Pathology RR
Definition:
Chronic, diffuse, irreversible disorder of the liver characterized by loss of the normal liver architecture and replacement by regenerating nodules. diffuse liver diseases characterized by (degeneration, regenerating nodules, fibrosis and loss of architecture)
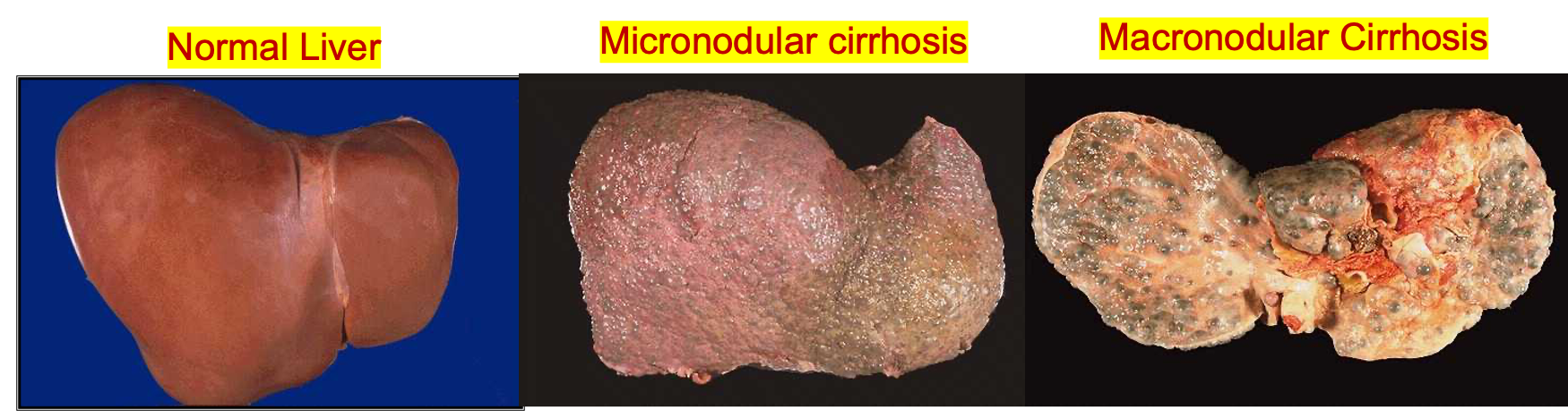
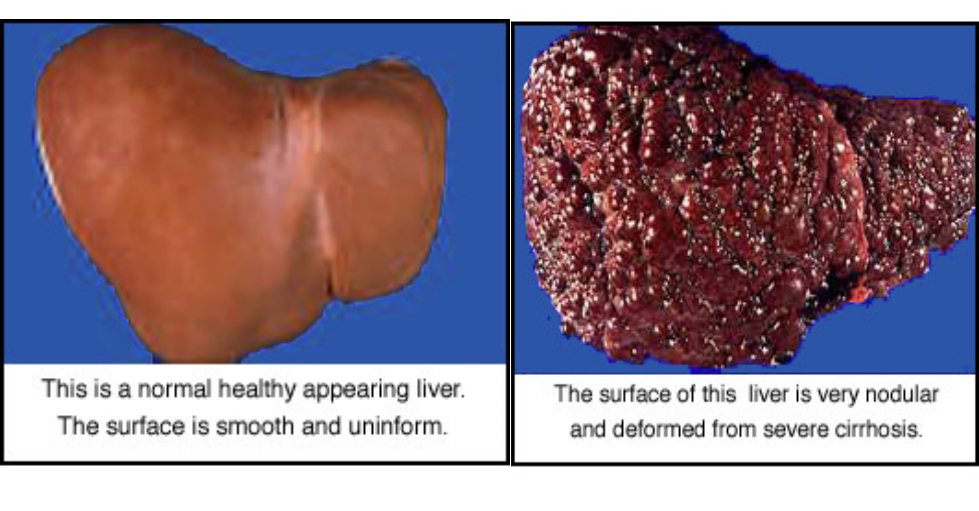
liver with sharp edge and firm in consistency (shrunken).
Cirrhosis Facts:
- Progressive, leads to liver failure
- Insidious, prolonged course
- 9th leading cause of death in U.S.
- Twice as common in men
- Highest incidence between ages 40 and 60.
 Portal Tract - Central Vein
Portal Tract - Central Vein
Causes
- Chronic viral hepatitis (HCV, HBV±HDV)
- Alcoholic liver diseases.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Biliary cirrhosis.
- Prolonged cholestasis (PBC, PSC)
- Chronic venous congestion of the liver: right sided heart failure , Budd-Chiari syndrome.
- Metabolic causes: Hemochromatosis, Wilson disease, α1 antitrypsin deficiency, NASH
- Drugs and toxins, Alcohol
- Cryptogenic: unknown etiology
Pathogenesis
The major source of collagen in cirrhosis is the peri-sinsoidal stellate cells (Ito cells) which lie in the space of disse.
They are activated to myofibroblasts by stimuli released from damaged hepatocytes, activated von kupffer cells or sinusoidal endothelial cells RR e.g. oxygen free radicals, growth factors, TNF, IL-1 and lymphotoxins
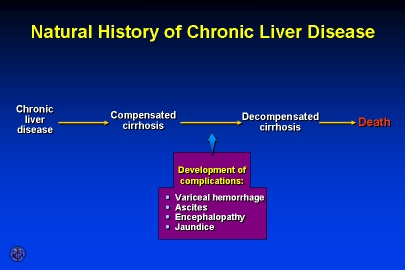
Complications
- Liver cell Failure.
- Portal hypertension.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma.
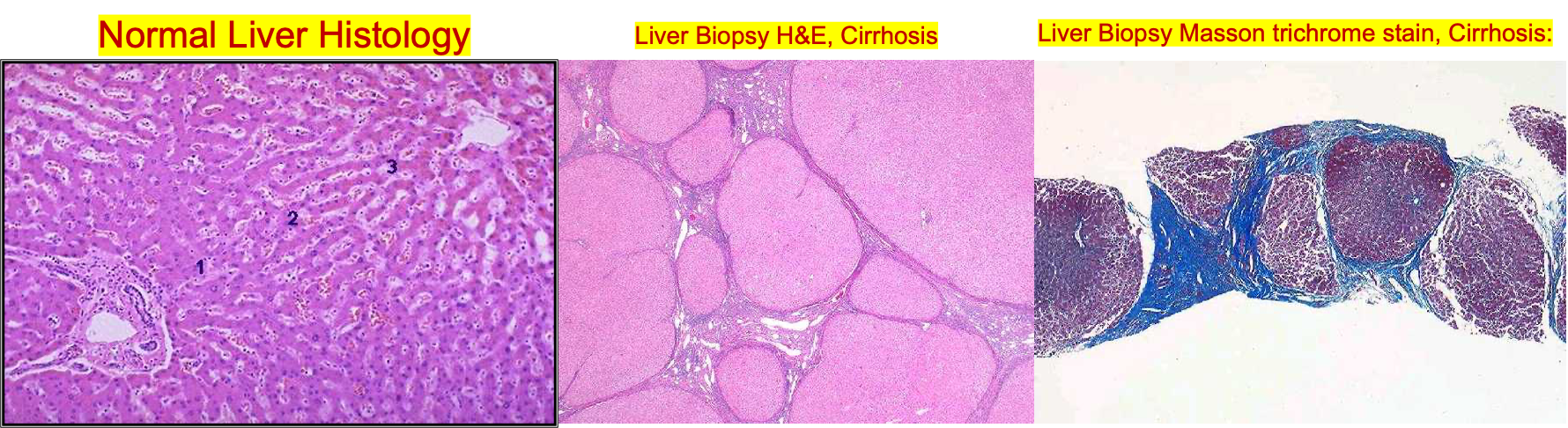
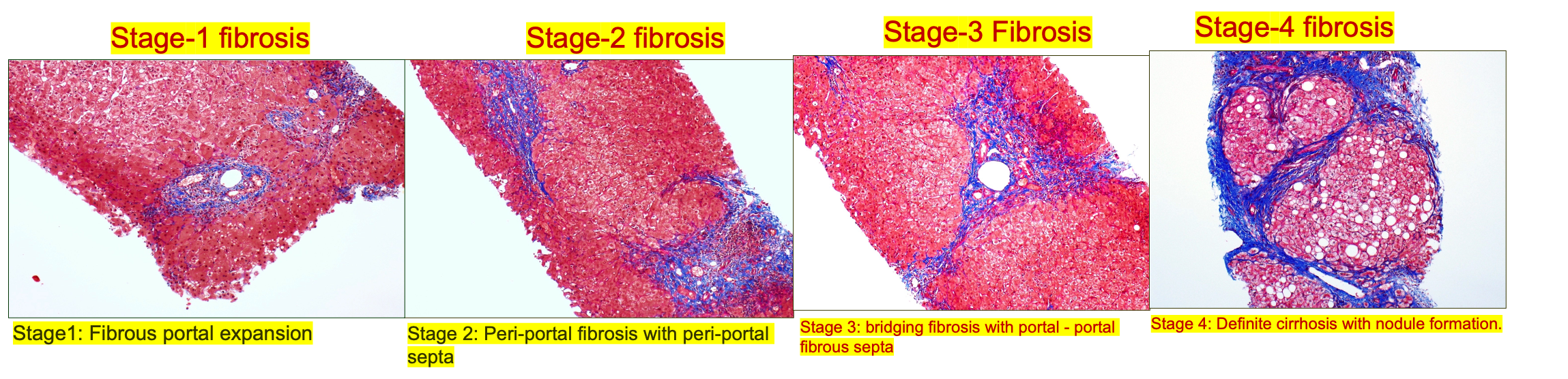
Staging of hepatic fibrosis:
- 0: No increased fibrous tissue.
- 1: Fibrous portal expansion.
- 2: Periportal fibrosis with periportal septa.
- 3: Bridging fibrosis with portal - portal fibrous septa. = Fibrosis; Reversible
- 4: Definite cirrhosis with nodule formation. = Cirrhosis; Irreversible
Clinical picture: Y
1- latent well compensated with no liver functions impairment.
2-active and decompensated : may be :
- loss of functions of liver cells = liver cell failure.
- vascular decompensation:= portal hypertension.
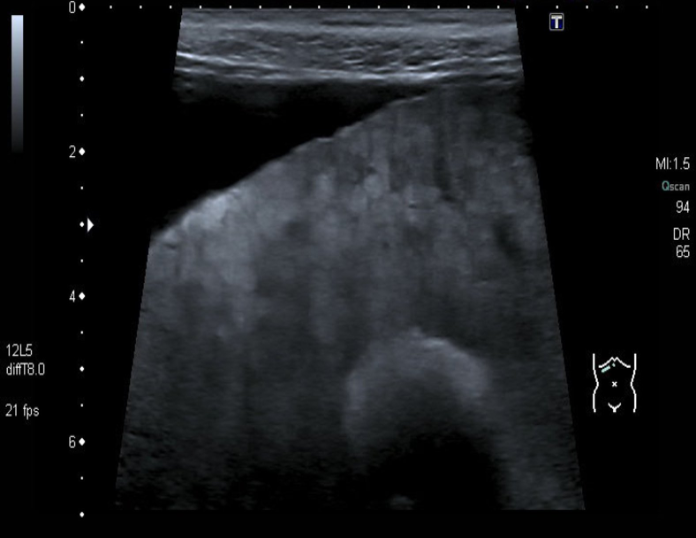
Radiology
The signs of cirrhosis of the liver at CT and ultrasound are:
- Reduction in size of the right lobe of the liver.
- Irregularity of the surface of the liver.
- Diffuse nodular texture of the liver
- Splenomegaly.
- Ascites
- Liver size Initially enlarged
- Atrophies and shrinks with disease progression
- Hypertrophy of the caudate lobe and left lobe
Decompensated liver cirrhosis
- Ultrasound liver (oblique view)
- Heterogeneous liver parenchyma, nodular liver margin, and ascites can be seen.
- These findings are consistent with decompensated liver cirrhosis.