-
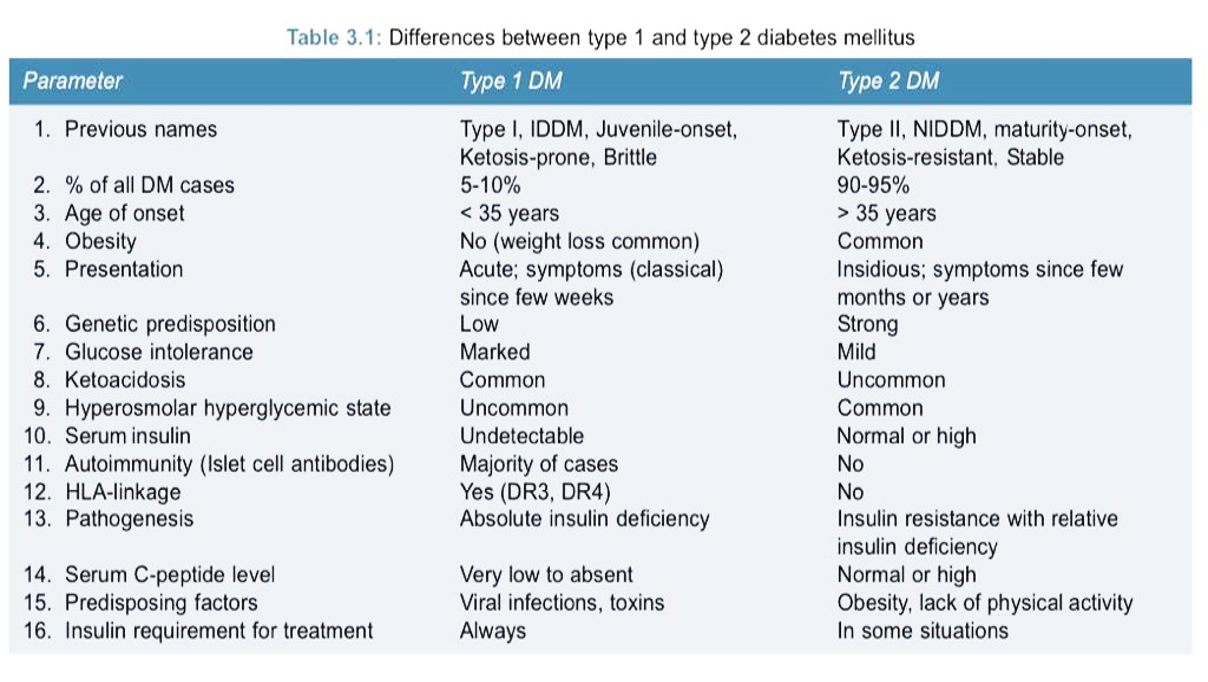
Type 2 DM patients constitutes about 90% of diabetics
-
Age: common to in middle age (over 35 years)
-
Symptoms are mild & develops gradually (mainly polyuria & polydepsia) BUT may be in some cases without obvious symptoms & may be detected by routine screening tests. Many cases present with complications even before DM is diagnosed
Type 2 DM: is a combination of insulin resistance & dysfunctional β cells
Most cases produce normal amounts of insulin (in early periods), but it is unable to work properly due to insulin resistance (hyperinsulinemia may occur in some cases)
-
DKA is NOT common in type 2 DM as insulin secretion is available & although not adequate yet it still can prevent the occurrence of ketoacidosis
Treatment :
- NO requirement for insulin to sustain life (not given in all cases)
- Diet & weight reduction esp. in obese can control type 2 DM
Aetiology of Type 2 DM insulin resistance & Dysfunctional b-cells
Insulin Resistance is the decreased ability of target tissues, such as liver, adipose & muscles to respond properly to normal circulating insulin
Obesity
is the most common cause of insulin resistance