Case
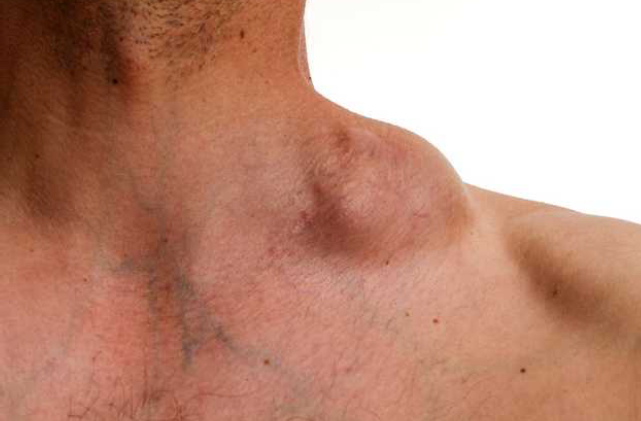
A53-year old female presented with a neck swelling.
Q1: Mention 5 relevant questions you will ask this patient regarding history of present illness. Answer:
- How did she notice it?
- Is it painful or not?
- Does it affect the breathing, swallowing?
- Any change of skin color or discharge?
- Does it move with swallowing?
Q2: Mention a method to assess for retrosternal extension of neck swelling during clinical examination? Answer: By percussion over the sternum; it will be dull.
Q3: Mention TWO initially required diagnostic tools in this case? Answer: labs order TFT (TSH,T3,T4), also chest x-ray and ultrasound, TSH / TFT
Q4: Mention Two examples of swellings located at the anterior neck triangle? Answer: goiter (as due to hyper or hypothyroidism), lymphadenopathy, thyroglossal cyst.
- Thyroglossal duct cyst
- Dermoid cyst
- Ranula
- Submental lymph node
Q5) Mention 2 complications of total thyroidectomy? Answer
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Recurrent Laryngeal nerve injury
- Hemorrhage which can compromise patient’s airway
- Infection
Since when?
Case
 1- 5 Presenting Features
1- 5 Presenting Features
- Lymphadenopathy: cervical, mediastinal, inguinal
- B-symptoms: fever, night sweat, weight loss
- Pain with alcohol drinking
- Chest pain due to mediastinal masses
- Pruritis
- Splenomegaly
- Hepatomegaly
2- Diagnostic Investigations x2
- Bone marrow: cytology and histology
- CXR
- ESR
3- Staging Tests x2
- PET
- CT
4- Management Options
- Chemotherapy: rituximab, methotrexate
- Radiotherapy
- Surgical resection
Case
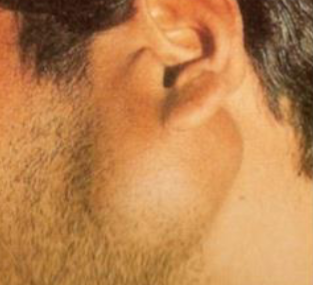 A 35-year male presented with this swelling (arrow) which he noticed 3 months back.
A 35-year male presented with this swelling (arrow) which he noticed 3 months back.
Q1: What are 3 important physical signs you will elicit on the palpation of this swelling? Answer:
- Tenderness
- Attachment
- Consistency
Q2: Mention 3 differential diagnoses. Answer:
- Parotid abscess
- Salivary gland tumor
- Branchial cyst
Q3: What 2 imaging investigations may be helpful in the diagnosis? Answer:
- U/S
- CT/MRI
Q4: How would you establish a diagnosis? Answer:
- By history, examination and imaging results (Double check the answer)
Case
Discharge foot wound • Question you want to ask in history?
- Duration of symptoms,
- what kind of discharge,
- Ass. sx?
- fever,
- if it was healed before,
- previous trauma?
- previous amputation
• Management? Local wound care Debride infected necrotic devitalized
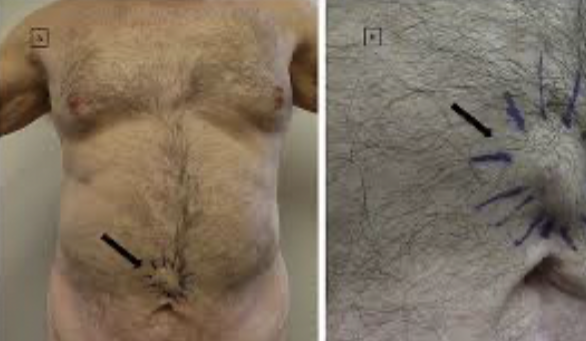
Sister Marry Joseph Nodule
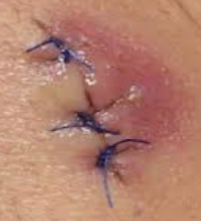 1- What is the diagnosis?
Surgical site infection.
1- What is the diagnosis?
Surgical site infection.
- 2- What is the most likely causative organism? Staphylococcus aureus.
3- What is the management 4 steps?
- Remove the sutures and send for C/S.,
- Incision and drain the pus.,
- Topical antibiotic.,
- Daily dressing.
Five days post abdominal surgery the given patient complained of right lower limb pain and swelling.
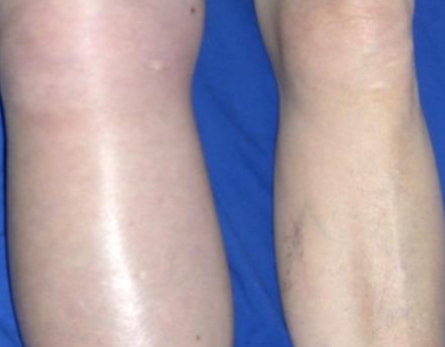 Q1: What is your diagnosis? DVT
Q1: What is your diagnosis? DVT
Q2: How to confirm the diagnosis? Doppler US & angiogram
The listed patient has presented with left neck swelling for 6 months.
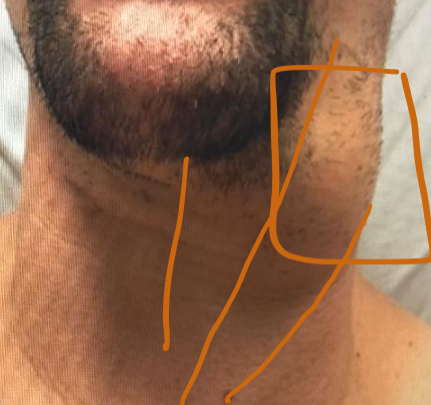 Q1: What is the best initial radiological investigation in this case? Ultrasound
Q1: What is the best initial radiological investigation in this case? Ultrasound
Q2: List FOUR possible causes of this lesion?
- Branchial cyst,
- Salivary gland tumor,
- Carotid body tumor,
- Lymphadenopathy
A young female was seen with this scar 3-month post abdominal surgery.
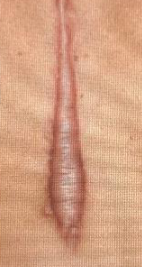 Q1: What is the abnormality? Hypertrophic scar
Q1: What is the abnormality? Hypertrophic scar
Q2: What is the treatment? No need for treatment, unless Pt want (by laser excision or corticosteroid injection)
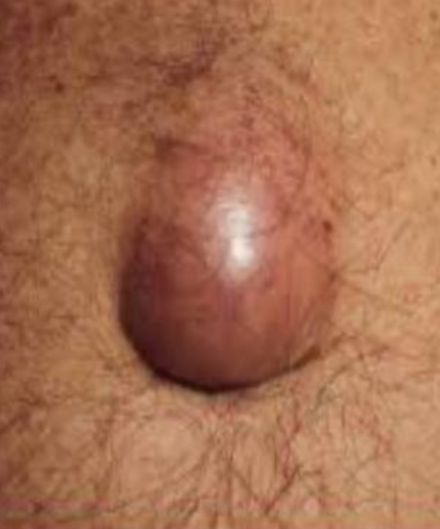
A 55-year male has presented with this reducible inguinal swelling for 6 months.
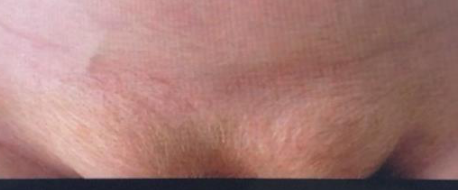 Q1: What is the most likely cause? Weakness in abdominal wall due to ↑ Intraabdominal pressure → hug out chronic chr strain; obstruction of the bowel
Q1: What is the most likely cause? Weakness in abdominal wall due to ↑ Intraabdominal pressure → hug out chronic chr strain; obstruction of the bowel
Q2: Mention TWO possible complications? Obstruction, Strangulation
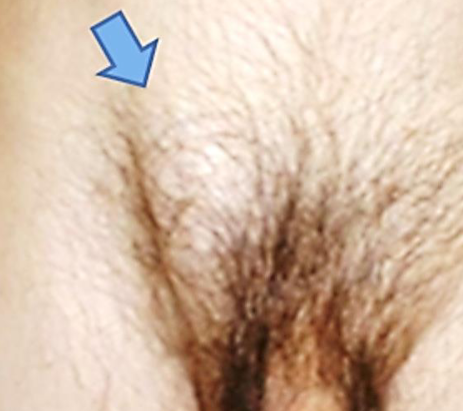 A 55-year male has presented with this right inguinal swelling for 6 months
A 55-year male has presented with this right inguinal swelling for 6 months
Q1: What is the most likely diagnosis? Inguinal hernia
Q2: Mention the definitive treatment. Surgical repair w mesh
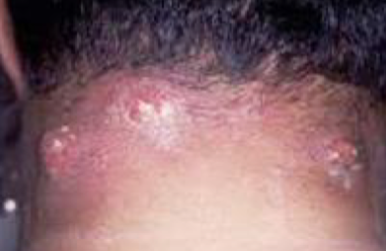
Describe what you see diagnosis and management
Carbuncle with multiple opening
I&D, Augmentin, Cruciate incision
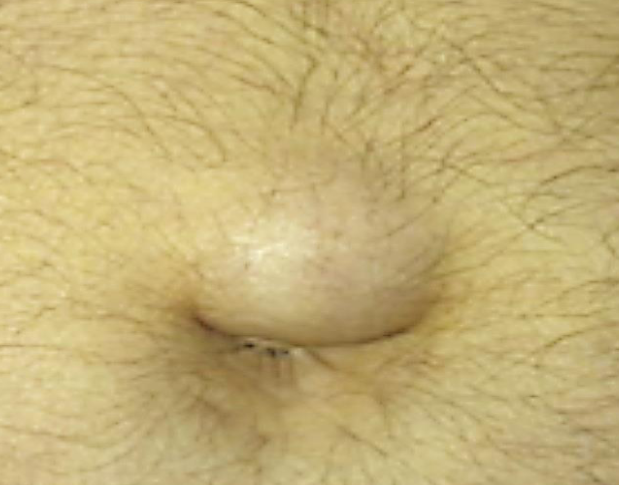
Q1/ What is your diagnosis? Paraumbilical hernia
Q2/ mention 4 complication? Bowel obstruction, strangulation, peritonitis, sepsis
Q3/ what is the management? Surgical repair w mesh
Diabetic patient presented with painless foot lesion
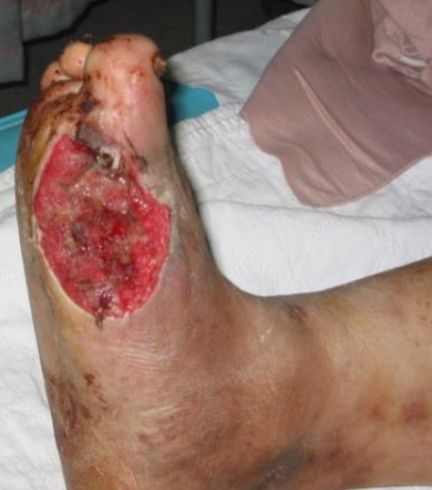 Q1-Describe what you see in the picture?
Q1-Describe what you see in the picture?
• As u learn in DF examination
• (Site size shape margin edge floor …etc.) in sole of foot irregular margin round in shape reddish colour
Q2-Give two factors that play roll in the pathogenesis
• Neuropathy
• Antipathy
Q3- most common complication this pt may have ?
• Infection
• Necrosis
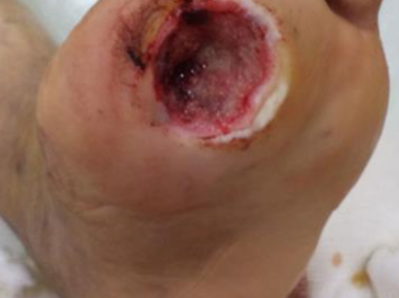
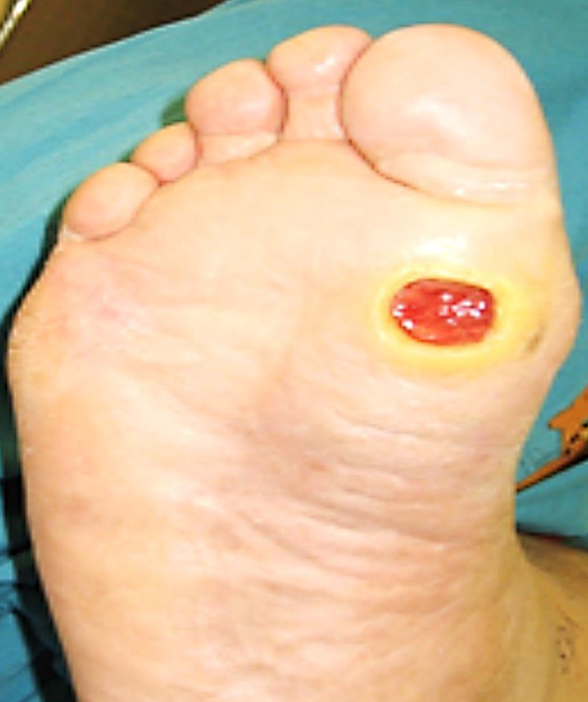 What do you see?
Ulcer over plantar surface of right foot just below big toe - most likely is trophic ulcer
What do you see?
Ulcer over plantar surface of right foot just below big toe - most likely is trophic ulcer
Two factors pathogenesis Neuropathy, and vasculo/angiopath; ischemia
Complications Osteomyelitis, Charcot foot
A view lower back young male who complained discomfort & recurrent purulent discharge
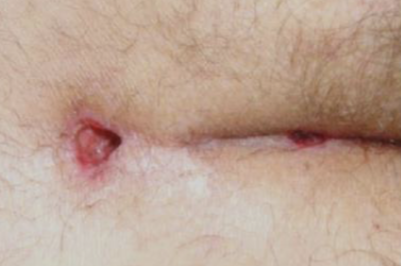 Diagnosis
Perianal fistula
Diagnosis
Perianal fistula
Treatment Fistulectomy seton procedure
clinical finding in patient compained of perianal pain, and swelling for 2 days
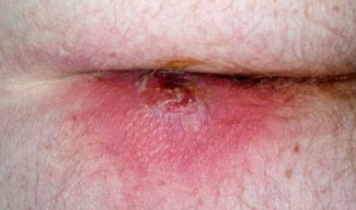 diagnosis
Perianal Abcess
diagnosis
Perianal Abcess
Management I/D + antibiotic
One year post- laparotomy, abdominal inspection has shown
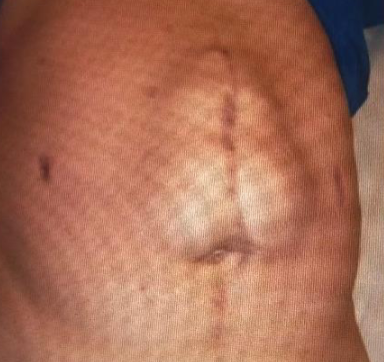
Q1: What is the detected abnormality? Incisional hernia
Q2: Mention the definitive management? Surgical repair of hernia and mesh
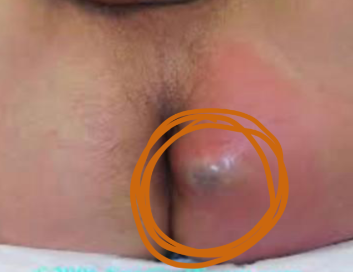 What is the diagnosis?
Peri-anal abscess
What is the diagnosis?
Peri-anal abscess
Management plan includes (mention three):
- Incision & drainage (+c/s).
- Antibiotics
- Daily dressing