Diseases of Large bowel
Dr. M. Almadani
Presentations
-
Diverticular disease
-
Ischemic colitis
-
Colonic polyps
-
Colonic volvulus
-
Large bowel obstruction
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
-
Colon cancer
Principles and Practice of Surgery
Pg 234-262Z
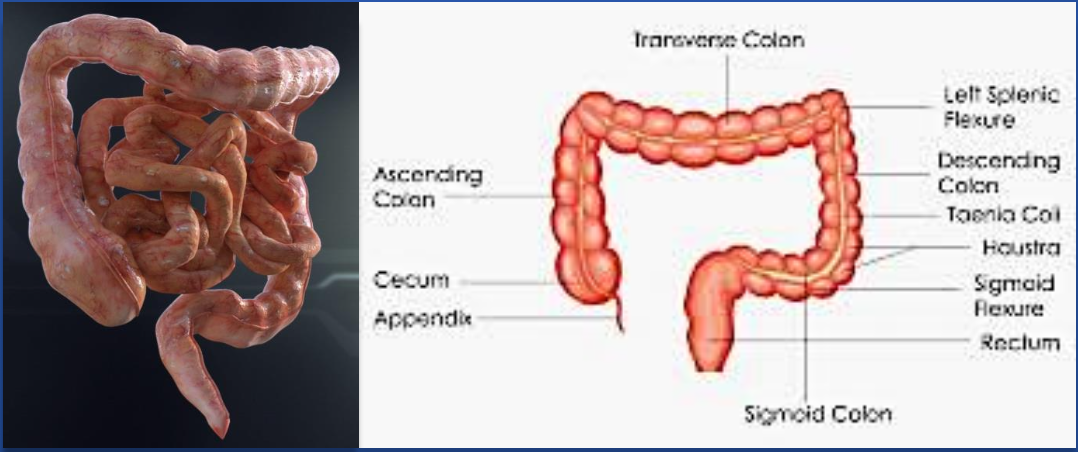
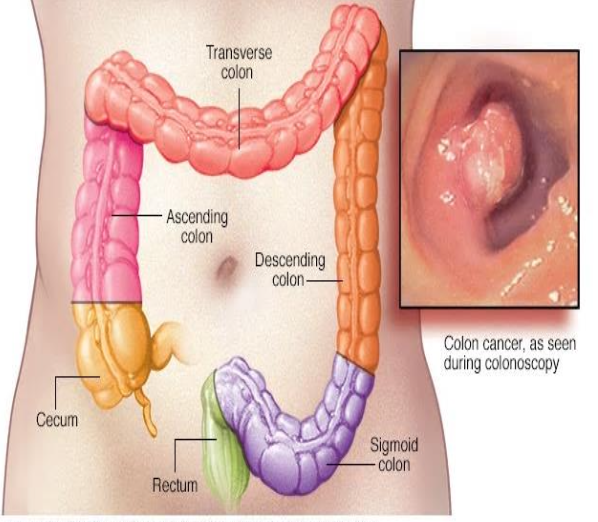
Anatomy & Features
- The colon is a 5-6-ft long, inverted, U-shaped.
Cecum (and appendix) and ano-rectum,
which are parts of the large intestine, are not included in the colon.
MAYO FOUNDATION FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Ascending colon
- Starts from a proximal blind end (pouch) called the cecum.
- The ascending colon takes a right-angled turn just below the liver (hepatic flexure) and becomes the transverse colon
Transverse colon
- Has a horizontal course from right to left, occupying the right hypochondrium, epigastrium, and left hypochondrium.
- At splenic flexure, it is attached to the diaphragm by the phrenocolic ligament) and becomes the descending colon,
- Splenic flexure is higher (cranial) to hepatic flexure.
Descending colon:
-
leads to the inverted V-shaped sigmoid colon, which then becomes the rectum at the S3 level
-
Ascending, & descending parts of the colon are retroperitoneal
-
The transverse colon and the sigmoid colon have a mesentery
-
Cecum is intraperitoneal but uses the mesentery of the ileum.
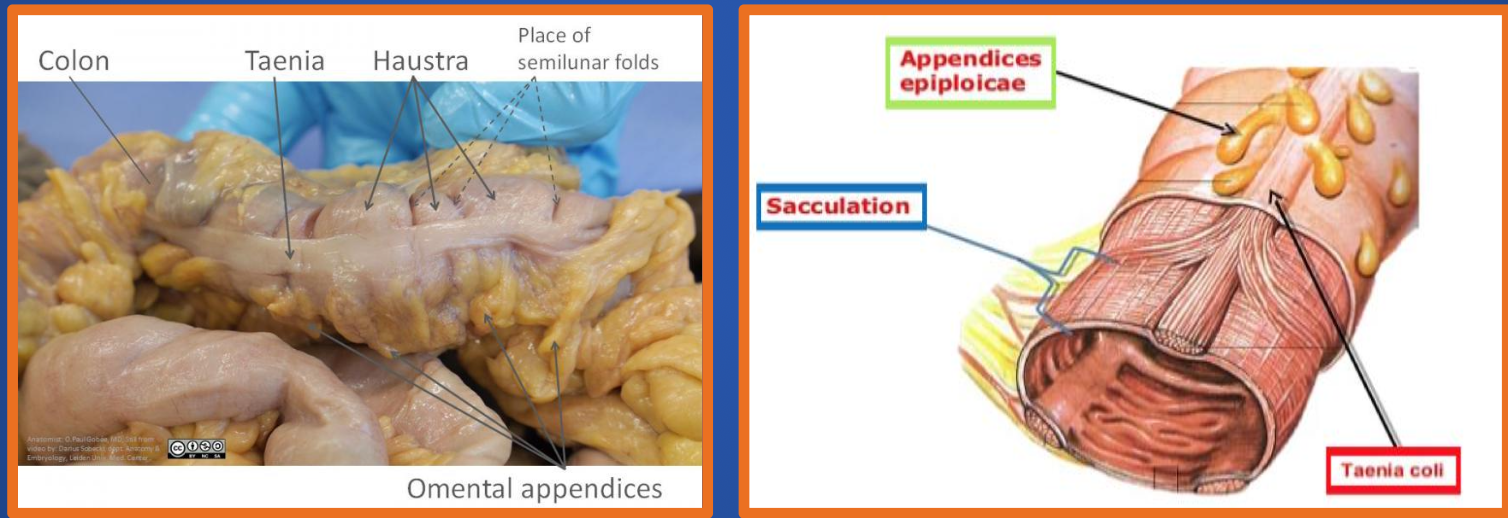
Teniae coli
are present in large bowel, but not present in the rectum.
- Appendages of fat, containing small blood vessels, called omental
- appendages (appendices epiploicae) are attached to colon.
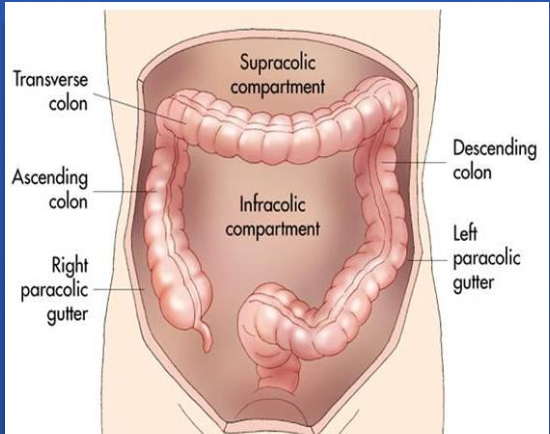
Paracolic gutters
- Lateral to ascending and descending colon are the right and left gutters of the peritoneal cavity,
- Fluid/pus in the upper abdomen can trickle down into the pelvic cavity.
Blood supply
- Superior mesenteric artery through its right colic and middle colic branches
- Inferior mesenteric artery through its left colic and multiple sigmoid branches.
- Vasa recta are terminal branches of these arteries entering the colonic wall
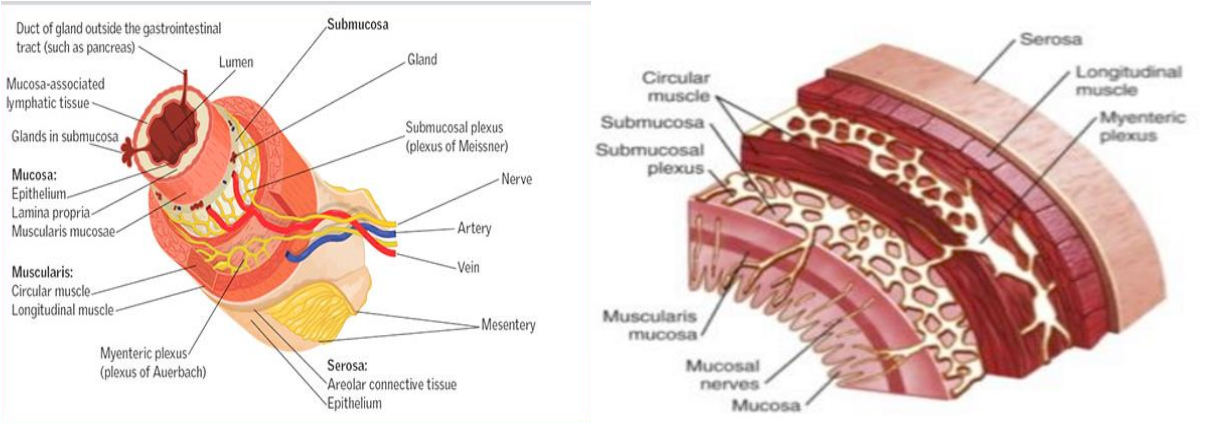
The colon has 4 layers:
-
Mucosa:
- Columnar epithelium with a large number of mucus secreting goblet cells
- No villi,
-
Submucosa
- Contains the blood vessels and Meissner nerve plexus.
-
Muscularis propria
- Contains the inner circular and outer longitudinal
- Muscles and myenteric (Auerbach) nerve plexus
-
Serosa
- visceral peritoneum.
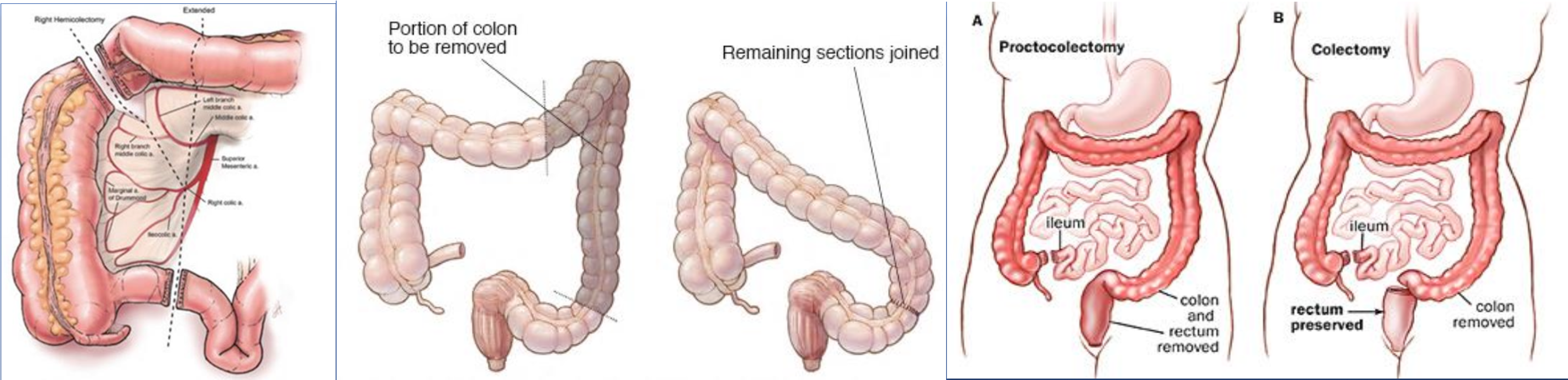
Right hemicolectomy:
- Includes the removal of a few centimeters of terminal ileum, cecum (with appendix), ascending colon, & proximal transverse colon
- Ileotransverse anastomosis
Left hemicolectomy
- Includes the removal of the distal transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon
- Colorectal anastomosis
Total colectomy
- Includes removal of the cecum (with appendix), ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon
- Ileorectal anastomosis
 1 right
2, 3 left
4, 5 total
1 right
2, 3 left
4, 5 total