Adult Femur Fractures
Proximal Femur Fractures
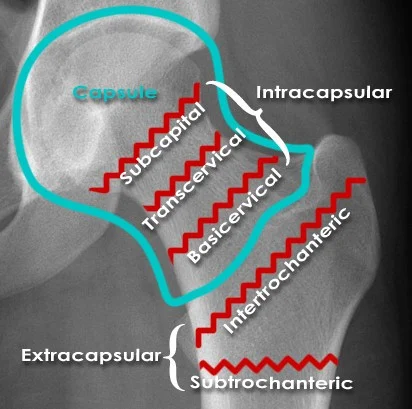
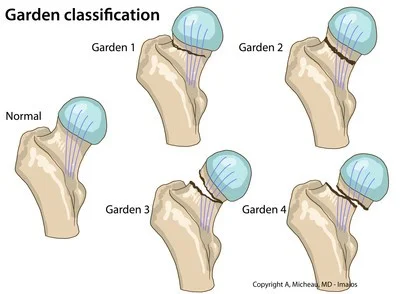
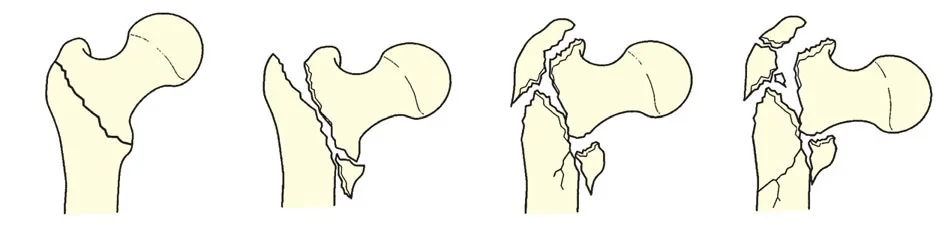
Classification
- Femoral Neck
- Intra-capsular

- Intra-capsular
- Inter-trochantric
- Extra-capsular

- Extra-capsular
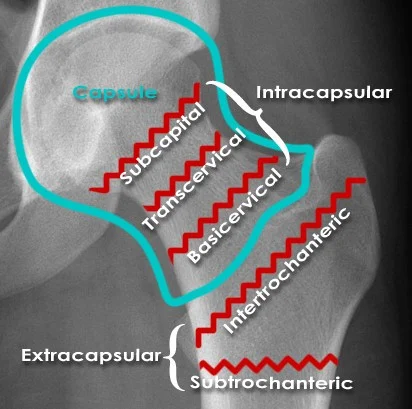
Intra-capsular vs. Extra-capsular
- The capsule envelopes the femoral head and neck
- Intertrochanteric and sub-trochanteric fractures are extra-capsular
Mechanism of Injury
Elderly vs. Young Patients
- In elderly people 95%:
- Low energy: slipping at home, pathological bones
- In young patients 5%:
- High energy trauma like MVA, falls from heights




Types of Fracture
- Indirect injury:
- Falls
- Dash-board injury
- Possibly with patellar fracture
- Types of fracture depend on:
- Position of limb during impaction and
- Magnitude of force
Holistic Approach
- Look at the patient as whole, not to injured limb alone!
- In elderly: other diseases
- In young: major trauma, other injuries
- Save life first, then save limb, then save function
Femoral Neck Fractures
Epidemiology
- Most common in the elderly
- 53% of all fractures of proximal femur
- 1.7 million hip fractures annually world wide
- Expected to triple in the next 50 years
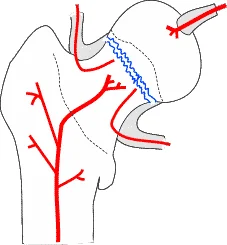
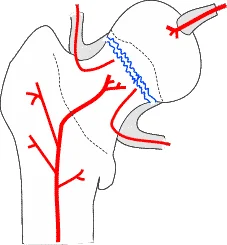
Vascular Supply C ?
- Anterior View
- The Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery is shown supplying the femoral head.
- Posterior View
- The Medial Femoral Circumflex Artery is depicted as the primary supplier to the femoral head.

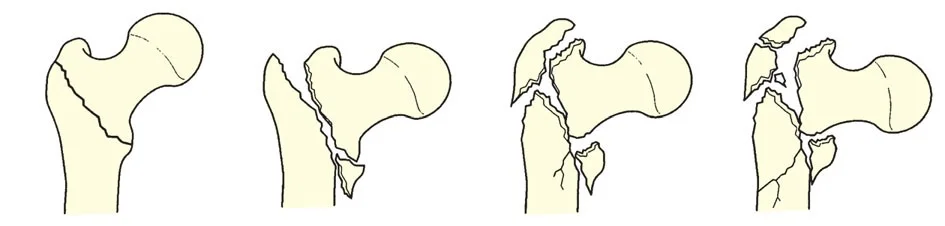
Risk of Avascular Necrosis
- Risk of osteonecrosis (Avascular Necrosis)
- More in near head (Sub-capital)
- More in displaced fractures
Presentation and Investigations
- Presentation:
- In elderly:
- Mild trauma/fall
- Pain in hip/ thigh
- Inability to walk
- May walk if impacted
- In the young:
- Major trauma
- Pain in hip
- Inability to walk
- In elderly:
- Investigations:
- In elderly:
- X-ray: AP/?Lateral
- May need MRI:
- If X-rays inconclusive
- Other diseases
- In the young:
- X-ray: AP/?Lateral
- Other injuries
- In elderly:
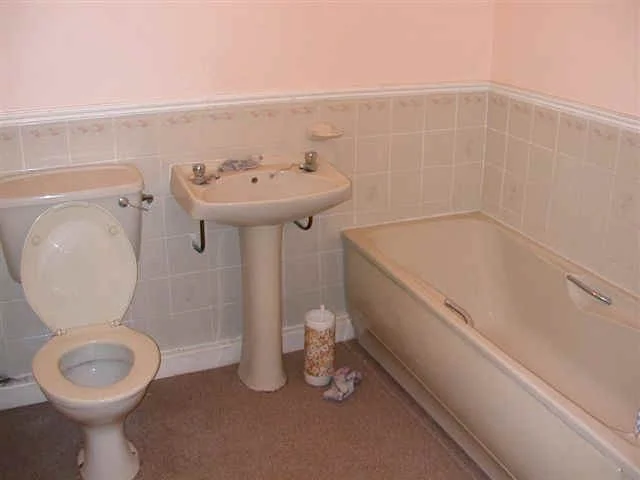
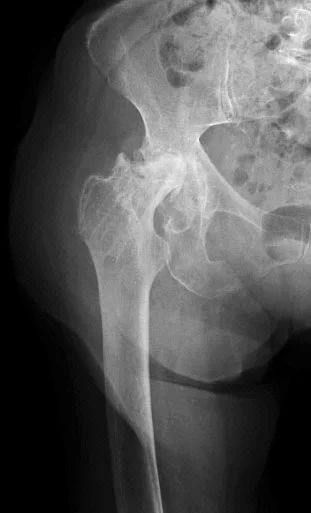
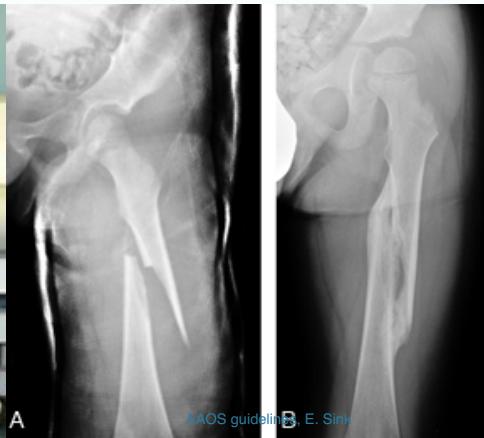
 A 65 year old: slipped in the toilet
A 65 year old: slipped in the toilet
 A 55 year old, tripped at edge of carpet
A 55 year old, tripped at edge of carpet
Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures
Operative Treatment
- Operative
- The treatment of choice
- Surgery should be performed urgently
Internal Fixation and Replacement
-
Internal fixation:
- Multiple Screws
- Young patient: Stable fracture
- Dynamic Hip Screw

- Multiple Screws
-
Replacement:
- Old patients
- hemi or total

Complications
-
Nonunion
- 5% of non-displaced
- 25% of displaced fractures

-
Avascular necrosis
- 0% of non-displaced
- 27% of displaced fractures
Intertrochanteric Fractures
Characteristics
- Extra-capsular
- Good blood supply
- Heal well
- Low risk for avascular necrosis
Demographics and Presentation
- Elderly, osteoporotic women
- Simple fall

Blood Supply Comparison
Intertrochanteric
Good blood supply maintained
Good healing / no AVN
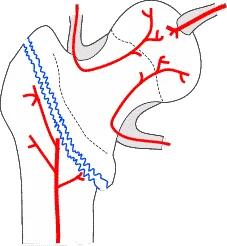
Femoral neck
Blood supply interrupted Non-union / AVN
Evaluation
- Clinical evaluation
- Pain in the hip
- Inability to bear-weight
- Limb is short and externally rotated
- c.f dislocated hip
- Short, adducted, internally rotated

- Short, adducted, internally rotated
Radiological Evaluation
- Radiological evaluation
- AP and ?Lateral (cross-table)
- Evaluation of medical condition

Treatment
- Usually operative
- Dynamic hip screw (DHS)
- Proximal femoral nail

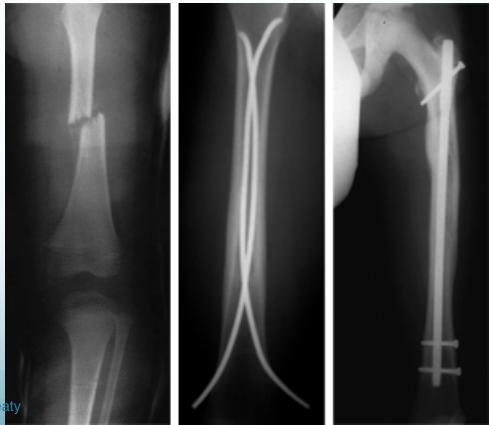
Femoral Shaft Fractures
Mechanism and Complications
- Mechanism: high energy
- Bleeding:
- Can easily loose 2L of blood
- Need good resuscitation
- Early fixation
- Inability to bear weight
- Risk of thrombo-embolism
- X-rays:
- AP & lateral radiographs
- Two joints (above and below)
- Very important

Surgical Treatment
- IMN: Intramedullary nail / Locked(with screws)
- The treatment of choice
- Relative stability
- Allows early weight-bearing
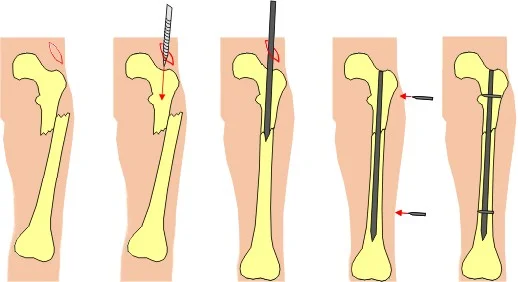
Intramedullary Nailing
- IMN: Intramedullary nail
- The treatment of choice
- Locked IMN (with screws)
http://www.synthes.com www.healio.com
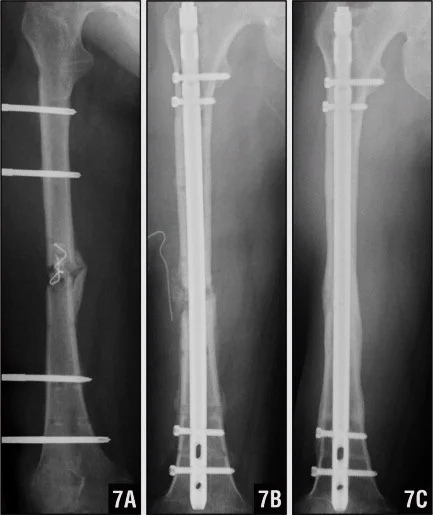
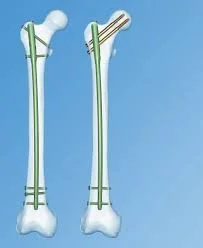

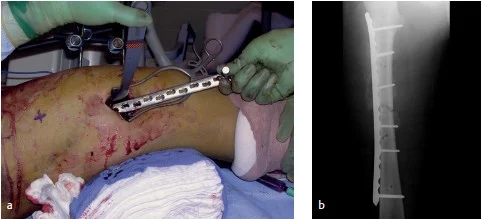
Plate Fixation
- Plate fixation
- The second choice
- Could use minimal invasive methods
- No early weight-bearing
Pediatrics Femur Fractures
Problems
- Bleeding - May bleed more than 1 L
Treatment Approaches
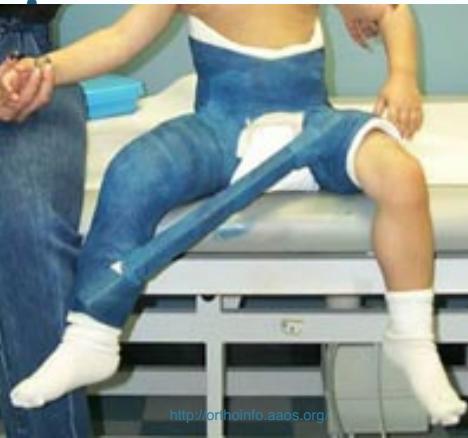
Conservative (up to 5-year-old)
- High remodeling rate
- Hip spica cast
- 1-2 cm shortening will be compensated by growth
- Monitor for mal-union
Operative (older children, >5 years)
- Accepted alignment, length & rotation
- Nailing better than plating
- Another surgery needed to remove implants