Barrier Methods
WHAT ARE BARRIER METHODS? Barrier methods prevent sperm from fertilizing ovum.
Types of barrier methods:
- Male condom.
- Female condom.
- diaphragm.
- spermicidal.
Male Condom
- Cheap and widely available.
- They made of latex.
- They protect against STIs including HIV. Z
- They are the only reversible male method.
- Used before sex.
The Female Condom
- Is a lubricated polyurethane condom
- Inserted into the vagina.
- It protects against STIs
Non-Contraceptive Uses of Condoms
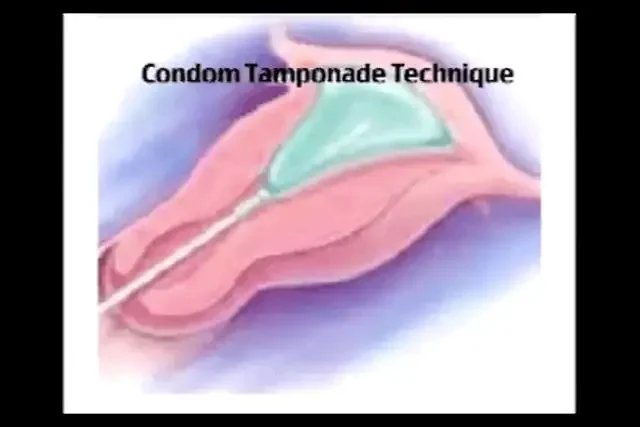
- Condom catheter.
- In post partum haemorrhage as condom tamponade.
Condom Tamponade Technique
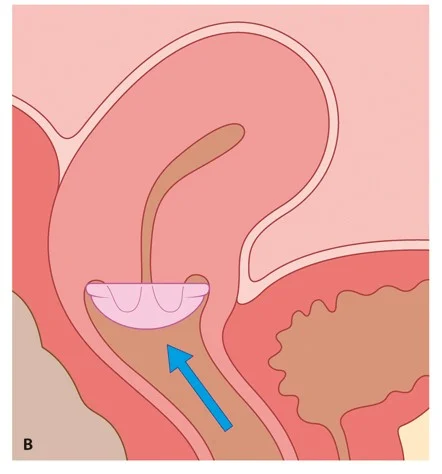
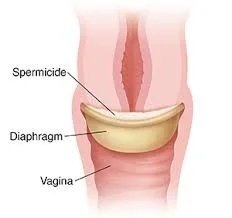
Diaphragm and Cap
- These are latex or non-latex devices that are
- inserted into the vagina to prevent passage of
- sperm to the cervix .
- Caps fit over the cervix.
- They are often used in with a spermicide.
Disadvantages
- women need to be taught how to insert and remove.
- High failure rate.
- May be associated with increased vaginal discharge
- Associated urinary tract infections.
Spermicides
Spermicide alone is not recommended for prevention of pregnancy as it is of low effectiveness.
Nonoxynol 9 (N-9) is a spermicidal product sold as:
- a gel
- cream
- Foam
- sponge
- or pessary for use with diaphragms or caps.
Long Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARC)
Types:
- injectable
- Implant
- intrauterine device (IUD).
LARC methods are the most effective
once inserted do not require any action by the user until they need to be renewed.
Long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) is a contraceptive that lasts for a long time. ➢Types of LARC : ✓Intrauterine devices: (IUCD Mirena) which lasts for three, five or ten years ✓Implants: which lasts for five years. ➢LARCs are the most effective types of contraception.
Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD)
- Life span 10 years
- Contraindications :
- Pregnancy.
- DUB.
- PID.
- cervical cancer.
- endometrial cancer.
- Time of insertion :
- at menstruation time(within 10 days).
- post partum(within 48 hs).
- after puerperium (6 weeks after delivery)
Side Effects of IUCD
Side effects:
Pregnancy(failure)
Pain.
Bleeding.
PID.(increase vaginal discharge).
Perforation.
Ectopic pregnancy.
Expulsion.
Difficult removal.
Actinomyces-like organisms (ALOs)
‘Missing’ threads may indicate
Pregnancy
expulsion
or perforation.
Progestogen-Releasing Intrauterine System
-
Contain 52 mg of progesterone. Release 20 ug /day. Life span 5 years.
-
(Mirena®) is licensed for 5 years for contraceptive use (but if inserted in women 45 years or older, may be used for contraception until the menopause) The LNG-IUS does not prevent ovulation.
women experience unpredictable bleeding.
side-effects of the LNG-IUS include
- acne.
- tenderness.
- mood disturbance.
- and headaches.

Non-Contraceptive Benefits of LNG-IUS
- reducing HMB (reduced by 90% at 12 months).
- It is also effective for treating dysmenorrhoea,
- pain associated with endometriosis
- Adenomyosis pain
- and protecting the endometrium against hyperplasia
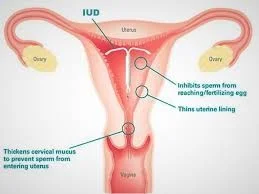
Mode of Action of IUDs
- IUDs stimulate an inflammatory reaction in the uterus.
- It is thought that these effects are toxic to both sperm and egg and interfere with sperm transport.
- If a healthy fertilized egg reaches the uterine cavity, implantation is inhibited.
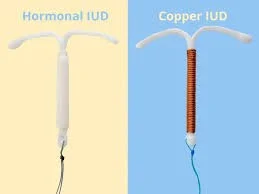
Hormonal IUD Copper IUD
 #OSPE
#OSPE
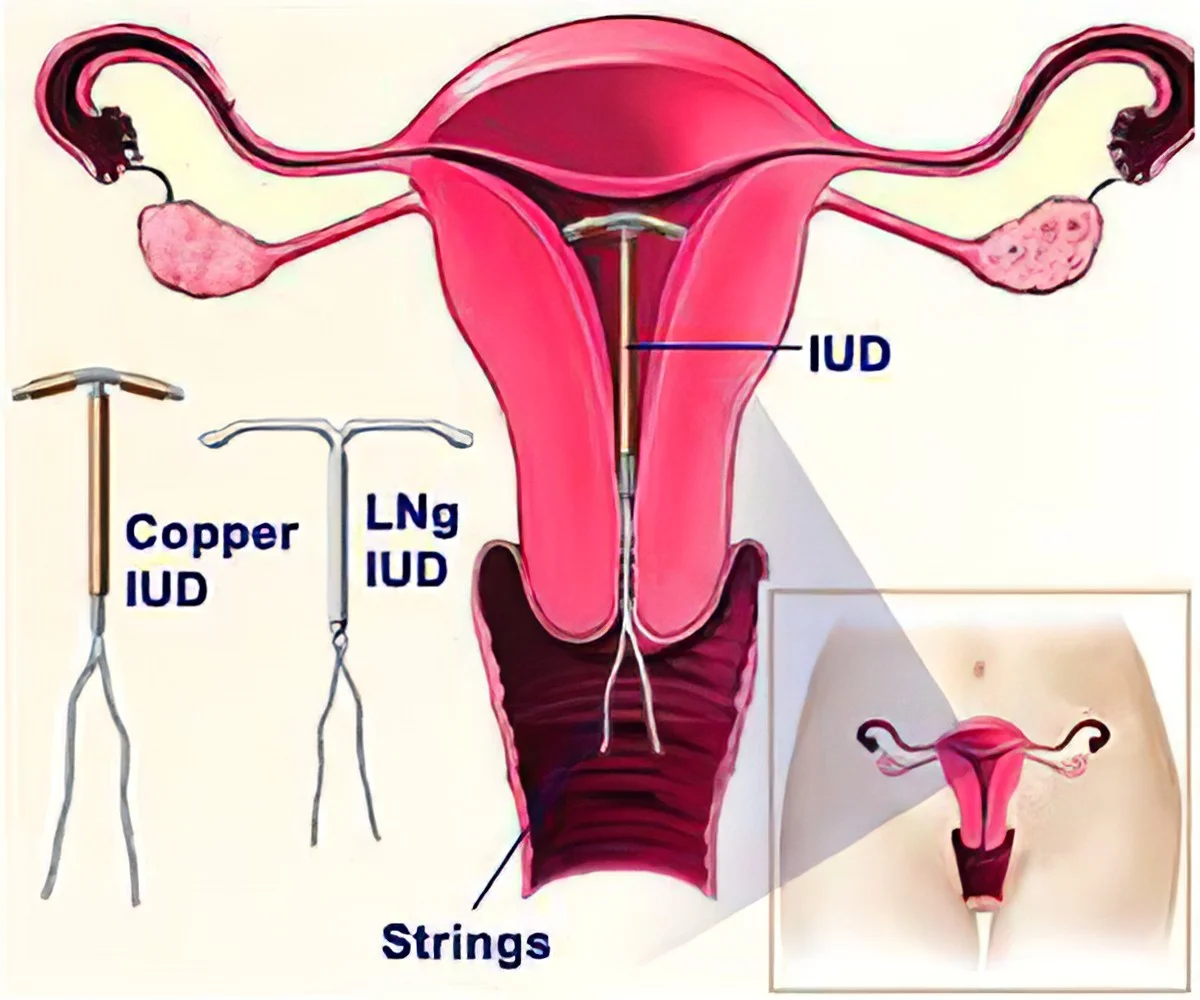
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Illustration
The image illustrates the placement and types of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) within the female reproductive system.
- IUD Types:
- Copper IUD
- LNg IUD
The diagram shows the IUD inserted into the uterus, with the Strings hanging down into the cervix and vagina.
- Key components labeled in the diagram:
- IUD
- Strings
Hormonal
Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives include the
- Pills
- Depo Provera injection.
There are two types of pill:
- combined oral contraceptive pill
- progestogen-only contraceptive pill
- The pill is more than 99% effective.
- Daily taking.
The Depo Provera injection is another type of hormonal contraceptive
- An injection every three months.
- Its is more than 99% effective .
COCP methods contain two hormones: an oestrogen and a progestogen.
They are available as
- oral pills
- a transdermal patch
- vaginal ring.
They are similar in terms of
- effectiveness, safety and side-effects.
These methods all work by inhibition of ovulation.
One tablet every day at the same time, without interruption.

Side-Effects of Combined Hormonal Contraception
- unexpected bleeding,.
- weight gain.
- Headaches.
- mood swings.
- loss of libido.
Below are examples of WHO medical eligibility criteria Category 4 conditions for use of combined hormonal contraception (CHC). These represent situations in which CHC is not recommended because the risks clearly outweigh any potential benefits:
- Age > 35 years and smoking
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure (systolic >160 mmHg and/or diastolic >100 mmHg)
- Hypertension with vascular disease
- Current or past venous thromboembolism (e.g., deep vein thrombosis)
- Current or past arterial thrombotic events (e.g., myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident/stroke)
- Multiple serious cardiovascular risk factors (combined risk profile that substantially increases thrombotic/cardiovascular risk)
- Known thrombogenic mutation (inherited or acquired thrombophilia)
- Current breast cancer
Safety of Combined Hormonal Contraception
- Cancer
- Cancer risks among users of COCPs
- A 12% reduction in the risk of any cancer.
- Reduced risk of colorectal cancer.
- Reduced risk of endometrial cancer.
- Reduced risk of ovarian cancer.
- Increased risk of breast cancer during use (decreases on stopping and similar risk to never used by 10 years after stopping).
- Increased risk of cervical cancer (but early changes detected by cervical cytology and human papillomavirus [HPV] vaccination).
Drugs that Decrease Efficacy of Hormonal Contraception
| Type of drug Z | Liver enzyme induction Y |
|---|---|
| Anticonvulsant | - Carbamazepine - Eslicarbaz - Oxcarbazepine - Phenobarbital - Phenytoin - Primidone - Topiramate |
| Antibiotic Z | Rifampicin Rifabutin |
| Antifungal | Griseofulvin |
| - Protease inhibitors - Amprenavir - Atazanavir - Nelfinavir - Lopinavir | |
| Antiretroviral | - Saquinavir Ritonavir - Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors - Efavirenz - Nevirapine |
3 Missed Pill Guideline
If one pill has been missed >24 hs and <48hs
- Continue contraceptive cover
- Missed pill should be taken as soon as possible
- Then continue pills as usual
Minimizing risk of pregnancy
- EC if missed pill in the early packet or last week of previous packet
If one pill has been missed >48 hs
- Continue contraceptive cover
- Missed pill should be taken as soon as possible
- Remaining should continue at usual time
- Pack up for 7 pills
Minimizing risk of pregnancy
- If missed pill in the 1st week EC
- If pill missed in the 2nd week (8-14 d)
- If missed pill in the 3rd week (15-21 d) omit the pill free period
Progestogen-Only Contraceptive Methods
Progestogen-only methods are available as
- Oral
- Injectable
- Implant
- and intrauterine system.
The mechanism of action All progestogen-only contraceptive methods by thicken cervical mucus Z so reducing sperm penetrability and transport.
The progestogens that are used are referred to as second-generation (levonorgestrel, norethisterone)
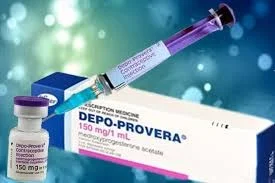
Progestogen-only Injectable Contraception
Description and Administration
- One injection every 13 weeks.
- There are 2 forms:
- DMPA-IM administered by IM. Depo-Provera (150 mg)
- DMPA-SC by SC route. Sayana press (104 mg)
Protection and Advantages/Disadvantages
- Protection: 3 months.
- Advantages & disadvantages:
- No daily administration.
- Self-administration possible.
- Long delay in return to fertility ..on average 5 months after stopping injections, sometimes up to 1 year
- Bleeding may occur at any time (irregular) or there may be no monthly bleeding (amenorrhoea).
Side Effects of Progestogen-only Contraception
Common Side Effects
- Cause weight gain in a minority of women
- Loss of bone mineral density (BMD)
- Other progesterone side effects.
- Irregularity of cycle
- Difficulties in resuming fertility after stopping.
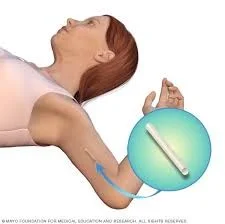
Implant Contraception
Description and Administration
- Containing the progestogen etonorgestrel (Implanon & Nexplanon) 68 mg
- Providing contraception for 3 years.
- One (or two) rods inserted under the skin of the upper arm, under local anaesthesia.
Protection and PRO & CON
- Protection: 3 years.
- PRO & CON
- Effectiveness does not depend on compliance.
- Bleeding may occur at any time (irregular)
- There may be no monthly bleeding (amenorrhoea).
- The implant is discreet but palpable under the skin.
Permanent Contraception Methods
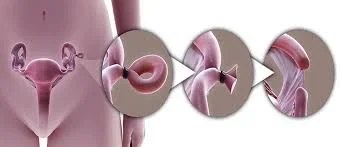
Female Sterilization
- This is a permanent method of contraception that prevents sperm reaching the oocyte in the Fallopian tube.
- Tubal ligation.
- Effectiveness 99%.
- It can be performed by
- (1) Laparoscopy
- (2) Hysteroscopy or
- (3) Laparotomy (e.g., at caesarean section).
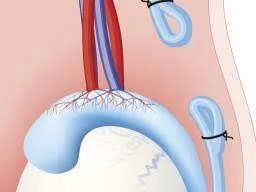
Vasectomy
- This is the technique of interrupting the vas deferens to provide permanent occlusion.
- There is a small risk of a scrotal haematoma and infection with the procedure.
- Post-vasectomy semen analysis should be conducted at 12 weeks to confirm the absence of spermatozoa.
- Alternative contraception should be used until azoospermia is confirmed.
Emergency Contraception
Effective Methods
- The most effective method of EC is an IUD (about 99% effective).
- An IUD can be inserted up to 5 days after ovulation for EC.
- Ulipristal acetate (UPA) or levonorgestrel (LNG) are available as oral methods of EC.
- UPA can be given within 120 hours of unprotected intercourse.
- LNG can be used within 96 hours of unprotected intercourse.
- Effective ongoing contraception should be started after EC.
