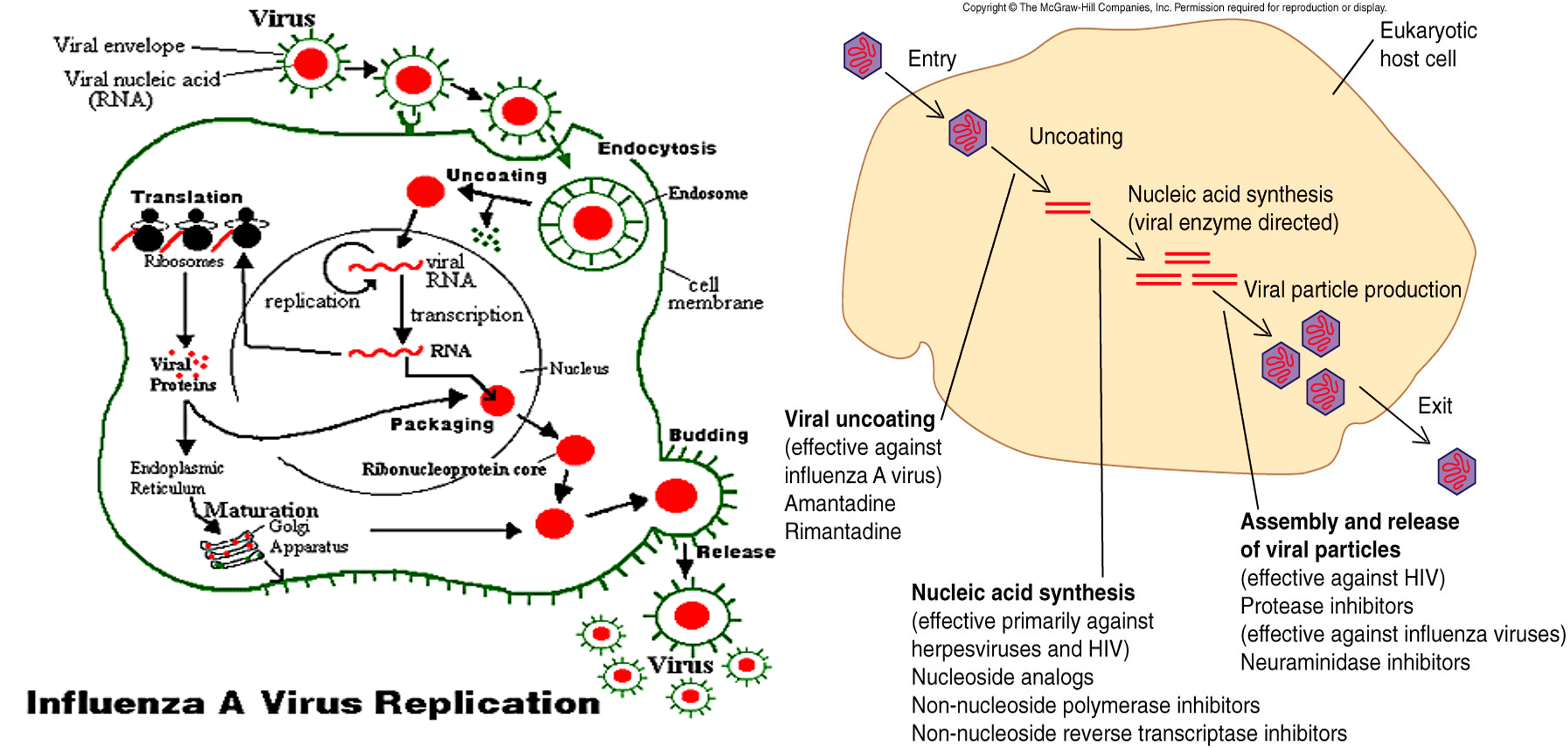
I. INHIBITION OF ATTACHMENT TO OR PENETRATION OF HOST CELL:
Phase 1: Attachment and penetration: The viruses attach and bind to the host cell membrane. Specific receptor sites on the host cell are recognized by corresponding areas on the specific virus. Then, the receptor-virus complex penetrates the cell and is encapsulated by host cell cytoplasm.
- GAMMA GLOBULINS (Immuno Globulins)
- - Enfuvirtide & Maraviroc
II. INHIBITION OF VIRAL UNCOATING:
Phase 2: Uncoating: The protein coat of the virus is dissolved liberating free DNA or RNA i.e. the viral genome.
- Amantadine + phase 1
III. INHIBITION OF SYNTHESIS OF VIRAL COMPONENTS (Non-structural protein, DNA and RNA)
Phase 3: Synthesis of viral components: The genome of the virus is duplicated and viral proteins are synthesized. At this time, host synthesis of nucleic acid and or protein is inhibited because the synthetic processes of host cell are directed for synthesis of viral components.
- RIBAVIRIN - liver
- Acyclovir - herpes
- Ganciclovir: Y
- IDOXURIDINE Y
- VIDARABINE Y
- ZIDOVUDINE Y
- Interferons
IV. INHIBITION OF ASSEMBLY OR RELEASE OF VIRAL PARTICLES:
Phase 4: Assembly of the virus particle and their release from the cell: The viral genome is encapsulated by viral protein. The mature virus is then released from cell.
- Rifampin - anti TB drug