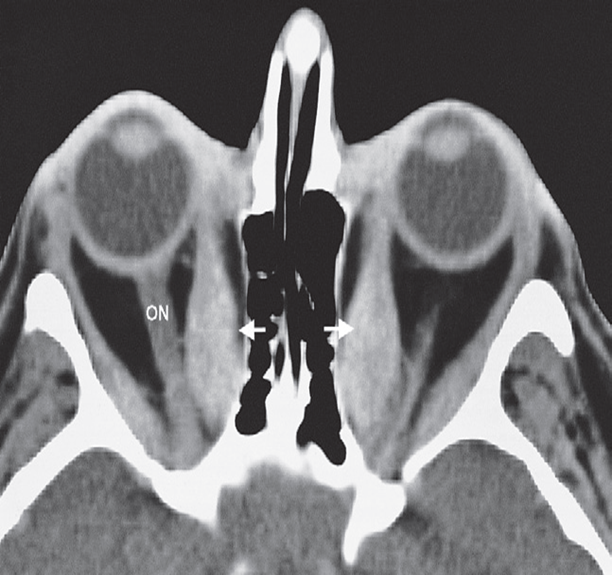
In thyroid eye disease, there is enlargement of the extraocular muscles which is frequently bilateral and may affect one, several or all the eye muscles.
There is also hypertrophy and oedema of the fat behind the eye which adds to the exophthalmos. - When severe, these changes can lead to compression of the optic nerve.
Thyroid eye disease. CT scan through the orbits
showing enlargement of the extraocular muscles, particularly the medial rectus (arrows). ON; optic nerve.