Internal Medicine
Prof. Salih Bin Salih
DEFINITION
These are some tests done to see the functioning of the lungs. They tell us about the amount of air moving in & out of the lungs, the amount of air inside the lungs & also the diffusion of air in the alveoli. They are very useful in the following situations:
- To diagnose certain lung diseases
- To monitor the response to treatment
They also tell us if the pathology is in small airways or large ones.
LUNG VOLUMES & CAPACITIES
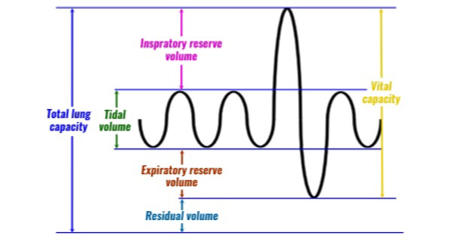
Definitions of volumes & capacities
- Tidal Volume (TV): amount of air moving in & out of the lungs with each breath ( N: 500cc)
- Inspiratory reserve vol.(IRV): Extra air which you can inhale with full force, after a normal inspiration ( after TV). (N is about 3000 cc)
- Expiratory reserve vol.(ERV): Extra air which can be blown out forcefully, at the end of normal expiration(after TV). (N is about 1000cc)
- Residual volume(RV): Even after full forceful blowing out, some air remains in the lungs, which is called RV.
CAPACITIES
2 or more volumes, added together, give a capacity. Remember two most important capacities:
-
Vital Capacity( V.C.): Maximum forceful
- inhaling + maximum forceful exhaling
- ( TV + IRV + ERV)
-
Capacities contd.
- b) Total lung capacity(TLC): Maximum amount of air which the lungs can hold after a deep inspiration
- ( T.V. + IRV + ERV + RV) or ( VC + RV)
- When you take a deep breath in & then hold, this is the total capacity of your lungs.
- (N: about 5700cc)
NAMES OF PULM. FUNC. TESTS
- Spirometry
- Peak expiratory flow
- DLCO ( diffusing lung capacity of carbon monoxide). Here we check how good is the diffusion of gases in the alveoli)
- ABGs
- Pulse oximetry
*In practice, PFT usually means spirometry *
THERA
Classification A) Ventilatory function tests:
- Lung volumes & capacities
- Test based on mechanical efficiency in breathing (PEFR)
B) Respiratory function test:
- measurement of arterial PO2, PCO2, pH
RESP sys function
- Ventilation; Spirometry
- Diffusion; DLCO - once air inside lung, oxygen is absorbed and CO2 thrown away
- Transport
- Regulation; brain center
RESP Sys Diseases
- Obstructive lung diseases
- Restrictive lung diseases
PFT
- Spirometry for ventilation
- DLCO for diffusion