EM
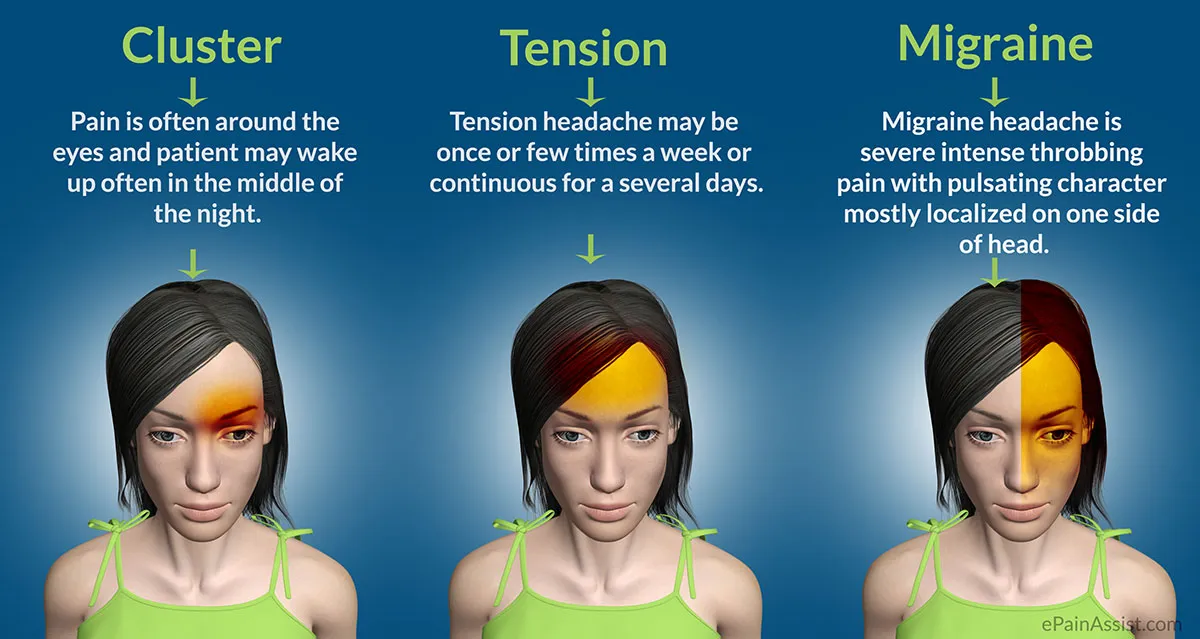
Cluster headache
not Common
Cluster headache
is an infrequent neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, severe unilateral headaches, typically around the eye
- Men are more commonly affected
- Occurs in people younger than 30
- Often has nocturnal onset
Pathophysiology
- The cause is unknown, does have some genetic association, and is linked to smoking, some theoretical association with hypothalamic activation of the trigeminal nerve
- Most common associated trigger is seasonality often occurring in spring and autumn.
Signs and symptoms
-
Cluster headache is always unilateral, or one-sided
-
The pain of a cluster headache is generally very intense and severe and is often described as having a burning or piercing quality
-
The pain is retroorbital/periorbital. It may radiate to the forehead, temple, nose, cheek, or upper gum on the affected side.
-
the pain of a cluster headache lasts a short time, generally 30 to 90 minutes. It may, however, last from 15 minutes to three hours.
-
Most sufferers get one to three headaches per day during a cluster period. They occur very regularly, generally at the same time each day, hence called “alarm clock headaches”
-
Need to be accompanied by autonomic symptoms such as: dropping eyelid, pupil constriction, conjunctival injection, tearing rhinorrhea and rarely facial blushing, swelling and sweating.
-
Cluster headaches are typically associated with nausea and vomiting
-
cluster headaches occurring in two or more cluster periods, lasting from 7 to 365 days with a pain-free remission of one month or longer between the headache attacks, may be classified as episodic. If headache attacks occur for more than a year without pain-free remission of at least one month, the condition is classified as chronic
Treatment
Acute treatment
-
100% oxygen at 10–12 L/min for 15–20 min
-
sumatriptan- Subcutaneous(6 mg) or intranasal
-
Preventive treatment
-
Verapamil, methysergide, prednisolone, topiramate, lithium
-
-Neurostimulation therapy — deep brain stimulation or occipital nerve stimulation
IM
Cluster Headache
Clinical Features:
- Recurrent episodes of severe unilateral headache, around the eye & temples (trigeminal distribution)
- Sudden onset, very very severe headache
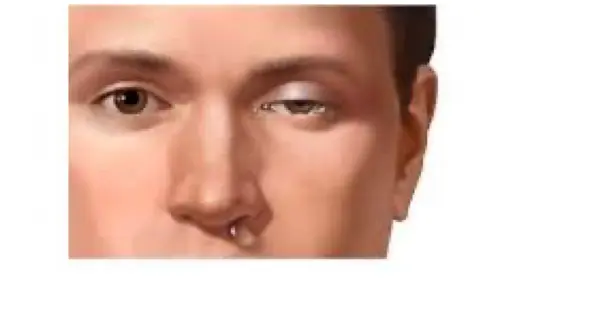
- Accompanied by same side lacrimation, eye redness & swelling, nasal congestion, runny nose & Horner’s syndrome (ptosis + meiosis + anhidrosis) (may be cause due pancoast tumor + Horner’s syndrome)
- Each episode lasts for few minutes to hours
- Attacks occur daily for few weeks, then stop, then recur after a variable period (clusters)
- No aura
- Occur at the same time each year (e.g., spring, winter)
Triggering Factors:
Many of them same as migraine
Etiology:
Unknown
Where is the problem?:
Hypothalamus, which somehow affects the trigeminal nerve
Diagnosis:
Based on symptoms
Differential Diagnosis:
Migraine, Trigeminal neuralgia, Temporal arteritis
Treatment
A) Acute Attack:
- 100% O2 at high flow rate (15L/min) for about 20 min
- Triptans (intranasal or subcutaneous sumatriptan). Oral tabs not very effective)
B) Maintenance Prophylactic Treatment (if attacks are frequent)
Rapid Fire Questions on Cluster Headache
- Location of cluster headache? around the eye
- Where is the pathology? hypothalamus
- Clinical features? Congestion, swelling, tearing
- What is Horner’s syndrome? Ptosis, Myosis, Anhidrosis
- Any triggers? same
- Acute treatment? O2 100% 15L
- Chronic treatment? Verapmil, Lithum tablets
- Differential diagnosis? Temporal Artiritis, Migraine, trigeminal neuralgia
- Any aura? no aura
FM
Cluster Headache
- Very Severe
- Frequent
Associated with parasympathetic autonomic features:
- Injected sclera
- Lacrimation
- Rhinorrhea
- Facial sweating
- Eyelid swelling
Treatment
Cluster Headache
Acute Treatment:
- Subcutaneous sumatriptan
- Oxygen inhalation.
Prevention:
- Verapamil – corticosteroids – lithium - Methysergide.