SURGERY
**A high-resolution x-ray taken in 2 views- medio-lateral oblique (MLO) & cranio-caudal (CC).
Abnormalities: architectural distortion, nodularity, mass, stellate lesion, microcalcifications, skin retraction, nipple changes and duct changes.
- Calcifications ranging from:
- benign involutional changes to suspicious
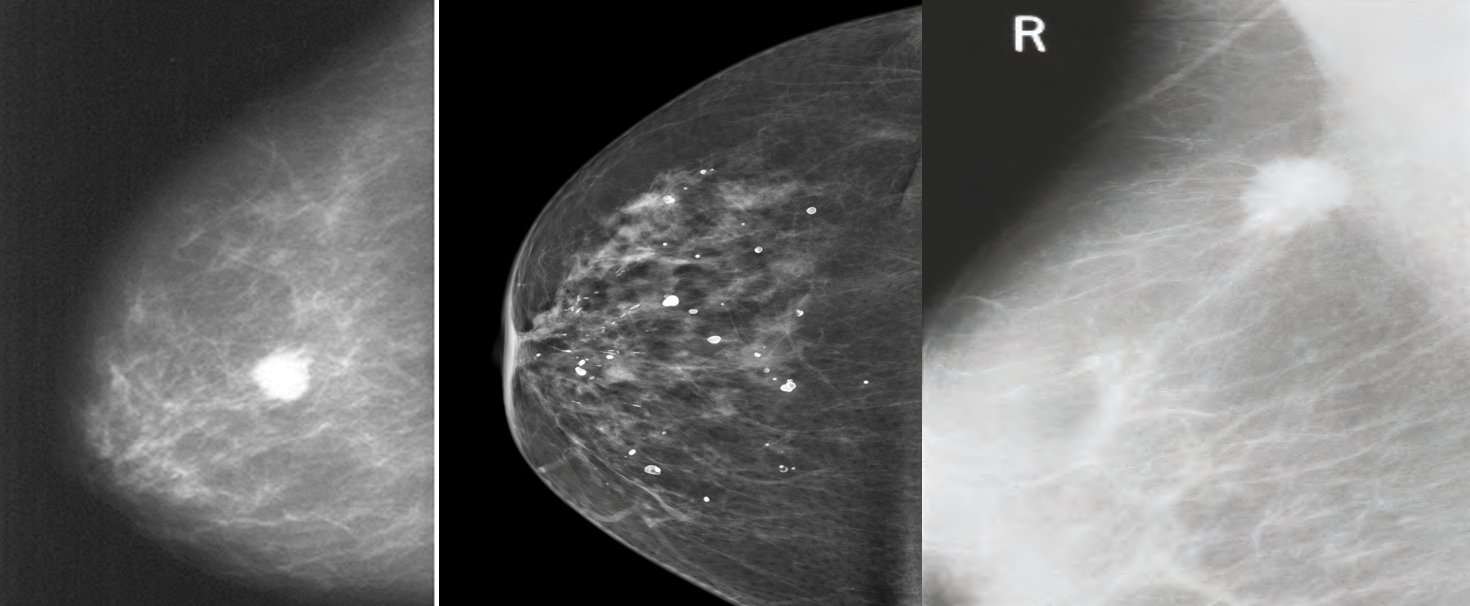
- suspicious micro-calcifications:
- pleomorphic, clustered, linear or branching (spiculated)
- Benign calcifications tend to be larger, more regular, white spots or flecks
Mammogram showing: (B) Benign calcifications (C) a carcinoma.
BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Database System) scores:
- 0 = Needs further imaging; assessment incomplete.
- 1 = Normal
- 2 = Benign lesion
- 3 = Probably benign lesion; needs 4 to 6 months follow-up (risk of malignancy: 1% to 2%).
- 4 = Suspicious for breast cancer; biopsy recommended (risk of malignancy: 25% to 50%).
- 5 = Highly suspicious for breast cancer; biopsy required (75% to 99% are malignant).
- 6 = Known biopsy-proven malignancy.
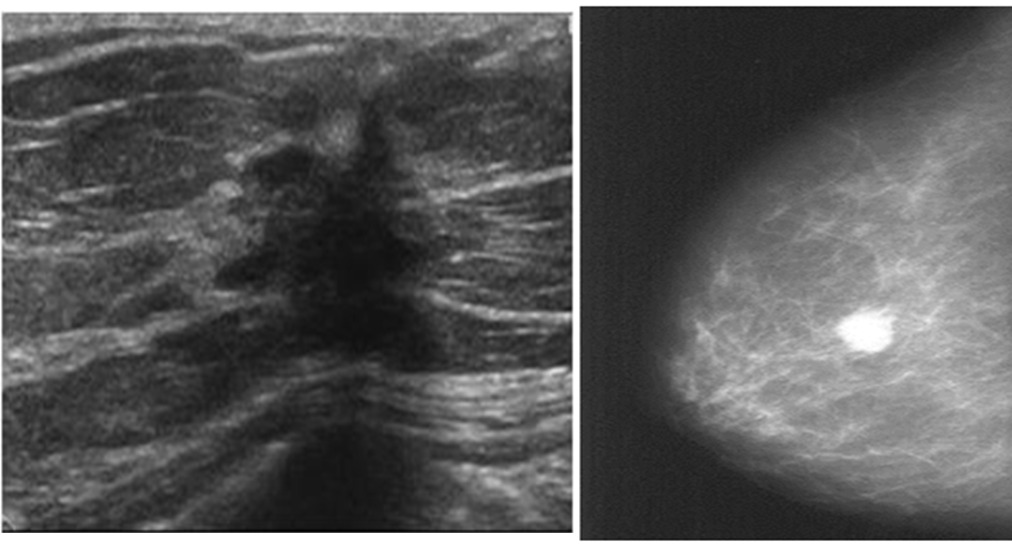
IMAGING
is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to image the human breast and is used as a diagnostic and a screening tool
Mammography detects the majority of cancers and can detect lesions ∼ z 2 years before they are clinically evident.
Mammogram technique and type:
1.screening:
- Screening mammograms are routinely administered to detect breast cancer in women who have no apparent symptoms. It is recommended after the age of 40 years.; for US <30 yrs
- The goal of screening mammography is the early detection of breast cancer.
- Single Medio lateral oblique view(MLO) is done only
2.Diagnostic Mammogram
- Diagnostic mammograms are used after suspicious results on a screening mammogram or after some signs of breast cancer alert the physician to check the tissue.
- For woman presenting with clinical evidence of breast disease, palpable mass or other symptoms such as breast pain and nipple discharge
Routine diagnostic mammography projections
- Craniocaudal (CC)
- Medio lateral oblique (MLO)
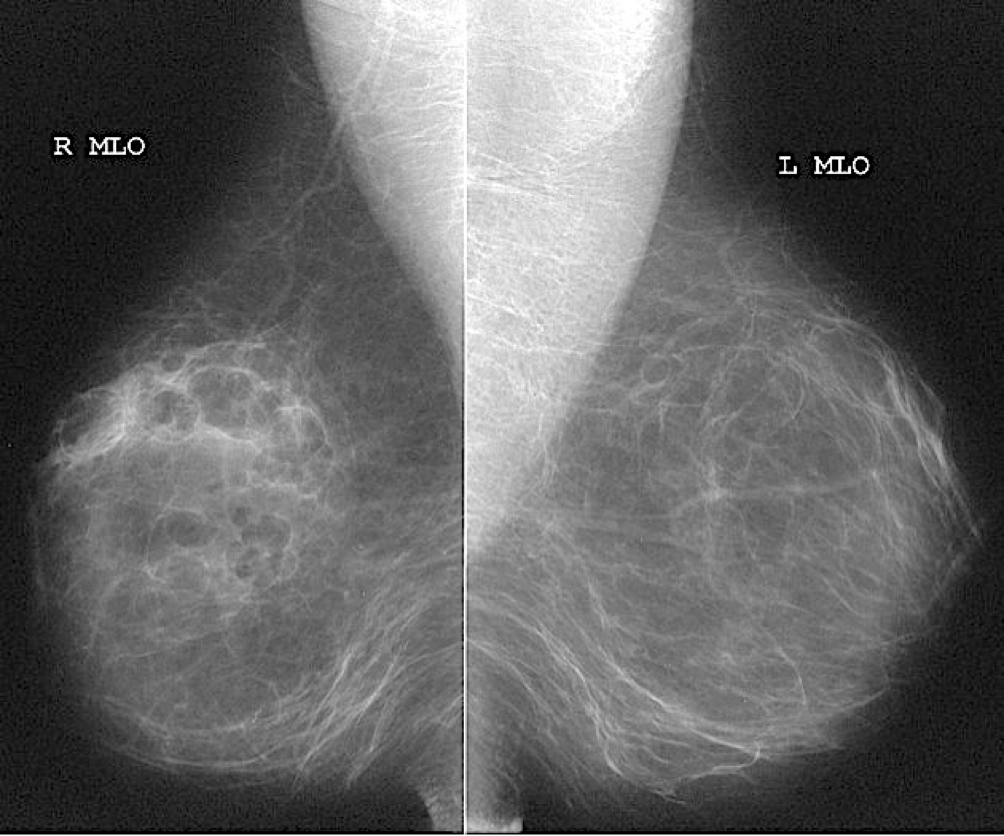
Additional views. Such as magnification views are done to detect microcalcifications
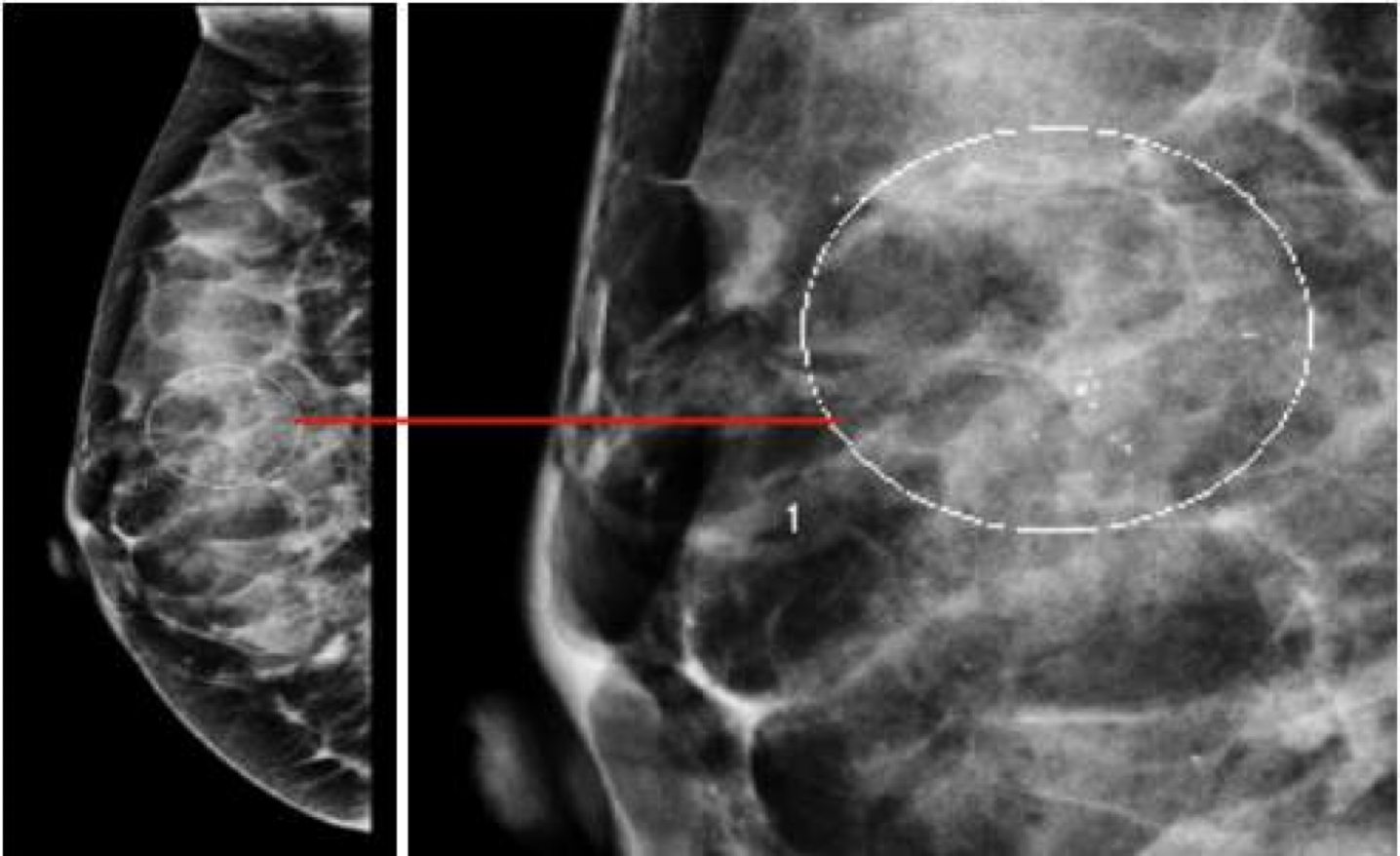
Mammography findings of benign and malignant breast lesions #Z
| Benign lesion | Malignant lesion | |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance of the lesion | - •Well-defined, circumscribed mass | - •Focal mass or density |
| Margins z | - •Surrounding radiolucent ring (halo sign) | - •Poorly defined, spiculated margins |
| Calcifications | - •Diffuse microcalcification or coarse calcification | - • Clustered microcalcifications |
| Further management z | - •Regular check-ups - •Possibly surgical excision | - •Fine needle aspiration or core needle biopsy |
-
In Breast Cancer Z