Instruments in OBG
BY DR. MONA AHMED
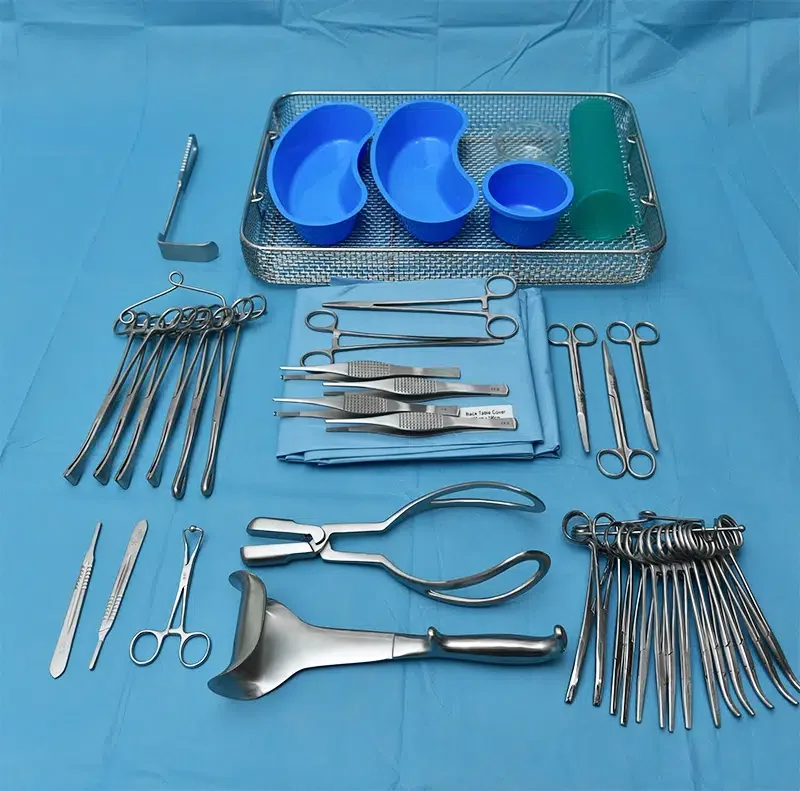
Cesarean Section Instrument Sets

Instrument Details
Back Table Cover
Back Table Cover
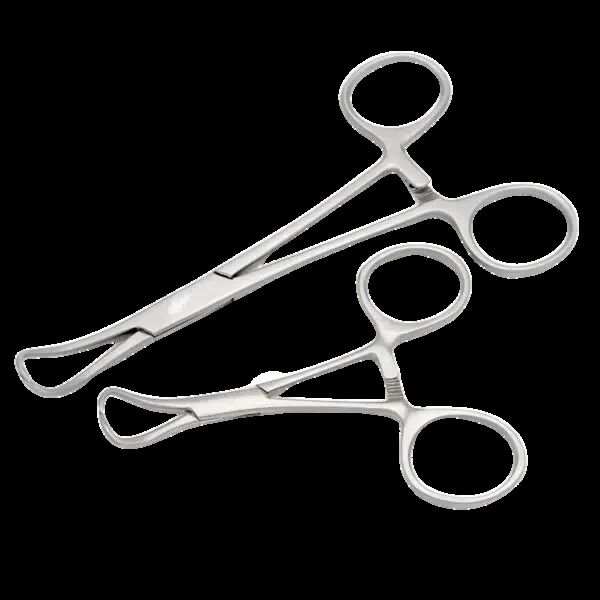
Sponge Holding Forceps
- Used during surgical procedures to hold sponges.
- Use to hold Swabs for scrubbing the abdomen before Operation.

BACKHAUS TOWEL CLAMPS
- A PERFORATING CLAMP.
- USED FOR GRASPING THE TISSUE, SECURING TOWELS OR DRAPES,
- HOLDING OR REDUCING SMALL BONE FRACTURES. USED TO FASTEN DRAPES OR TOWELS.


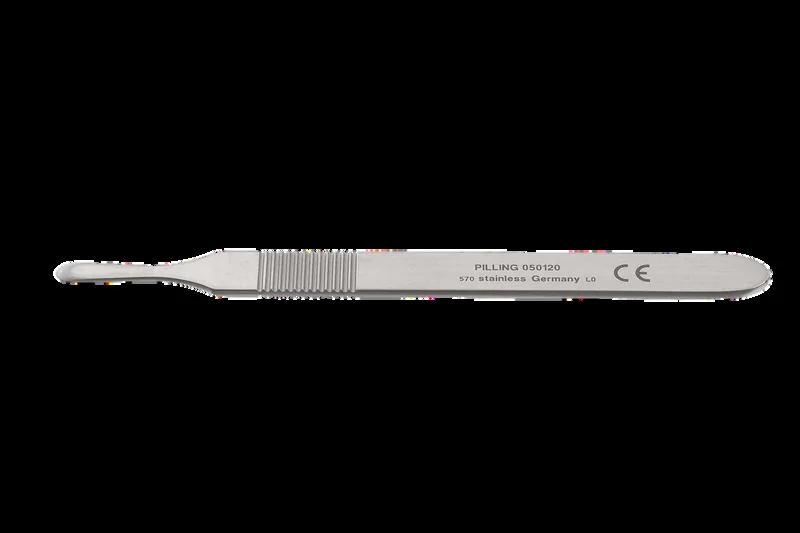
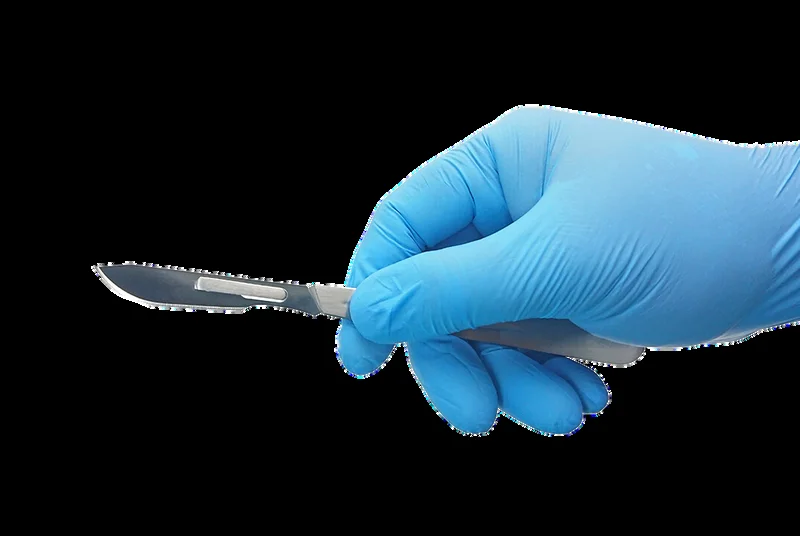
Scalpel Handles
used for skin incisions in c-section.

Surgical Instruments
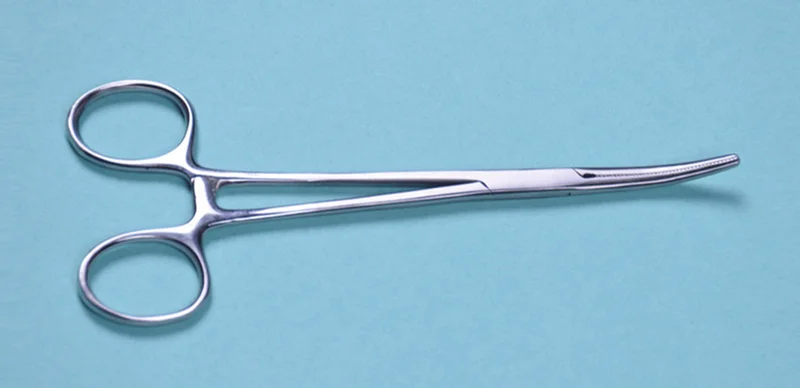
Artery Forceps
Indications:
- For controlling bleeding
- Retraction of tissues, skin, etc.
- To hold stay stature.
- Its also used to hold the tissue and skin
![]()
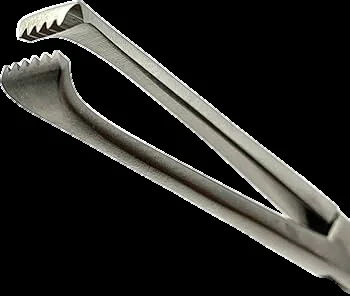
Allis Forceps
- Used to hold tough tissue(rectus sheath).
- used to hold soft tissues without causing damage for long periods.
- It is also used to grasp fascia and soft tissues such as breast or bowel tissue

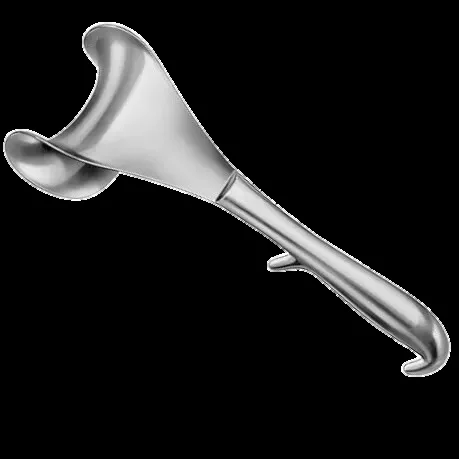
Doyens Retractor
- used at caesarean section for retracting the bladder away from the incision site on the uterus
- Guarding it against potential injury when suturing.
- They removed prior to delivery of the baby and reinserted after delivery to allow good view of the lower edge
Complications: if placed on the uterine segment or retracting the lower abdominal segment may cause bladder contusion

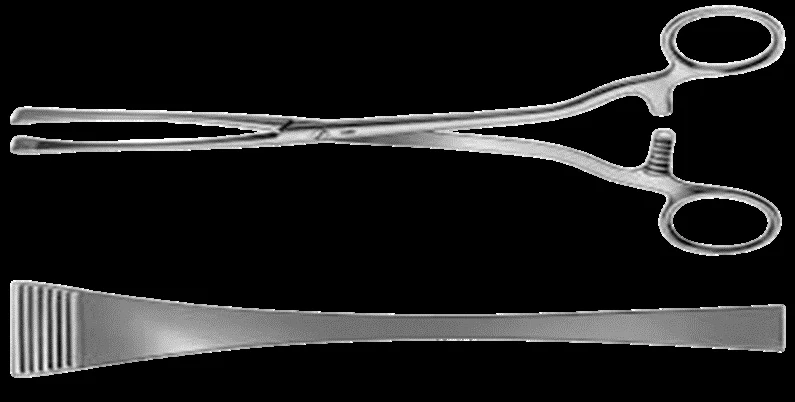
Green Armytage Forceps
- usually used during C-section
- to control bleeding from the
- edges & to help in suturing
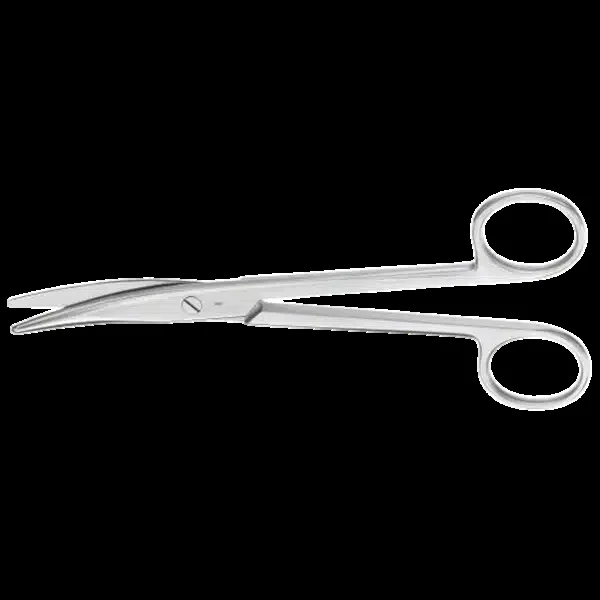
MAYO SCISSORS
The curve style of Mayo scissors
is used to cut thick tissues such as
those found in the uterus & muscles.

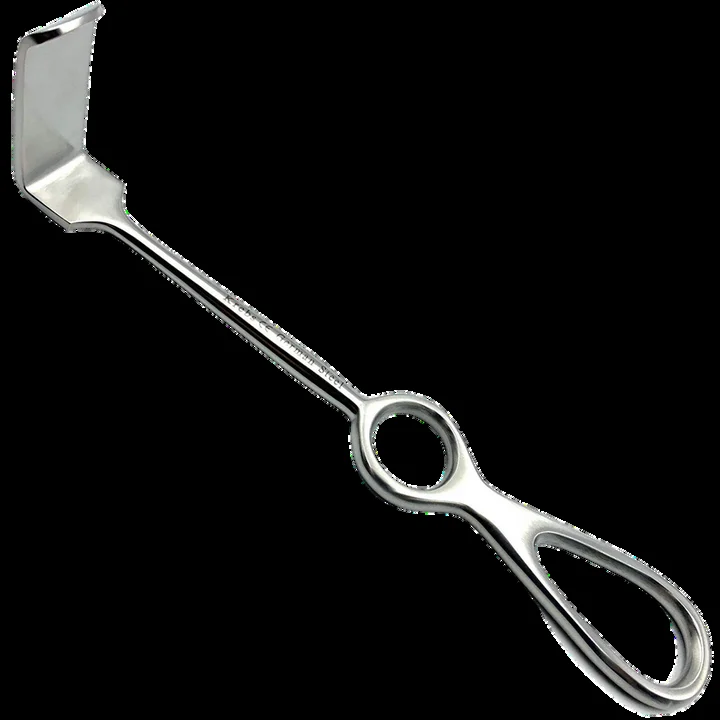
Lange Beck Retractors
Used to retract skin during closure of the rectus sheath at caesarean section and laparotomy.

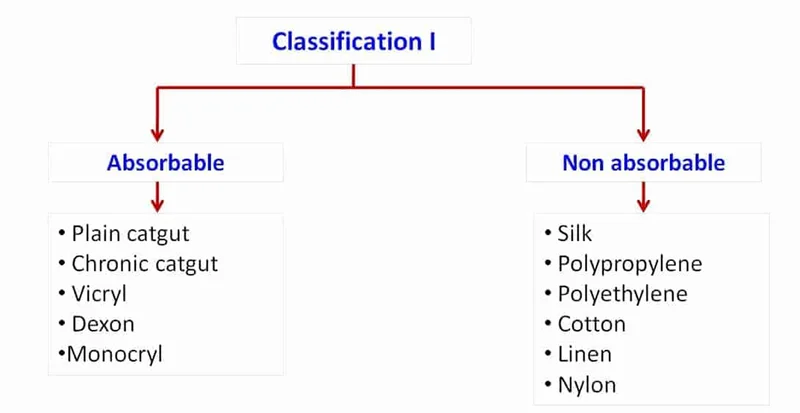
Suture Materials

Needle Holders
Have a clamp mechanism that locks the needle in place (In order to maintain a firm grip on the needle).

Cusco’s Speculum (Duck’s Speculum)
Self retaining double bladed vaginal speculum
INDICATIONS:
- It’s used to expose the cervix & vaginal walls.
- It allows the application of local instruments to the cervix or obtaining swabs.
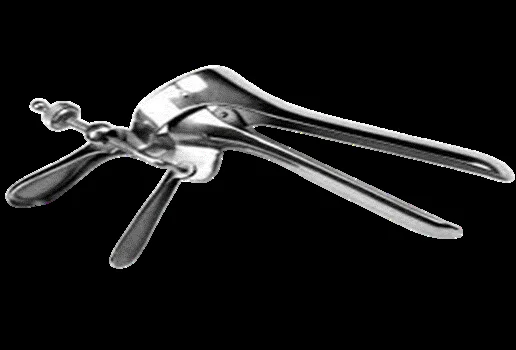
Advantage: It’s easy to introduce Self-retaining. Can be adjusted to the size of the vagina. Disadvantage: It hides the anterior & posterior vaginal walls; however, we can overcome this disadvantage by inspecting the vaginal walls during gradual withdrawal. It doesn’t offer complete protection of the vaginal walls during cauterization of the cervix.

Sim’s Vaginal Speculum
Advantages:
- It exposes the anterior vaginal wall. It’s the only and best one for the vaginal wall visualization
- The grooved blade directs the blood or the urine outside.
- provides a space for the operative work.
Disadvantages:
- Assistance is required during surgical procedures because it’s not a self-retaining specula.
- In the presence of cystocele exposure of the cervix is often difficult.
Tenaculum / Vulsellum
Types:
- Single toothed (bullet forceps) tenaculum.
- Double toothed (the lions forceps).
- Multiple toothed vulsellum.
Indications:
- To grasp or handle the anterior lip of the cervix.
- Vaginal operations for e.g. D & C and repair of prolapsed.
- To grasp a prolapsed Submucous myoma during a vaginal myomectomy.
- During a hysterectomy
Complications of Tenaculum / Vulsellum
- Laceration of the cervix.
- Infections.
- Bleeding from the site of the bite of the teeth of the vulsellum.
Contraindications:
- The soft pregnant cervix .
- Infections.

Sim’s Uterine Sound
Indications:
- To measure uterine cavity length.
- To determine the direction and length of the uterus
Complications:
- Perforation of the cervix or body of the uterus.
- Ascending infection.
Contraindications:
- Suspicion of pregnancy.
- Soft uterus (malignancy, infection or molar pregnancy).

Hegar’s Uterine Dilator
- They are used to gradually dilate the uterus.
- can be single or double ended.
- They are 15. Graduated by a number written on them ranging from 0 to 14.
Indications:
a) Diagnostic: Cervical incompetence.
b) Therapeutic:
- Cervical stenosis.
- Dysmenorrhea
c) As a step in the course of other operations:
- Prior to D & C or evacuation.
- Vaginal hysterectomy.
- Before the insertion or removal of certain contraceptive devices
![]()
Complications of Hegar’s Uterine Dilator
- Perforation of the cervix or body of the uterus.
- Cervical incompetence & habitual abortion (Most Common).
- Ascending infection (cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, peritonitis & parametritis).
- Laceration of the cervix.
Contraindications:
- Active Genital infection.
- Pregnant uterus.
Never used in Obstetrics only gyn cases
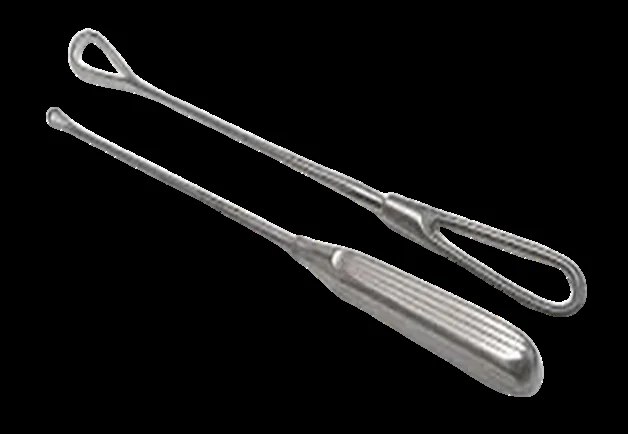
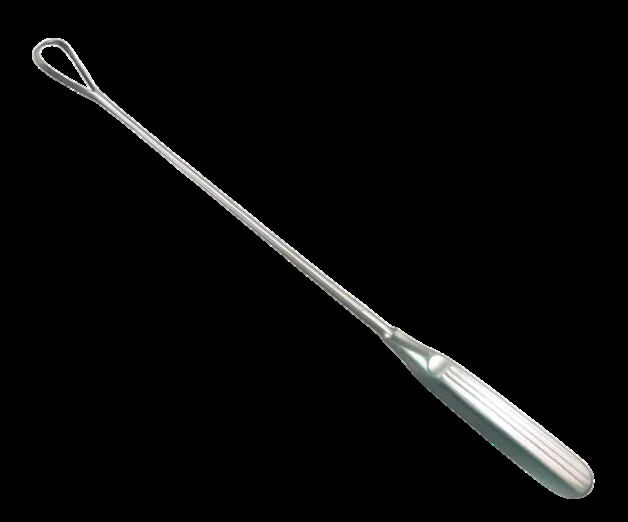
Ovum Forceps
- Used to remove an intact separated ovum.
- It’s also used to evacuate the uterine content in D & C.
- Used to remove IUCD & conception products
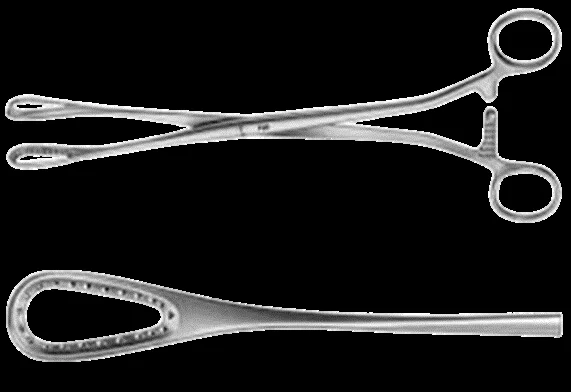
Uterine Curette
Describe:
Each curette consists of 3 parts:
- Handle.
- Shank.
- Curetting end.
The curetting end may be sharp or blunt
Indications:
- Diagnostic curettage:
- Therapeutic curettage:
Complications:
- Sepsis.
- Perforation.
- Infertility (e.g. Asherman’s syndrome)
- Excessive bleeding.
- Endometriosis or peritonitis.

Urinary Catheter
a) Metal urinary catheter:
b) And Foley catheter (rubber)
Complications of foley’s catheter:
- Infections.
- Injury to the urethra
Advantages: Advantages of metal over Folly’s catheter:
- Less induction of infections
- Less pain.
Contraindications:
- pressure necrosis.
- Traumatic injury to the lower urinary tract (eg, urethral tearing).

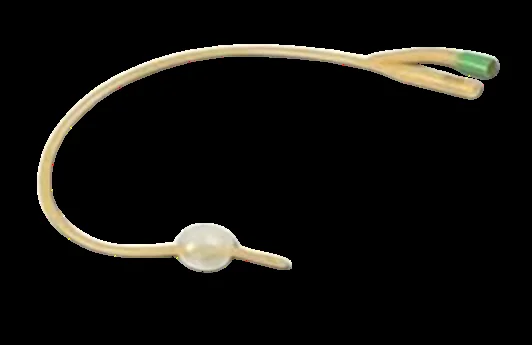
Indications for Urinary Catheter
- induction of labour. (The foley )(mechanical dilation)
- Used in the 1st stage of labour to prevent uterine inertia.
- Used in the 3rd stage of labour to prevent retention of the placenta & guard against PPH.
- Used in the diagnosis of urinary fistula.
Complications of Metal Catheter
- Introduction of sepsis.
- False passage in the urethra.
- perforation of the bladder wall.
- Urethral shock & fever.
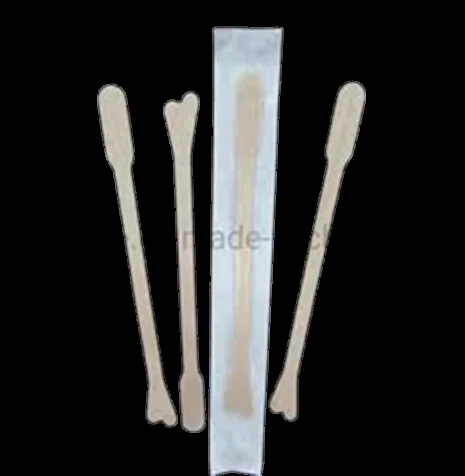
Wooden Spatula & Roller(Cervical -Cyto) Brush
Indications:
- For endocervical sampling (PAP smear).
- For screening & diagnosing cervical cancer.
Site:
- sample is taken from the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix.
- (the transformation zone).
It’s neither a true biopsy nor a smear It’s a scraping.

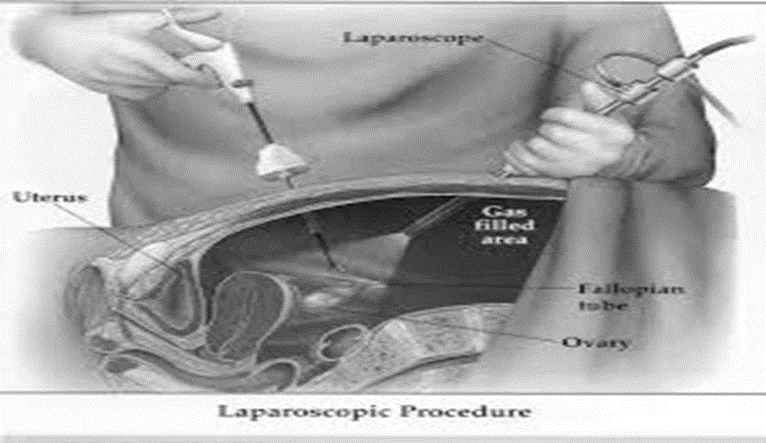
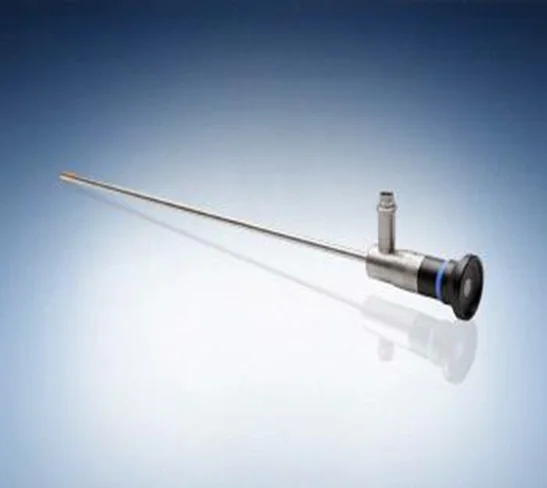
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy set: A- Verses needle: B- Trochar (sleeve and needle)& cannula : C-Laparoscope.

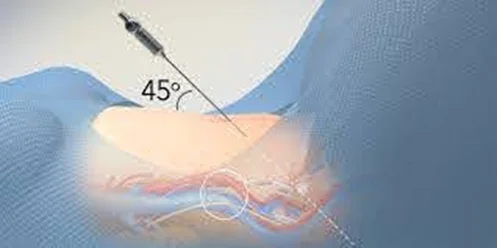

The AmniHook
is an amniotome used for rupturing the amniotic membrane.


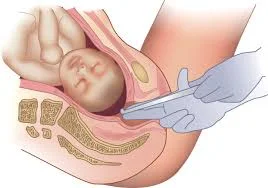
Umbilical Cord Clamp