ORTHO
Osteomalacia
Etiology
Caused by defective Vitamin D metabolism:
- Deficiency: lack of sun exposure
- Intestinal malabsorption
- Defective formation of active Vitamin D:
- Liver disease
- Renal disease
Clinical Features
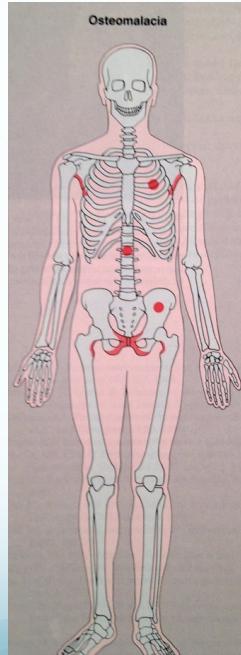
- Bone aches – backache, hip pain
- Compressed vertebral fractures
- Insufficiency fractures of femur/tibia
Radiological Features
Primary Findings
- Weak osteopenic bone
- Biconcave vertebrae & compression fractures
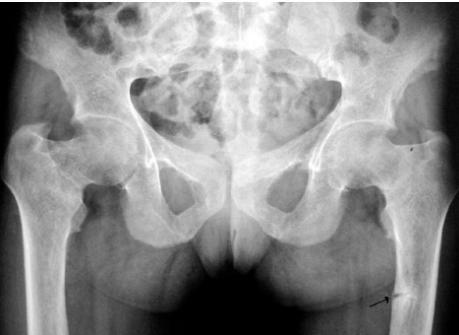
- Trefoil pelvis – acetabular protrusion
Characteristic Sign: Looser’s Zones
- Poorly healing stress fractures typically occurring at:
- Neck of scapula
- Neck of femur
- Pubic bones
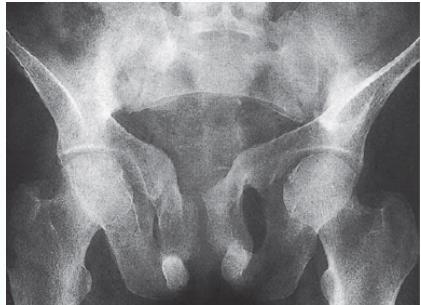
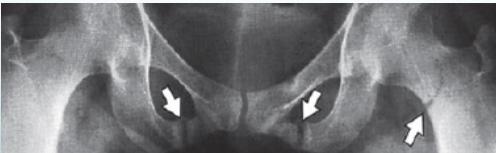
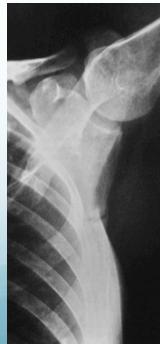
Treatment
- Treat the underlying cause:
- Vitamin D supplementation
- Calcium supplementation
- Adequate sun exposure
IMAGING
Osteomalacia is the softening of the bones caused by defective bone mineralization secondary to inadequate amounts of available phosphorus and calcium, or because of overactive resorption of calcium from the bone as a result of hyperparathyroidism.
Patients with osteomalacia usually present with bone pain and tenderness.
Characteristic radiological features:
- Loss of bone density.
- Thinning of the trabeculae and cortex. z
- Looser’s Zones (pseudo fractures). z
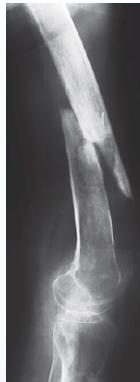
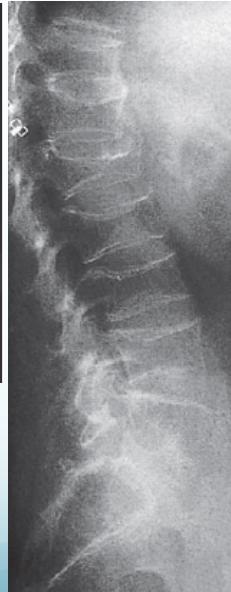
- Bone deformity. (vertebral bodies are biconcave, the femora may be bowed)
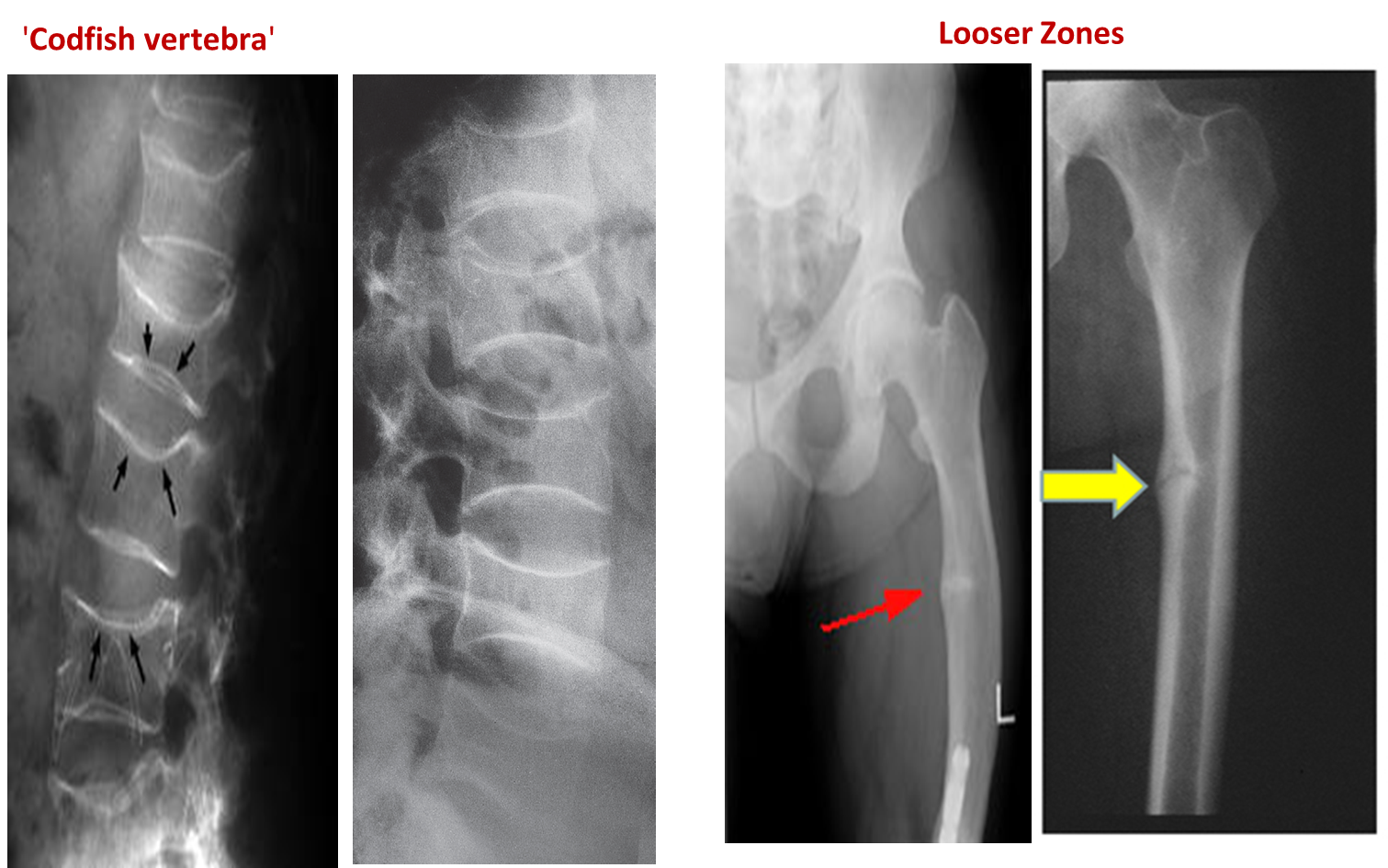
Vertebral bodies are biconcave
Looser’s zones Z are short lucent bands running through the cortex at right angles, usually going only part way across the bone
Rickets - Children counterpart of Osteomalacia
is a disorder of impaired mineralization of cartilaginous growth plates. - Rickets in children is due to vitamin D deficiency which in turn result in to decrease calcium in the body.
- Patients with rickets usually present with bone deformities and impaired growth
On x-ray: z
- Cupping and fraying of metaphysis
- Irregular widened growth plate
- Chest X-ray: prominent costochondral junctions (Rachitic rosary)
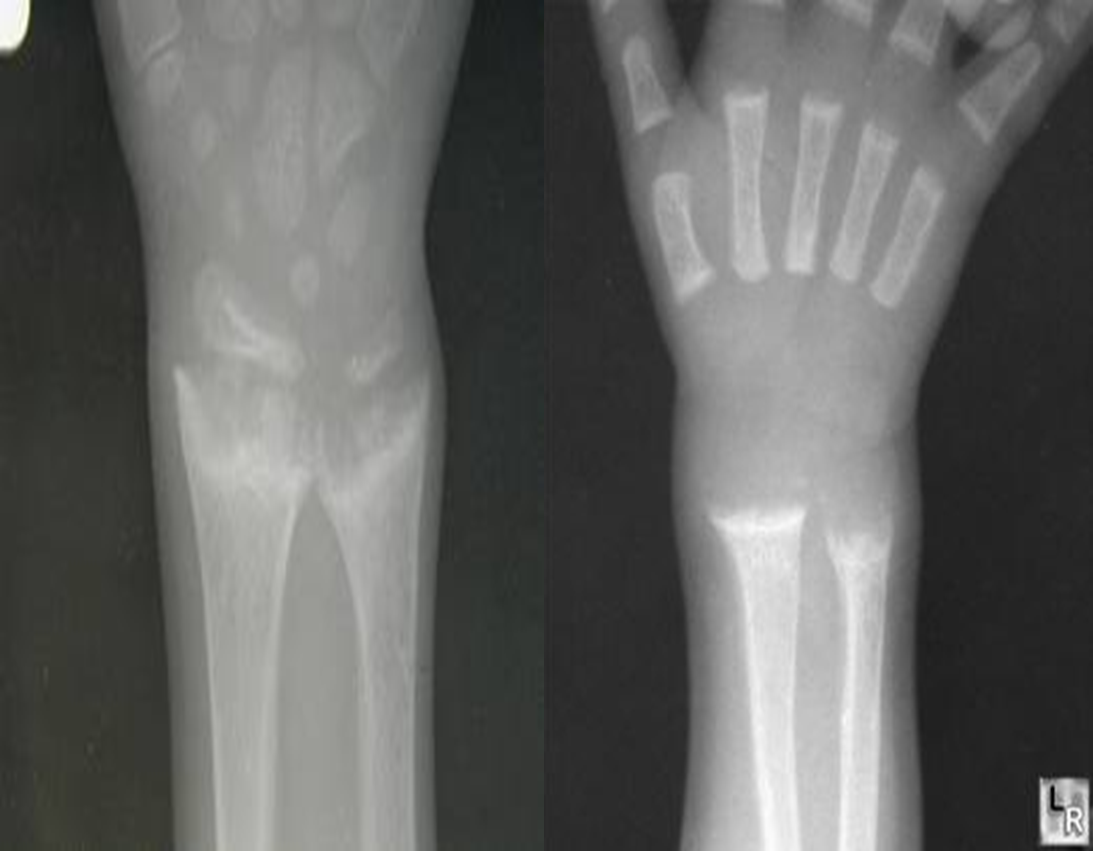
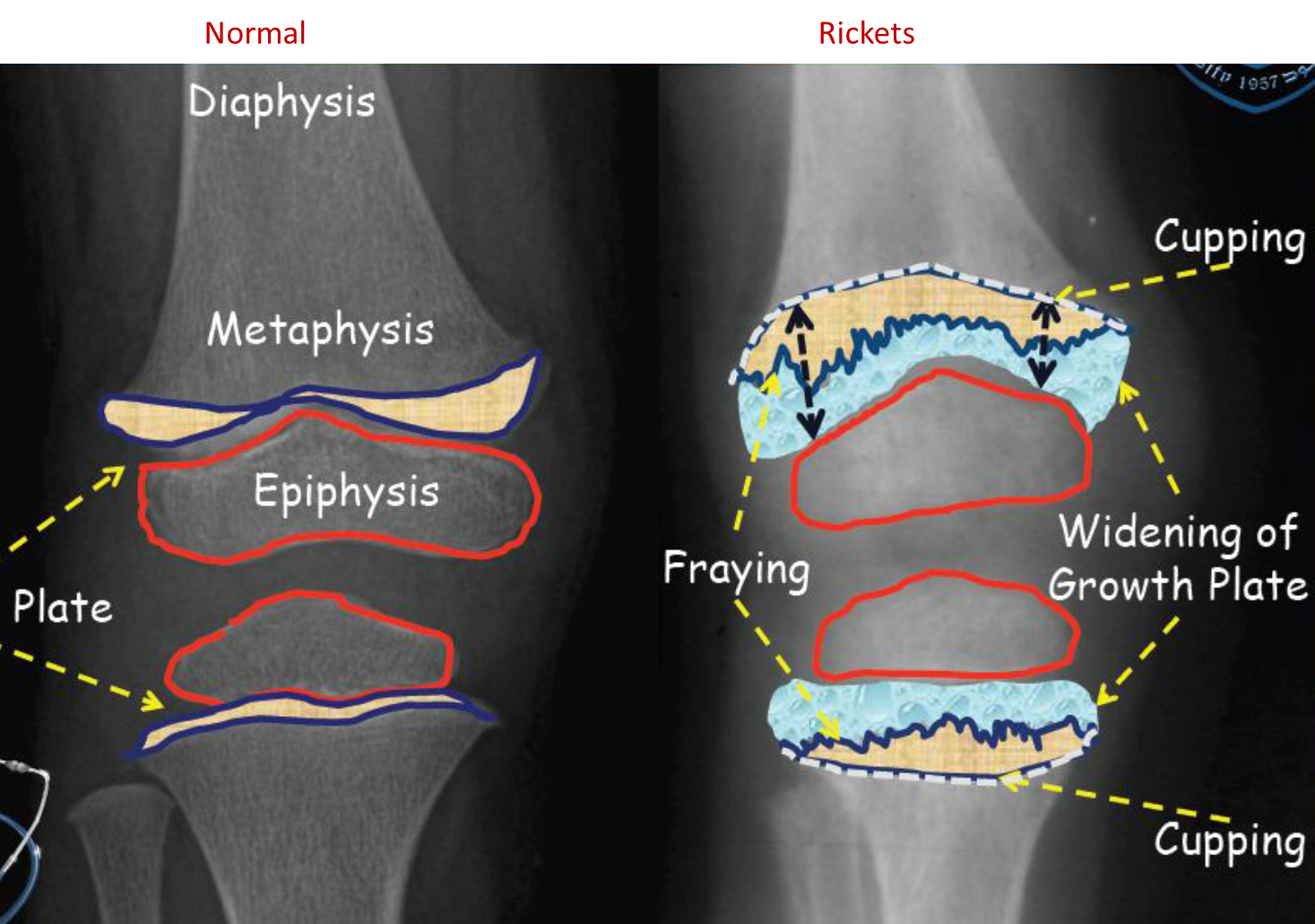 2years child with failure to thrive and repeated chest infections
2years child with failure to thrive and repeated chest infections - •Growth plate is widened
- •Metaphysical margin is cupped and irregular
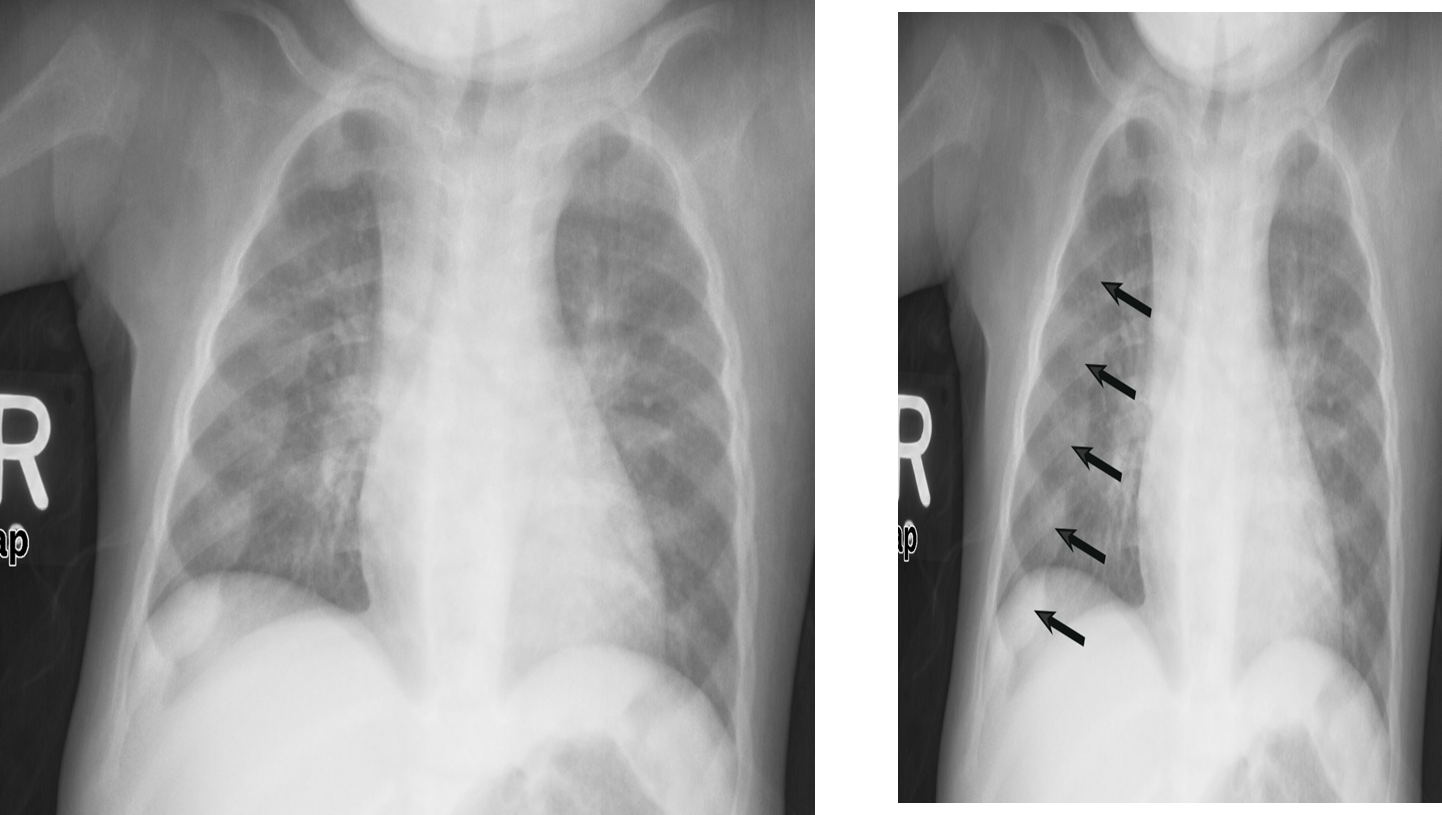 X-ray chest (AP view) of a child.
There are prominent nodular costochondral junctions z (black arrows) on the right side of the chest due to the expansion of the anterior ribs.
These findings are referred to as rachitic rosary because of their resemblance to beads on a rosary.
X-ray chest (AP view) of a child.
There are prominent nodular costochondral junctions z (black arrows) on the right side of the chest due to the expansion of the anterior ribs.
These findings are referred to as rachitic rosary because of their resemblance to beads on a rosary.