Mainly to assess behind bone, with eliminating gasses for image to be in better quality.
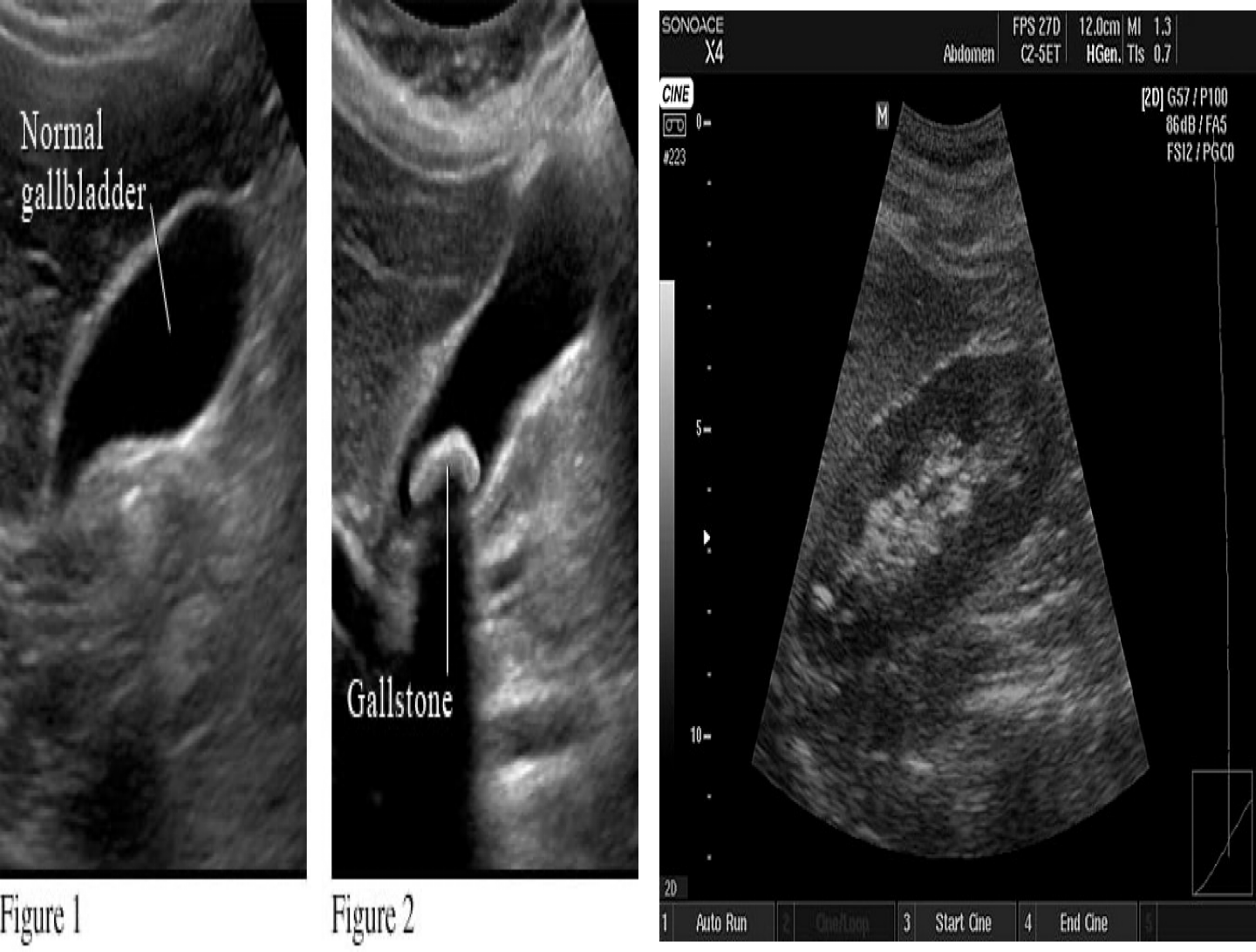
Best action directed to fluids: hydrocephalus, Amniocentesis, Pleural effusion, ascites, gall bladder stones etc… Z
-
Echoic definition - Hyper, Iso (similiar echonigicity, normal tissue), hypo, ane (very black). Hyperechoic – More echogenic (brighter) than normal. Hypoechoic – Less echogenic (darker) than normal. Isoechoic – The same echogenicity as another tissue. Anechoic - Black than normal
-
High frequency of 2-20 MHz
-
Used Endoscopically (Trans; rectally, vaginally, esophageally, gastrically) to better evaluate internal organs and otherwise difficult to evaluate structures such as the prostate, ovaries, heart valves, and pancreas.
Advantages: Low cost, quick, safe with no radiation, availability, portable, non-invasive
Disadvantages: Z
- Cant penetrate bone, nor air/gasses
- Needs skill; operator dependent
Acoustic shadow:
If ultrasound waves are strongly absorbed and echoed at the surface, the waves will fail to penetrate the tissue. All structures behind the surface will appear black. - Hypo-echoic shadow
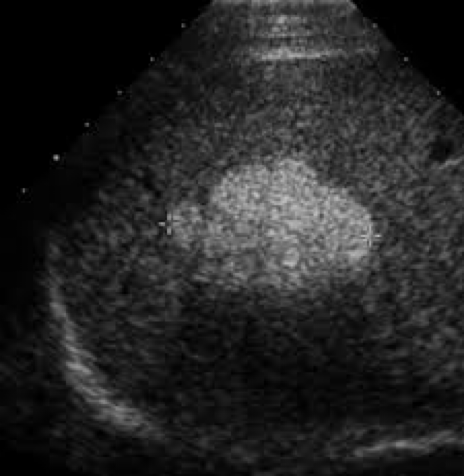
Acoustic enhancement:
- Because ultrasound waves are hardly weakened in fluids, structures that are located behind fluid-filled spaces will appear hyper-echoic shadow (brighter).
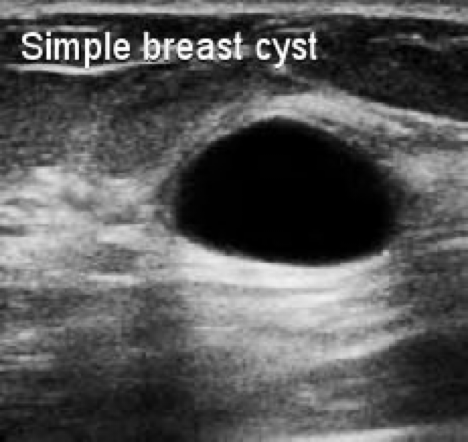
- Ultrasound is often used to Z **determine whether the structure is solid or cystic
Doppler ultrasound
Doppler studies are used to detect #Z venous thrombosis, arterial stenosis and occlusion.
Doppler or duplex mode used to visualize motion within structures, e.g., the velocity and direction of blood flow.
In obstetrics, Doppler ultrasound is used particularly to Z determine fetal blood flow through the umbilical artery
With Doppler echocardiography it is possible to demonstrate Z Regurgitation through incompetent valves.
