External Ear
The external ear consists of:
- Auricle or Pinna
- External Auditory Canal
- Tympanic Membrane
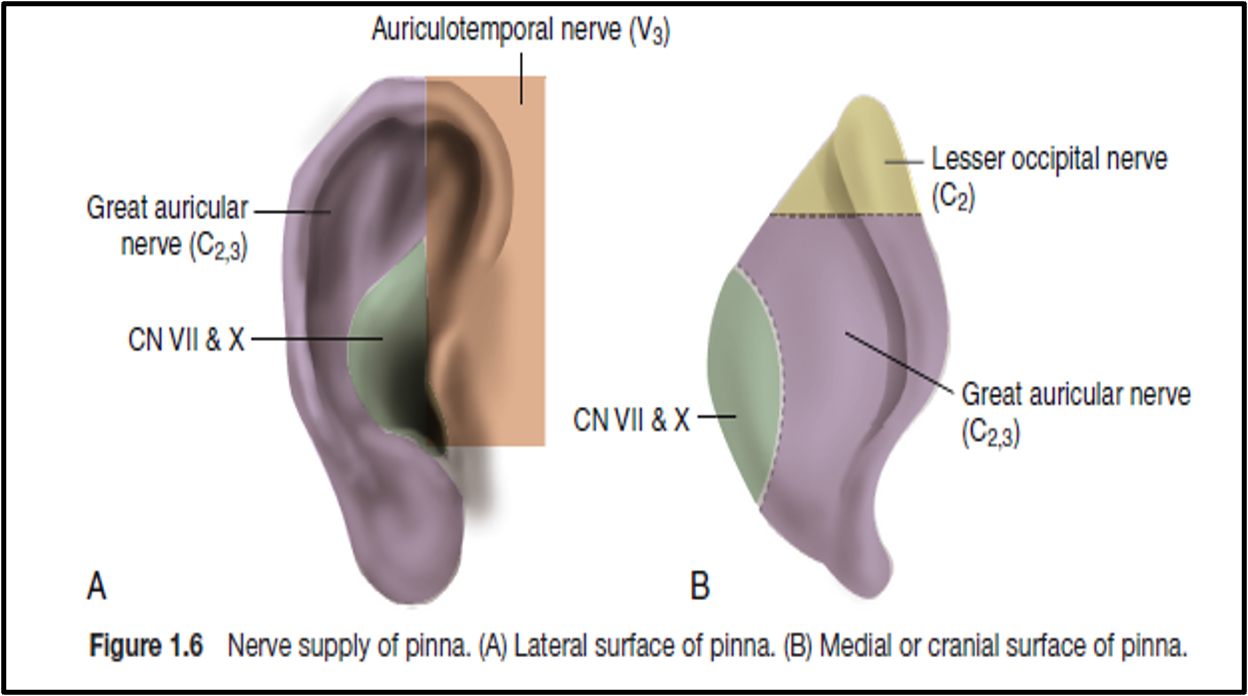
Auricle or Pinna
- Made up of single elastic cartilage except the lobule.
- Continuous medially with the external auditory meatus.
- Covered by skin.

External Auditory Canal (EAC)
- Extends from the pinna to the tympanic membrane.
- Approximately 24 mm in length.
- Not a straight tube:
- Inner part is directed upwards and backwards.
- Outer part is directed downwards and forwards.
- Two parts:
- Outer one-third: Cartilaginous (8 mm).
- Contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and ceruminous glands.
- Inner two-thirds: Bony (16 mm).
- No hair follicles.
- Outer one-third: Cartilaginous (8 mm).
Relations of EAC
- Superiorly: Middle cranial fossa.
- Posteriorly: Mastoid air cells and the facial nerve.
- Inferiorly: Parotid gland.
- Anteriorly: Temporomandibular joint.
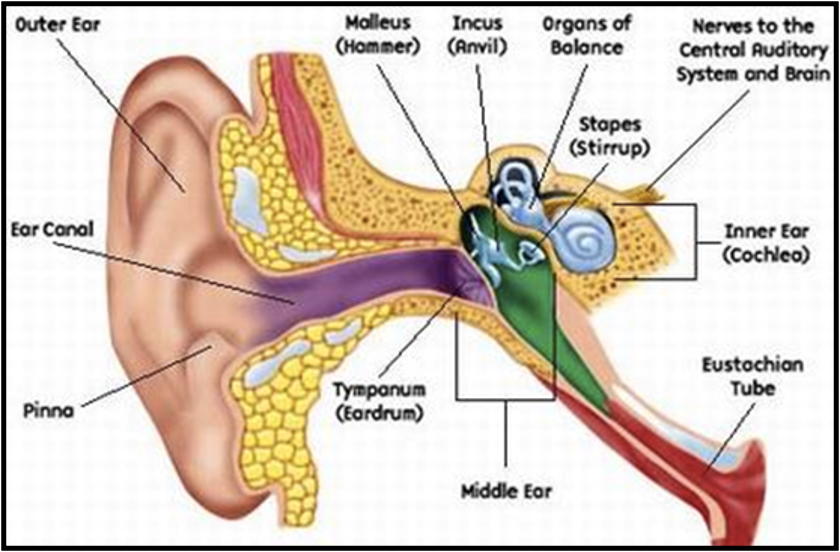
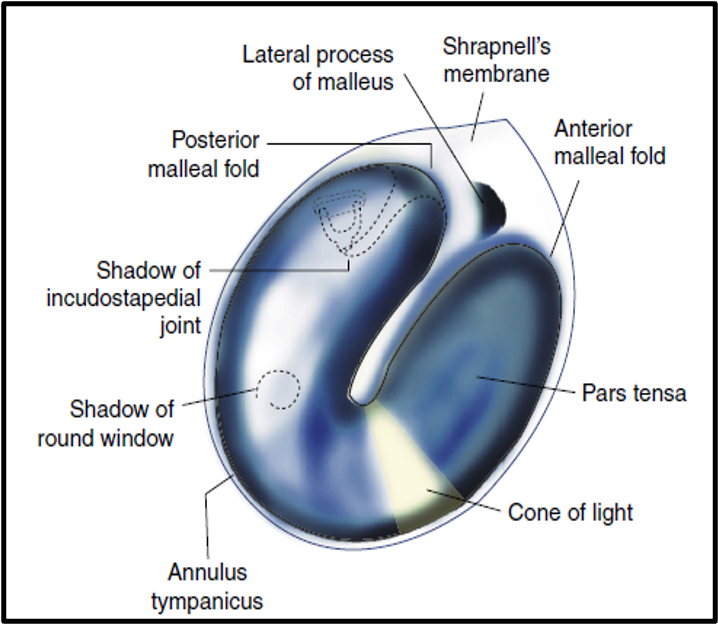
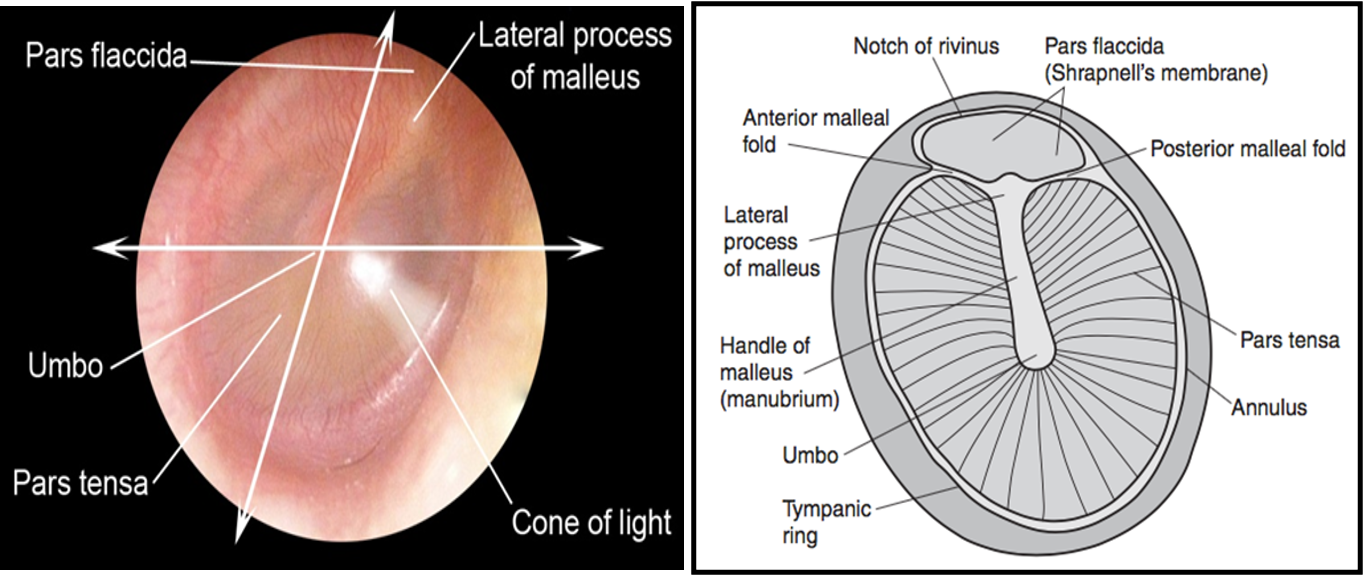
Tympanic Membrane
- Semi-transparent, pearl-white oval membrane.
- Separates the external and middle ear.
- Obliquely placed.
- Dimensions: 9–10 mm tall, 8–9 mm wide.
- Two parts:
- Pars Tensa: Pearl white.
- Pars Flaccida: Pinkish.
Layers of Tympanic Membrane
- Outer epithelial layer: Continuous with the skin lining the meatus.
- Inner mucosal layer: Continuous with the mucosa of the middle ear.
- Middle fibrous layer.