Pediatrics
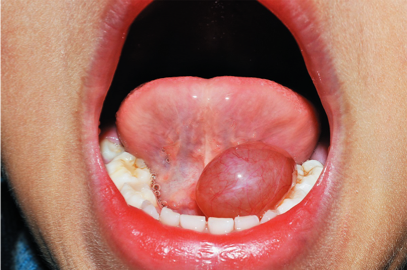
- Benign mass originating in the floor of the mouth: sublingual dilatation of a salivary gland
- Treatment: Excision
- It may interfere with feeding
Surgery
Ranula
It arises from a damaged sublingual gland.
Diagnosis: A child or young adult, Bluish in color, in the floor of the mouth, soft, fluctuant and transilluminate, noncompressible and nonreducible.
On Examination: Shape and size-1 to 5 cms in diameter, smooth surface with diffuse borders, not attached to the overlying mucosa, mylohyoid m.
Differential Diagnosis:
-
Sublingual dermoid-Transillumination negative
-
Hemangioma-Compressible (Other compressible swellings-Lymphangioma and meningocele).
Plunging ranula:
So-called when extends into the neck, passing beyond the floor of mouth and appears in the submandibular region
Diagnosis
- by bidigital palpation (one finger in the oral cavity and the other on the neck).
- The cross fluctuation will be positive.
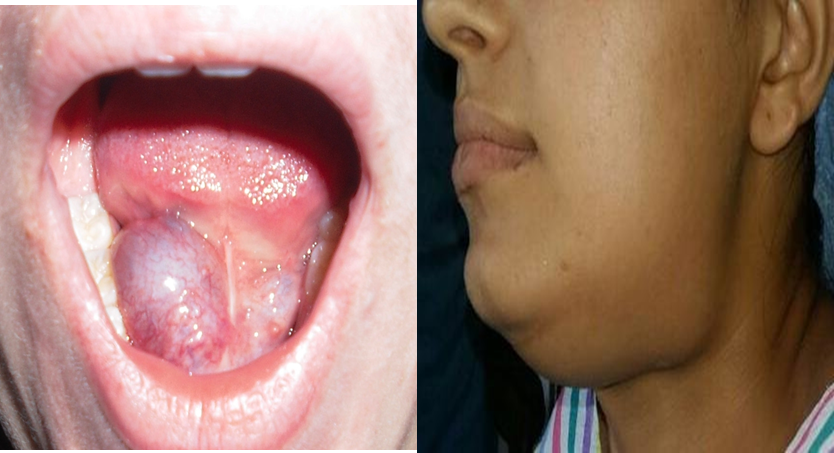
(example of compressible swellings —Lymphangioma and meningocele). Plunging ranula: when large ranula pass to the upper neck through the mylohyoid bone
Clinical Medicine
It arises from a damaged sublingual gland .
Diagnosis:
A child or young adult , Bluish in color, in the floor of the mouth, soft, fluctuant and transilluminate
Plunging ranula :
when large ranula pass to the upper neck through the mylohyoid bone
- So called when extends into the neck, passing beyond the floor of mouth and appears in the submandibular region
- Diagnosis—by bidigital palpation (one finger in the oral cavity and the other on the neck).
