Case 1
This patient presents with palpitations, excess sweating and unintentional
5KG weight loss.
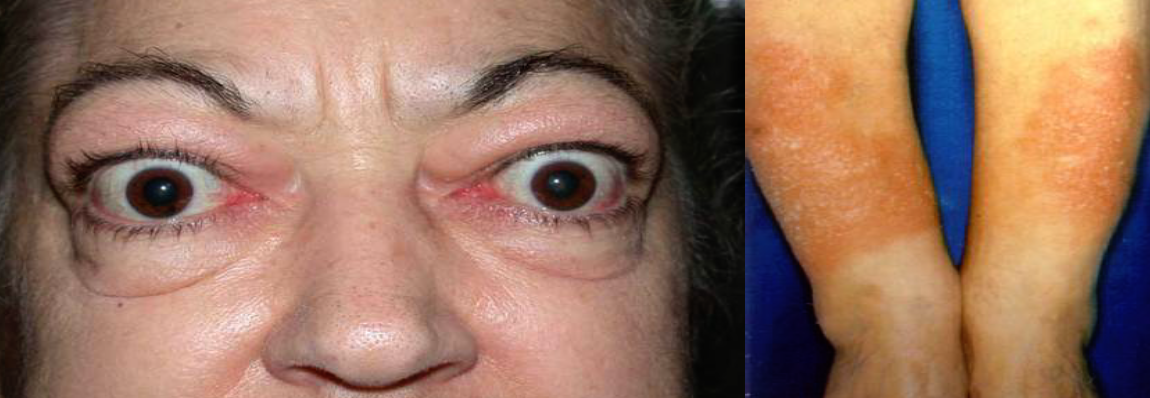
-
Describe the characteristic physical sign (Eye)? Z
- **Exophthalmos / Thyrotoxicosis **
-
Describe the lesion seen on the anterior aspects of her legs? Z
- Bilateral asymmetrical plaques with shiny pinky color
-
What is your diagnosis?
- Graves disease
-
Mention 2 blood tests which you will do for the diagnosis?
- **Thyroid function tests (T3, T4, TSH, TSH receptor stimulating antibodies)
- Anti TPO titter
-
Mention 3 treatment options for this medical condition?
- **Medications (Carbimazole and Methimazole)
- Radioactive iodine 131 therapy
- Surgical removal of thyroid
-
Mention 3 diseases of thyroid that present with thyrotoxicosis?
- Graves disease/Thyrotoxicosis
- Toxic nodule
- Thyroiditis
-
Name skin lesion may be associated with the disease Z
- Vitiligo
Case 2
 A 40- year- old lady complains of lethargy & vomiting. Her examination showed that her BP is 90/50 .Increased pigmentation of the skin & oral mucosa was noted
A 40- year- old lady complains of lethargy & vomiting. Her examination showed that her BP is 90/50 .Increased pigmentation of the skin & oral mucosa was noted
-
What is your clinical diagnosis?
- Addison’s disease.
-
Name any 1 etiology of this disease? Z
- TB, Autoimmune adrenalitis, Amylodosis, sarcoidosis
-
Name any 2 investigations which you will do for diagnosis of this disease? Z
- ACTH stimulating test, Adrenal antibodies, serum cortisol, ACTH.
-
What electrolyte changes can occur in the blood in this disease?
- Hyponatremia, hyperkalemia.
-
The patient suddenly collapses and is transferred to the ICU. What will be your immediate management? Name any 2.
- Follow ABC, IV hydrocortisone, IV fluids.
Case 3
An Old lady presented to ER with change in level of consciousness and was severely dehydrated. She is K/C of diabetes mellitus on insulin. The results of U/E’s and ABG’s are shown below. - 50 year old obese lady presented with altered level of consciousness and severe dehydration.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Serum Sugar | 18.6 mmol/L | 2.2 - 4.9 mmol/L |
| Serum osmolality | 400 mOsm/kg | 275-295 mOsmol/kg |
| Serum pH | 7.30 nmol/L | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| Bicarbonate | 15 mEq/L | (22 -28) |
| Sodium | 128 mmol/L | (136 -145) |
| Potassium | 4.8 mmol/L | (3.5 – 5.00) |
| Urea | 4 mmol/L | 1.2-3.0 mmol urea/L |
| Creatinine | 80µ mmol/L | 53 -106 µ mol/L |
| Serum Ketones | Normal |
-
Name 3 abnormal laboratory findings present?
- 1- High glucose level
- 2- high osmolality
- 3- low sodium
- 4- low pH
-
What is the clinical diagnosis?
- Hyperglycaemia hyperosmolar non ketotic “hyperglycaemia hyperosmolar state”
-
Name 2 conditions that may precipitate this hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic coma?
- 1- dehydration
- 2- infection
Case 4
A 24 year old woman presented with symptoms of tachycardia and 3 Kg weight loss. She was on estrogen containing contraceptive pill.
Investigations showed:
- Total serum thyroxine 186 nmol/l (NR 60 – 160)
- Free T4 12.5 pmol/l (NR 9.4 – 24.5)
- Free T3 11.8 pmol/l (NR 2.9 – 8.9)
- Serum TSH <0.1 mU/l at 0 min & 30 min after I/V TRH (200µg)
What is the diagnosis?
a. T3 thyrotoxicosis
What are treatment options for this condition?
a. Radioiodine therapy
b. anti thyroid drugs
c. Surgery
Case 5
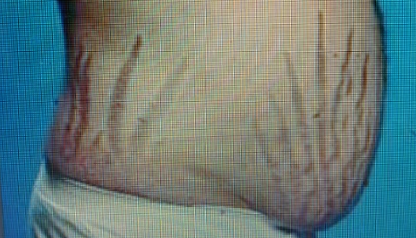
 Patient diagnosed recently as hypertensive. The dr. refer him for this stiae..
this young woman was found have HTN on routine exam and referred to derma for excessive hair growth of hair
Patient diagnosed recently as hypertensive. The dr. refer him for this stiae..
this young woman was found have HTN on routine exam and referred to derma for excessive hair growth of hair
-
What is your clinical diagnosis? Cushing’s syndrome/disease
-
Name any 3 clinical features of this condition? Buffalo hump, violaceous striae, HTN/DM, acanthosis nigricans, Moon Face, Central Obesity, Proximal muscle weakness
-
Name 2 screening tests used for diagnosis of this condition
- Dexamethasone suppression test
- Late night salivary cortisol,
- 24 h urinary free cortisol
-
Name 2 imaging tests for localization of the disease?
- Pituitary MRI
- MRI/CT for adrenals
-
Describe 2 treatment options? Z
- Transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary
- total bilateral adrenalectomy
- Pituitary Radiotherapy
- Medical treatment
-
Whats hormonal abnormality high cortisol
Case 6
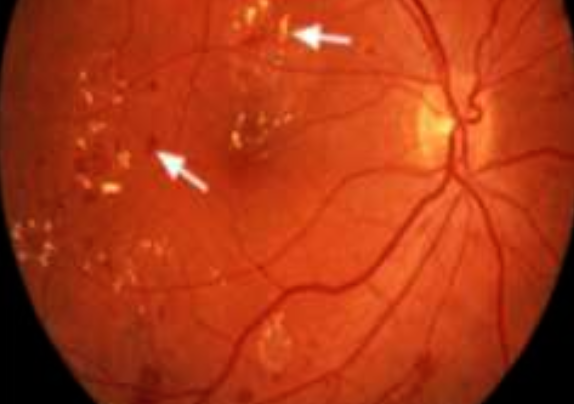
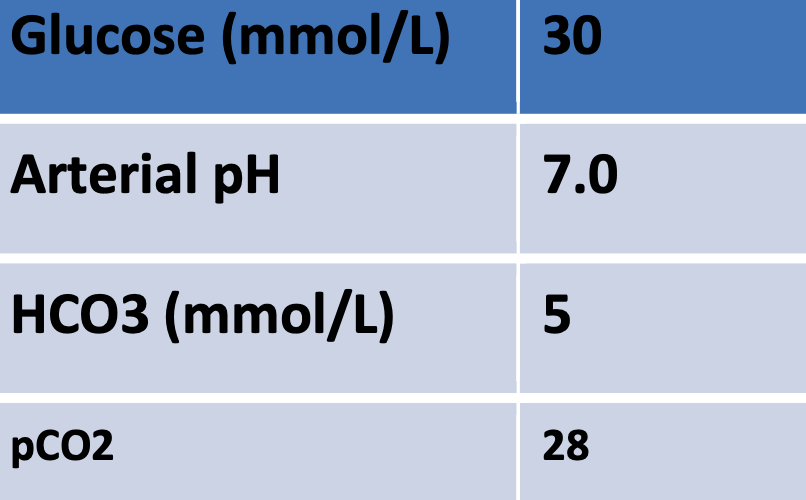
Young patient. Known case of type 1 DM. Brought to the E.R. in a confused state. His fundus examination is shown above
Blood tests :
- •Hb : 13g/dL
- •Blood sugar : 450mg/dL
- •Blood pH 7.20
- •Serum HCO3: 15meq
- •Arterial pCO2: 25mmHg
- •Urine ketones : ++
-
What fundus changes can you see here? Name any 2. Hard exudates and dots and blots hemorrhage
-
Name 3 abnormalities seen here in the blood tests? High blood sugar, low bicarb, and low PH
-
What is the acid base disorder present? High anion gap Metabolic acidosis (DKA)
-
What immediate treatment will you advise in this patient? Mention any 2. Insulin IV, and IV fluids (0.9 NS)
Case 7
LAB Results :
- Glucose 800
- PH 7.32
- Na 129
- serum ketones is Normal
what’re your findings ? Acidemia, hyperglycemia, hyponatremia
Diagnosis? Nonketotic hyperosmolar hyperglycemia
Case 8
A 40 year old man presented with fatigue, fever and painful goitre. The results of investigations were as follows:
- Hb 14.3 g/dl
- WBC 11.2 x 109/l
- ESR 100 mm in the first hour
- T4 32.4pmol/l (NR 9.4 – 24.5)
- TSH < 0.1mU/l (NR 0.5 – 5.5 )
- Radio-iodine 131 thyroid scan: uptake at 4 hours < 5% (normal range 6 -18%)
-
What are the lab result abnormalities? T4 high, low TSH, thyroid uptake scan is low
-
What is the most likely diagnosis? de Quervain’s thyroiditis
-
What treatment is required? Z Symptomatic treatment like beta blocker to control toxic symptoms, because it resolved spontaneous within 7 months
Case 9
A 34 year old lady with 8 year history of menorrhagia and anemia. She also complained of weight gain, cold intolerance. Visual field showed a bitemporal hemianopia. Investigations showed:
- ECG: Bradycardia, low voltage QRS complexes.
- CXR: globular heart outline.
- Prolactin: 3,600 (NR females <700)
- Gonadotrophins: Normal
- 9 am Cortisol: 519 nmol/l (NR 220 – 720)
- Free T4: 2.5pmol/l (NR 9.4 – 24.5)
- TSH: >61.0 mU/l (NR 0.5 – 5.5)
Thyroid autoantibodies: positive CT brain: Enhancing mass in pituitary with supracrllar extension of 17 mm.
-
What is the diagnosis? ---Pituitary adenoma---
-
What is the cause of raised prolactin? Z ---Pituitary adenoma---
Case 10
A 34 year old lady with 8 year history of menorrhagia and anemia. She also complained of weight gain, cold intolerance. Visual field showed a bitemporal hemianopia. Investigations showed:
- ECG: Bradycardia, low voltage QRS complexes.
- CXR: globular heart outline.
- Prolactin: 3,600 (NR females <700)
- Gonadotrophins: Normal
- 9 am Cortisol: 519 nmol/l (NR 220 – 720)
- Free T4: 2.5pmol/l (NR 9.4 – 24.5)
- TSH: >61.0 mU/l (NR 0.5 – 5.5)
Thyroid autoantibodies: positive
CT brain: Enhancing mass in pituitary with supracrllar extension of 17 mm.
-
What is the diagnosis?
---Primary? hypothyroidism--- -
What is the cause of raised prolactin?
---prolactinoma / profilation---
Case 11
A 45 year old man presented with paresthesia and numbness of his left hand. The results of his glucose tolerance test (75 grams orally, venous plasma sugar at 30 minute intervals) were as follows
| Time | Venous plasma glucose (mmol/l) | Growth hormone (mU/l) | Reference Growth hormone |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8.9 | 14 | 0-5 ng/mL (Fasting) |
| 30 | 14.2 | 19 | < 0.3 μg/L |
| 60 | 14.9 | 22 | < 0.3 μg/L |
| 90 | 13.6 | 43 | < 0.3 μg/L |
| 120 | 12.6 | 24 | < 0.3 μg/L |
-
Outline 2 abnormalities of the test results? a. ---abnormal GH level--- b. ---abnormal glucose level---
-
What two diagnoses in this patient are linked? a. ---acromegaly--- b. ---diabetes mellitus---
Case 12
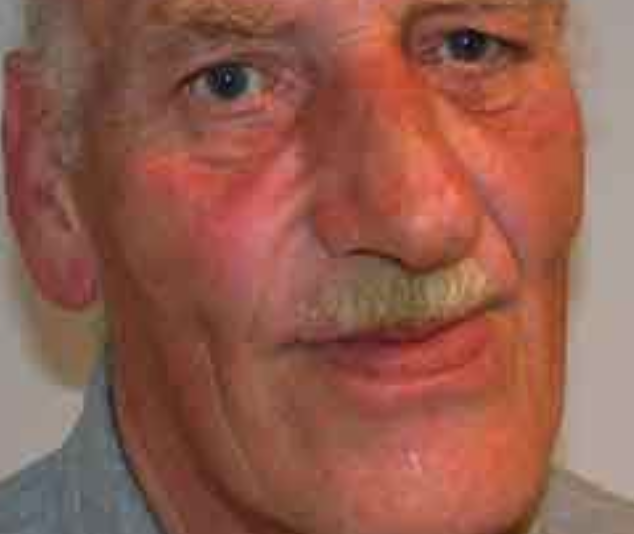 65 year old man presents with worsening hoarseness of voice and noticed progressive coarsening of his skin
65 year old man presents with worsening hoarseness of voice and noticed progressive coarsening of his skin
-
What is the clinical diagnosis?
acromegaly -
What investigation should be requested?
- GTT suprestion test
- insuline like growth factor 1
- serum growth hormone
IThis young man was found to have hypertension on routine examination and referred to dermatology for purple striae on his body.
-
What is the clinical diagnosis?
Cushing’s syndrome. The combination of hypertension and purple striae is highly suggestive of this condition. -
What is investigation of choice?
24-hour urinary free cortisol or a dexamethasone suppression test are common initial investigations to confirm the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome.