PCOS Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
By dr Mona Ahmed

Polycystic ovarian syndrome
PCOS is a syndrome of :
- ovarian dysfunction
- with features of hyperandrogenism.
- and polycystic ovary morphology .
Clinical manifestations
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Signs of androgen excess (e.g. hirsutism).
- Obesity.
- Elevated serum LH levels.
- Insulin resistance .
- Increased risk of type 2 DM and CVD events.
Affects around 5–10% of women of reproductive age.
The prevalence of PCOS on ultrasound is 25 %.
Aetiology
- Aetiology is not completely clear.
- There is often a family history (gene is important in its development).
Clinical features:
- Oligomenorrhoea/amenorrhoea up to 75% (due to chronic anovulation).
- Hirsutism.
- Subfertility (75 %).
- Obesity (40 %).
- Recurrent miscarriage in around (50–60 %).
- Acanthosis nigricans (areas of increased velvety skin pigmentation occur in the axillae and other flexures).
- May be symptomatic.
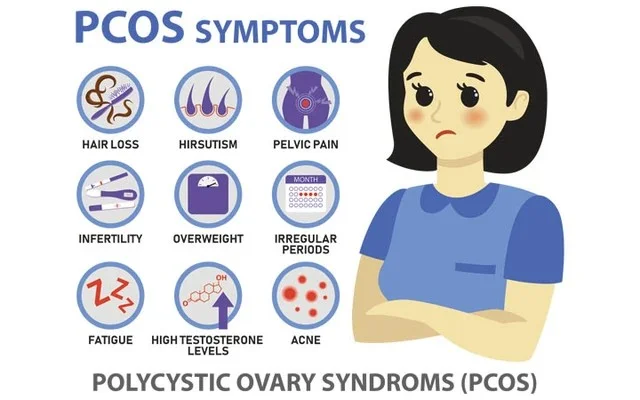
PCOS SYMPTOMS
- HAIR LOSS
- HIRSUTISM
- PELVIC PAIN
- INFERTILITY
- OVERWEIGHT
- IRREGULAR PERIODS
- FATIGUE
- HIGH TESTOSTERONE LEVELS
- ACNE
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROMS (PCOS)
Diagnosis
Patients must have two out of the three features below:
- Amenorrhoea/oligomenorrhoea.
- Clinical or biochemical hyperandrogenism.
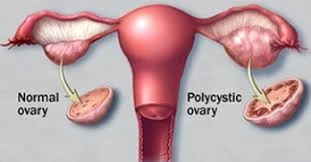
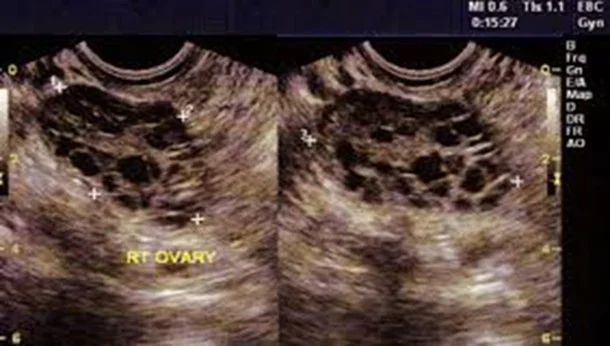
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound.
- The ultrasound criteria for the diagnosis of a polycystic ovary are:
- Eight or more subcapsular follicular cysts <10 mm in diameter.
- Increased ovarian stroma.
- The ultrasound criteria for the diagnosis of a polycystic ovary are:
While these findings support a diagnosis of PCOS, they are not by themselves sufficient to identify the syndrome.
Management
- Weight reduction.
- Lifestyle advice:
- Dietary modification and exercise because these patients are at an increased risk of developing DM and CVS.
- Medications:
- COCP:
- Regulate menstruation.
- Cyclical oral progesterone:
- Regulate menstruation.
- Metformin:
- In patients with PCOS with hyperinsulinemia and cardiovascular risk factors.
- Clomiphene:
- To induce ovulation where subfertility is a factor.
- COCP:

Hirsutism
- Medical treatment:
- Eflornithine cream topically.
- Cyproterone acetate.
- Dinetter anti-androgen contraceptive pill).
- Metformin:
- improves insulin resistance,
- Hyperandrogenaemia.
- anovulation.
- and acne .
- GnRH analogues with low-dose HRT: Reserved for women intolerant of other therapies.
- Surgical treatments, e.g. laser or electrolysis.
- Physical methods: shaving.