Describe the following
-
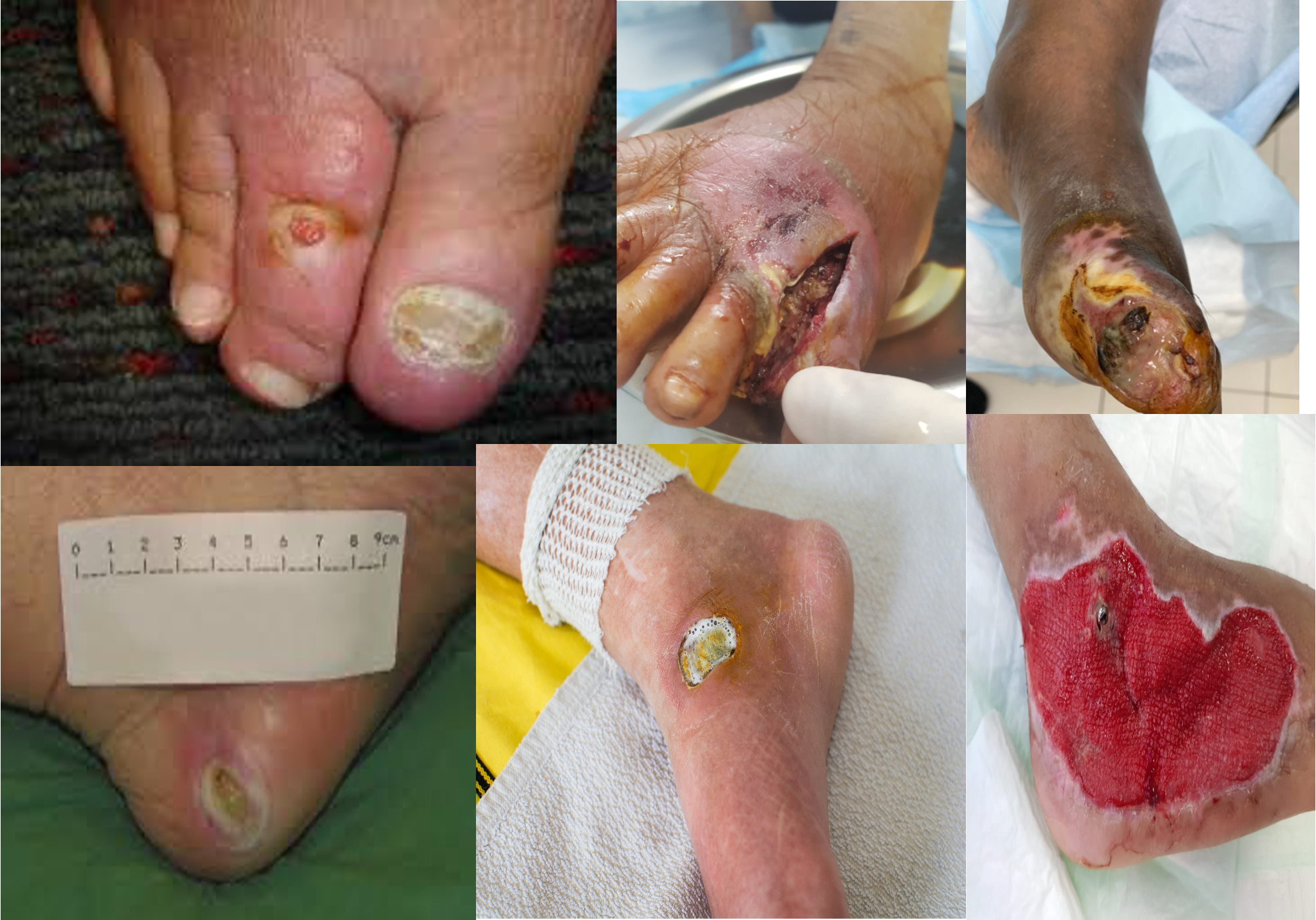
ulcer - if not say discontinuity of skin breakdown representing ulcers involving the second dorsum middle toe, 1x1 cm, circular, granulated healing tissue, edge punched out… shiny skin surrounding edema, erythema
-
Skin disconutiy on left foot between fourth and fifth toe longitudinal 5x2 cm looks like ulcer, floor with dead tissue, undermined edges proximal, punched distal, surrounding looks edematous, hair loss.
-
Ulcer on medial left big toe, 4x4, irregular shape, floor with dead tissue and granulation tissue, with sloping and punched edge, with scar, nair changes, edematous, hair loss.
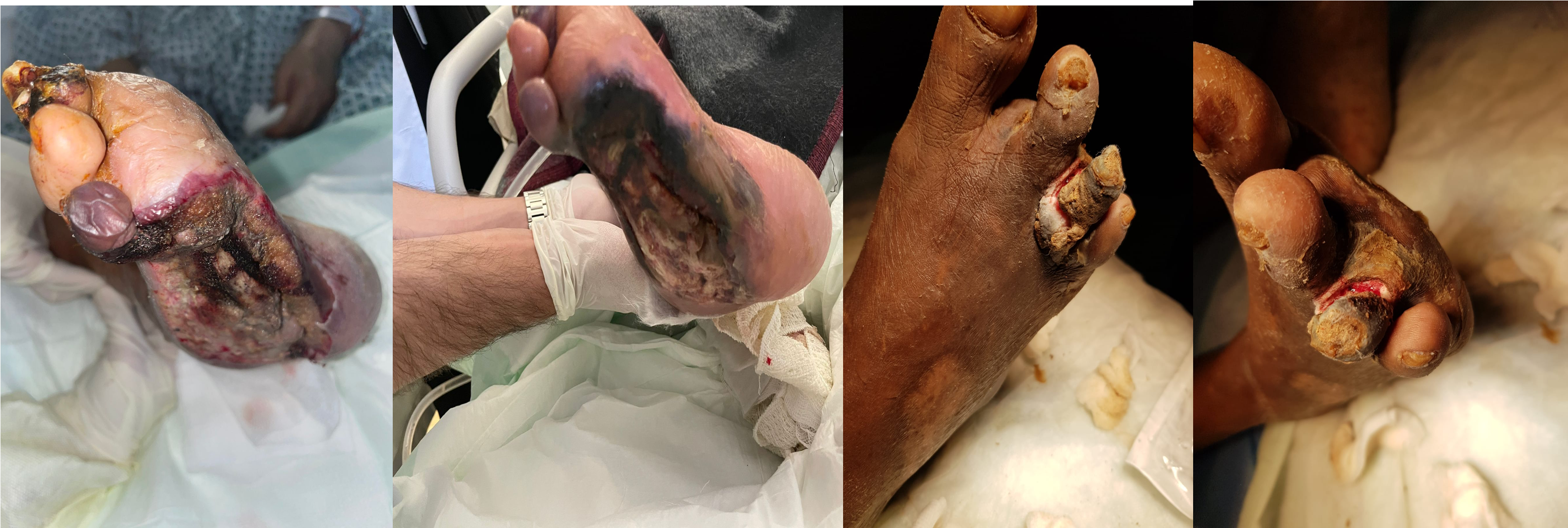
- Ulcer in sole of foot, 8x8 cm, granulation, necrotic tissue and wet gangeren, bone, irregular margins,
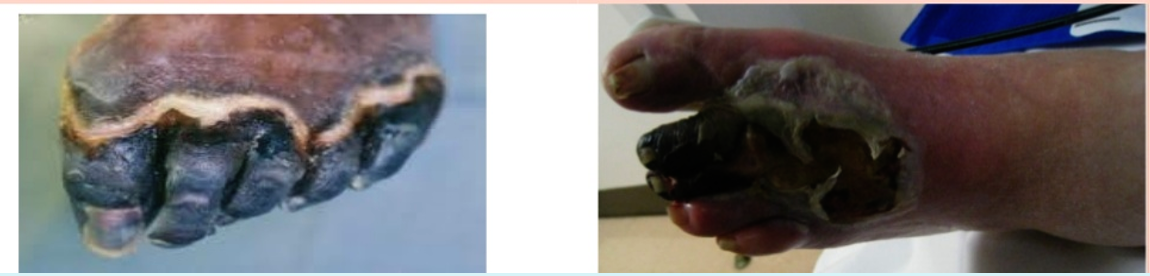 Black discoloration involving distal medially foor represent gang, no obvious discharge, foot is edematous, edematous, no hair, muscle wasting…
Black discoloration involving distal medially foor represent gang, no obvious discharge, foot is edematous, edematous, no hair, muscle wasting…
Gangrene typically refers to necrosis with putrefaction of tissue, the tissue will characteristically appear black.
There is Two types: wet and dry types.
- In “wet type”, the process is complicated by cellular destruction by bacterial enzymes.
- In “dry type”, cellular structure is maintained. It can be progress from (dry) to (wet). Best exemplified in peripheral vascular disease where an initial patch of dry gangrene progresses to wet gangrene as a result of super-added infection.
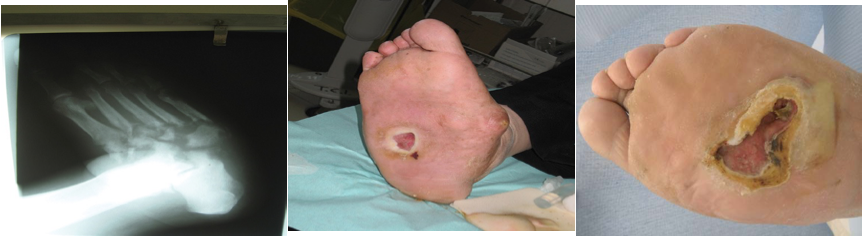
Charcot neuro‐osteoarthropathy (CNO), a progressive condition of the musculoskeletal system. Characterized by joint dislocations, pathologic fractures and debilitating deformities. It results in a progressive destruction of bone and soft tissues at weight‐bearing joints. It is one of the most serious complications of diabetes.
Treated by immobilization and a reduction of stress to the affected limb
Classic Charcot’s mid-foot ulcer following collapse of the foot arches.
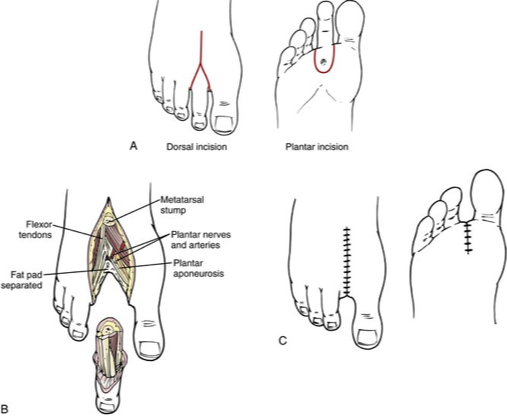
Amputations:
- Types ? Ray amputation, which involves the excision of the toe and part of the metatarsal
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Shianoya’s criteria for Buerger’s disease
- Tobacco use.
- Only in males
- Disease starts before 45 years
- Distal extremity involved first without embolic or atherosclerotic features
- Absence of diabetes mellitus or hyperlipidaemia
- With or without thrombophlebitis
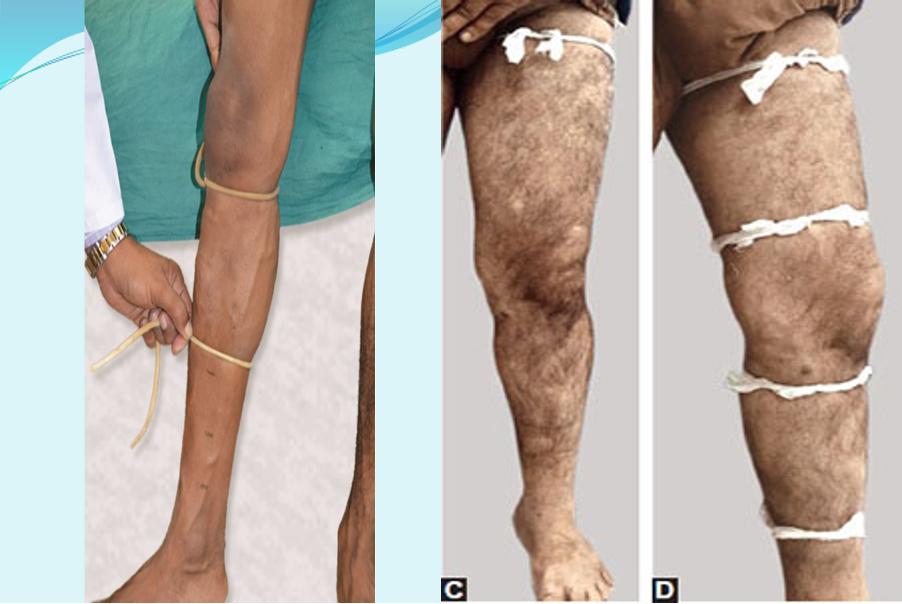
Multiple Tourniquet – Triple Test
Daflon tab 500 mgVenotonic
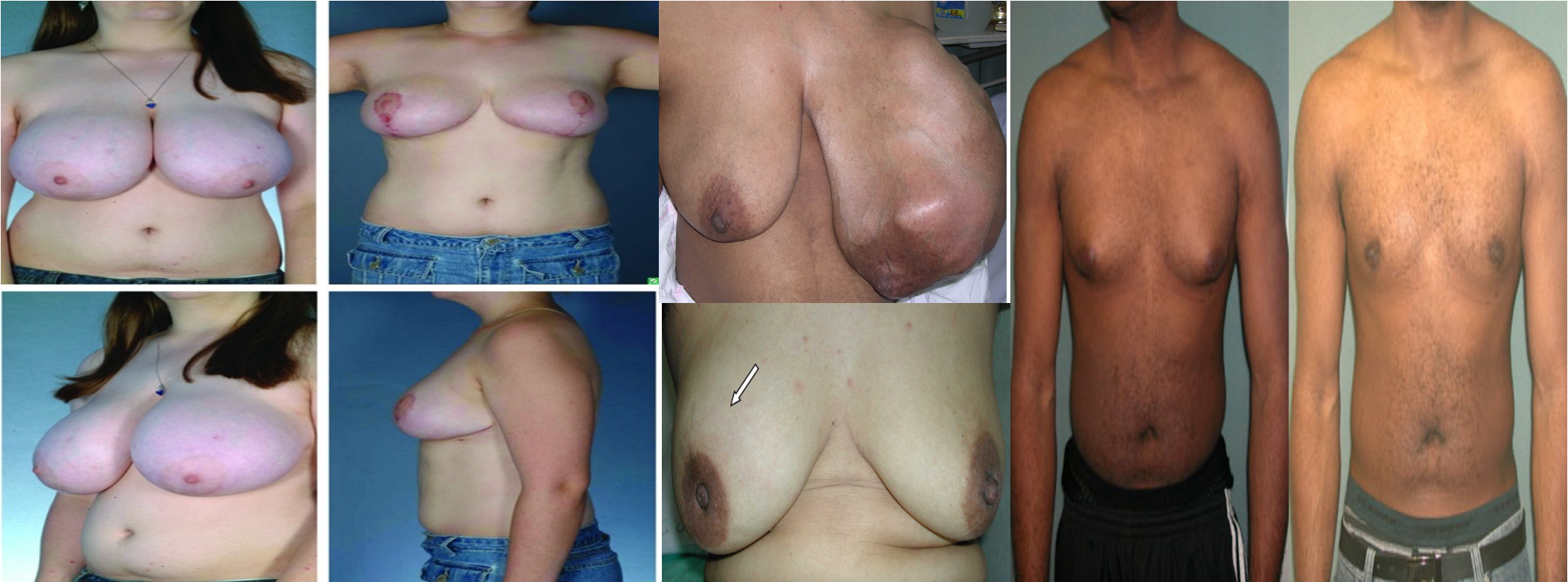 govenile hypertrophy cell - severe enlargement
in 3rd - Asymmetrical, alveoli extended, visible nodules, skin is shiny and thin, dilated vein,
4th image nipple is retracted; not inverted as its not inside yet
govenile hypertrophy cell - severe enlargement
in 3rd - Asymmetrical, alveoli extended, visible nodules, skin is shiny and thin, dilated vein,
4th image nipple is retracted; not inverted as its not inside yet
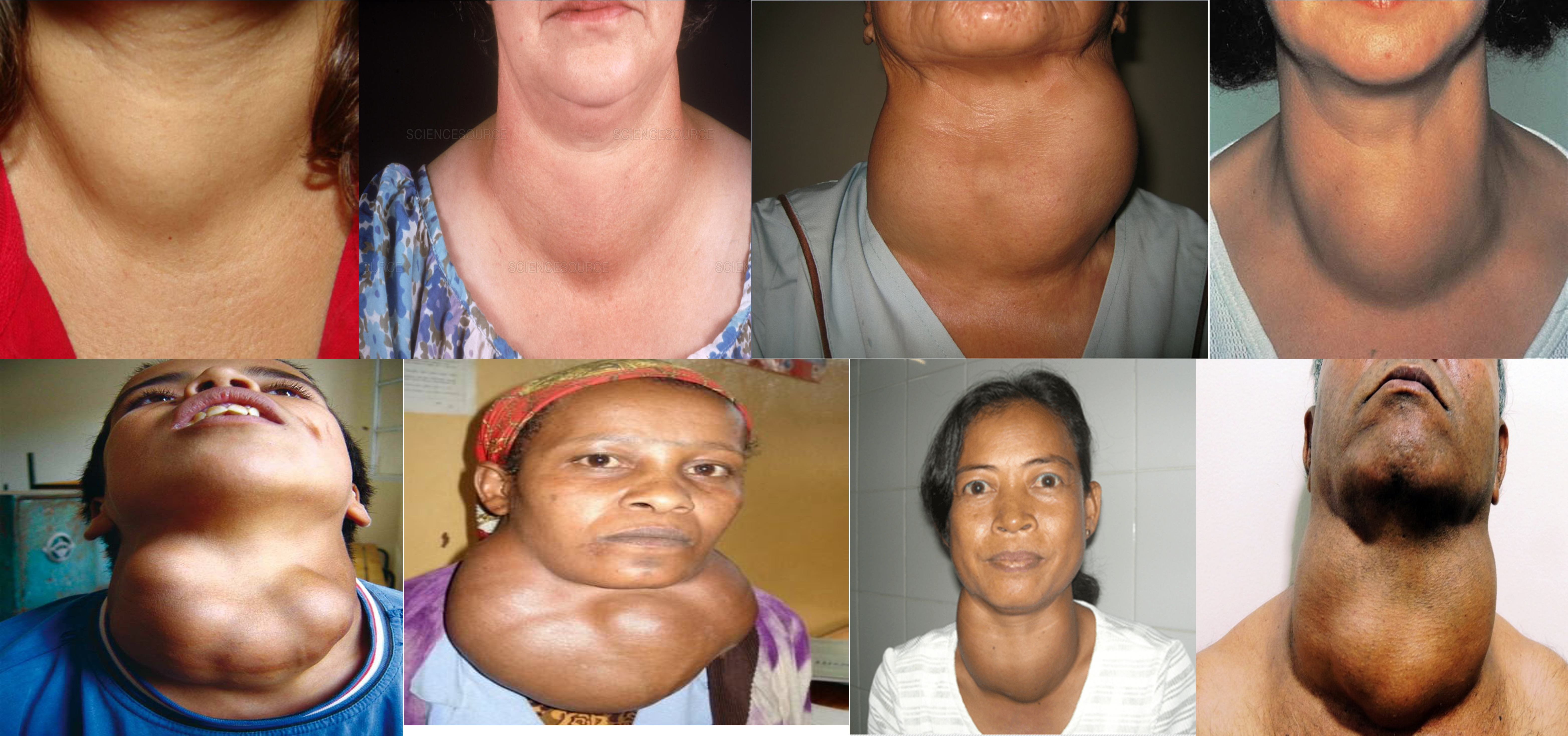
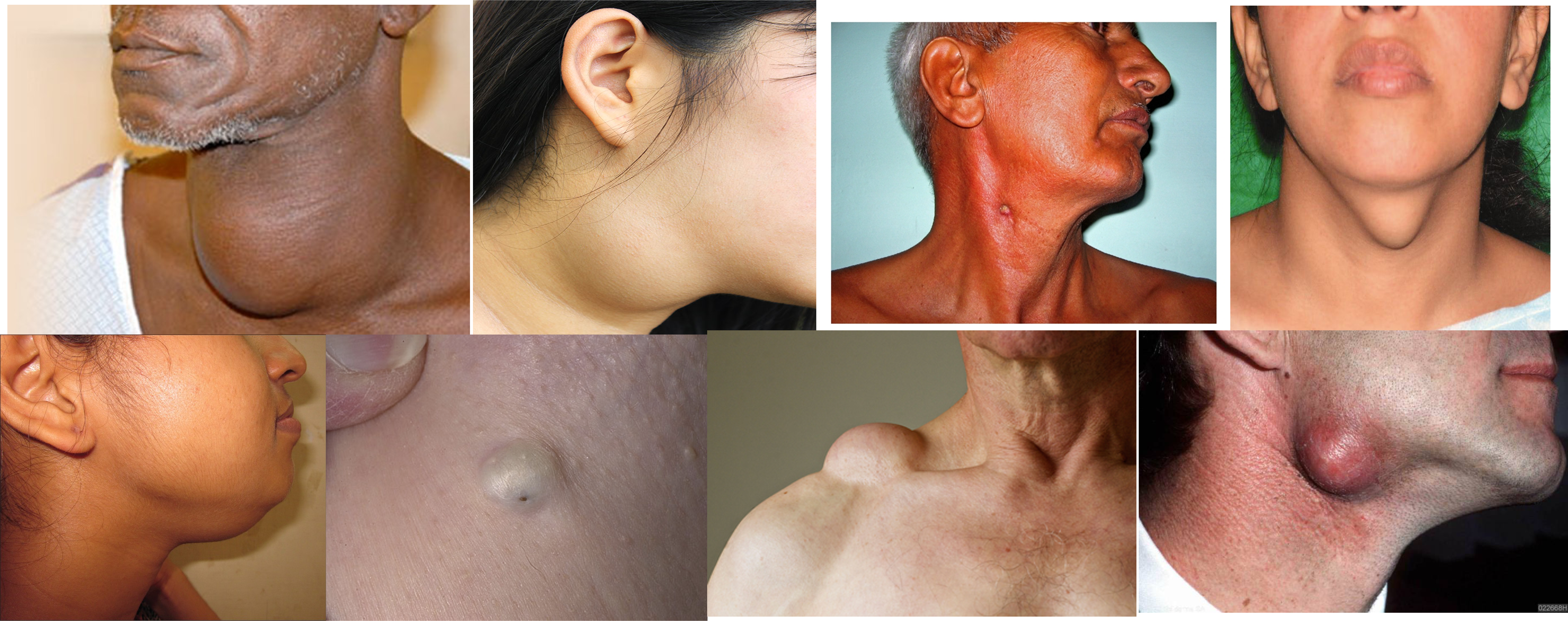
diffused (nodular? huge?) large neck mass more on left mass associated with (Lid retraction, exophlamos)
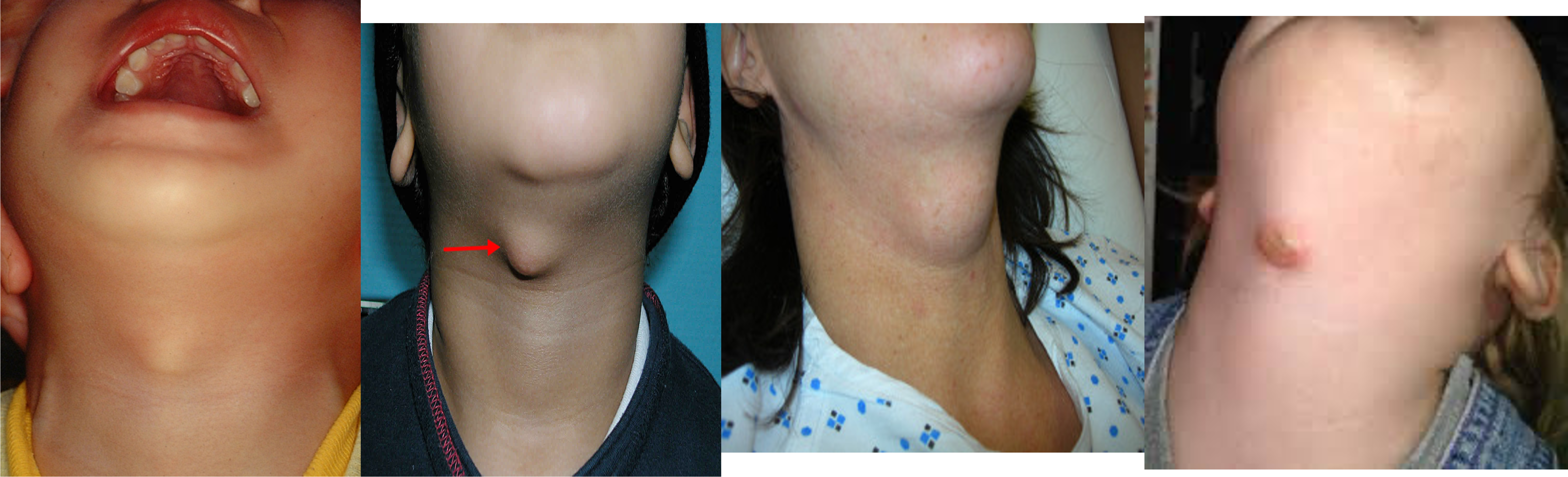 protrusion of tongue
Midline swelling (could be infection or congenital)
protrusion of tongue
Midline swelling (could be infection or congenital)
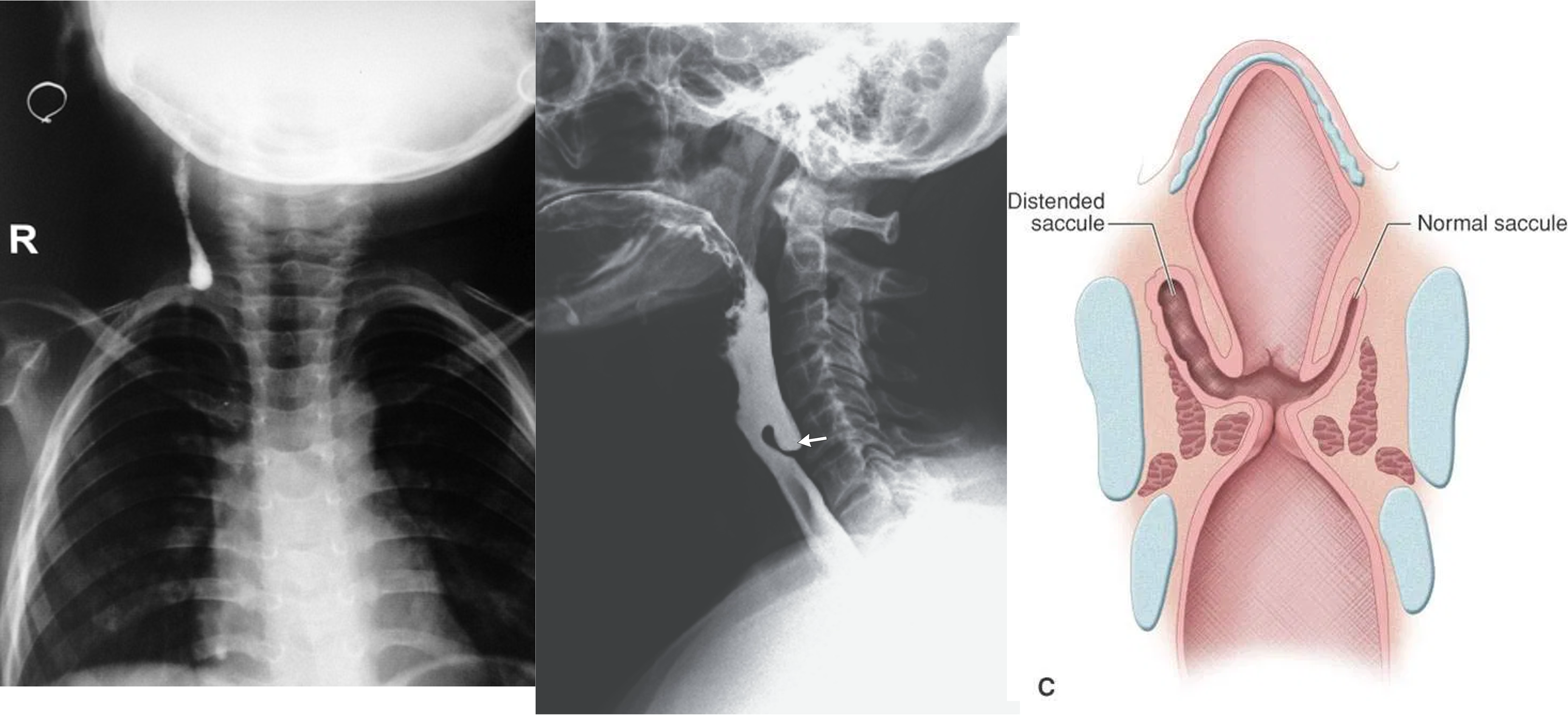
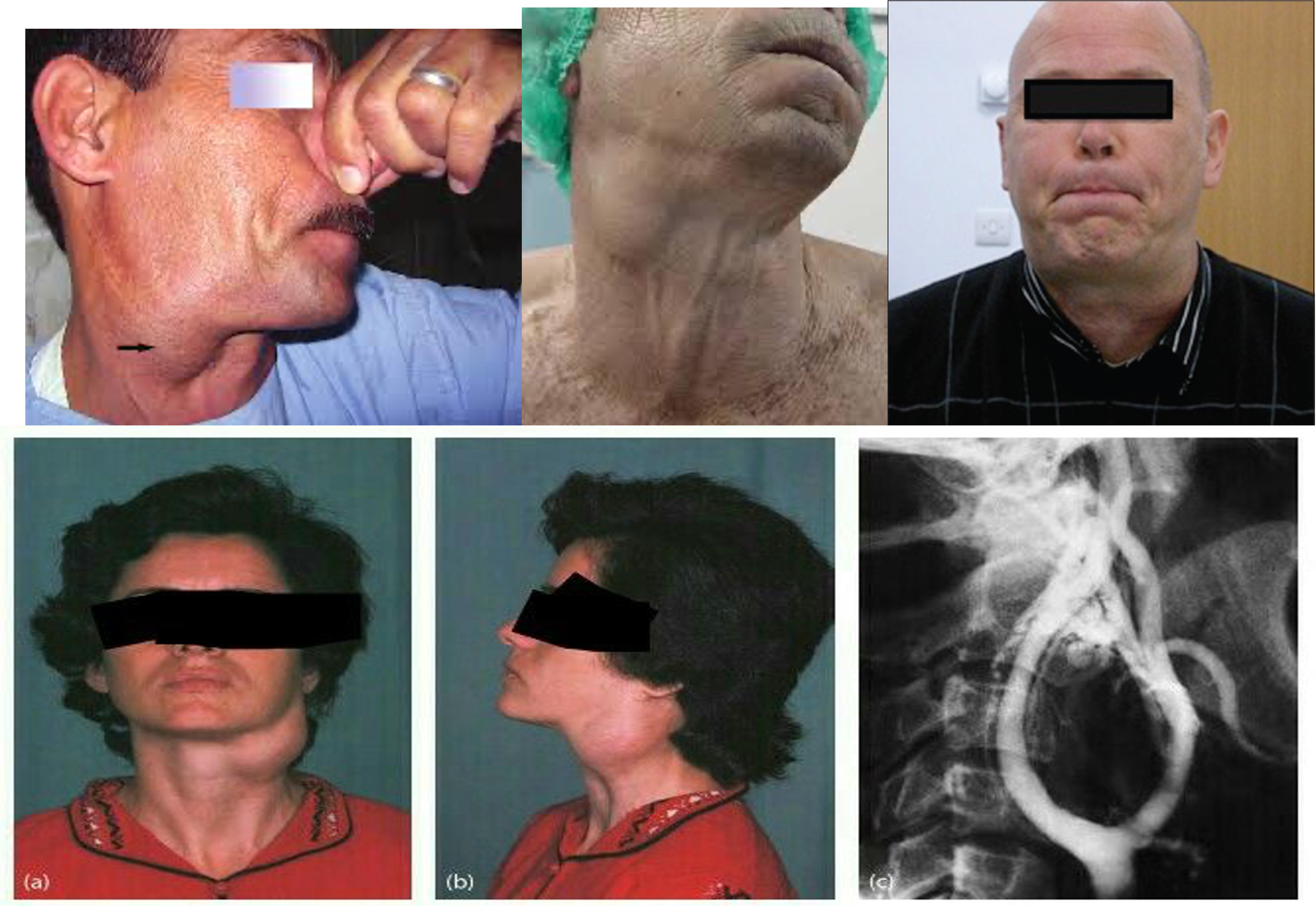
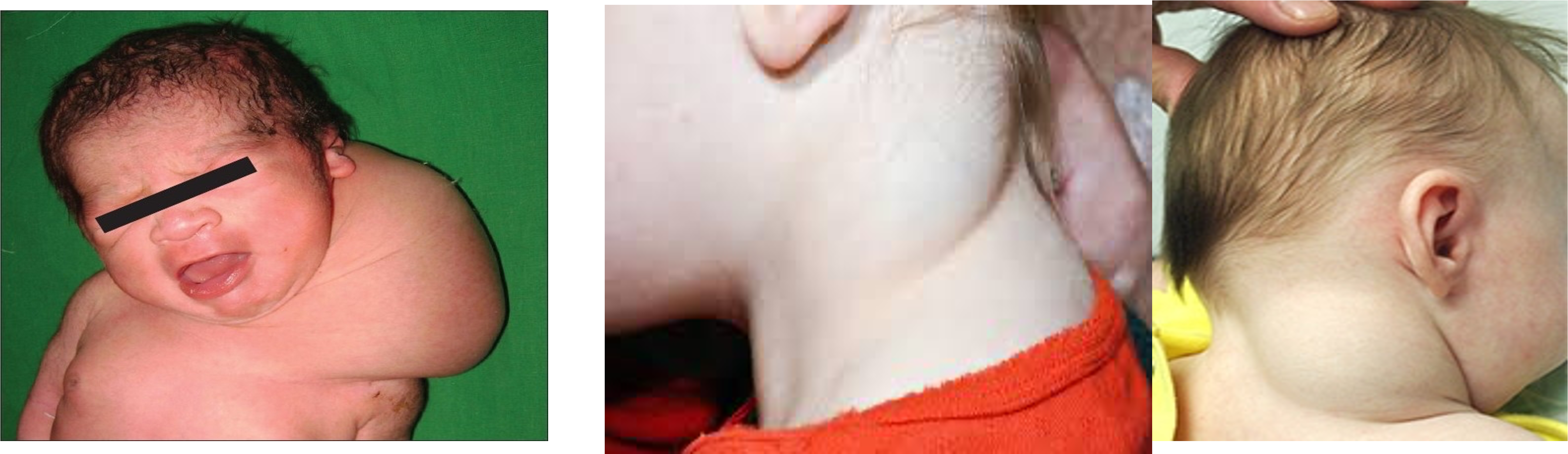 1- cystic hydroma
2-
1- cystic hydroma
2-
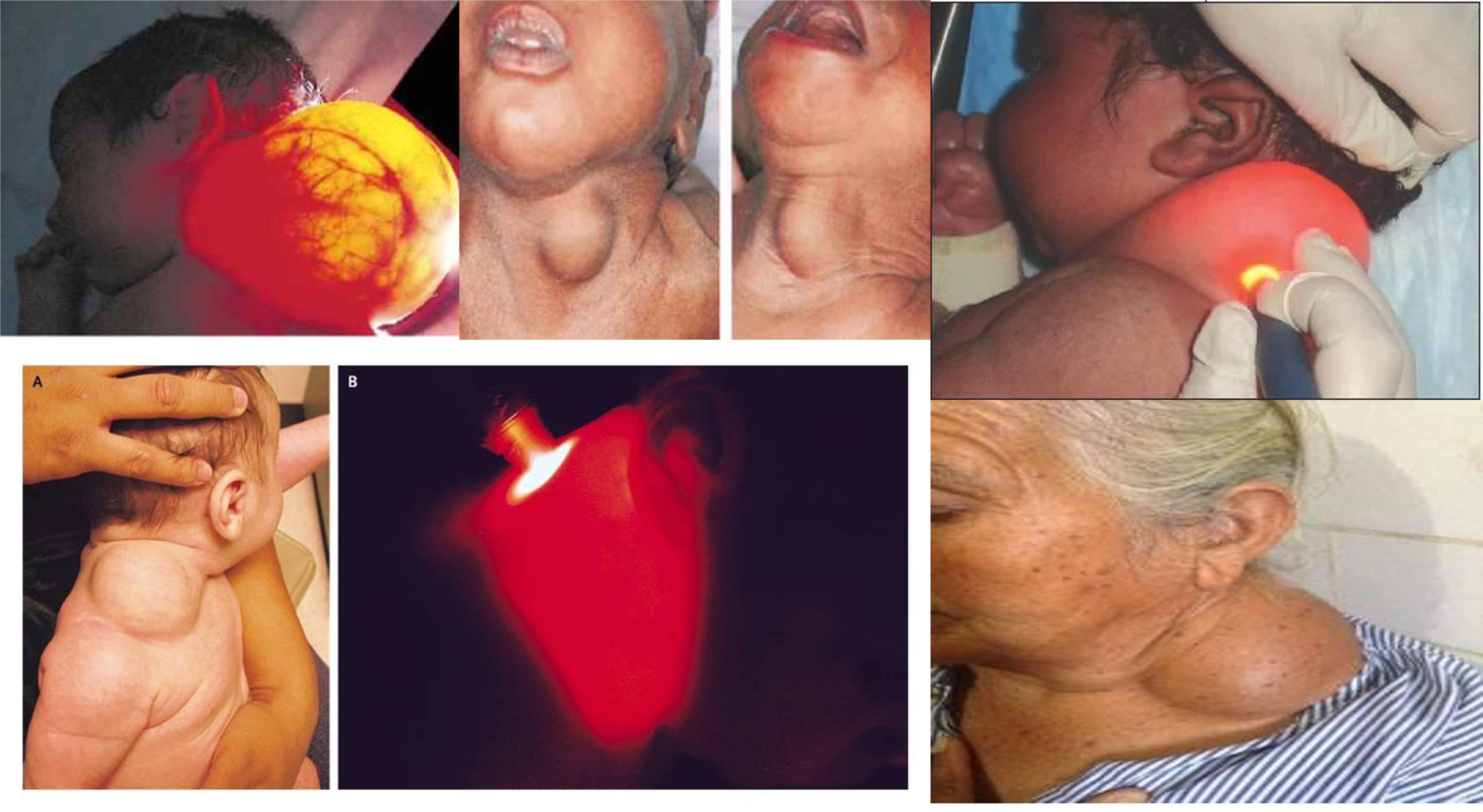 1- cystic hydroma
2- branchial/cleidomastoid tumors
1- cystic hydroma
2- branchial/cleidomastoid tumors
5,7- cystic hydrome
 1- branchial cyst - anterior 1/3 mass
3- branchial or carotid
1- branchial cyst - anterior 1/3 mass
3- branchial or carotid
4, 5- branchial fistula - secretion 67 - bilaternal branchial fistula
 Pharyngeal pouch, zenkers diverticulum
Pharyngeal pouch, zenkers diverticulum
 1,2,3- valsava maneuvear - laryngocele
1,2,3- valsava maneuvear - laryngocele
4,5,6 - carotid body tumour
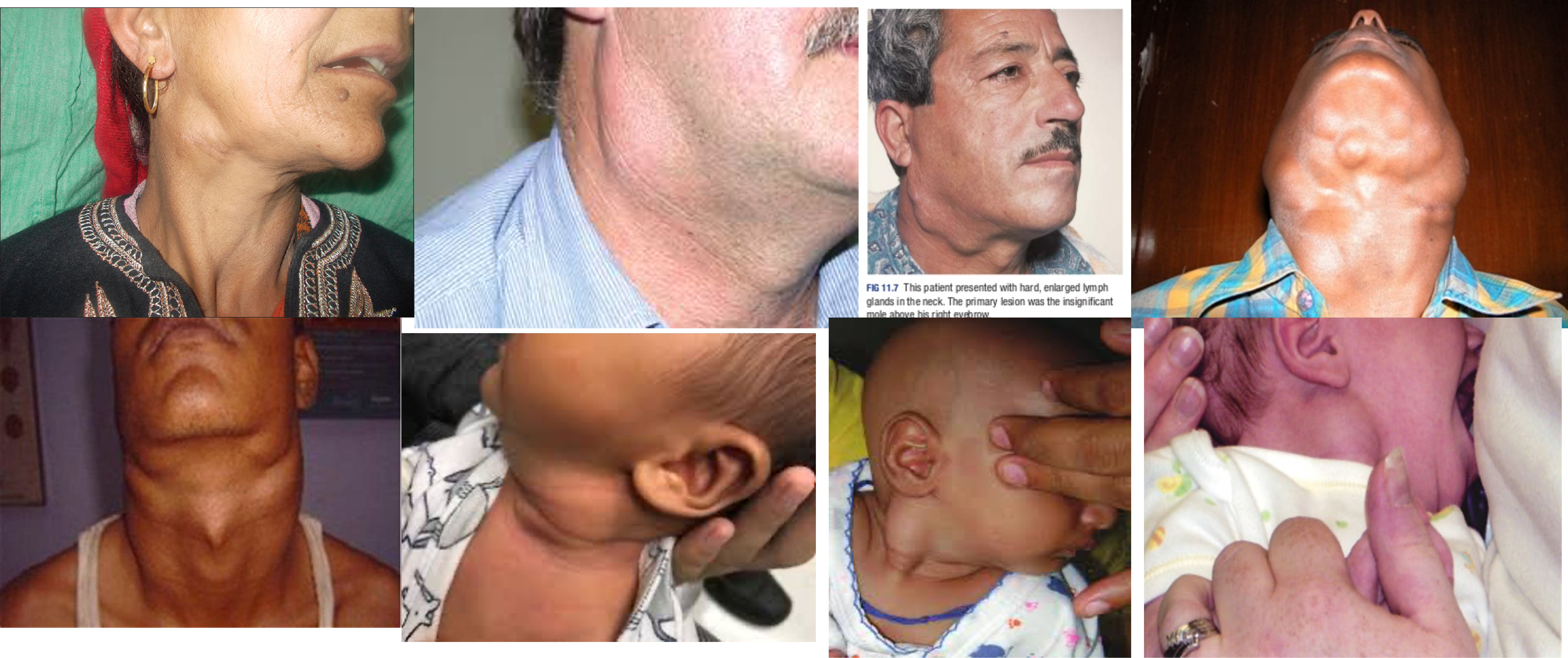 3,4 - lymphnedenopathy (secondary sacroma?) hard enlarge lymph nodes in neck - primary lesion was insiginifanct mole above his right eyebrow
3,4 - lymphnedenopathy (secondary sacroma?) hard enlarge lymph nodes in neck - primary lesion was insiginifanct mole above his right eyebrow
6,7,8 torticollus?
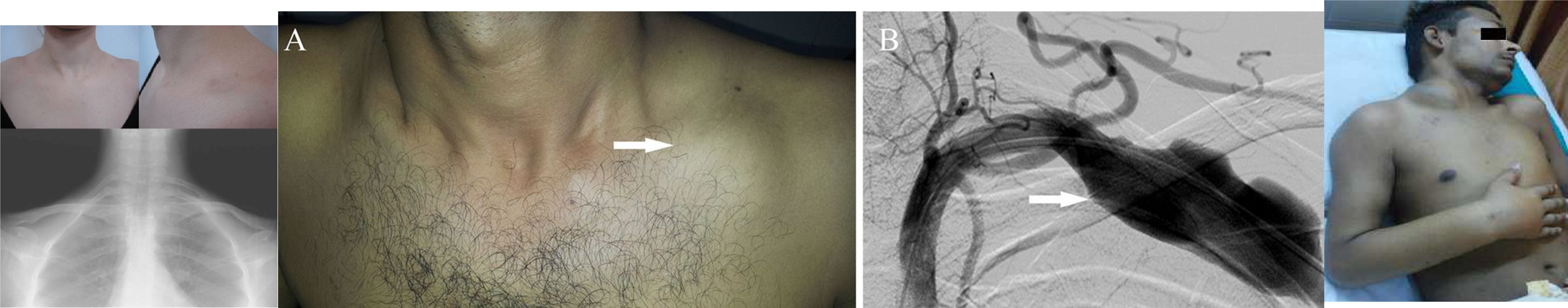
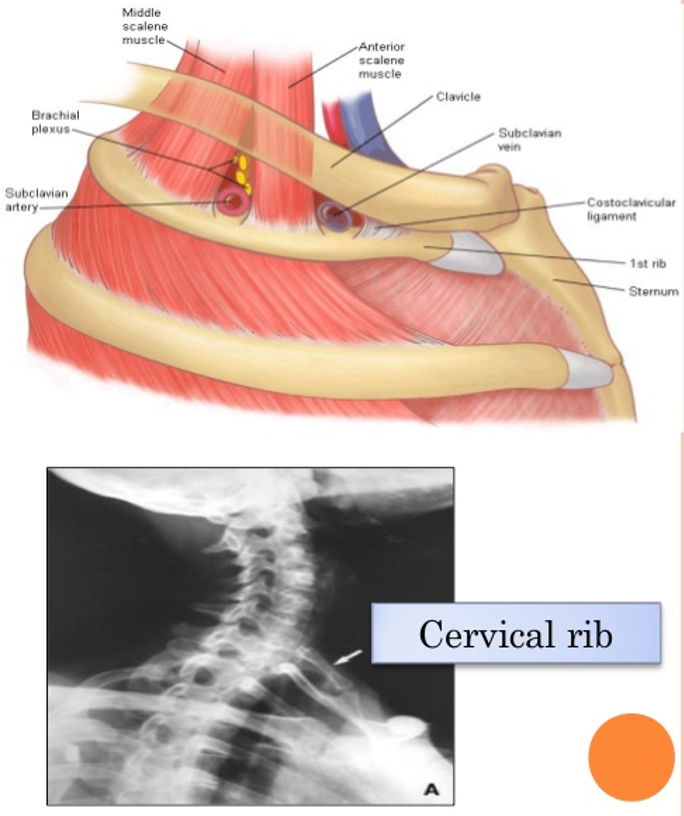
1,2 - Cervical Rib - from T1 - present as fullness at base of neck
3,4 - subclavian aneurysm
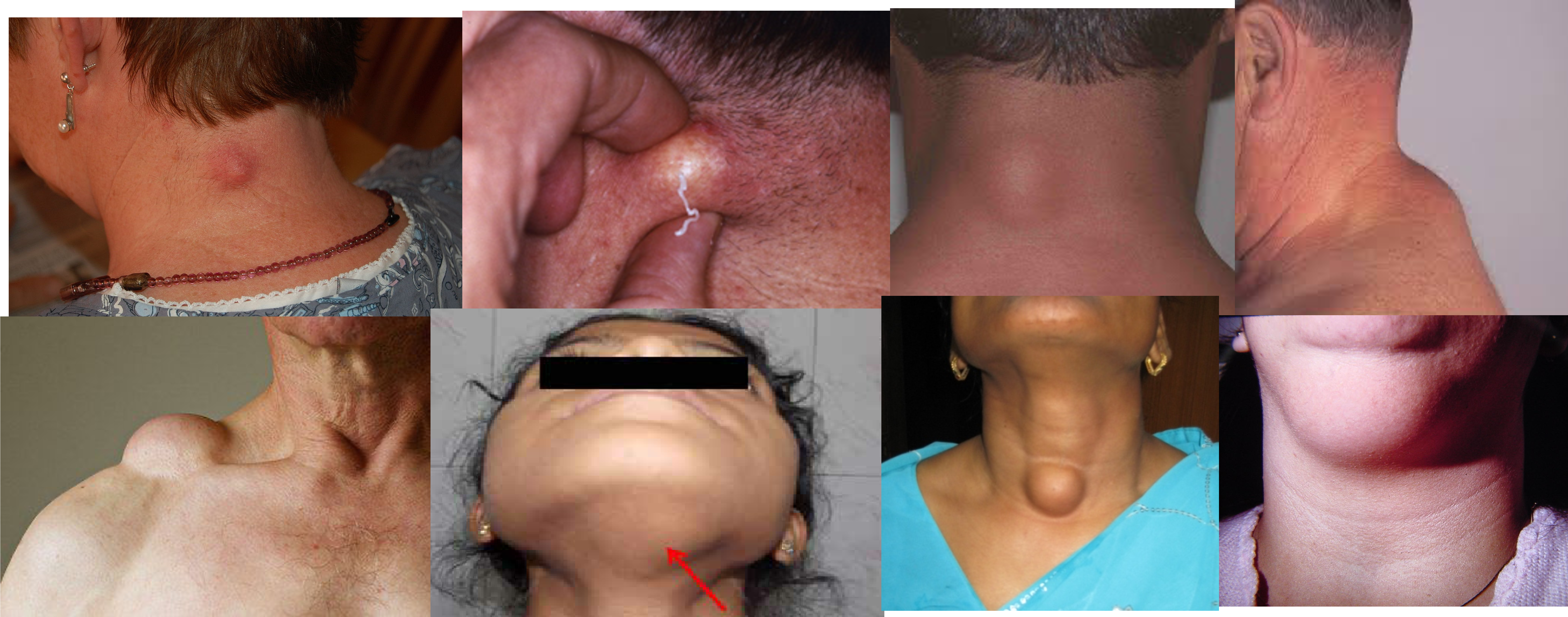
1 - epidermal 1,2 - sebeacous cyst
4 - fat pad?
5- lipoma
7 - thyroglossal cyst, sabbecous cyst, goiter - depending on protrusion, or swallow
3- brachial cyst 4- granula 6- sabbecous cyst 8- cold abcess
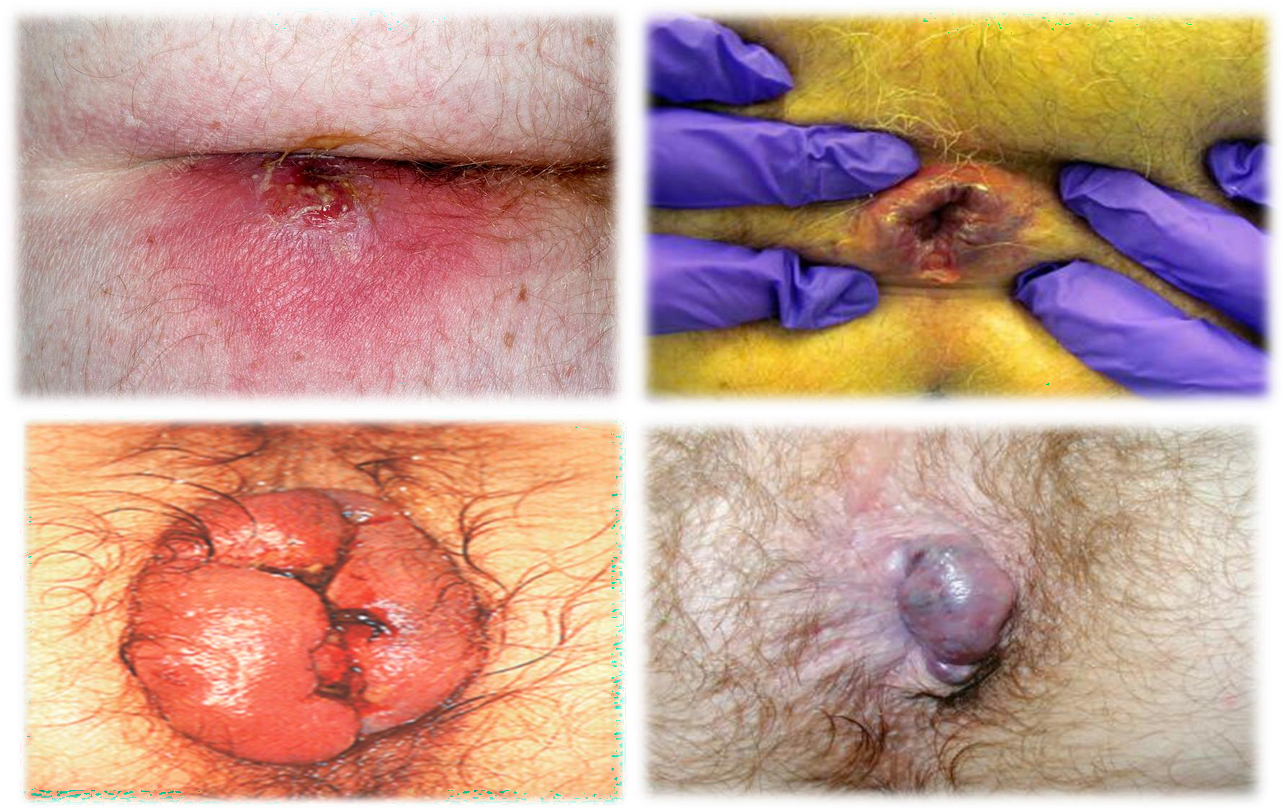 1- abscess 2- fissure - 3- thromb? 4- external hemmorhoids
1- abscess 2- fissure - 3- thromb? 4- external hemmorhoids
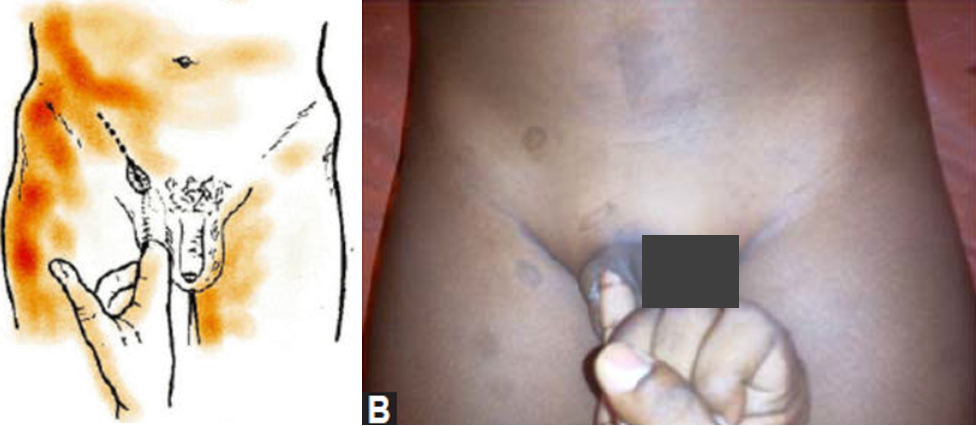
Ring invagination test
Deep ring occlusion test
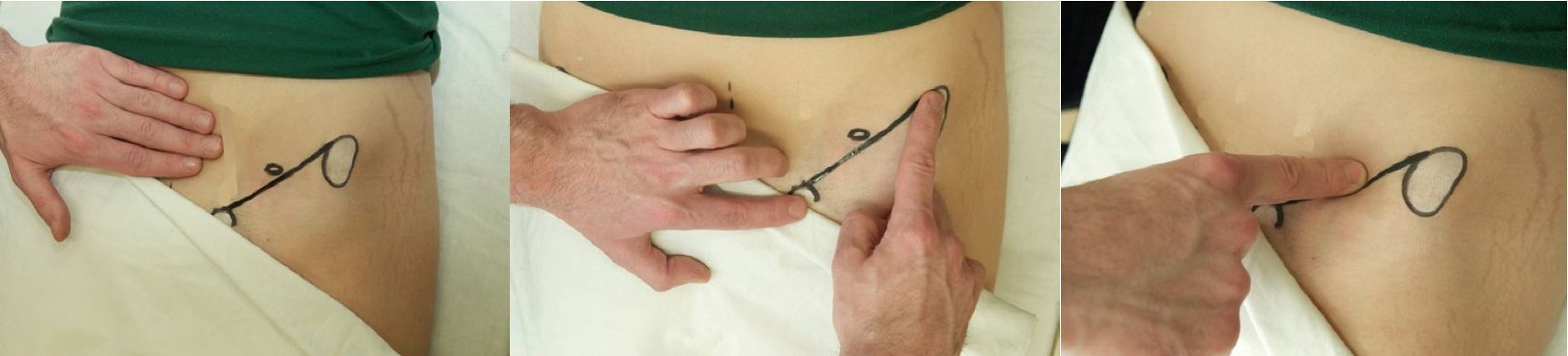
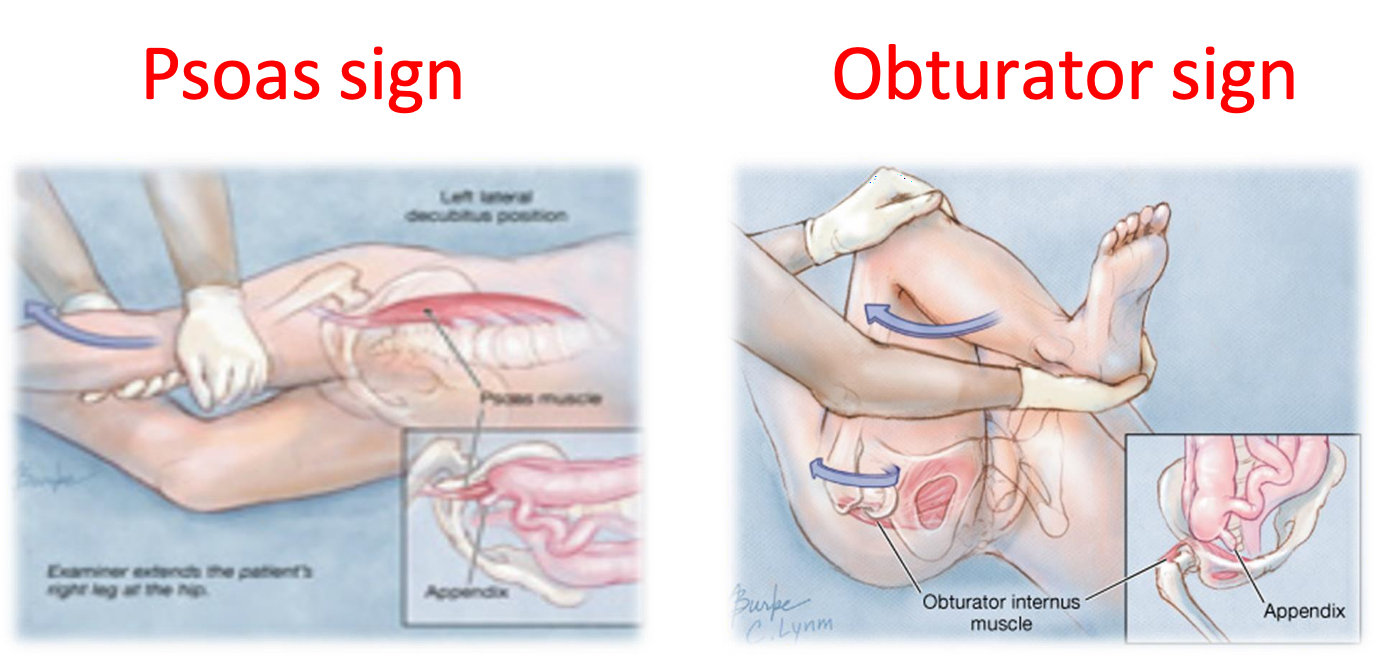 Psoas sign & Obturator sign
Psoas sign & Obturator sign
Contrast Imaging
-
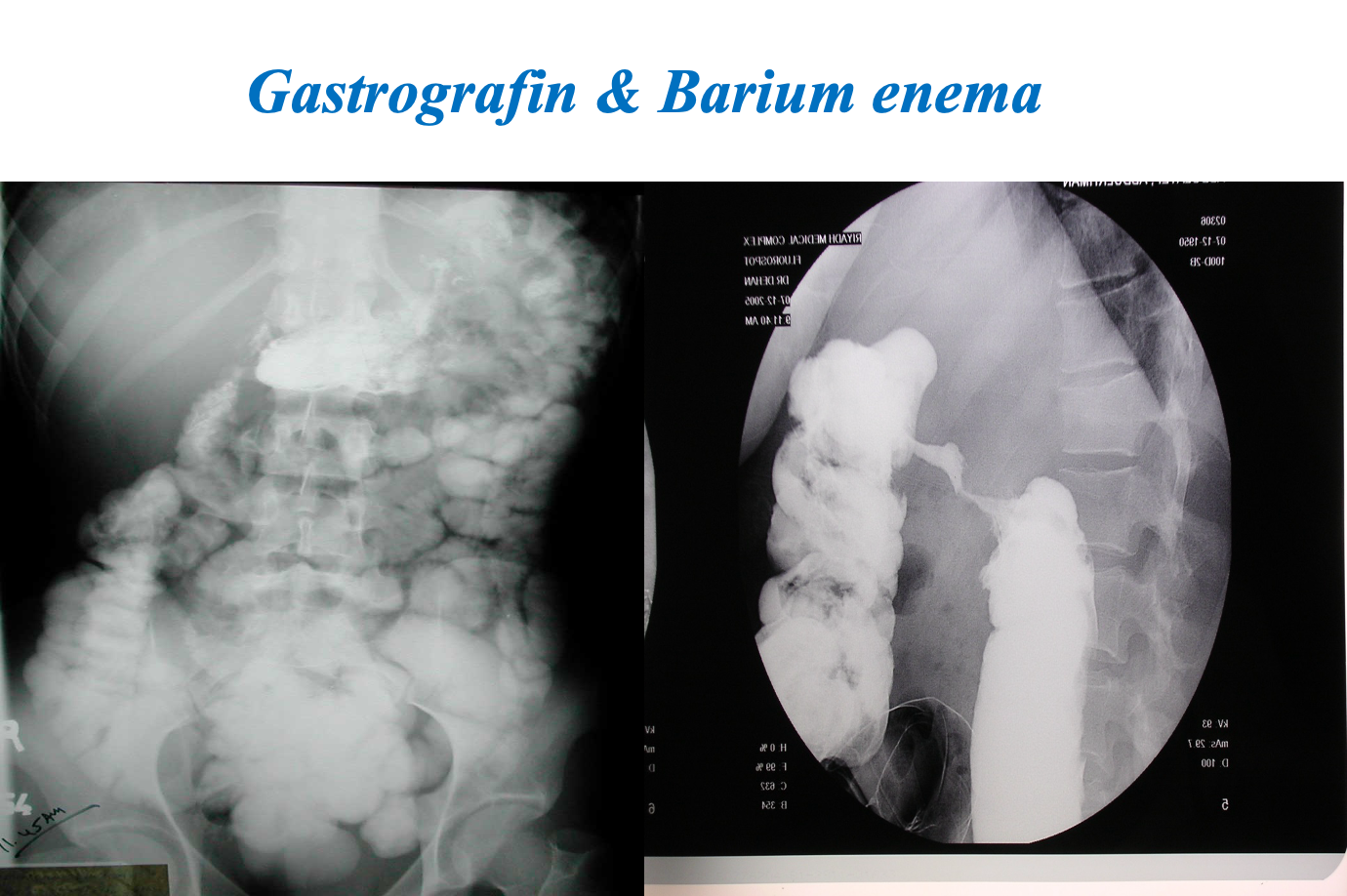
Gastrograffin swallow, Barium meal / enema
- Visualize GI tract
- Single/ double contrast
- Inferior to endoscopy
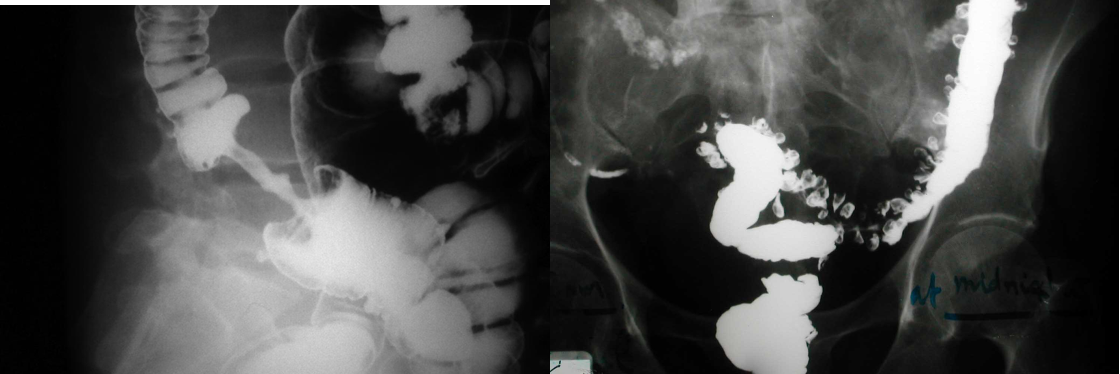
Modality: Gastrography swallow / Barium Enema Findings: apple core / out pouching lesions Differentials: colon cancer / diverticulum
 Modality: plain x-ray
Findings: radiopaque
Differentials: gallbladder
Modality: plain x-ray
Findings: radiopaque
Differentials: gallbladder
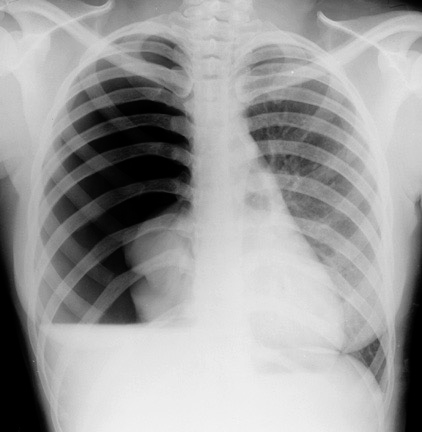 tension pneumothorax
tension pneumothorax
Brain Imaging
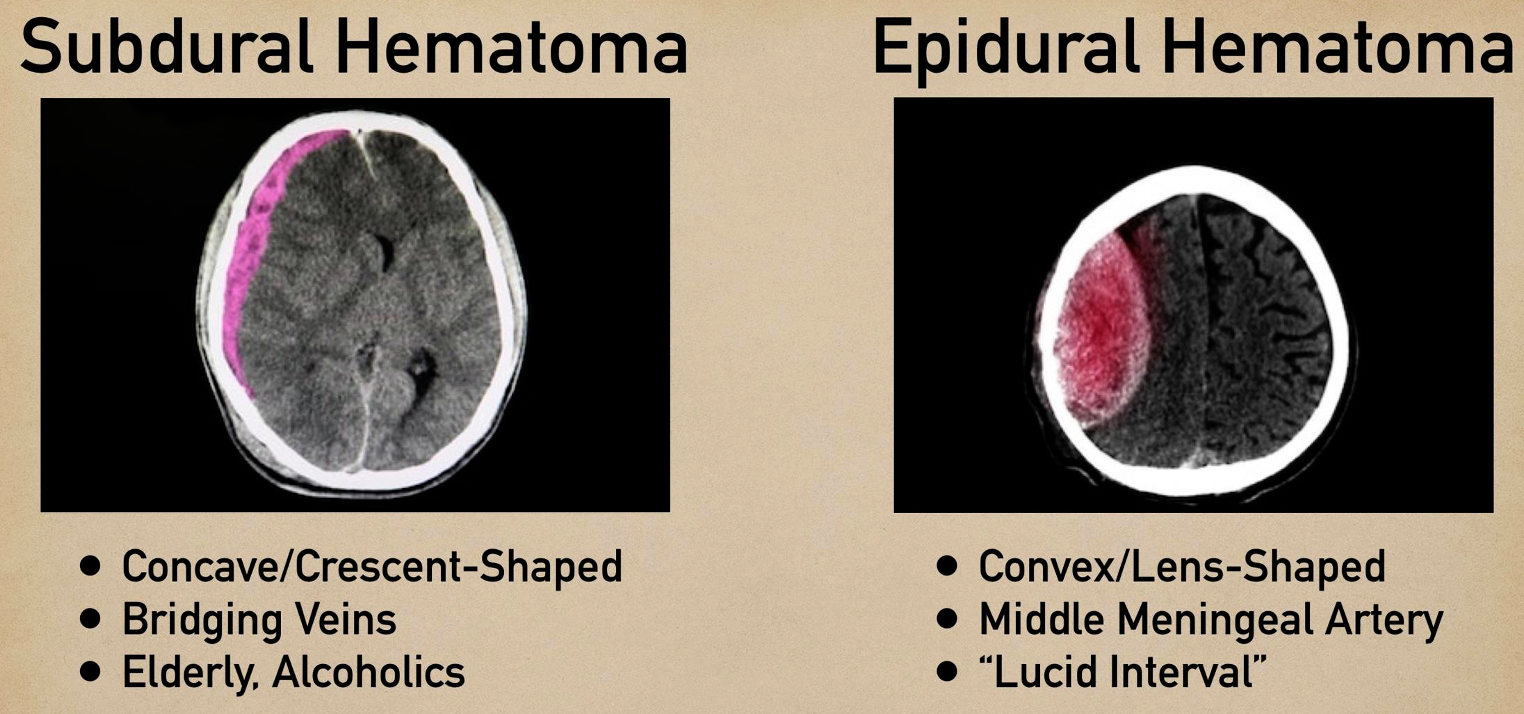
Epidural
- ipsilateral pupil diltation
Treatment: ligation of artery
Subdural
Bridging vein from brain to dural space - commonly elderly/pediatrics
s/s
- chronic
- change in personality
- hx of minor truama
Treatment Purr hole
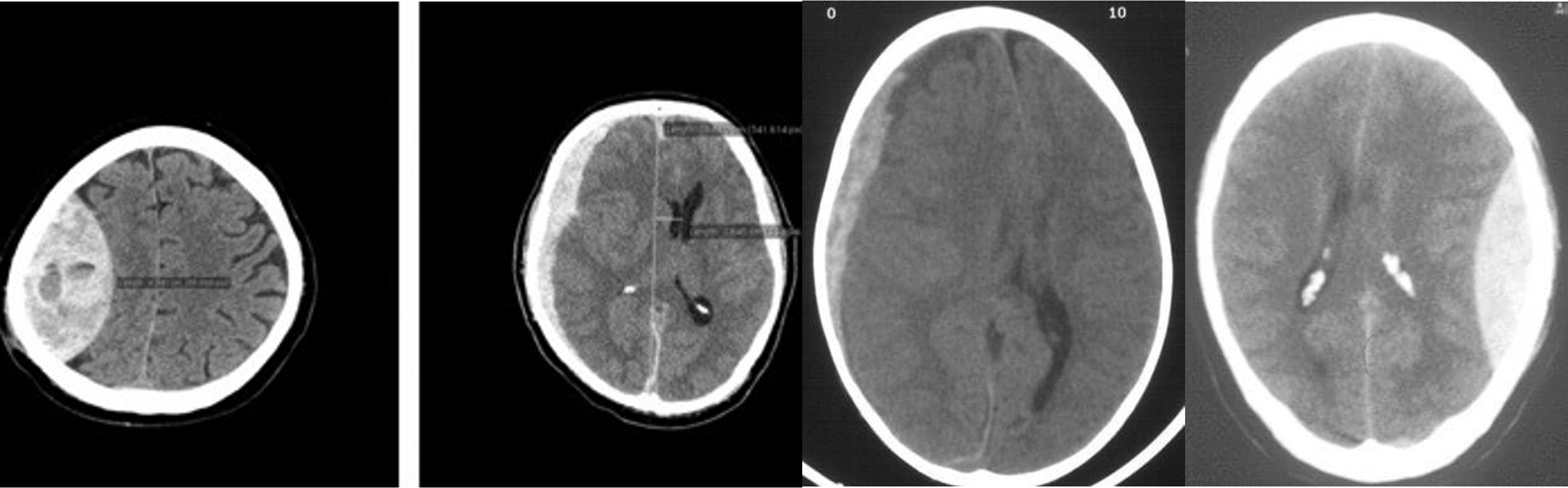
- Epidural - shifted lenticular
- Subdural - crescent
- Subdural -
- Epidural
Chest Imaging
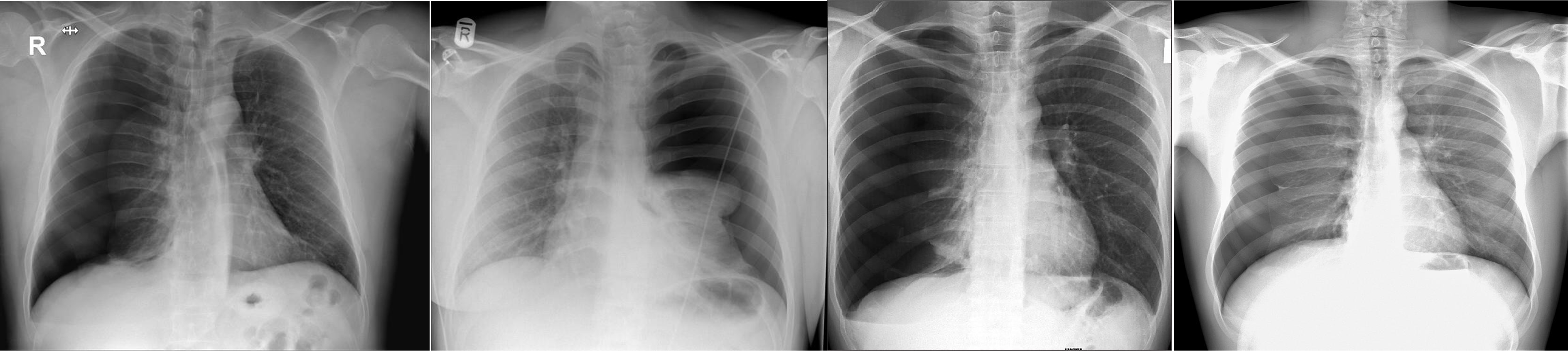
- Pneumothorax - Right lung
- Pneumothorax - Left lung - mediastinum pushed
- Pneumothorax - RT
- Pneumothorax - RT
Abdomen Imaging
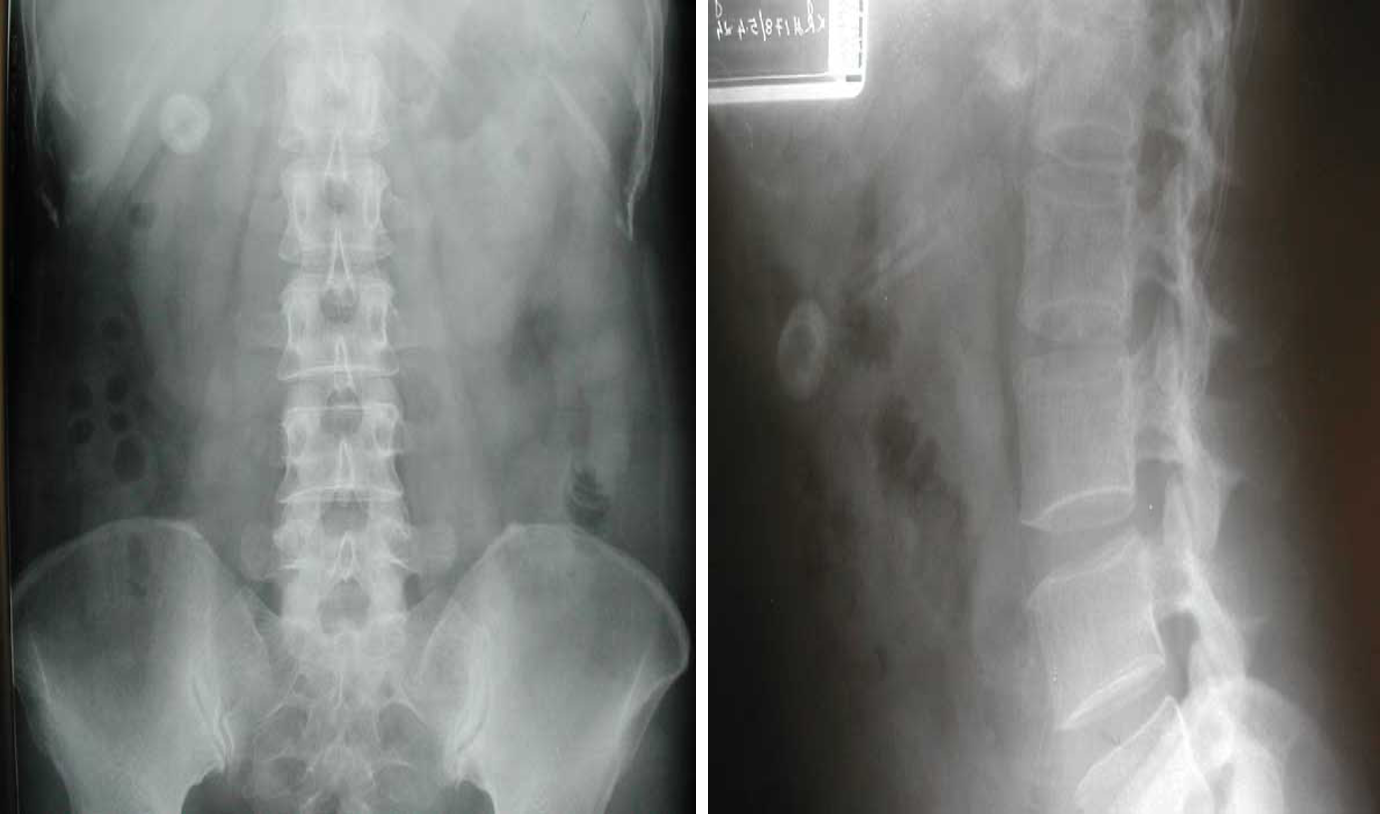
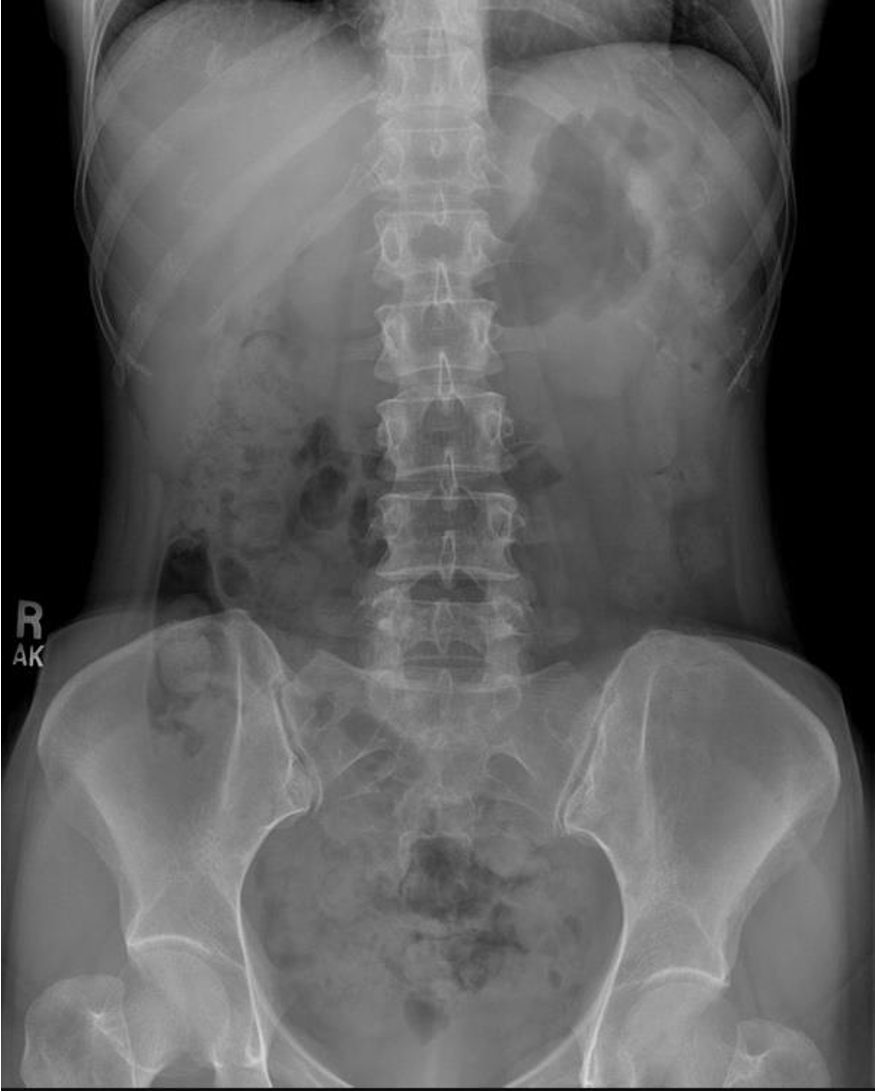 normal abdominal x-ray - normal gas pattern - lower pole kidney - gastric bubble is found - comment on bone
normal abdominal x-ray - normal gas pattern - lower pole kidney - gastric bubble is found - comment on bone
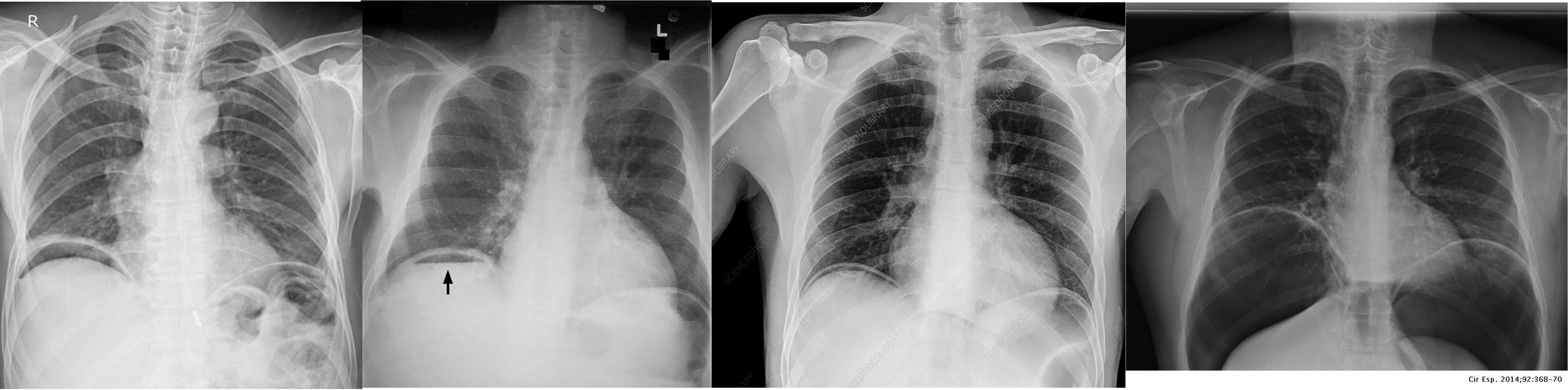 Free air under diaphragm - most commonly due duodenal perforation - (diff; perforated viscus, peptic ulcer, duodenal, penetrating truama, post surgical 8 days likely to disappear)
Free air under diaphragm - most commonly due duodenal perforation - (diff; perforated viscus, peptic ulcer, duodenal, penetrating truama, post surgical 8 days likely to disappear)
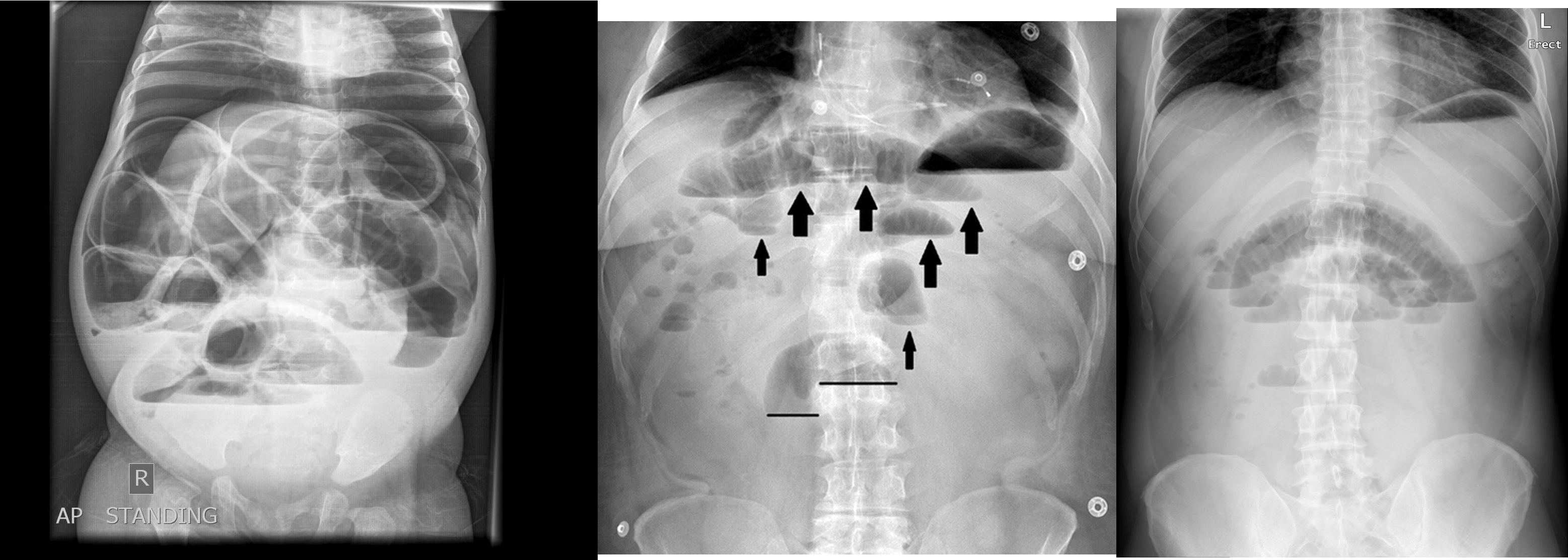
- free air
- erect - air fluid levels - should be not more than three - >5 significant 11 found -
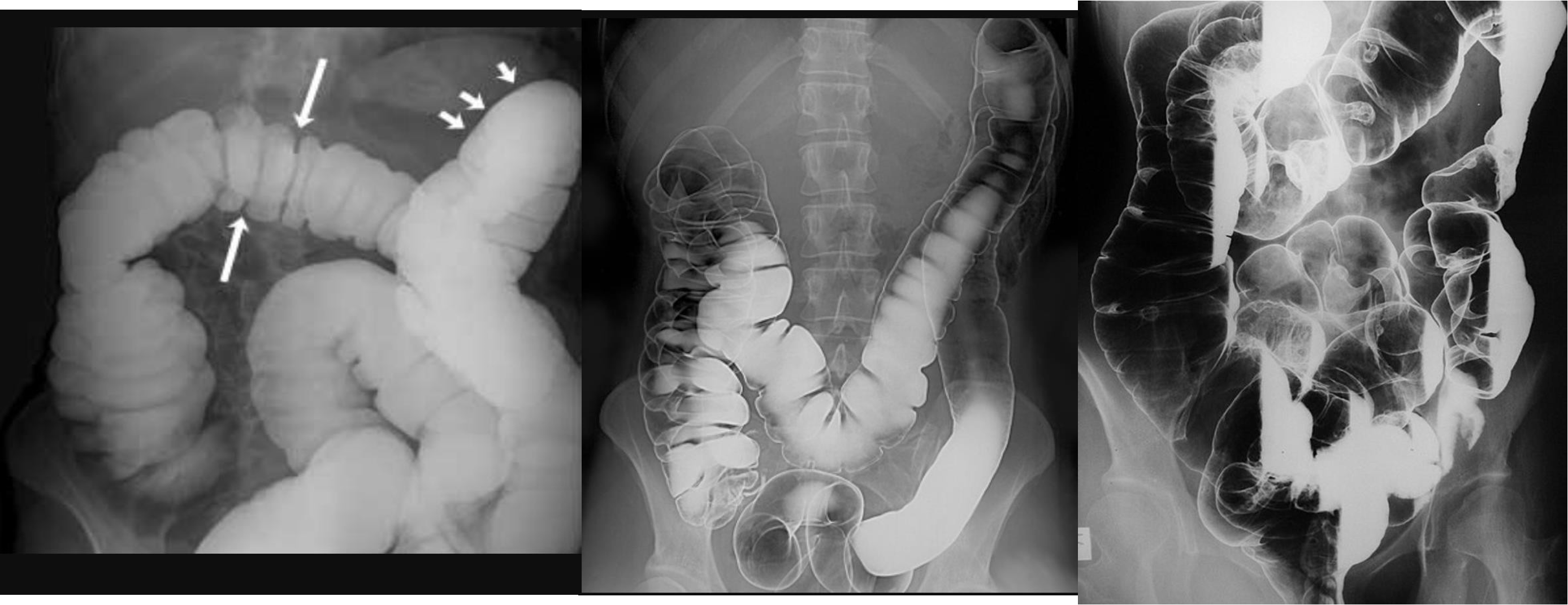
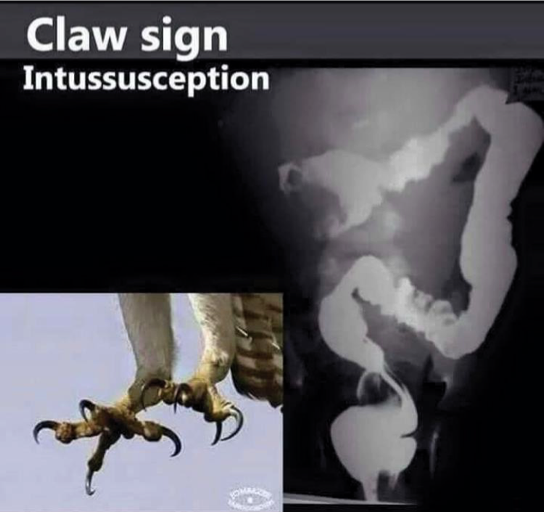
- no free air under diaphgram - 8 fluid level, (evidence of bowel obstruction) (adhesion, hernia, IBD; Crohn, cancer, inturcucception, gallstones)
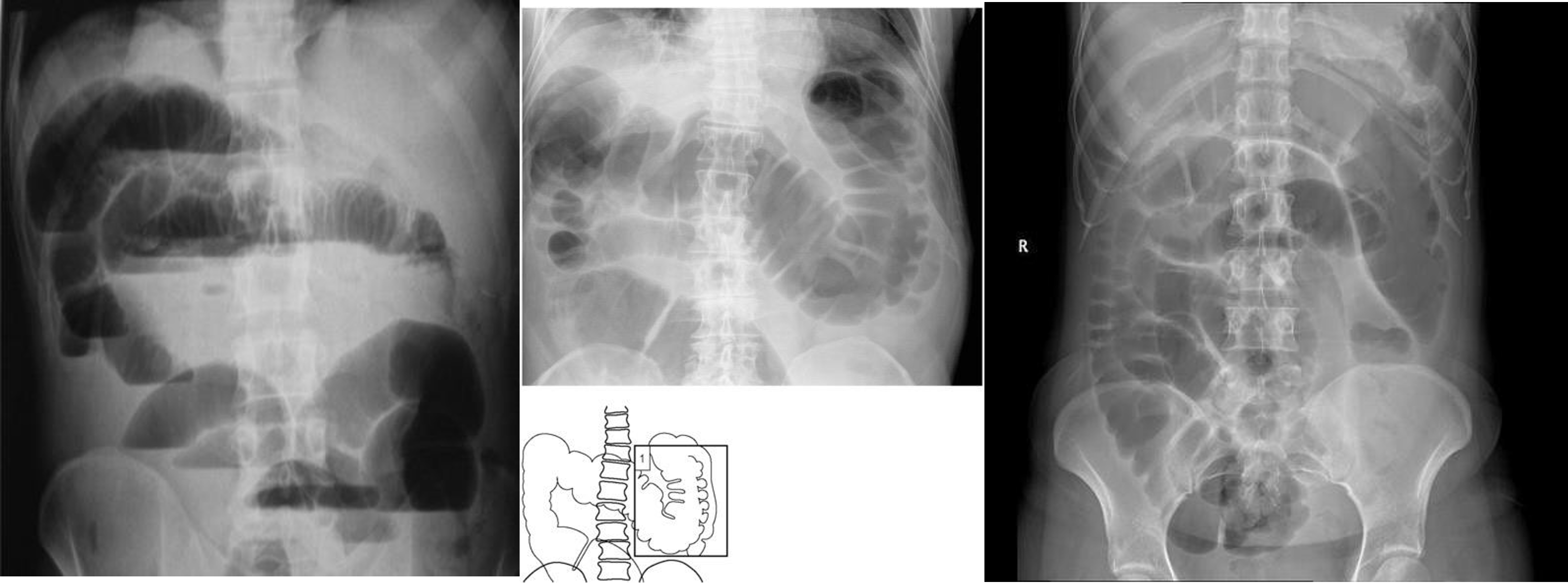
-
9 air fluids in large bowel - mucosal folds are not completed - highly suggestive of bowel obstruction
- dilated large bowel - mucosal folds are not complete - (diff; cancer, divertuclitis, volvolus, toxic megacolon?)
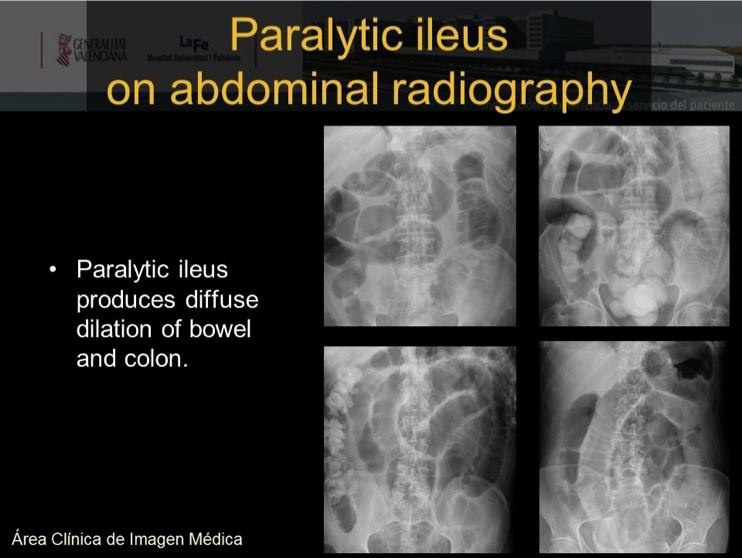
- if both small and large most likely nonmechanical paralytical illeus
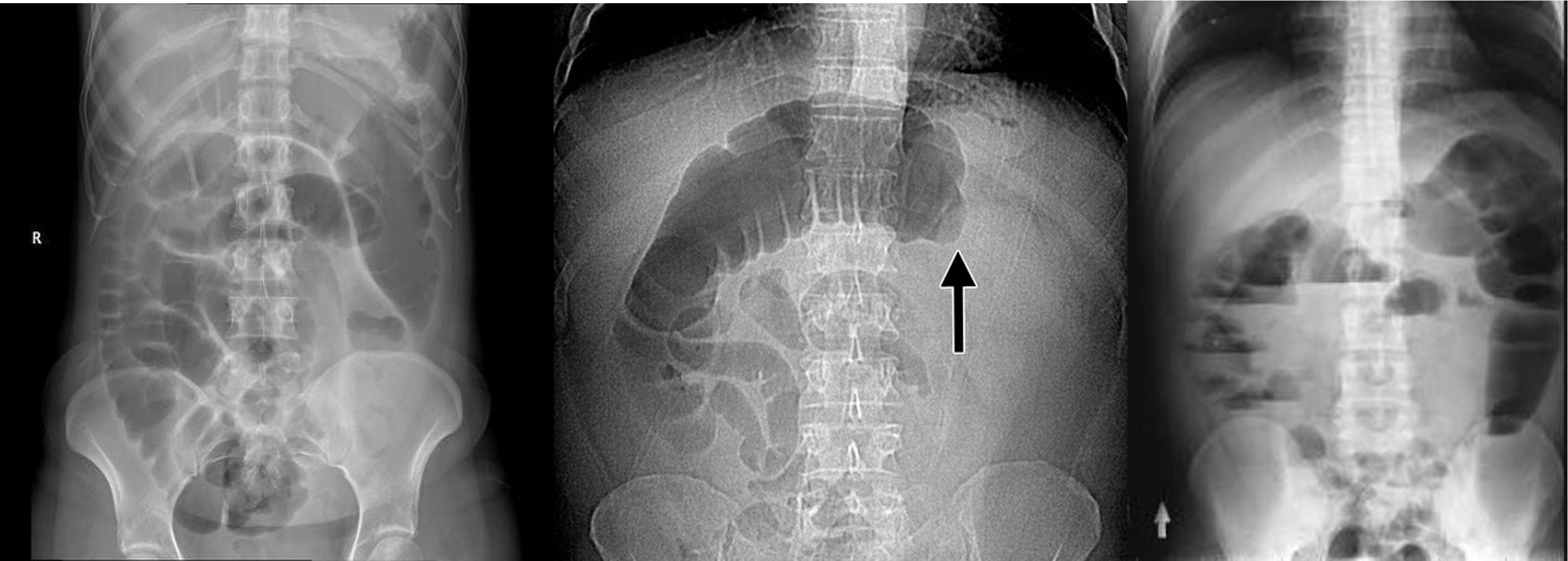 2) Dilated bowel (diff; cancer colon) -
2) Dilated bowel (diff; cancer colon) -
closed loop obstruction from both sides result large bowel most dangerous left side most common cancers
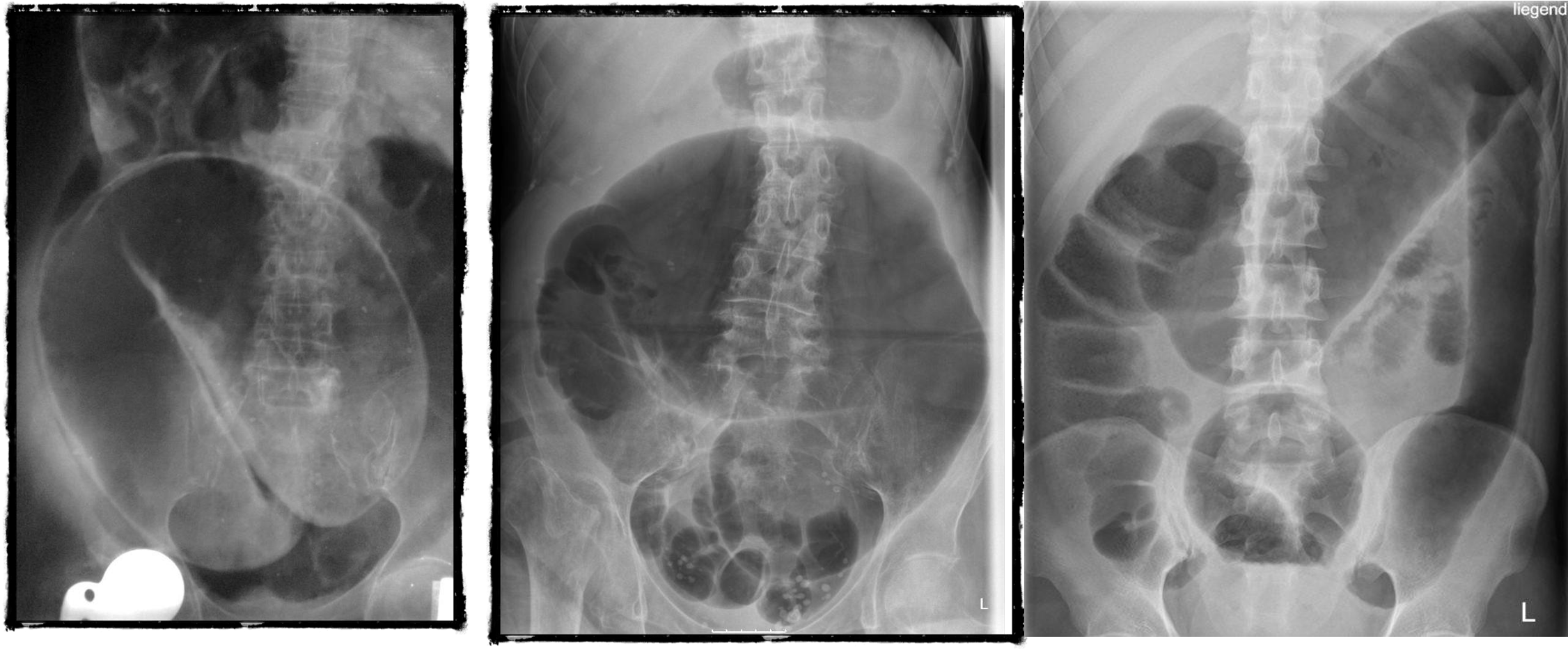
- coffe bean - omega sign - volvulus twisting around its axis - it is closed loop obstruction very dangerous - (treat clonoscopy decompression)
- volvulus
- abdominal x-ray - Dilated colon (diff - cancer colon, ulcerative colittis)
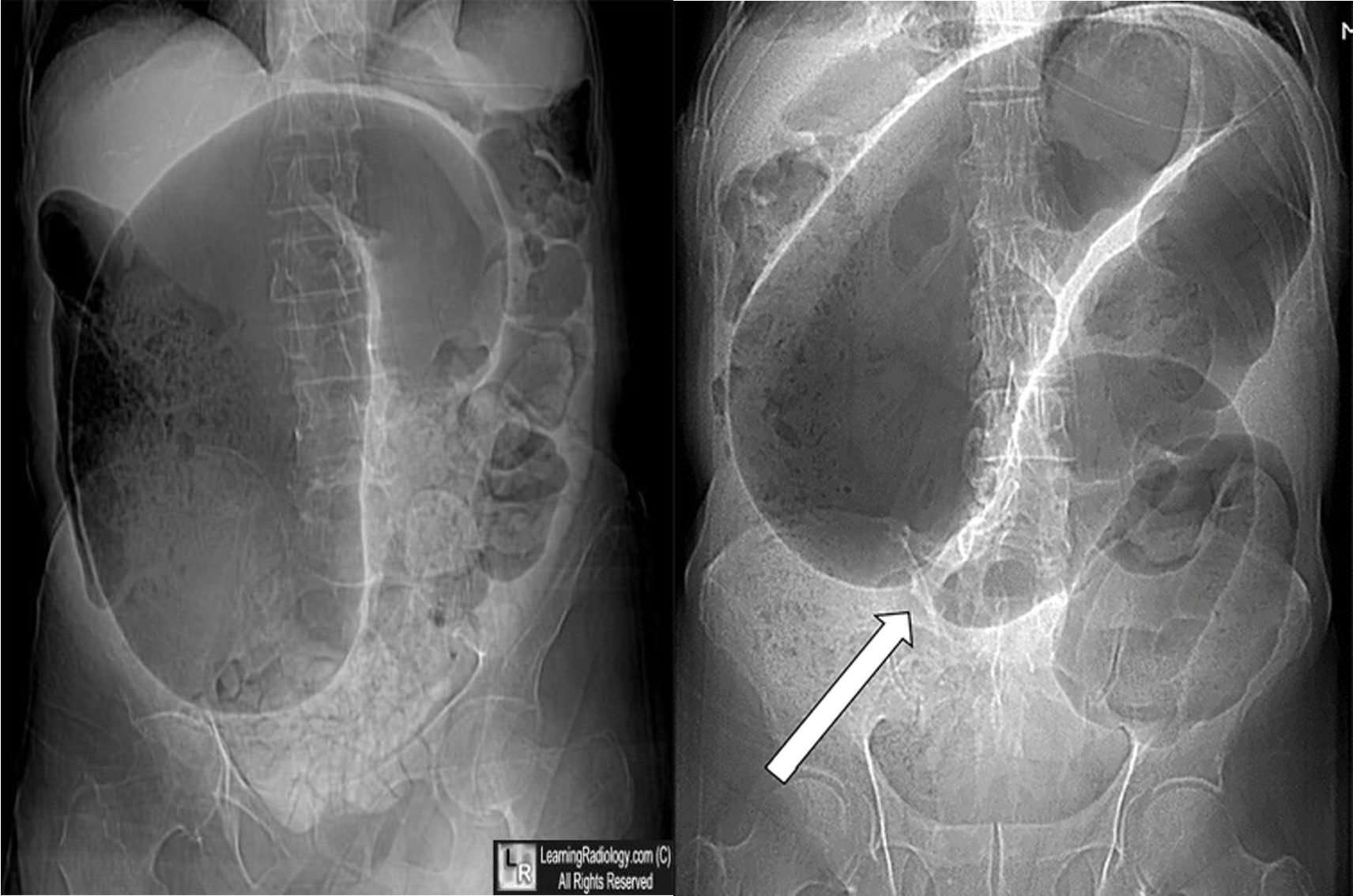
- volvulus
- volvulus
Pyelo
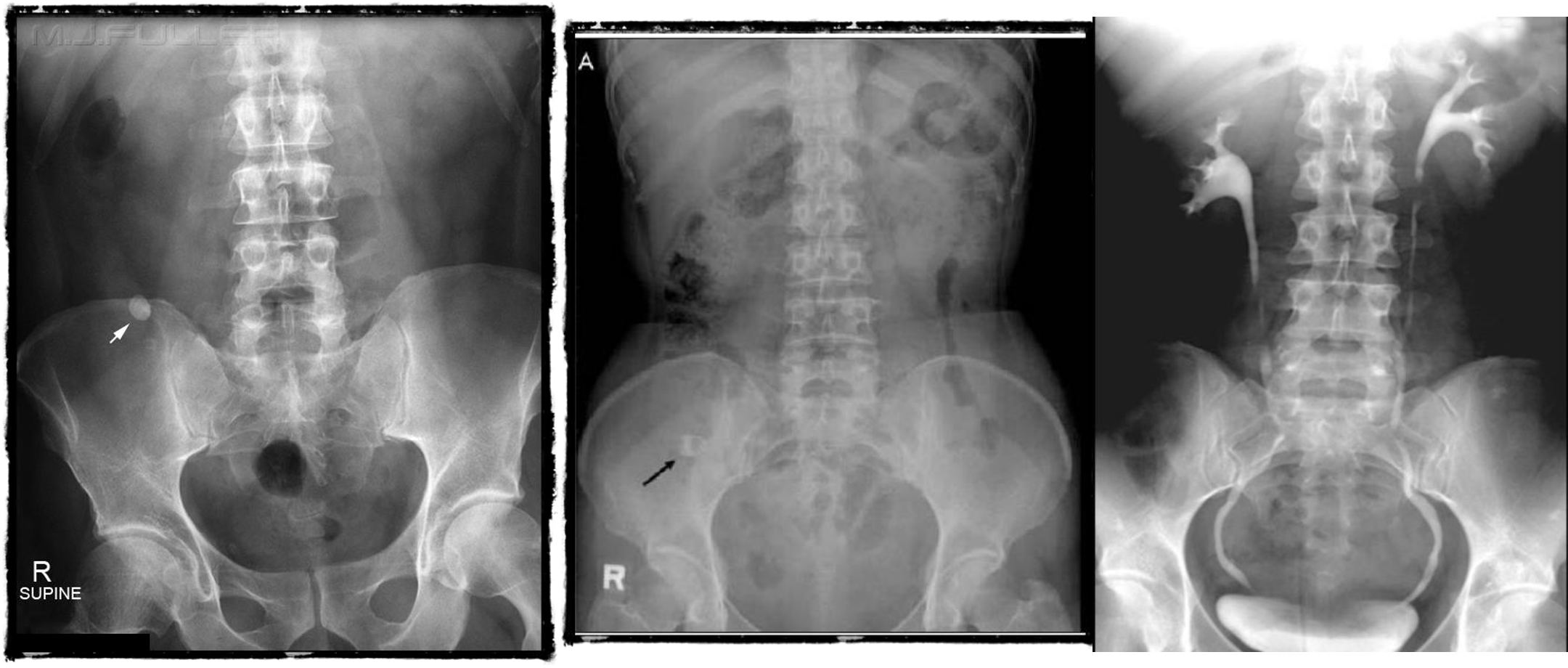
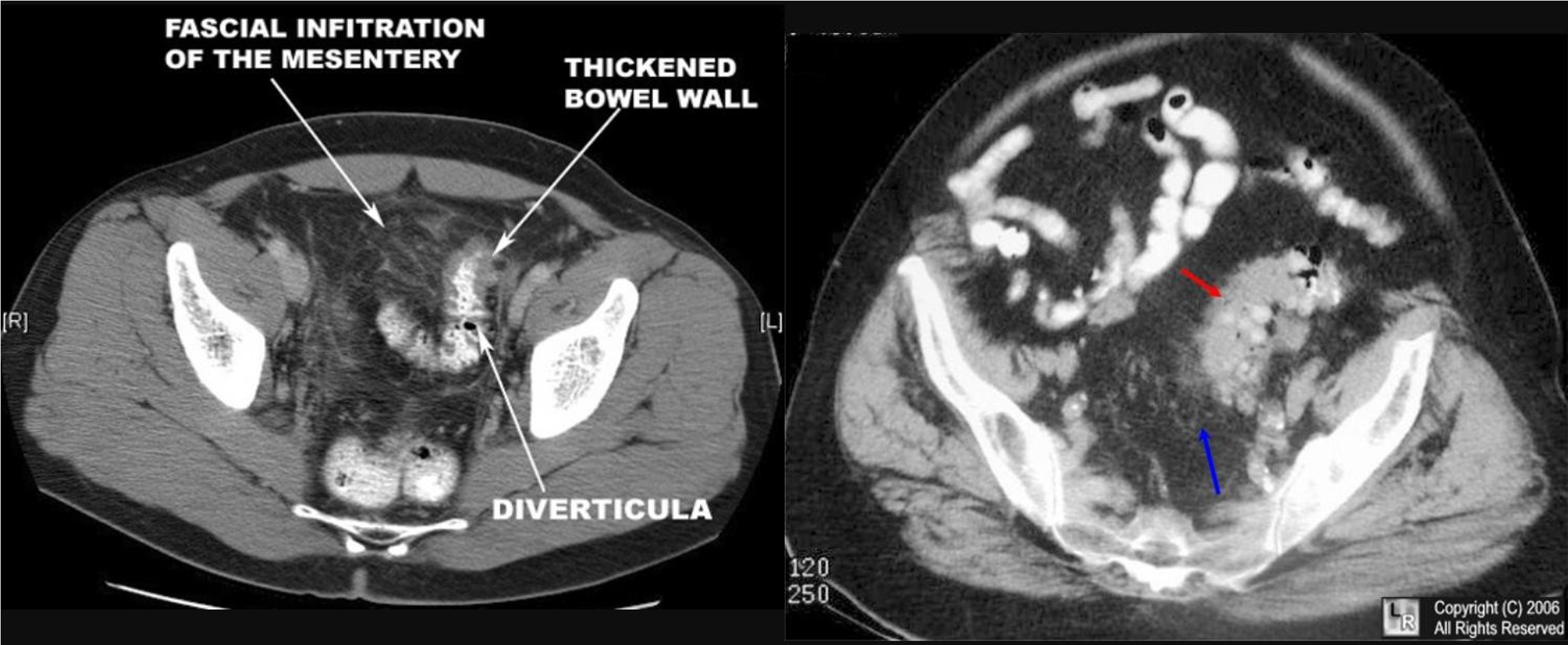
- & 2 Appendicitis - appendicolith/feacolith in young, MALT GALT
- IVP, normal
- IVP, Hydrouterer - sharp blunted
- /////
- ////
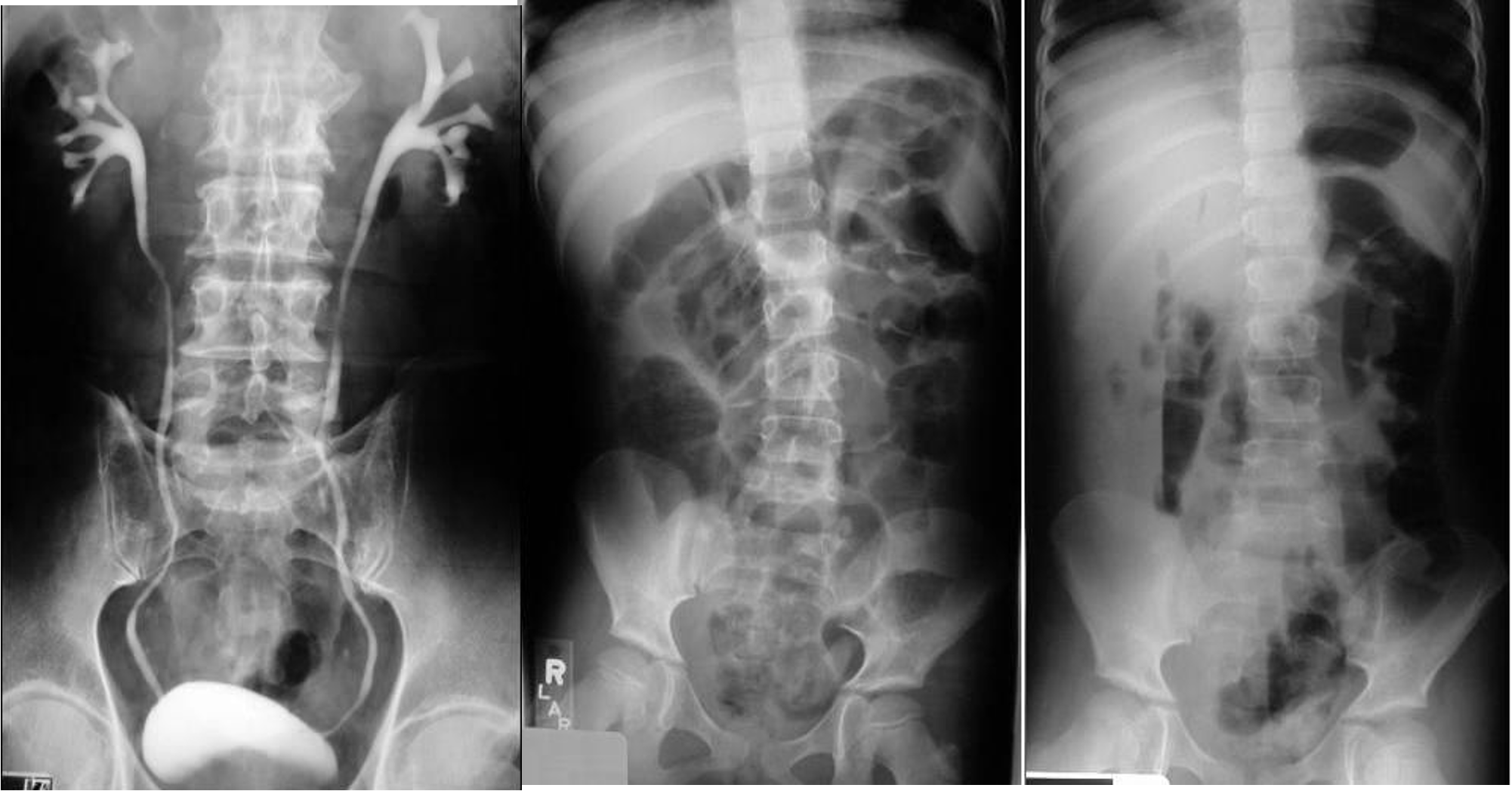
- 8 air fluid - small intestinal central - intistinal obstruction due adhesion - stack of coins. ++ NG tube aspiration relieve from vomitting
- dilated small bowel obstruction - stack of coins
- small bowel
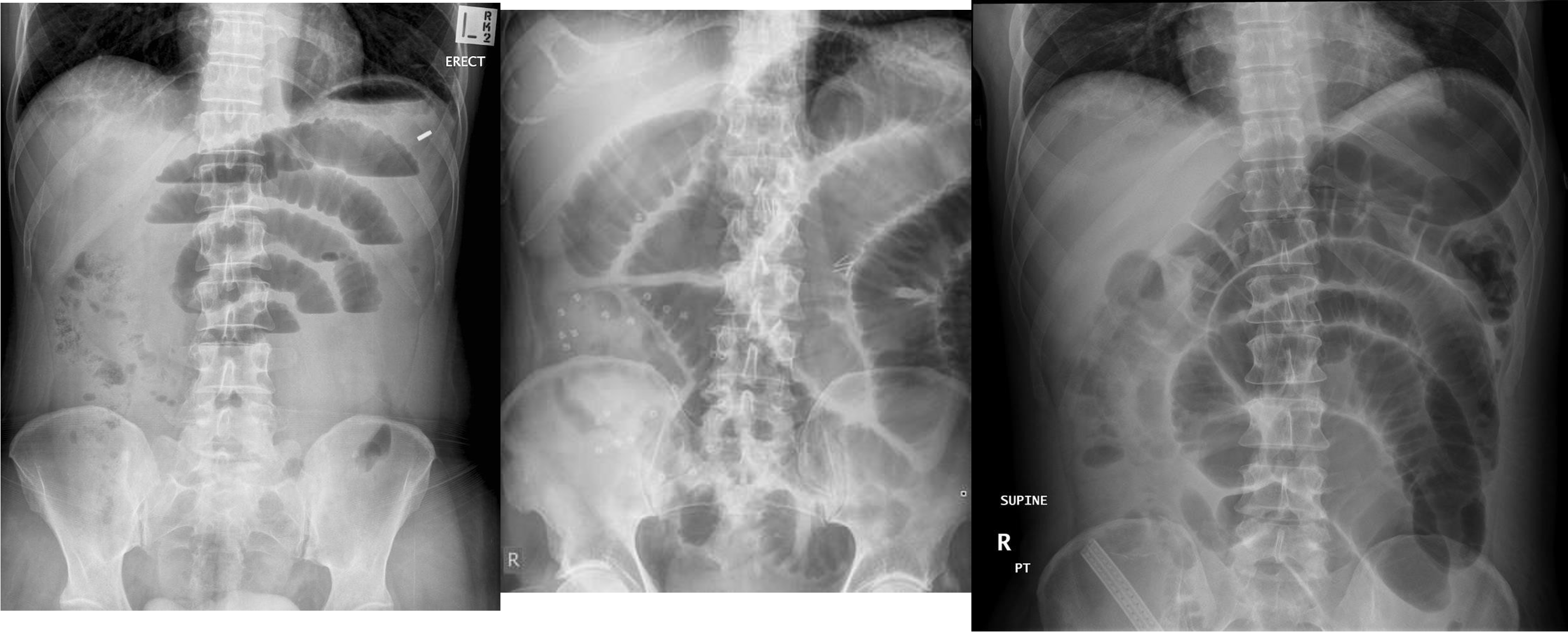
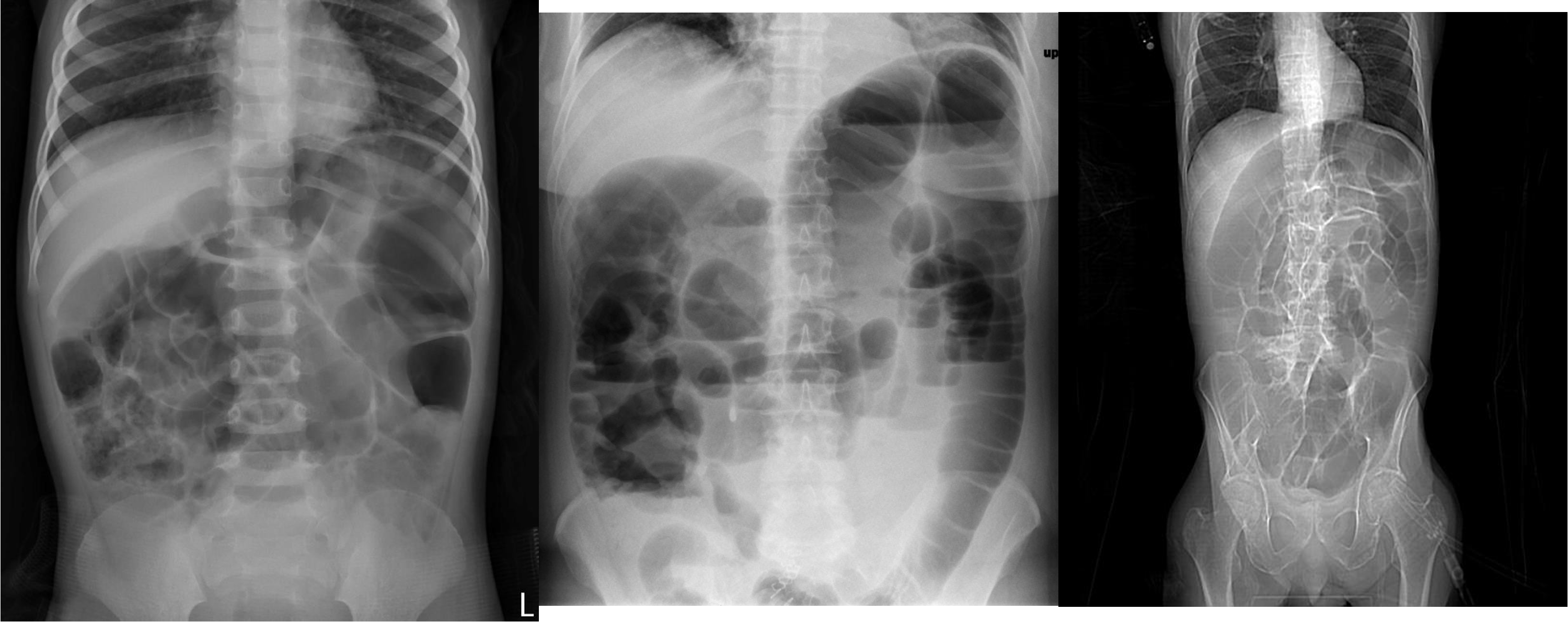 1)
2) large bowel - mucosal issnt complete periphery
3)
1)
2) large bowel - mucosal issnt complete periphery
3)
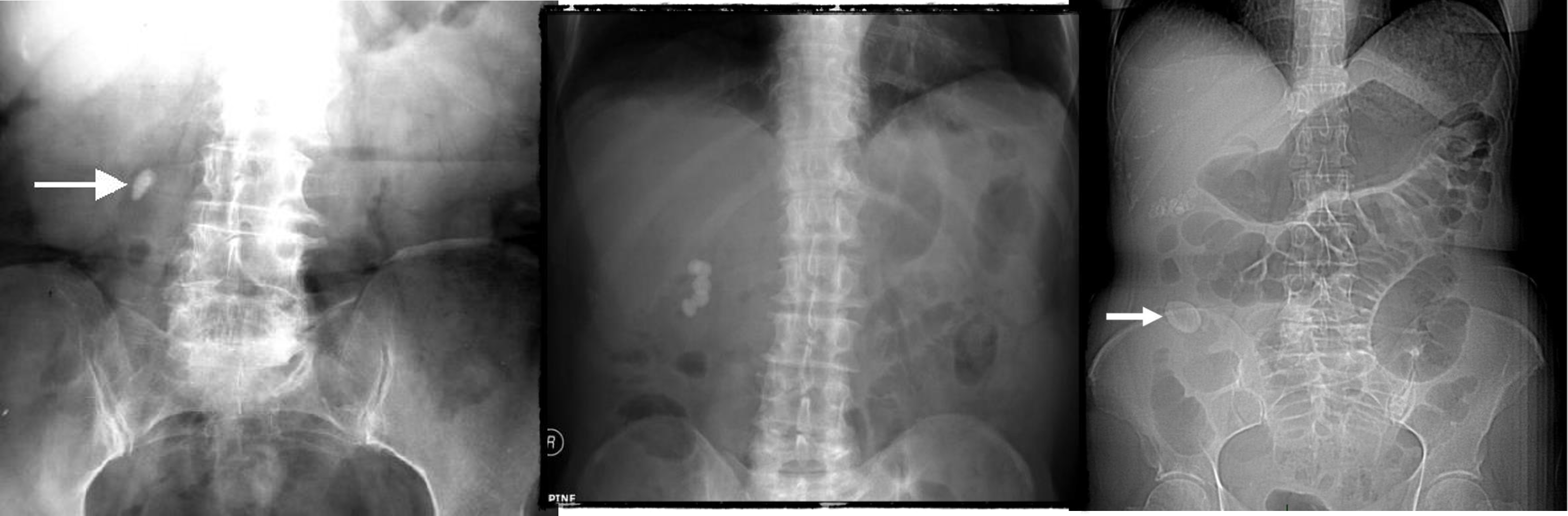
- Uretic stone
- radioopaque shadow on RUQ - renal stone
- Gallstone illeus - radioopaque shadow (regulars triad??)
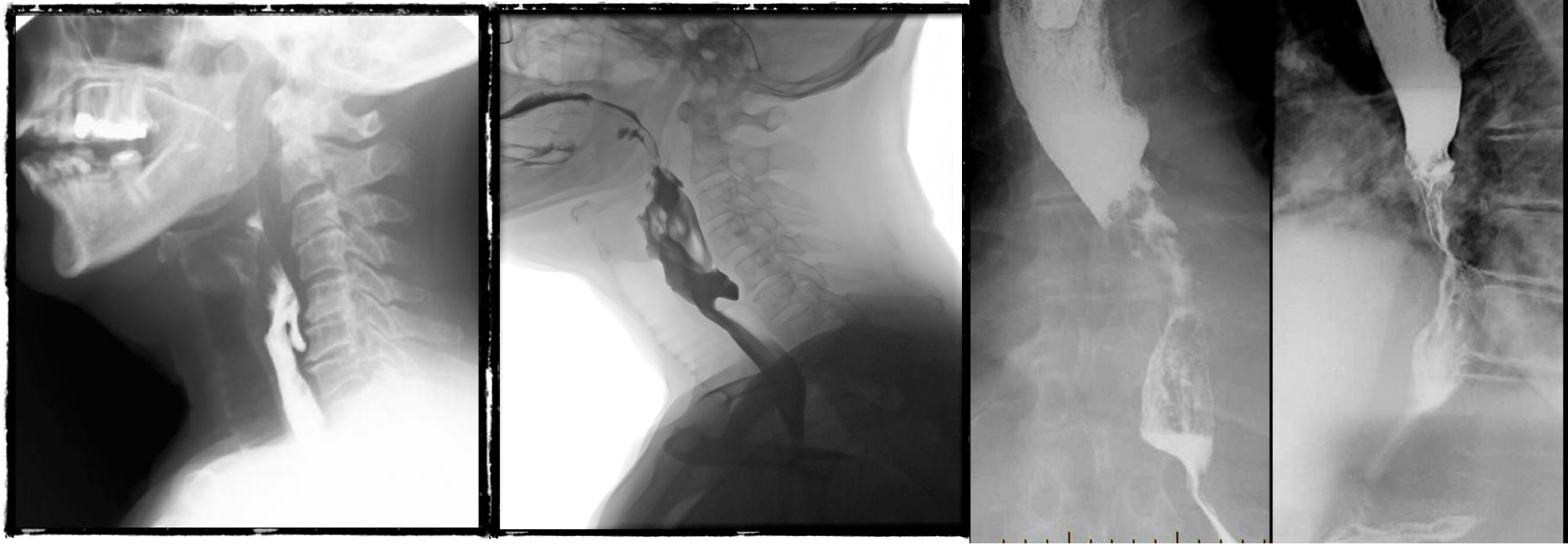
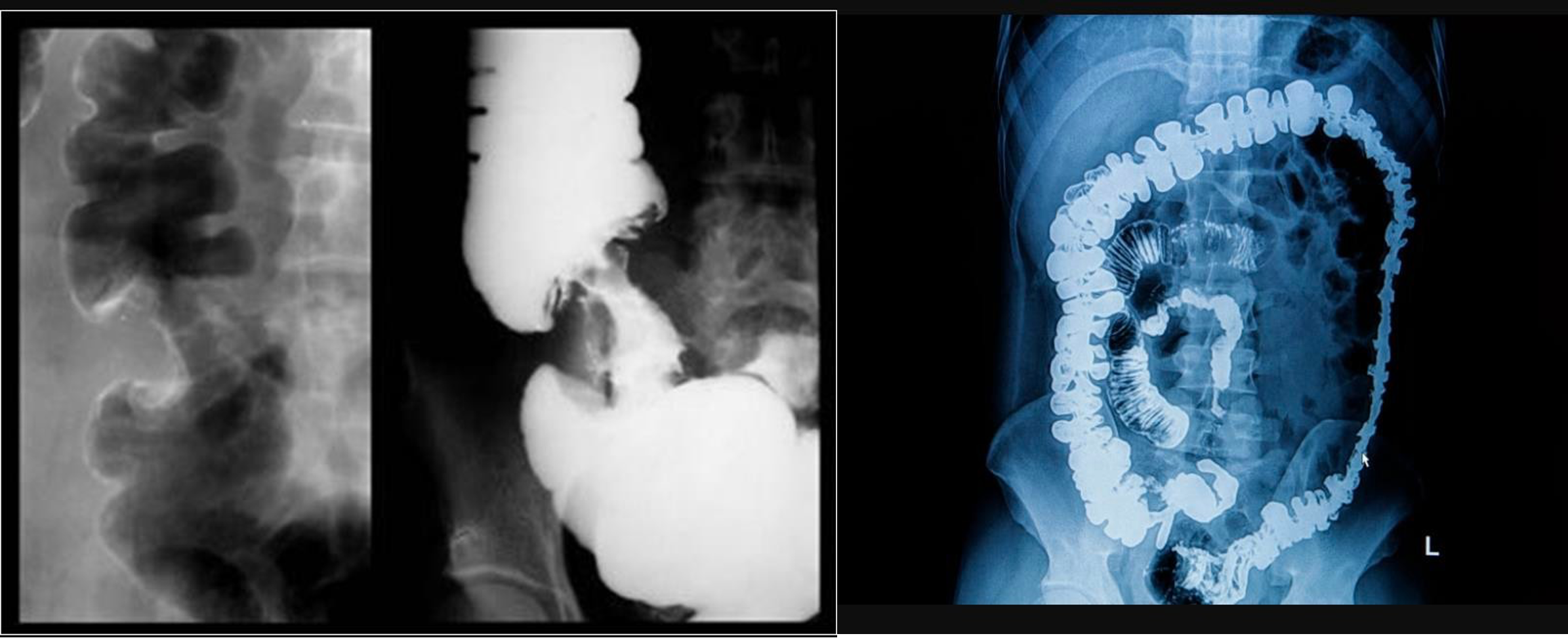
- barium swallow - zenkers diverticulum
- negative
- b swallow - diltation upper, stricture (diff cancer)
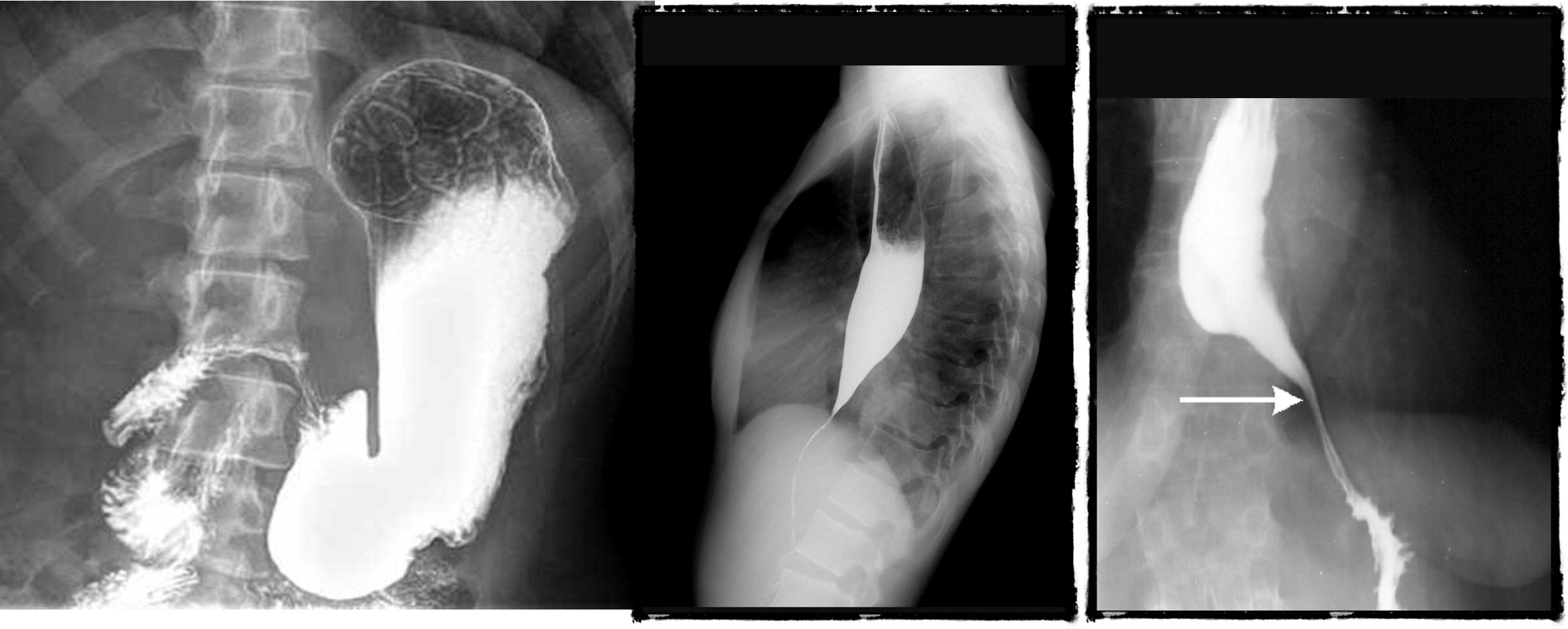
- normal (mucosal fold roge)
- dilated esophagus, stricture, bear beak/rat tail sign = aclasia
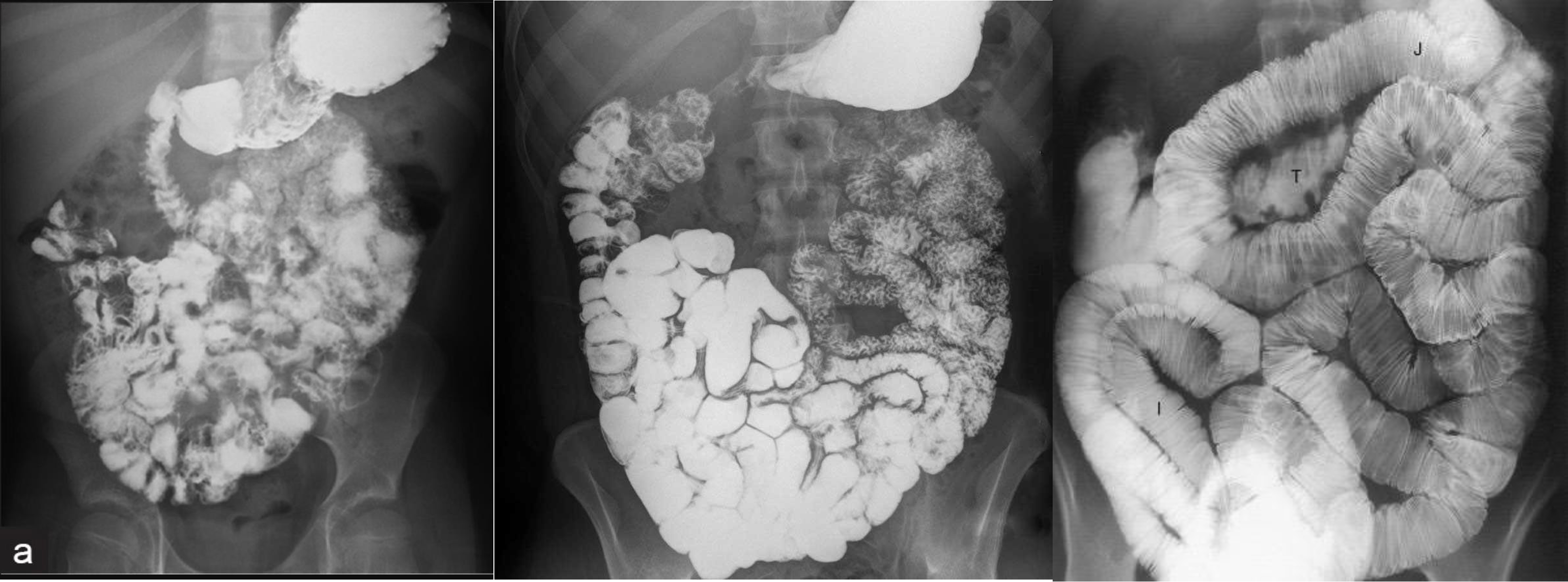
- follow through normal
- follow through (diff celiac; villus atrophy)
- barium enema from below
- apple core - neck and shoulder - stricture (cancer)
- Ulcerative collitis loss of haustration
- double enema - polyps
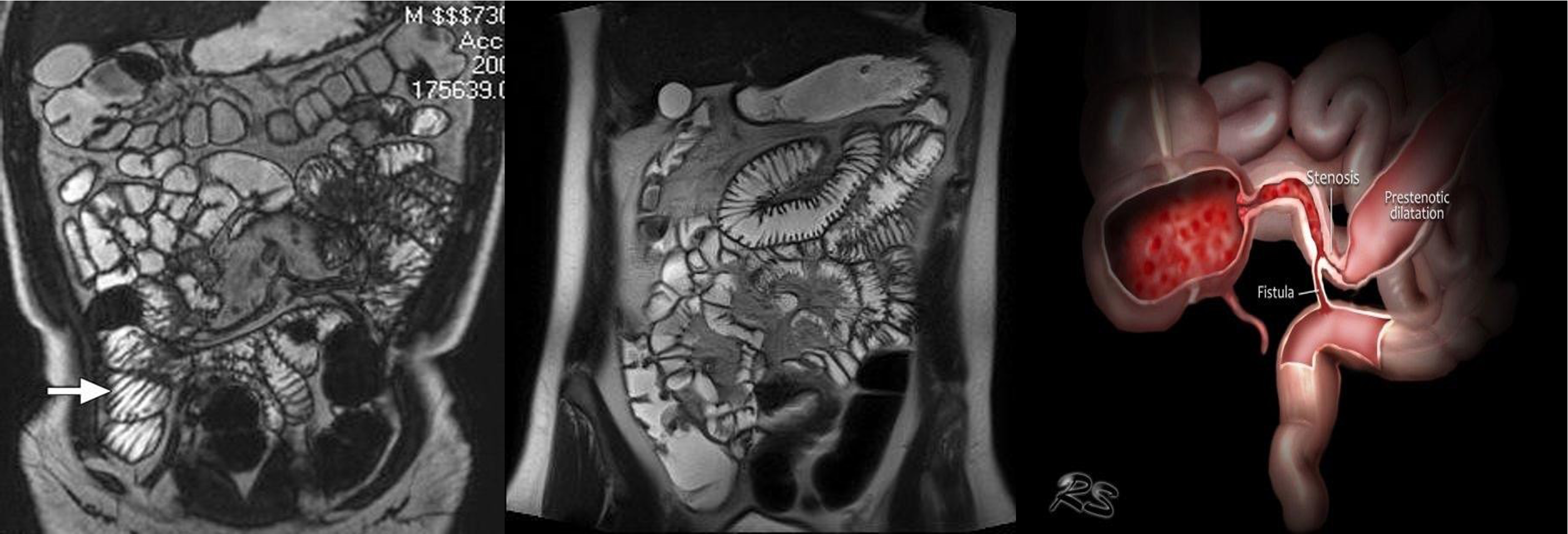
- & 2 MRE -
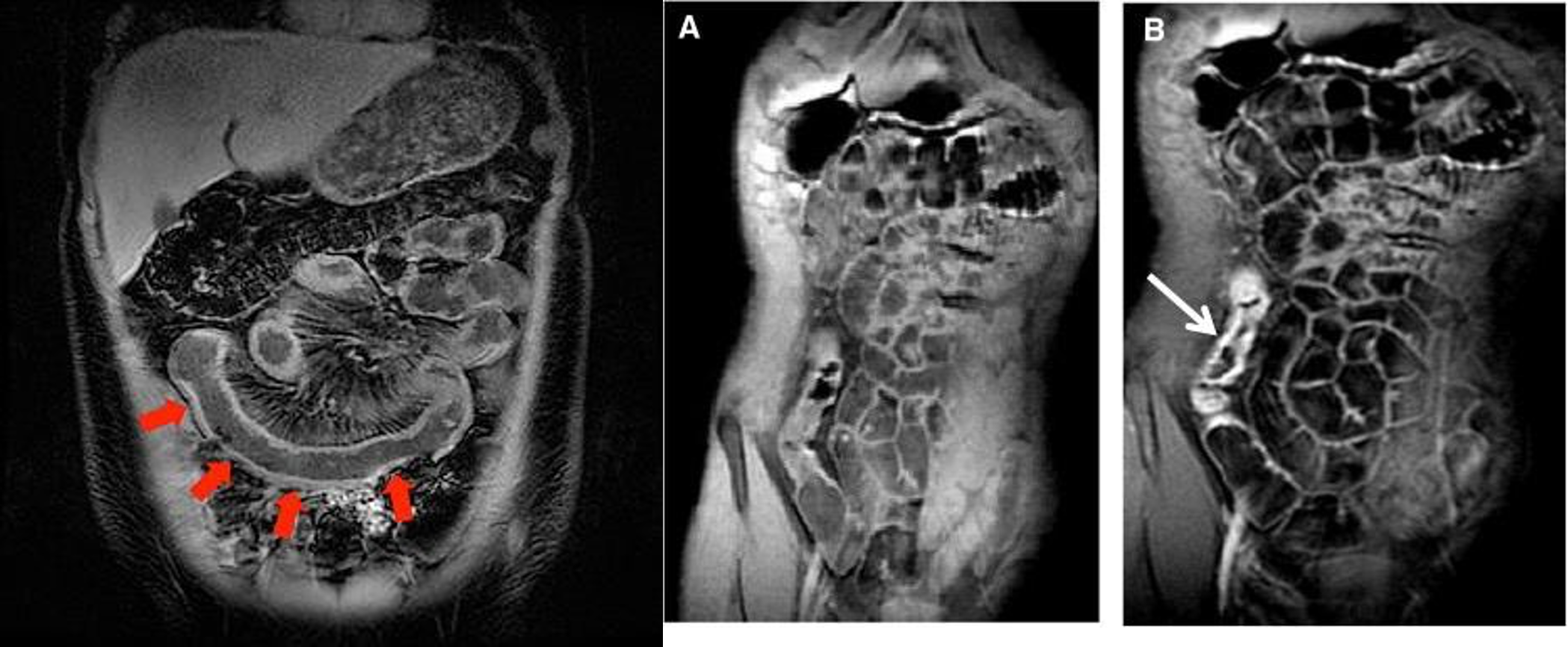
- MRE (crohn)
- MRE
- MRE
CT
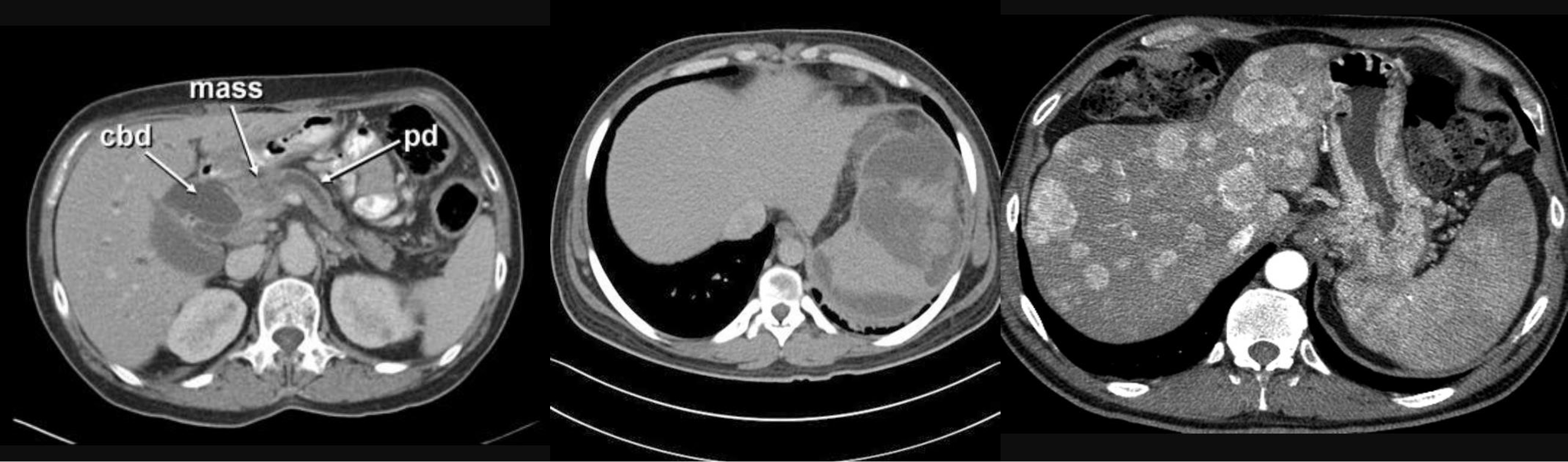
- CBD + METASTESIS
- hypodense - spleenomegaly with splenic infarct
- patient compl anemia vomit - mass stomach - adenocarcinoma - stage 4 gastric cancer (cannon ball sign) - ct scan contrast porta
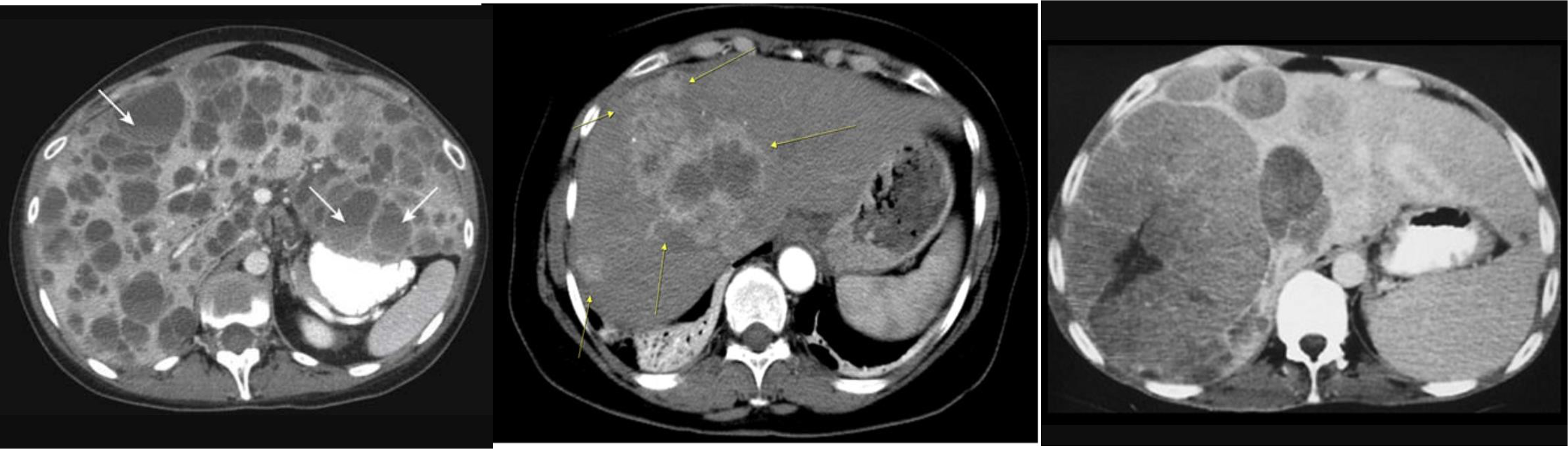
-
multiple lesion in liver due (Diff; cancer, multiple abcess pyogenic most likely)
-
Ireggular lesion peripheral enhancement - hypo in cent - febrile tender (liver abcess) - antibiotic + ct u/s guidance drainage
-
HCC, Cancer of liver, hepatic adenoma, FNH (with central scar star like)
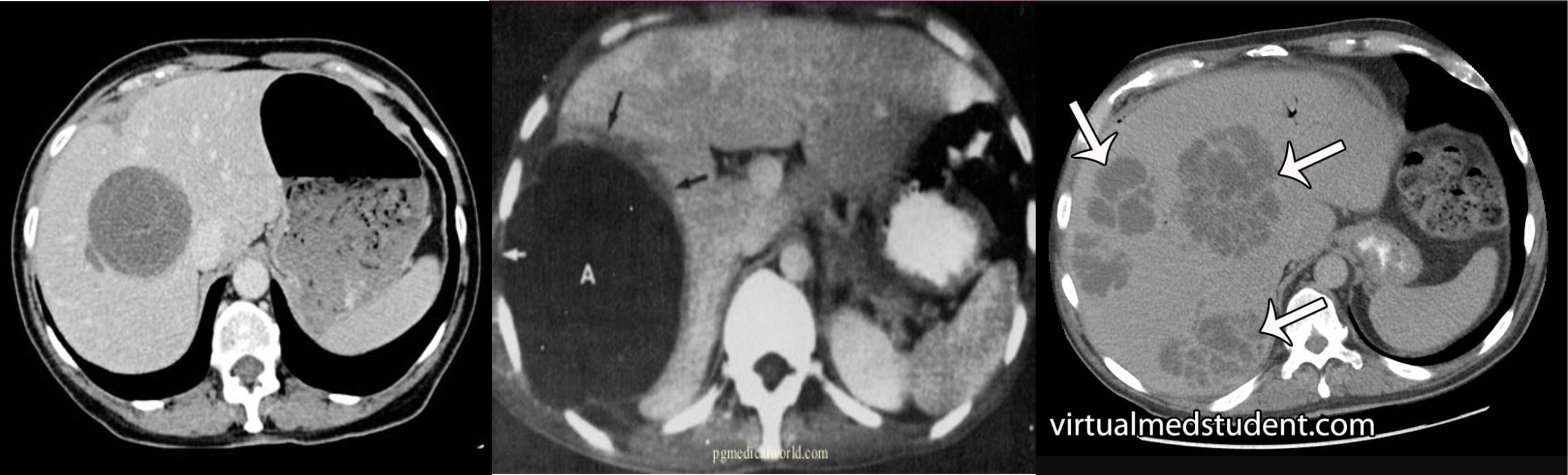
- ct scan (hypodense lesion in liver well circumscribed single - most likely amoebic liver abcess)
- multiple … metastasis
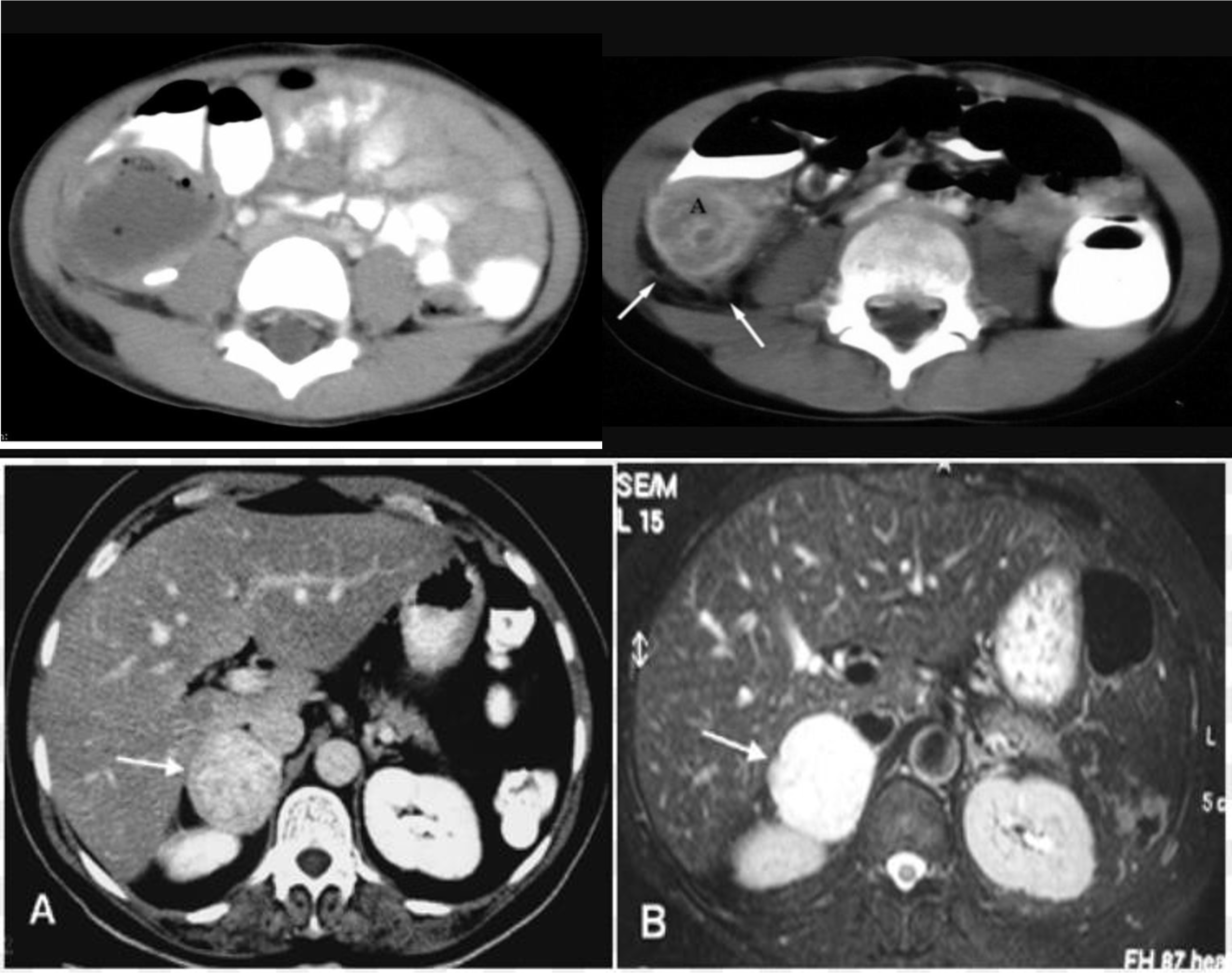
- fullness tenderness right illiac fossa 5D hx - appendicular mass incisional and drainage with antibiotic
- abscess
- ////
- ////
- ////
- ////
U/S
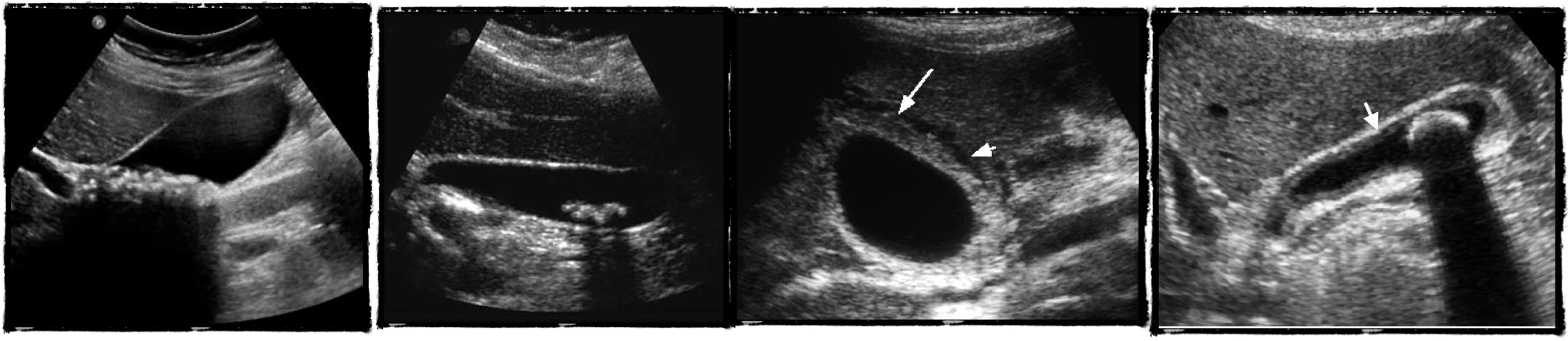
- chronic chole
- hyperechoic - post acoustic shadow…
- acute cholecystitis
- acute edematous thick gallbladder
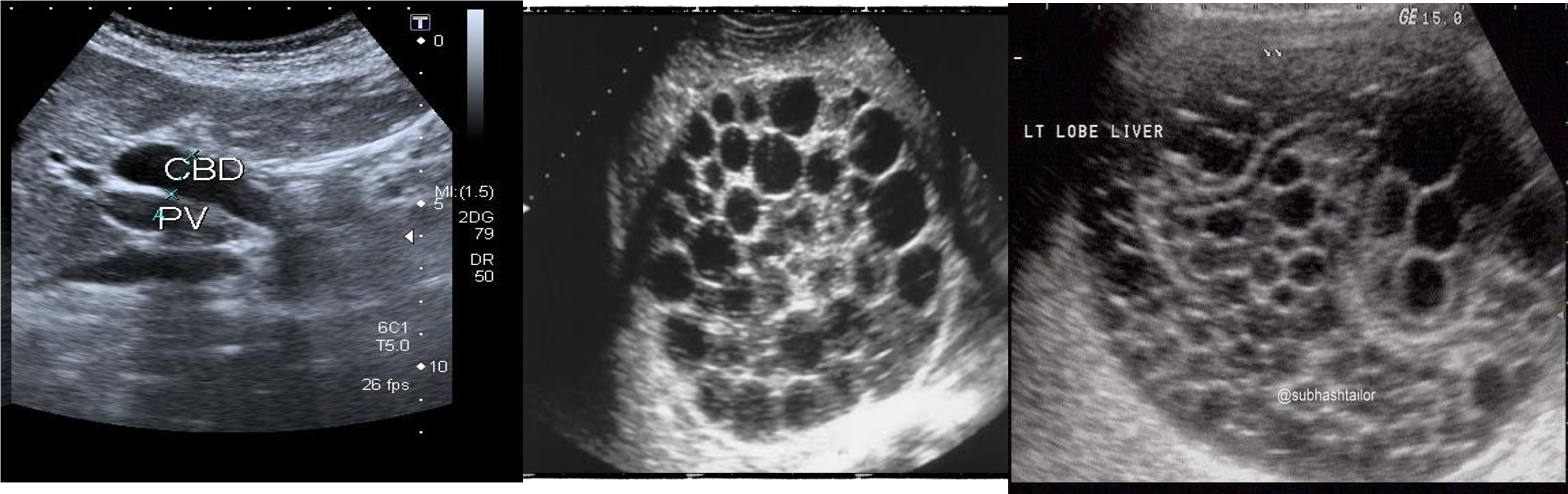
- stone tumour
 hydiatted
HCC
hydiatted
HCC
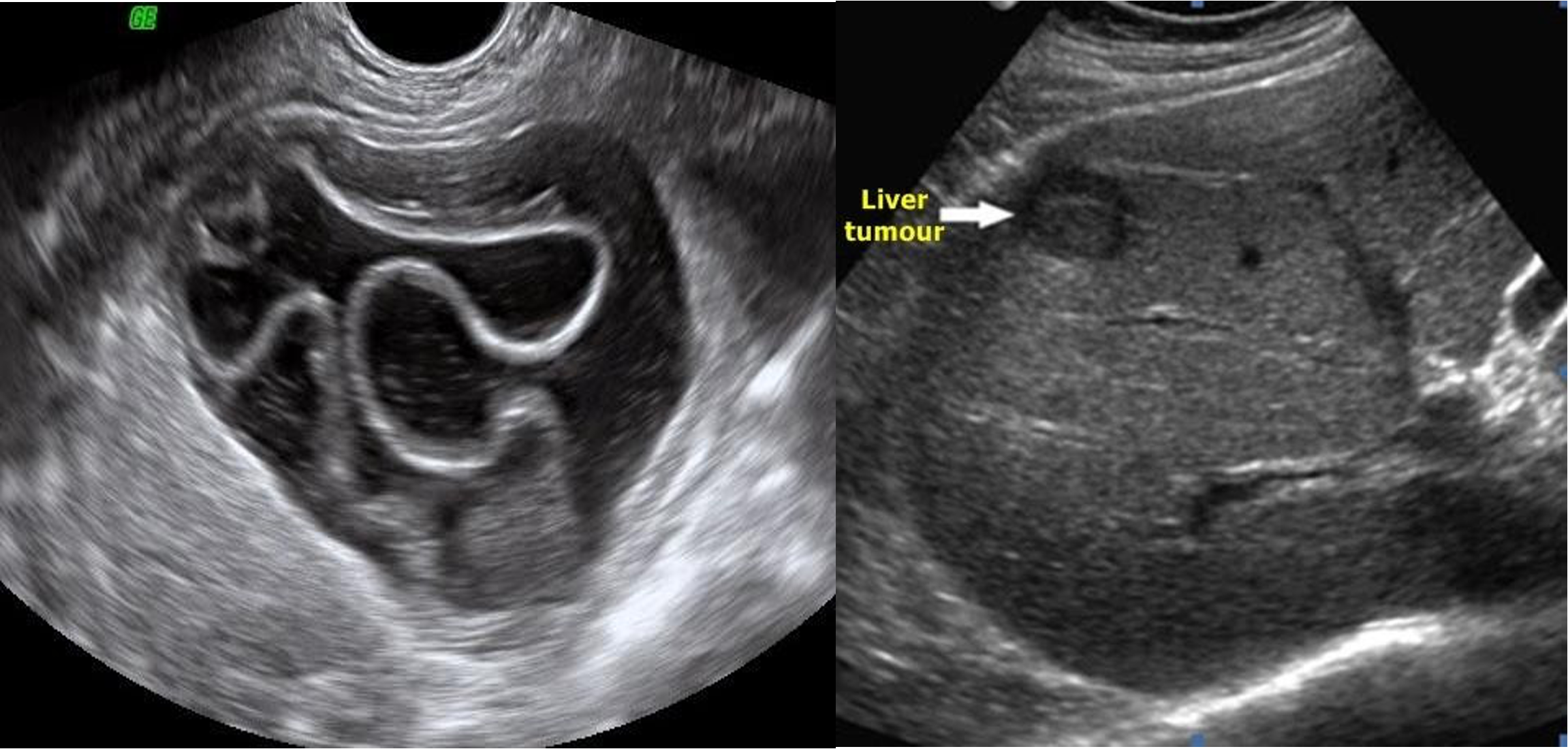
 ///
///
///
///
///
///
ERCP
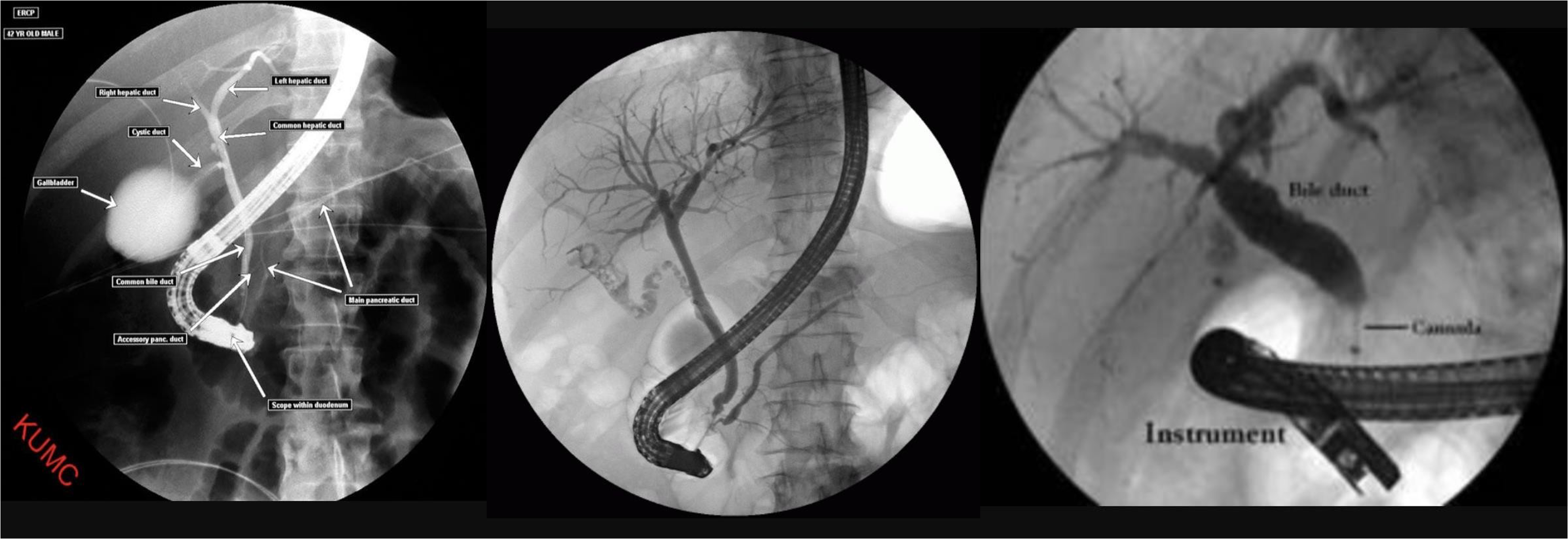
- ERCP
- ERCP
- ERCP dilated (diff stone, tumour)
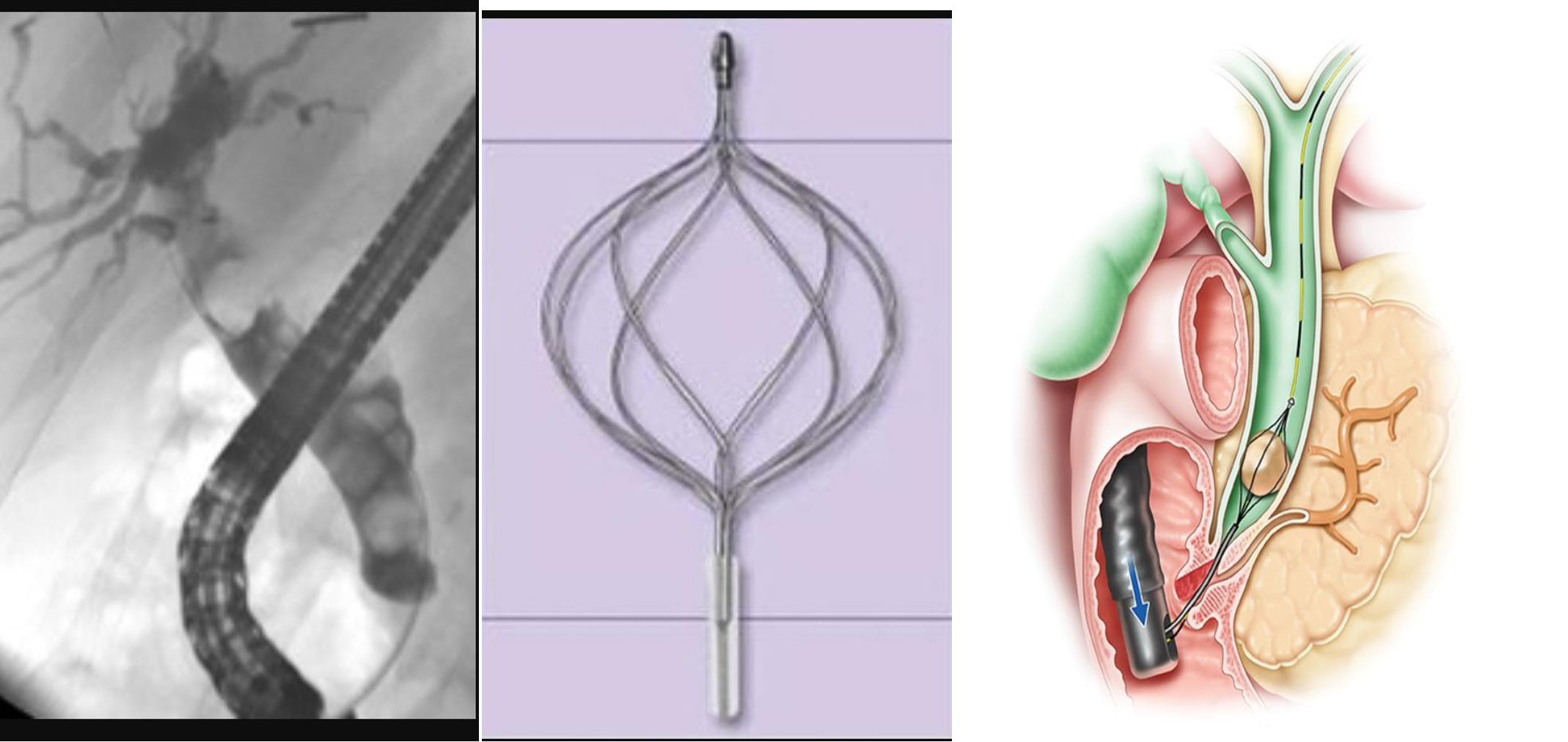
- dilated cbd, stone
- 3 - d. basket?
HIDA SCAN
gall - 100% - diff acute cholecystitis
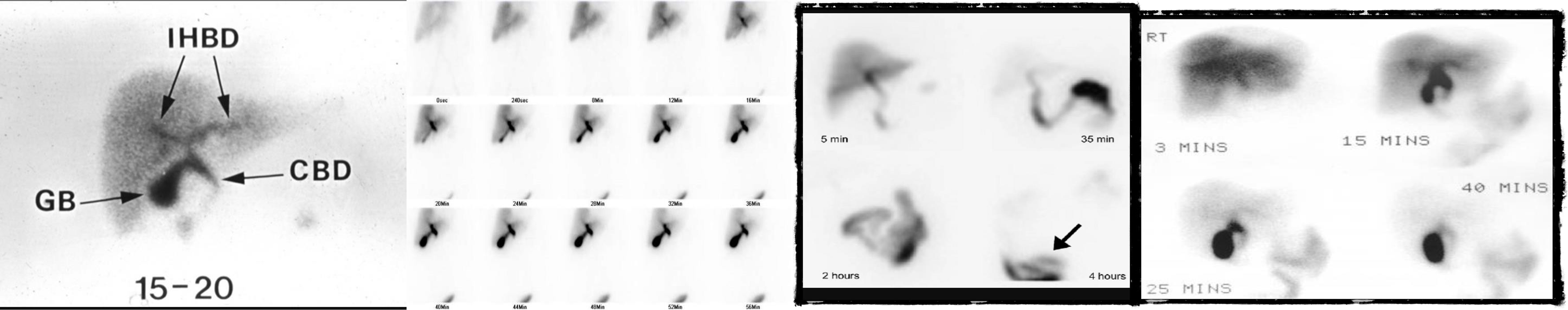 2) negative
3) positive
4)
2) negative
3) positive
4)
MRCP
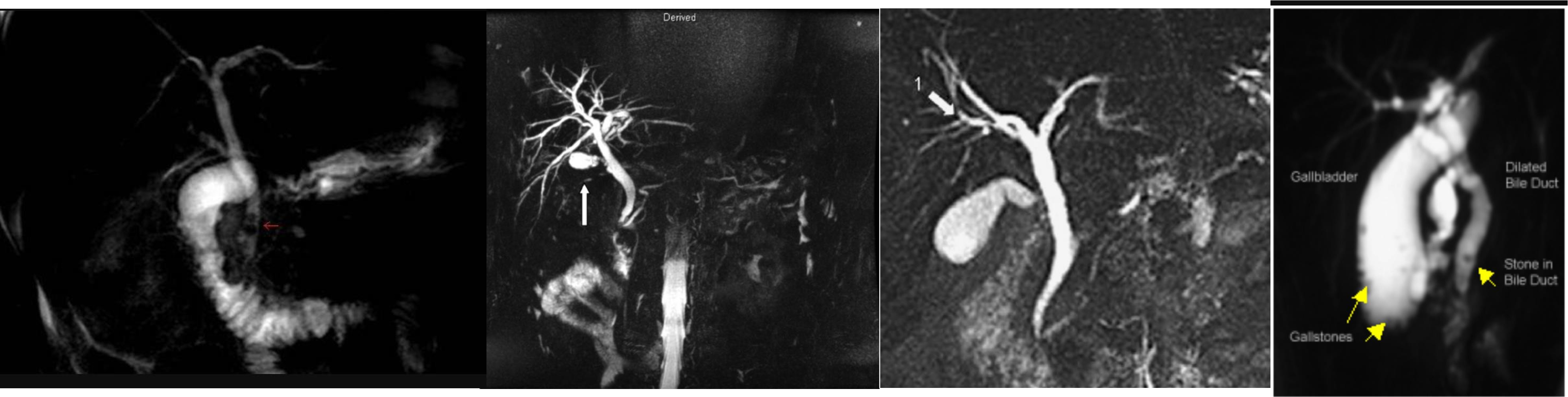 diagnostic therapeutic anatomical
diagnostic therapeutic anatomical
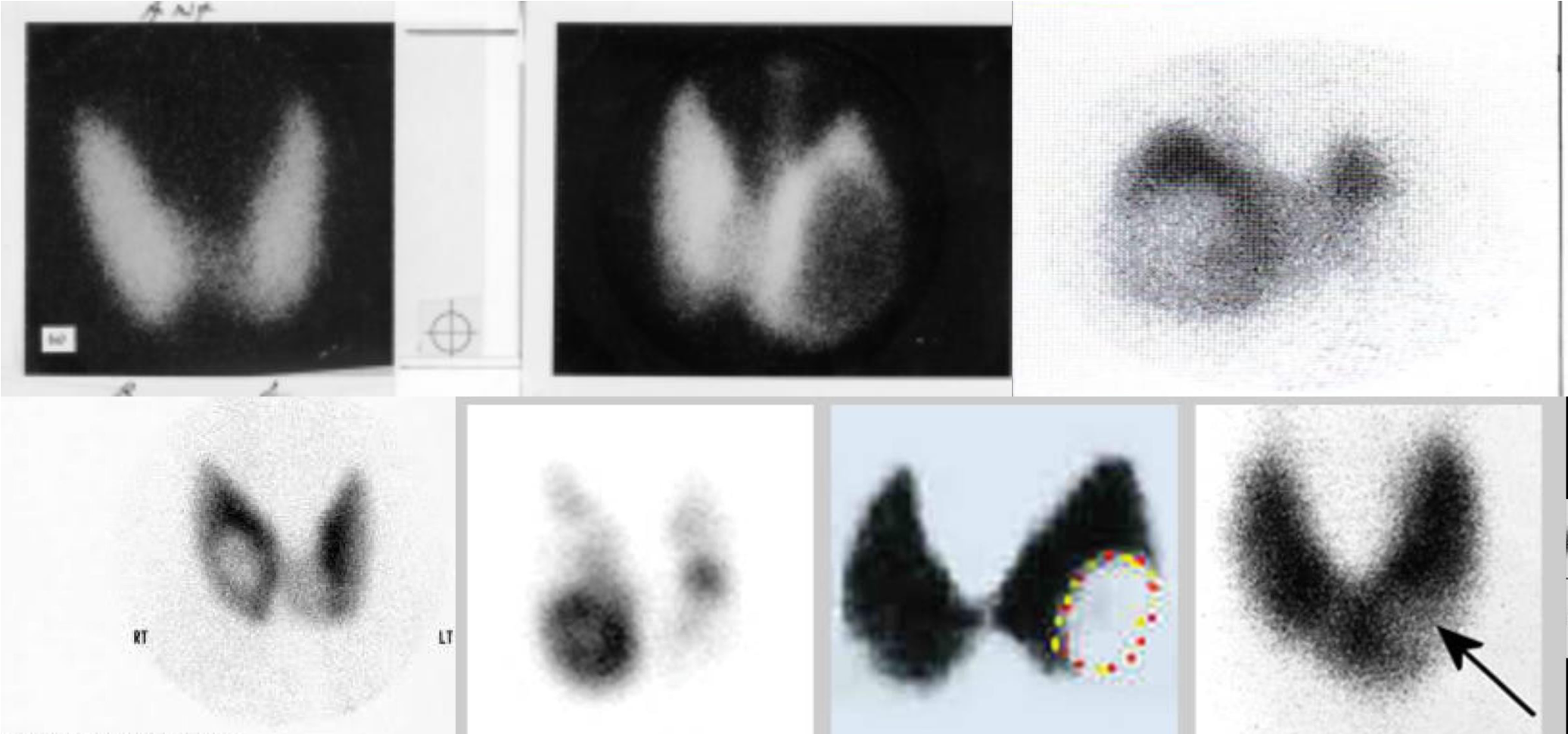
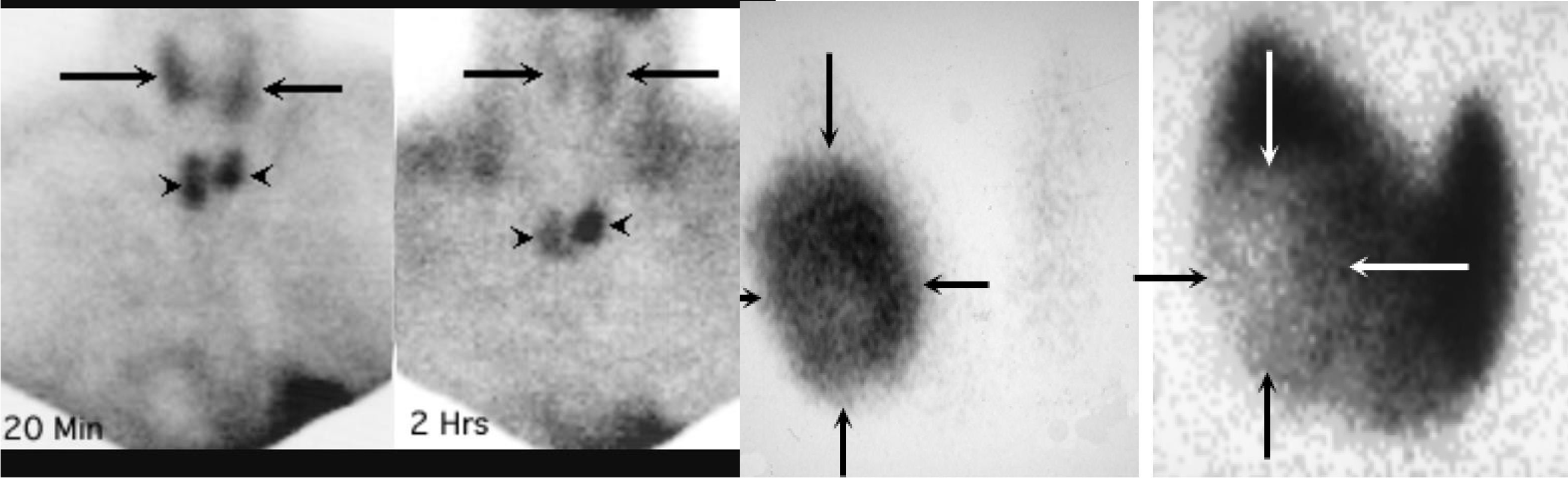
NUCLEAR SCAN
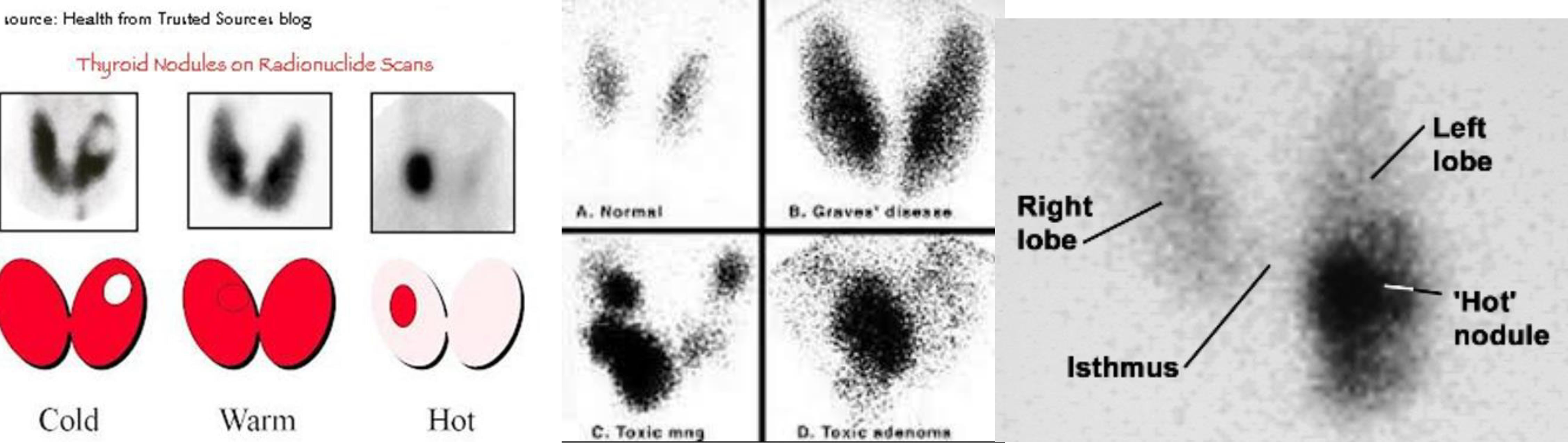
cold nodule = malignancy
MAMMOGRAM
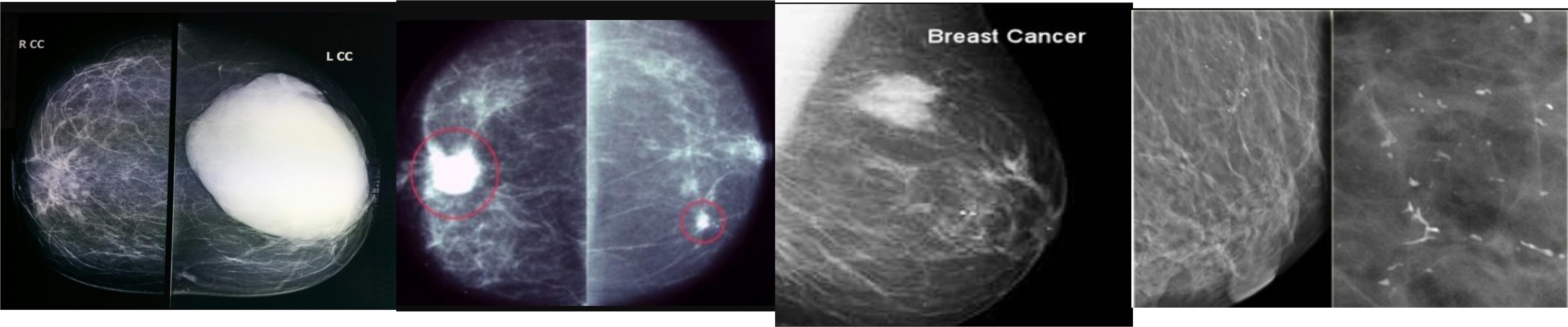 fibroadenoma
fibroadenoma
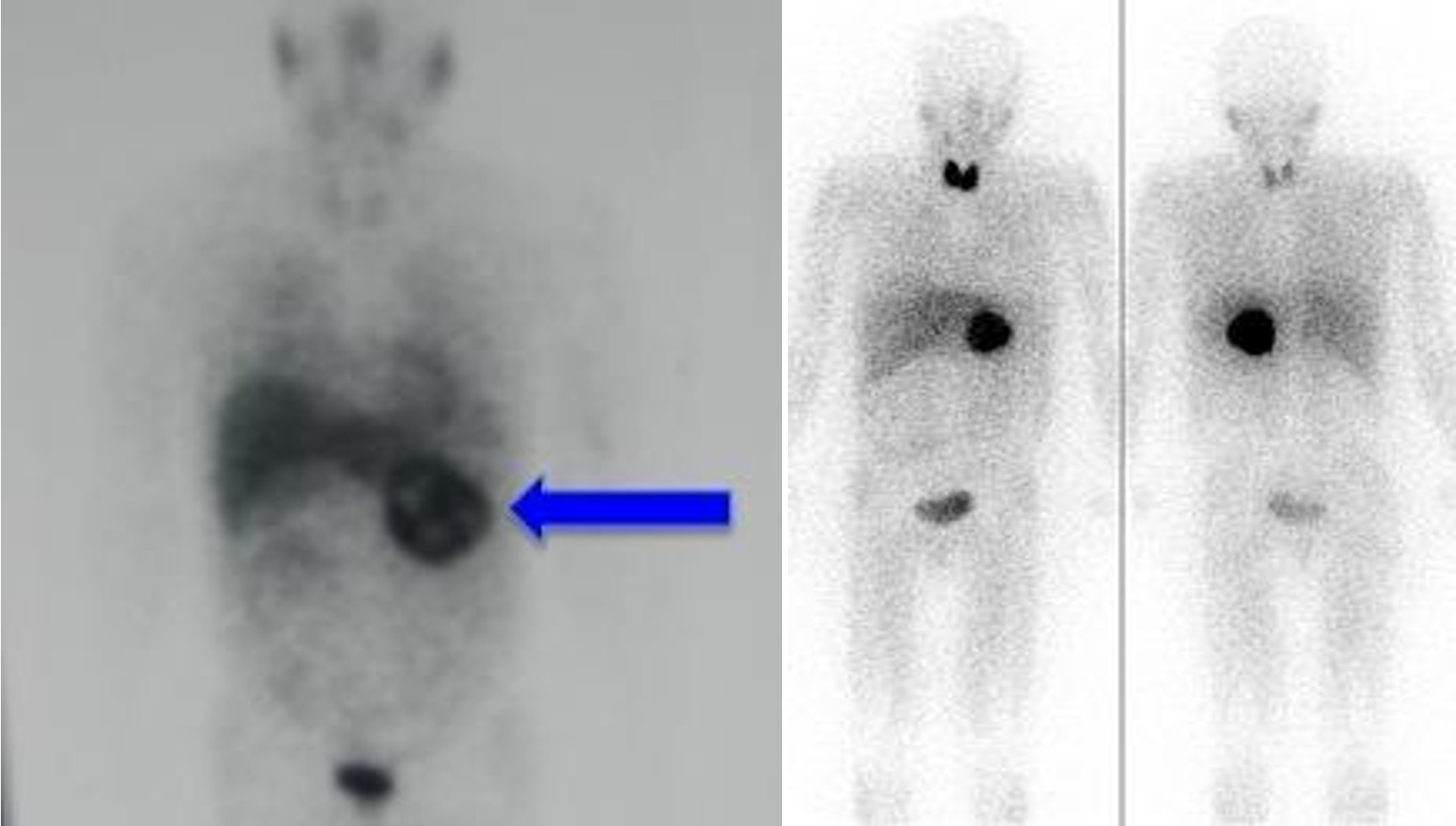
PET SCAN
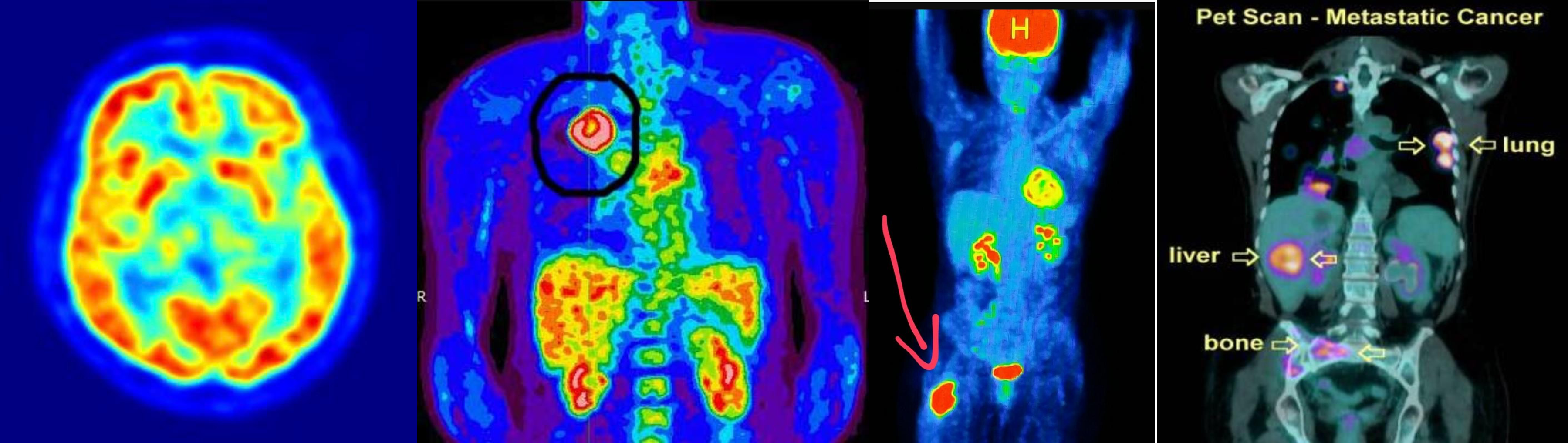 annual follow up
annual follow up
- soft tissue sarcoma -
- lung cancer metasteseses to bone