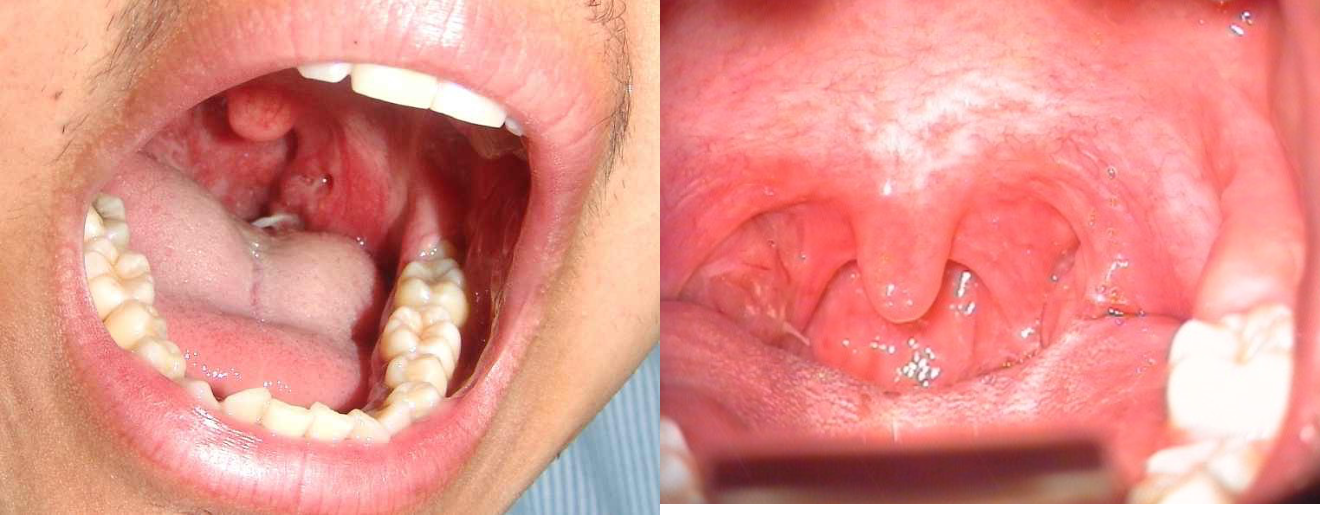
Pharynx Foreign Bodies
- Usually sharp FB
- Fish bone is the most common
- Common sites: tonsils, base of tongue, and vallecula
- Diagnosis by physical examination
- Treatment by removal


Esophagus Foreign Bodies
- Coins – 75%
- Meat, dentures, disc batteries, etc.
- Common locations: Cricopharyngeus, Aorta/left mainstem bronchus, Gastroesophageal junction
 Meat and vegetable matter less common in children – more in adults
Esophageal anomalies found in pts with recurrent impactions
Meat and vegetable matter less common in children – more in adults
Esophageal anomalies found in pts with recurrent impactions
Diagnosis
- Symptoms: Dysphagia, odynophagia, choking & cough
- Physical exam: Drooling, refuses oral intake
- Radiology
- Esophagoscopy
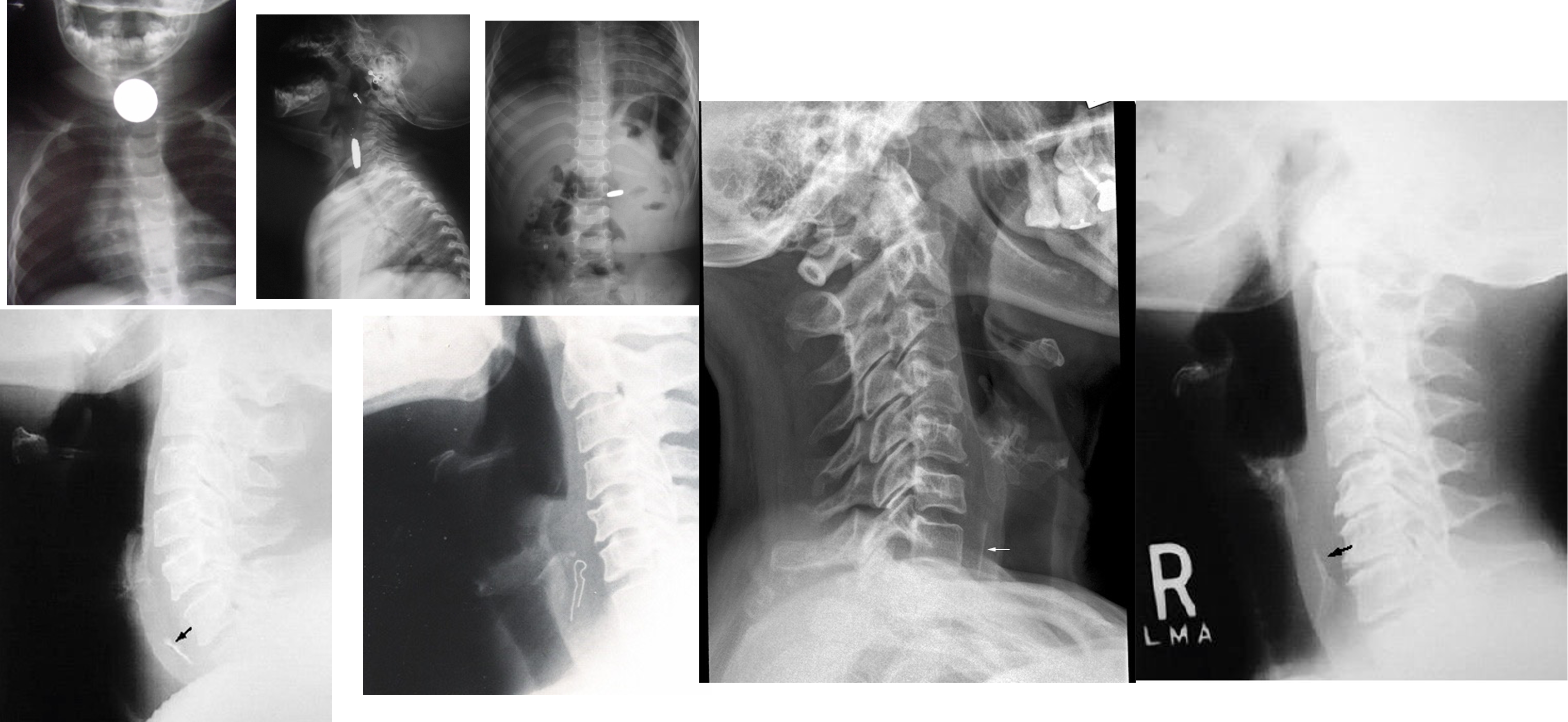
Treatment
- Removal via esophagoscopy
- Disc batteries and sharp objects removal is an emergency due to the risk of perforation

Choking/coughing – aspiration? Sx of resp compromise in 10% due to compression of trachea
Larynx Foreign Bodies
Presentation
- Dyspnea
- Cough
- Hoarseness or aphonia
Treatment
- Heimlich Maneuver
- Slapping the back with the patient’s head down
- Manual removal
- Removal by laryngoscopy
- Tracheostomy or laryngostomy (cricothyrotomy)
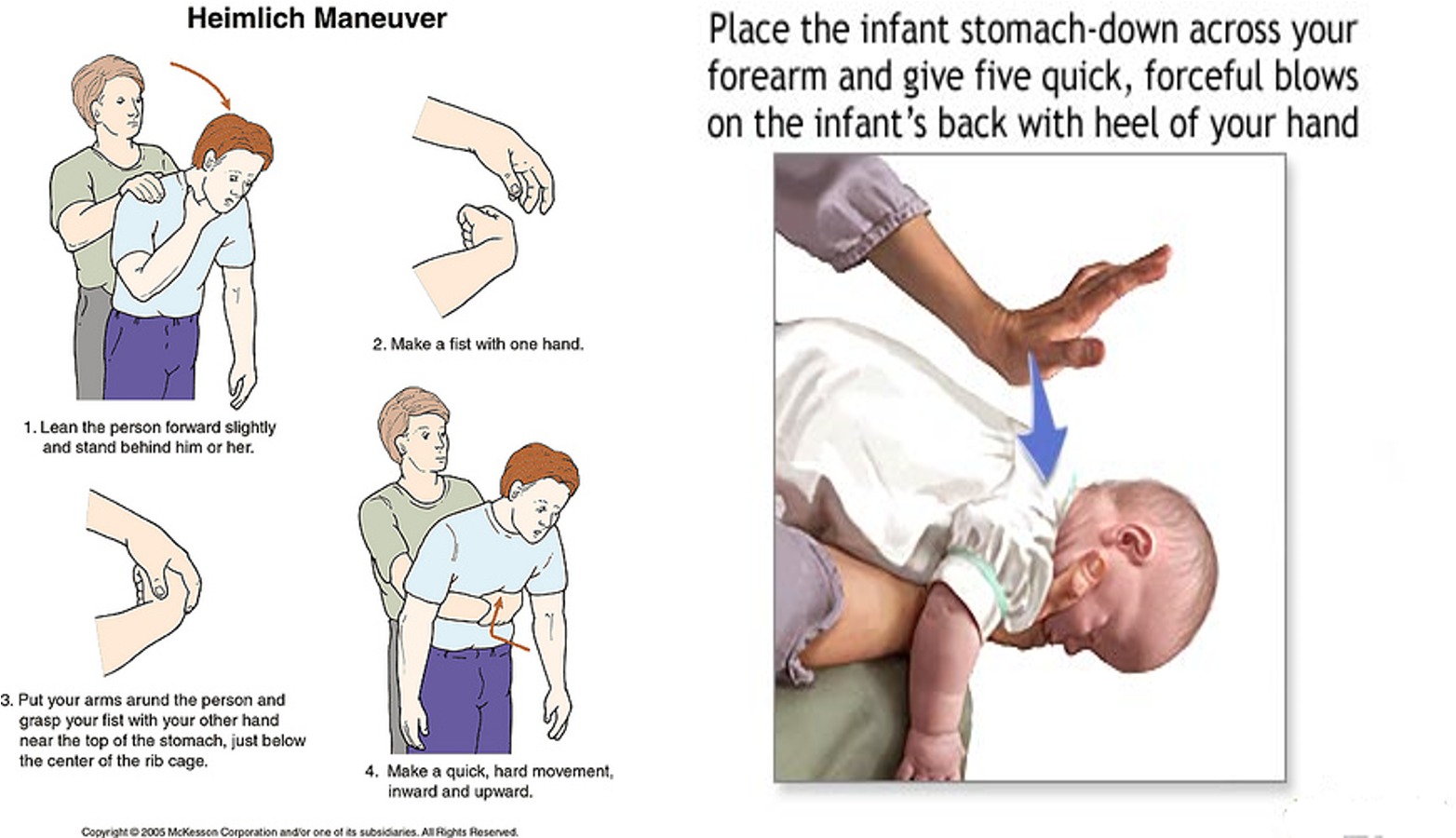 #Z heimlich Maneuver
#Z heimlich Maneuver
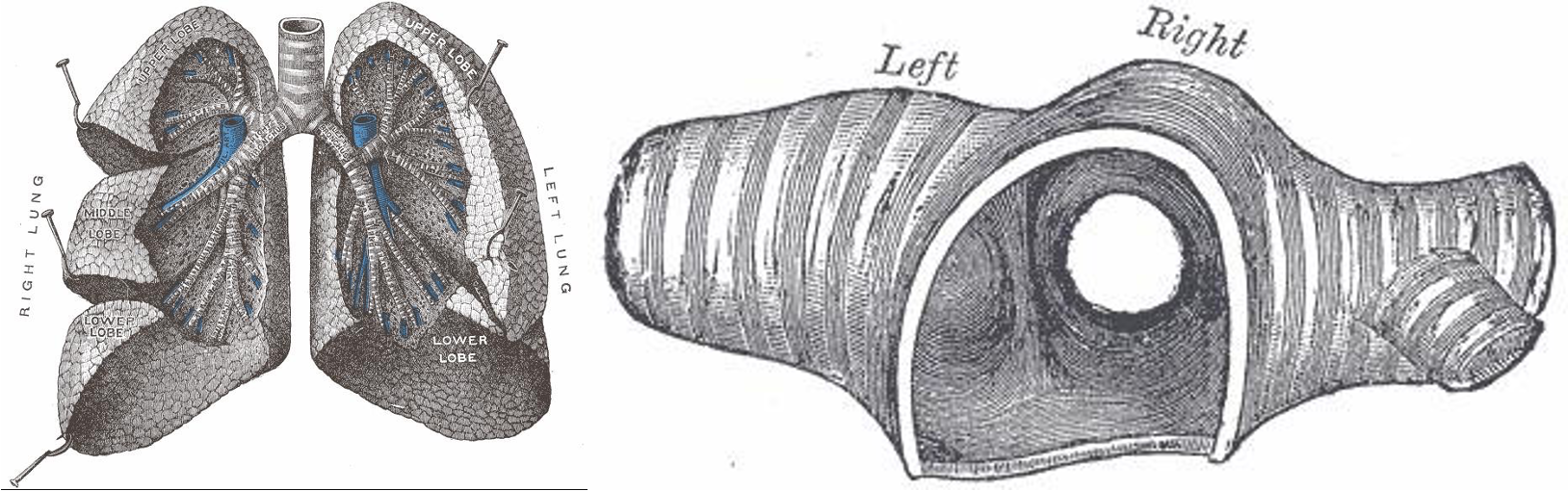
Tracheobronchial Tree Foreign Bodies
- Usually in infants and children
- Most FB’s are organic material (mostly food derivatives)
- Location: Mostly in the right side ( 60%)
Clinical Presentation
-
Choking, cough, gagging & cyanosis
- Caused by laryngeal reflexes
-
Asymptomatic phase
- Due to fatigue of cough reflex
-
Wheeze, intractable cough, persistent or recurrent chest infection
- due to emphysema, atelectasis, or infection
Treatment
To be initiated on clinical suspicion
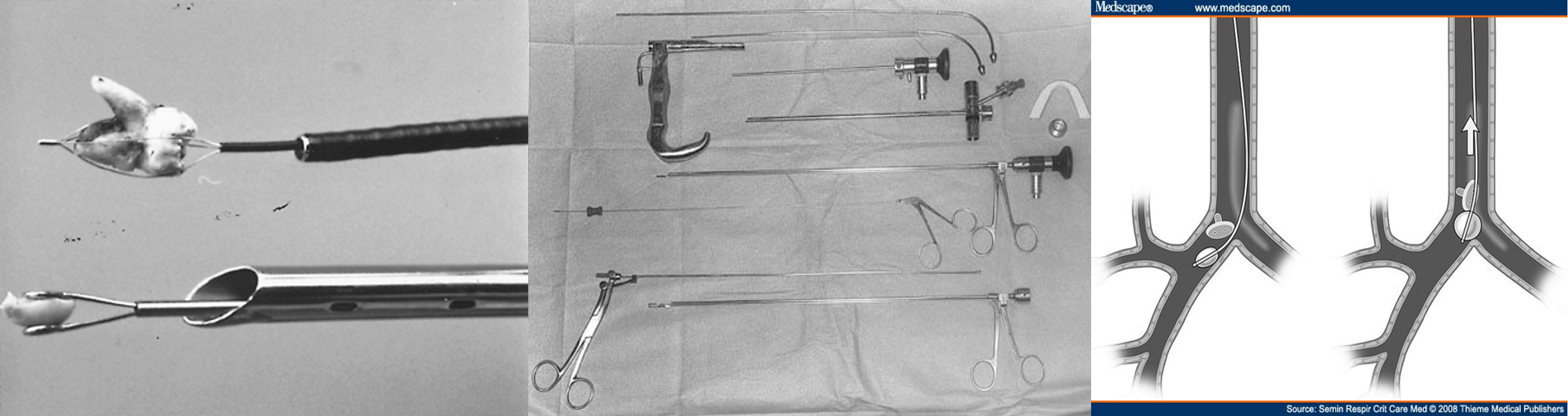
- Bronchoscopy: in most cases
- Bronchotomy
- Pulmonary resection
 OSPE
OSPE
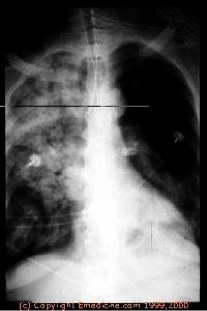
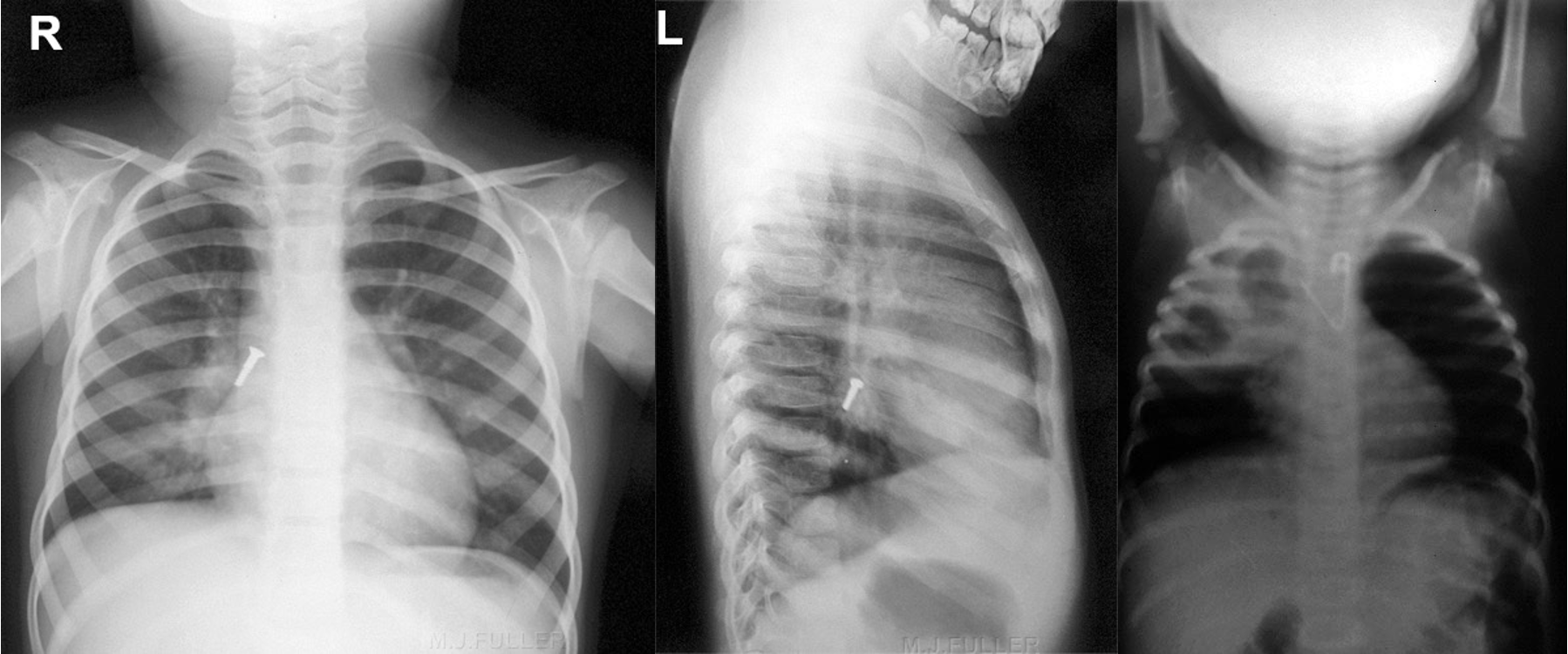
Radiology of Tracheobronchial F.Bs
- 2 Radio-opaque FB

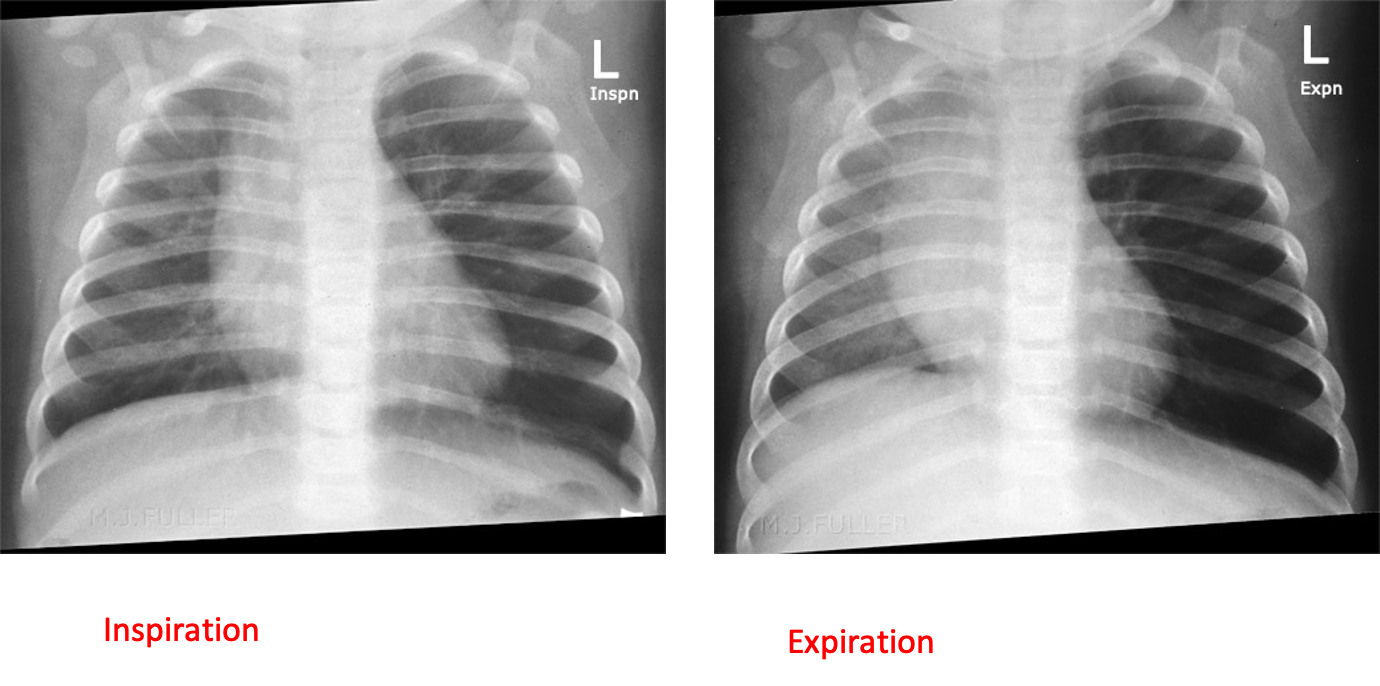
4 Collapse
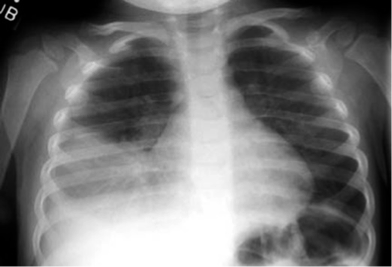
- Bronchopneumonia