Endometrial Cancer
Overview
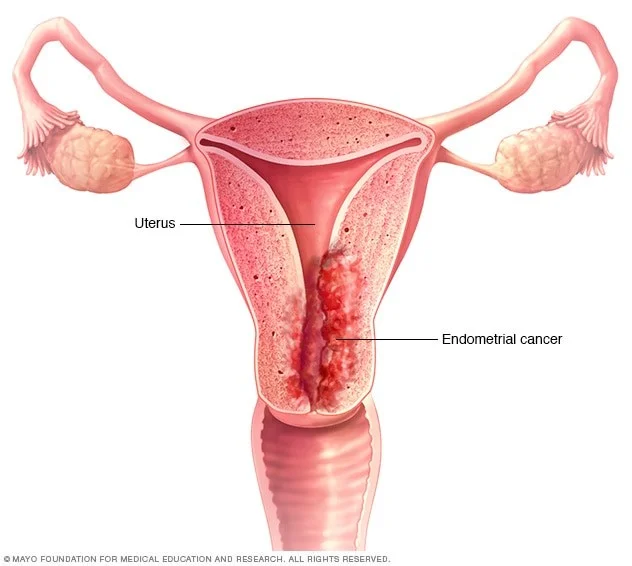
Endometrial cancer, also known as (uterine cancer), is malignant neoplastic growth of the uterine lining.

Epidemiology
- Approximately 95% of these malignancies are carcinomas of the endometrium.
- Most common in women > age 50 years.
- 75% of uterine cancers occur in postmenopausal women.
- Incidence is highly dependent on age.
Pathophysiology
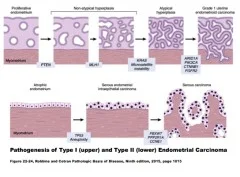
- Endometrial cancer may originate in a polyp or in a diffuse multifocal pattern.
- The pattern of spread partially depends on the degree of cellular differentiation.
- Early tumour growth is characterized by friable and spontaneous bleeding.
- Later tumour growth is characterized by growth toward the cervix.
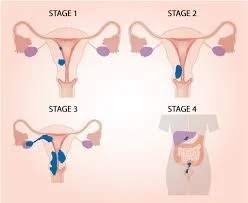
Stages of Endometrial Cancer
- In stage 1, it has spread to the muscle wall of the uterus.
- In stage 2, it has spread to the cervix.
- In stage 3, it has spread to the bowel or vagina, with metastases to pelvic lymph nodes.
- In stage 4, it has invaded the bladder mucosa with distant metastases to the lungs, inguinal, supraclavicular nodes, liver, bone
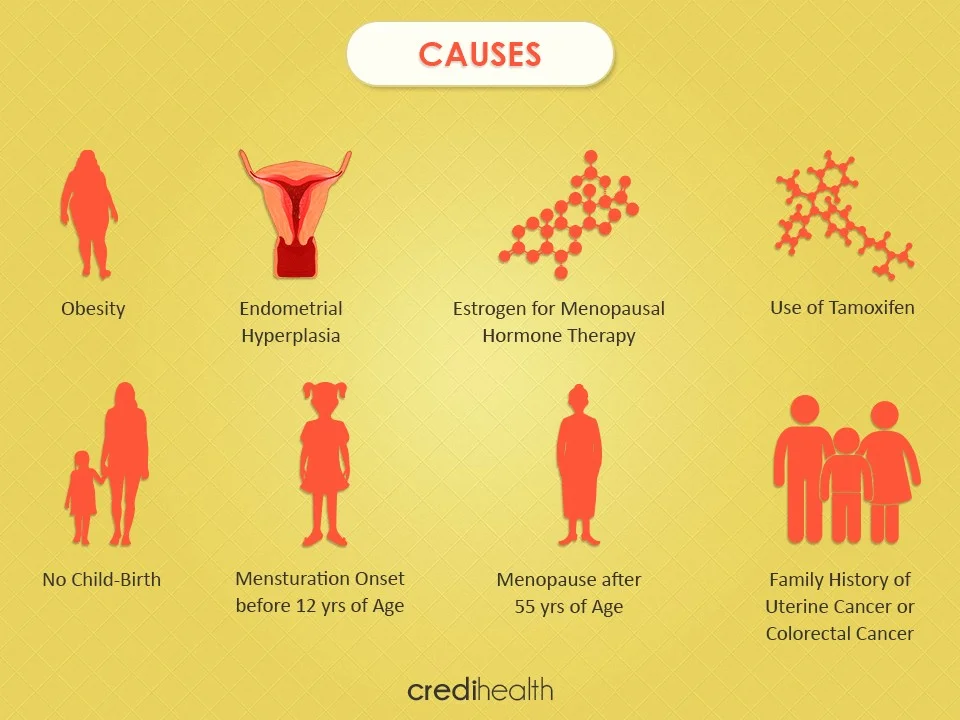
Causes & Risk Factors
- Early Menarche less than 12 years
- Late Menopause more than 52
- Infertility
- Obesity
- Treatment with tamoxifen for breast cancer
- Oestrogen replacement therapy (ERT) after menopause
- Diet high in animal fat
- DM
- Age greater than 40
- Family history of endometrial cancer or hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC)
- Personal history of breast cancer
- Prior radiation therapy for pelvic cancer
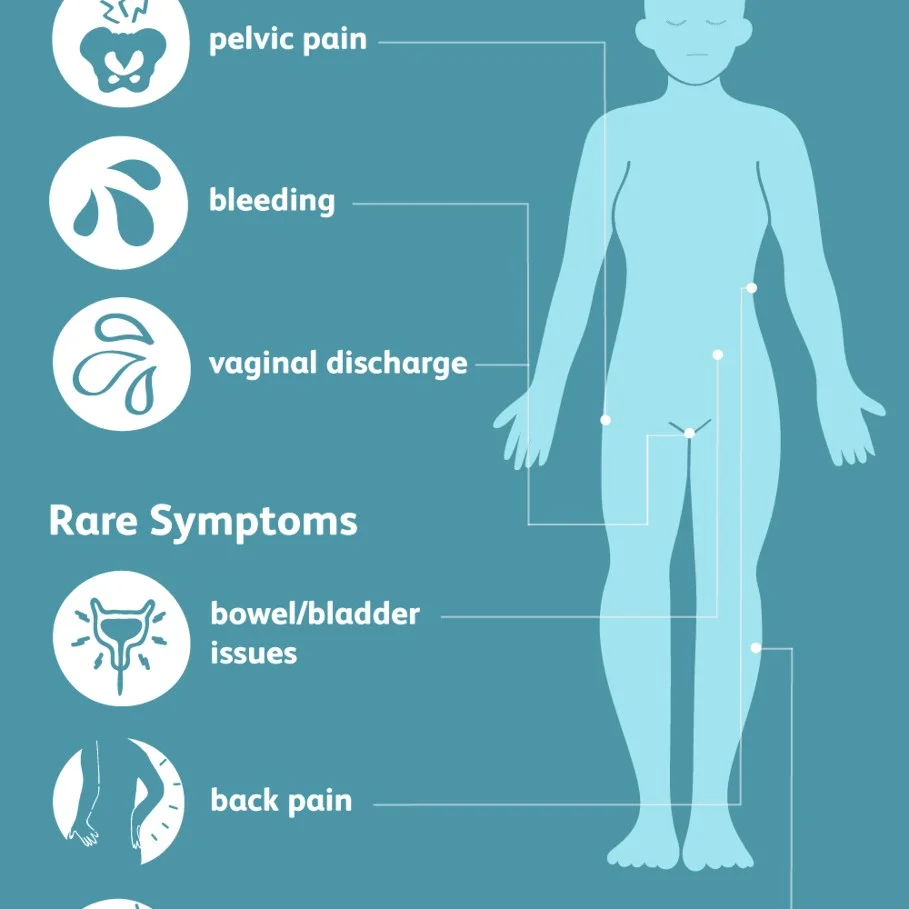
Clinical Manifestation
- Dyspareunia
- Low back pain
- Purulent genital discharge
- Dysuria
- Pelvic pain
- Weight loss
- A change in bladder and bowel habits
Assessment
- History.
- Physical examination
- Investigation:
- A pelvic examination is frequently normal in the early stages of the disease.
- Changes in the size, shape, or consistency of the uterus or its surrounding support structures may exist when the disease is more advanced
Investigation
- Pap Smear
- Only 30-50% patients with cancer will have an abnormal result
- Endometrial Biopsy
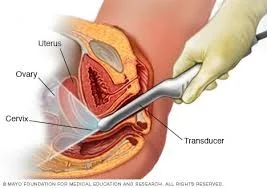
- Transvaginal Ultrasound Z
- Fractional Dilation and Curettage
- Use in cases of cervical stenosis, patient intolerance to exam, recurrent bleeding after negative biopsy*
Endometrial Carcinoma Treatment
- Surgery is the mainstay of treatment followed by
- Adjuvant radiation and/or chemotherapy based on stage of disease.
- Primary radiotherapy or hormonal therapy may be employed in patients who have contraindications to surgery