MED Intro
Measure the core temperature using thermometers
- Digital
- Mercury
Sites
- Mouth ⇒ 36.8 c
- Axilla ⇒ 36. 4 c
- Rectum ⇒ 37.3 c
MED CNS
- Often omitted if pain sensation normal
- Two test tubes
- filled with hot & cold water
- or tuning fork heated or cooled by water
SKILL Vital Signs
Types of Body Temperature
- Core Temperature
- Temperature of the deep tissues of the body
- Remains relatively constant unless exposed to severe extremes in environmental temperature
- Assessed by using a thermometer
- Surface Temperature
- Temperature of the skin
- May vary a great deal in response to the environment
- Assessed by touching the skin
Measuring Temperature
- It is measured using a thermometer with a Fahrenheit or Celsius scale
- There are some factors may could alter temp
- Eating, drinking hot or cold liquids and/or smoking can alter oral temp
- Make sure the patient has had nothing to eat, drink or smoke for at least 15 minutes prior to taking temp
- If so, wait 15 minutes before taking temp
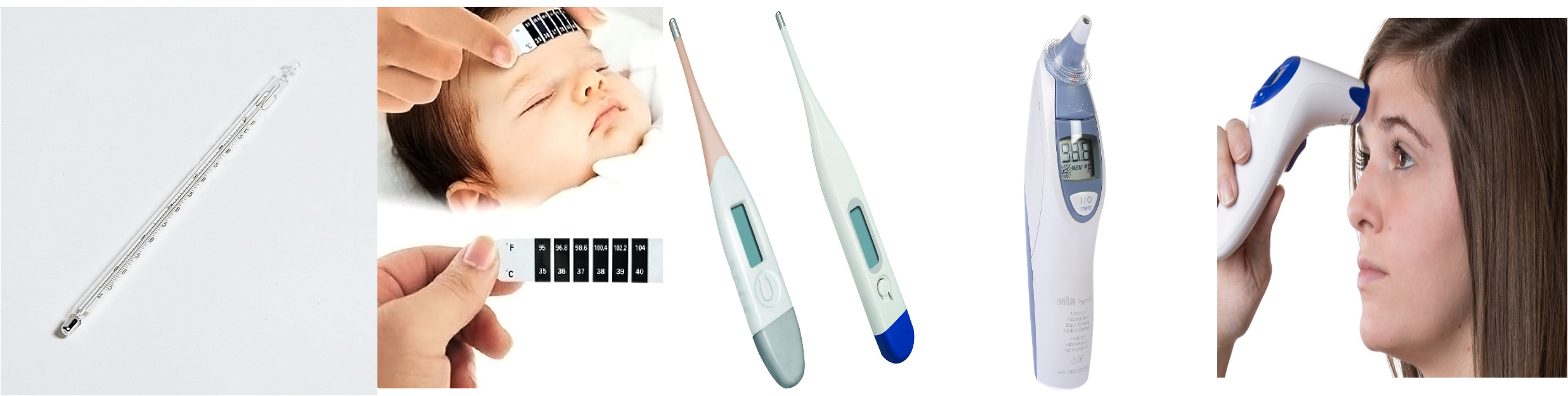
Types
- Glass Thermostat: may not be accurate
- Heat-sensitive patches: easy to use
- Digital thermometers: accurate, safe, fast
- Tympanic thermometer: accurate & fast, safe disposable cover can be used between patients
- Forehead thermometer
Best places to take temperature
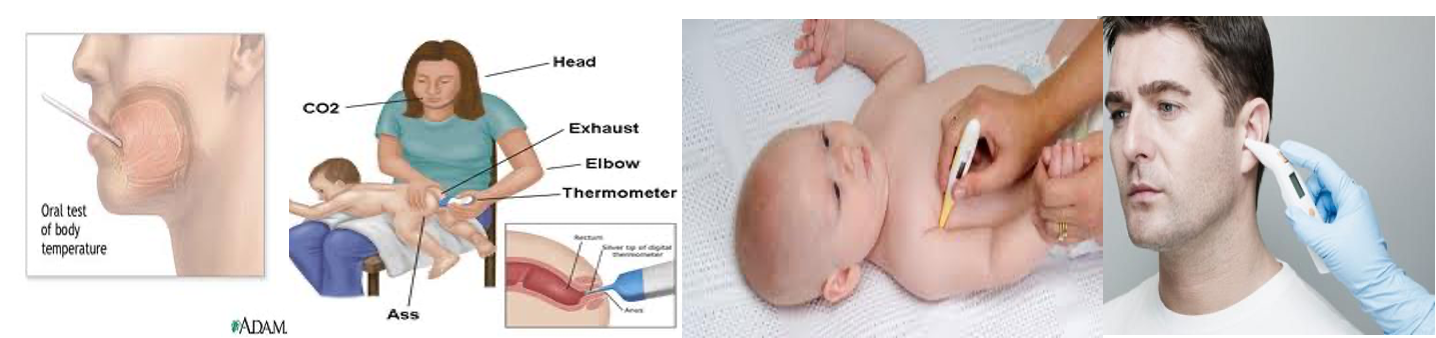
- Oral: most common & convenient
- Anus: most accurate
- Axilla or groin: mostly in pediatrics
- Aural
Causes of temperature fluctuation
- High: illness infection, exercise, excitement, high temperatures in environment
- Low: starvation, sleeping, inactivity, mouth breathing, cold temp environments
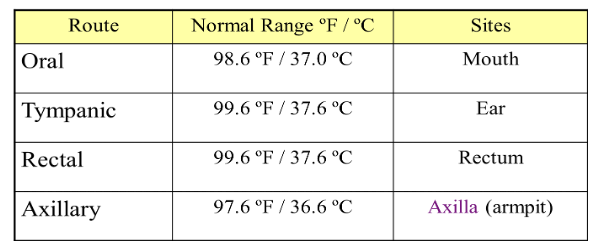
| Route | Normal Range | Sites |
|---|---|---|
| Oral | ||
| Tympanic |
Interpretation
-
Normal body temperature:
-
Fever (Hyperthermia): temp above the normal range (age dependent)
-
Hypothermia: Core body temperature less than 35oC (below 95° F).
-
Hyperpyrexia: Body temp exceeds 40-41 oC (104-106°F) rectally