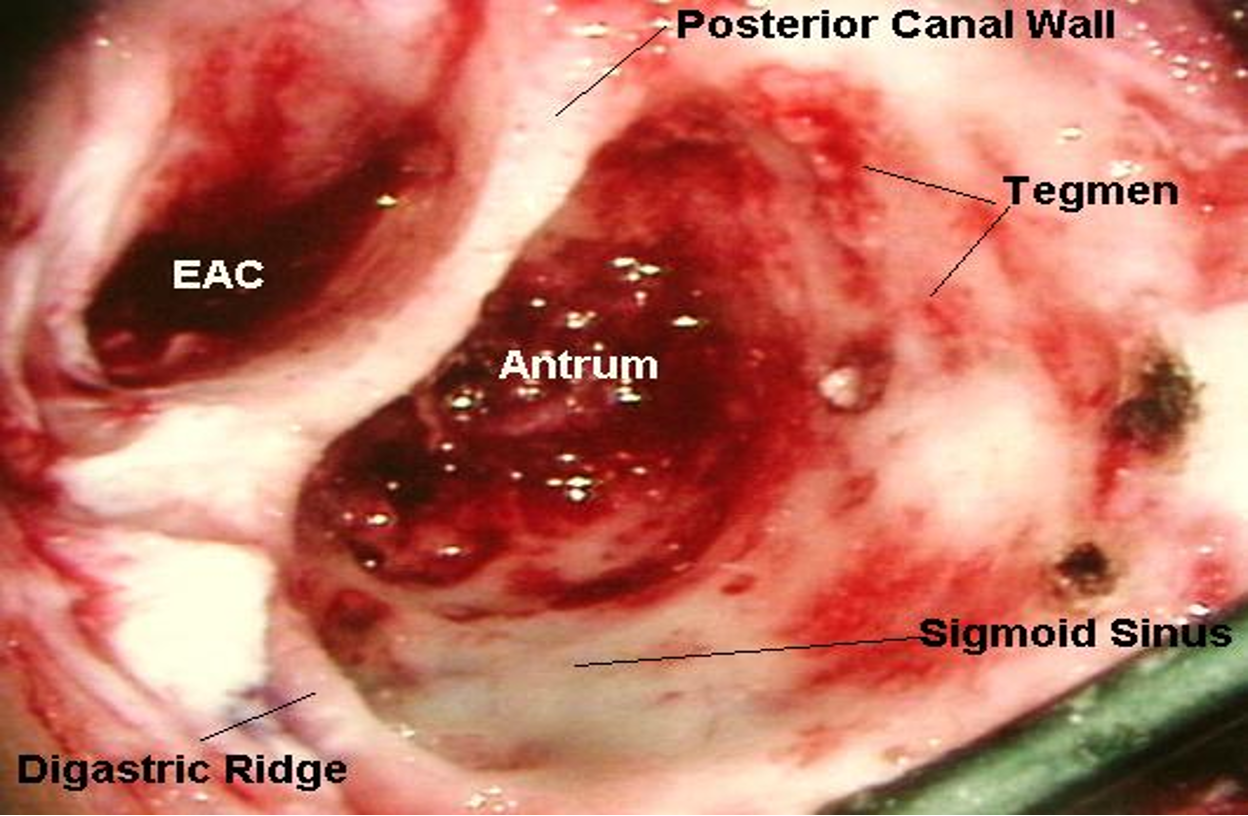
- Mastoidectomy.
- Reconstructive surgery.
Tympanoplasty & Mastoidectomy
-
Tympanoplasty: Surgical reconstruction of the tympanic membrane.
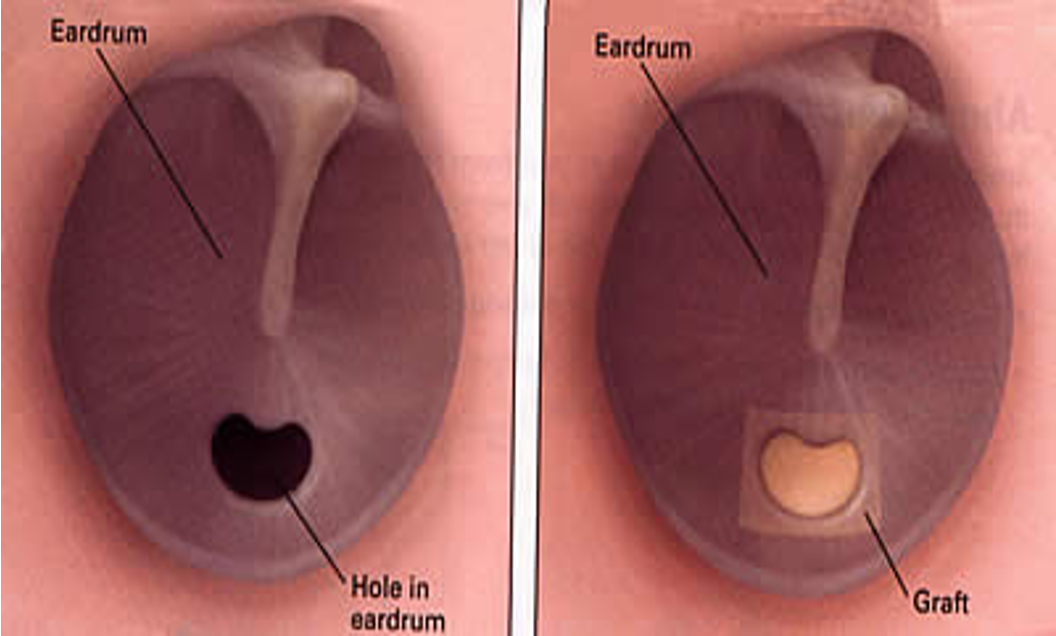
-
Mastoidectomy: Surgical procedure to remove infected mastoid air cells.