The Optic Nerve
The Optic nerve is tested in five ways:
- Visual Acuity; Snellen chart
- Colour; Ishihara plates
- Fields; Visual Inattention test
- Reflexes; Light stimuli direct/indirect action
- Fundoscopy Papilledema, Cotton wool’s
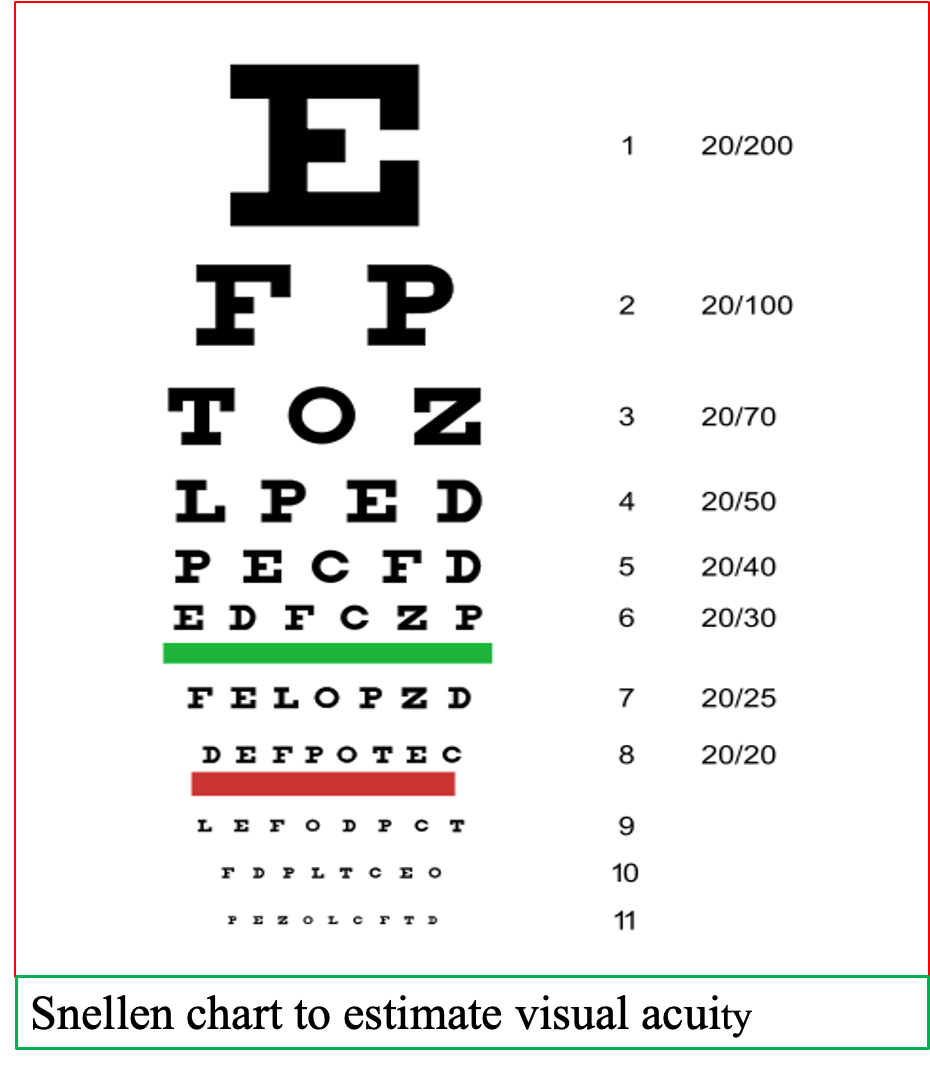
Visual Acuity
Visual acuity is tested using Snellen charts. If the patient normally wears glasses or contact lenses, then this test should be assessed both with and without their vision aids.
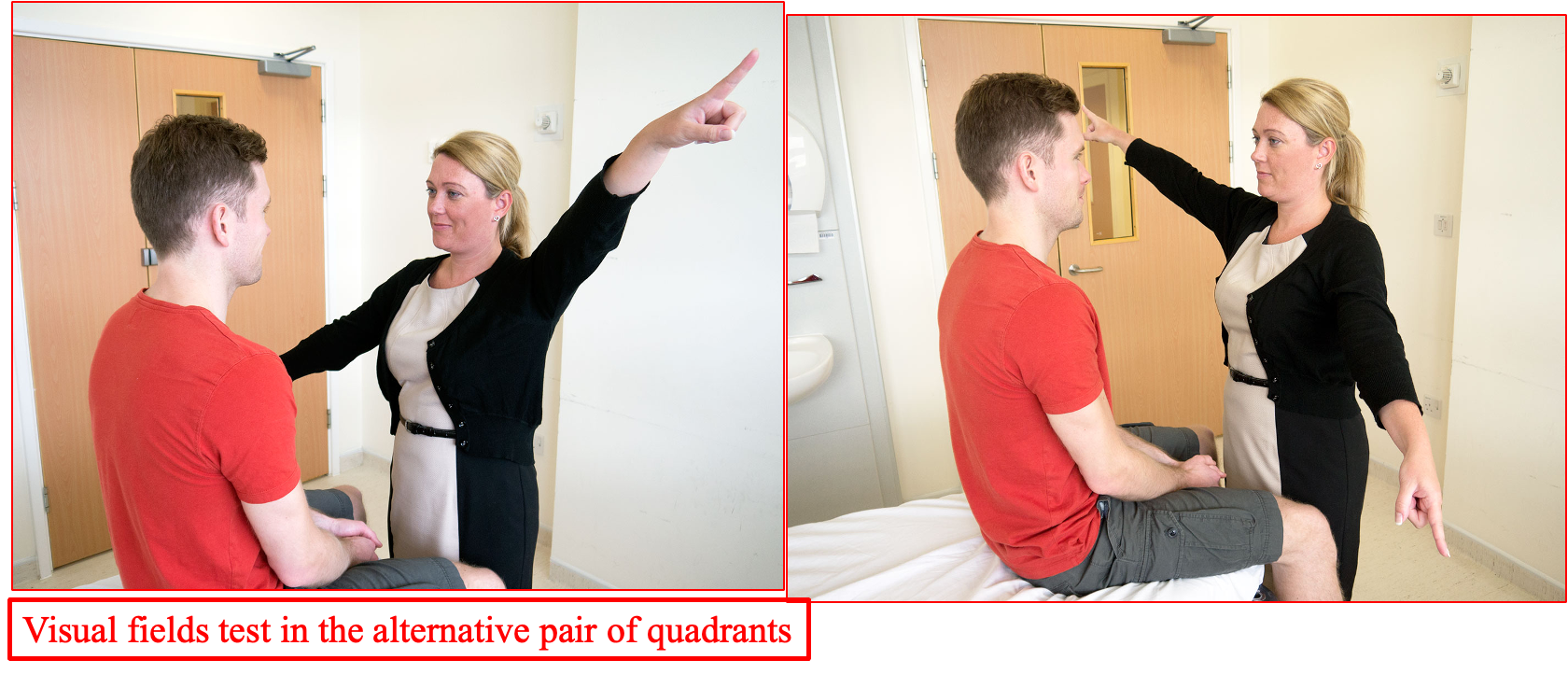
Visual field:
Is tested by asking the patient to look directly at you whilst you wiggle one of your fingers in each of the four quadrants. Ask the patient to identify which finger is moving.
Visual Inattention:
Visual inattention can be tested by moving both fingers at the same time and checking the patient identifies this.

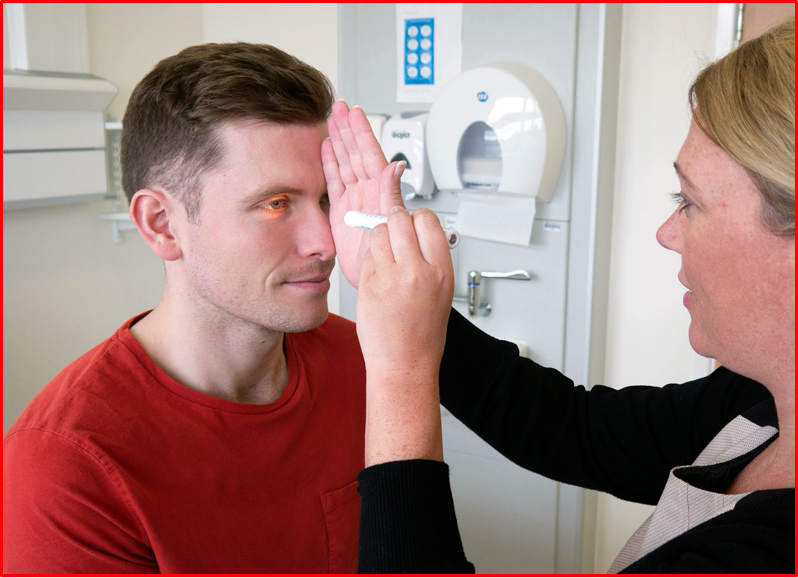
Visual REFEXES (DPR)
- Visual reflexes comprise direct and concentric reflexes.
- Place one hand vertically along the patients nose to block any light from entering the eye which is not being tested. Shine a pen torch into one eye and check that the pupils on both sides constrict. This should be tested on both sides.
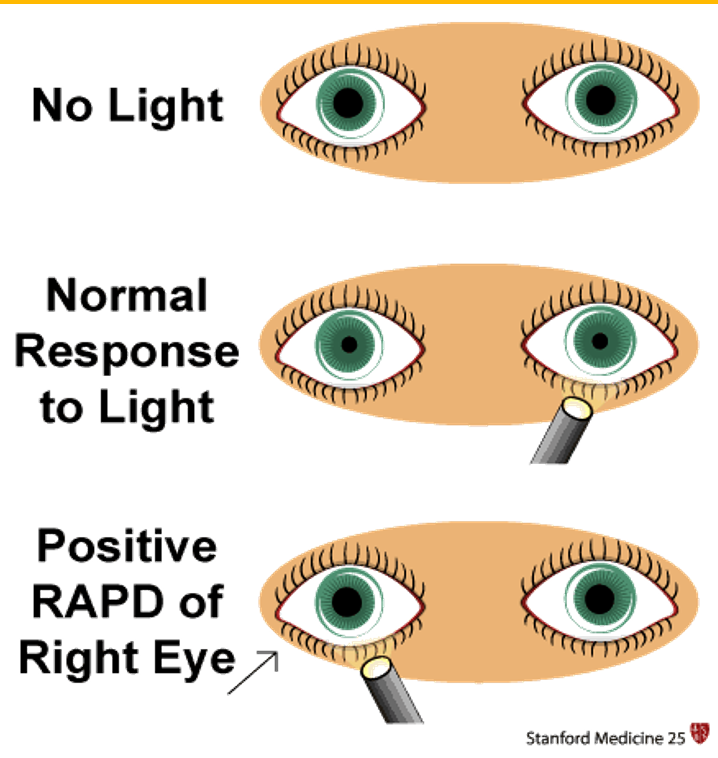
RAPD (REFLEX)
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD)
is a condition in which pupils respond differently to light stimuli shone in one eye at a time due to unilateral or asymmetrical disease of the retina or optic nerve (only optic nerve disease occurs in front of the lateral geniculate body).