Classic Presentation Scenario
You are in the dermatologic clinic and this patient came seeking advice. Assuming that the patient is your colleague, please take a full dermatological history.
-
HPI: Yasir is an 17-year-old healthy teenager who presents to his primary care physician with “pimples” on his face for the last 2 years. He reports a daily skin regimen of aggressive facial cleansing with a bar soap during his morning shower.
-
PMH: no chronic illnesses or prior hospitalizations
-
Allergies: no known allergies
-
Medications: none
-
Family history: father and mother had acne as teenagers
-
Social history: lives at home with parents, attends high school
-
ROS: negative
-
A 15-year-old boy presents with pleomorphic lesions on the central face consisting of papules, pustules, and open comedones. These began following puberty and have become progressively worse, leaving scars and red macules/patches on his face. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Lesion Description and Management
-
You and your colleague describe the dermatologic lesions you see.
-
What is your plan of management?
-
Advise your patient?
-
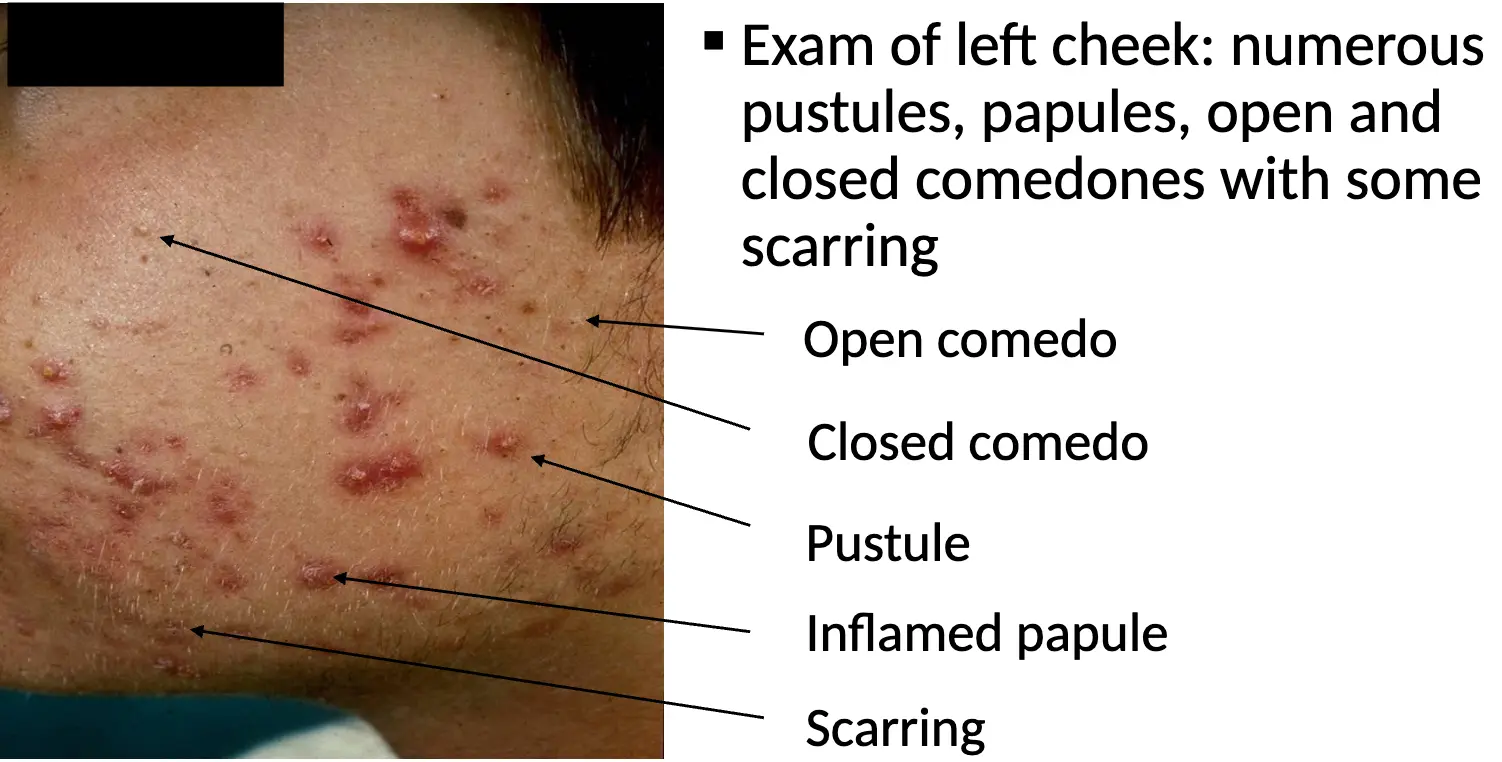
Exam of left cheek: numerous pustules, papules, open and closed comedones with some scarring
-
Open comedo
-
Closed comedo
-
Pustule
-
Inflamed papule
-
Scarring
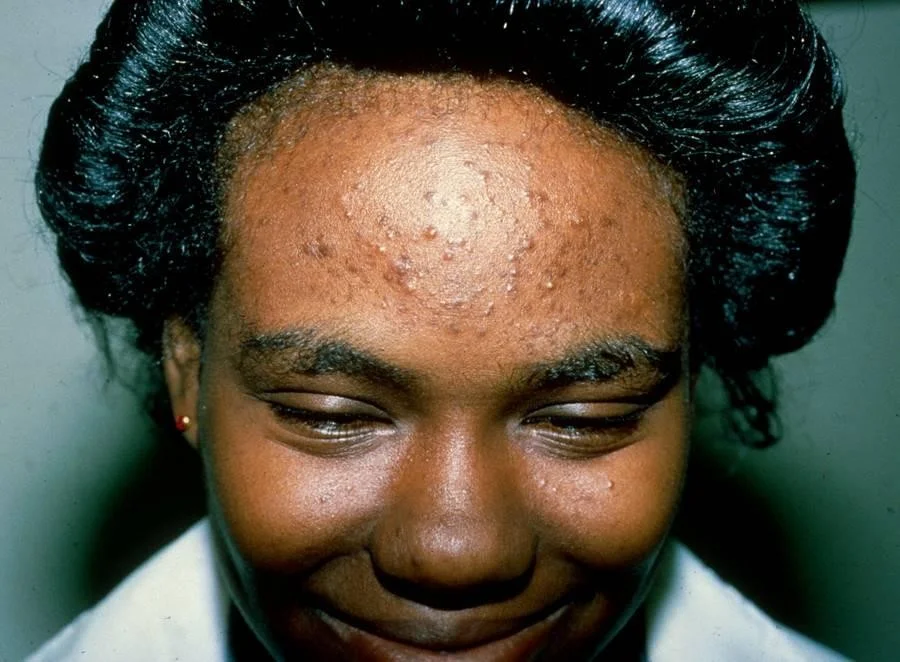 Moderate comedonal acne without evidence of scarring. ▪ Note the mild post- inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Moderate comedonal acne without evidence of scarring. ▪ Note the mild post- inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Acne vulgaris
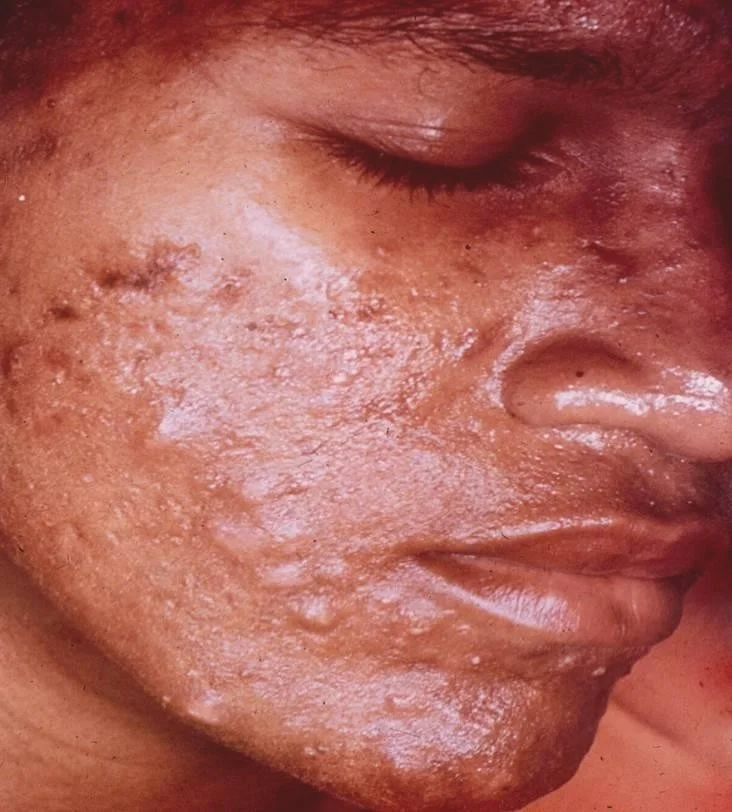
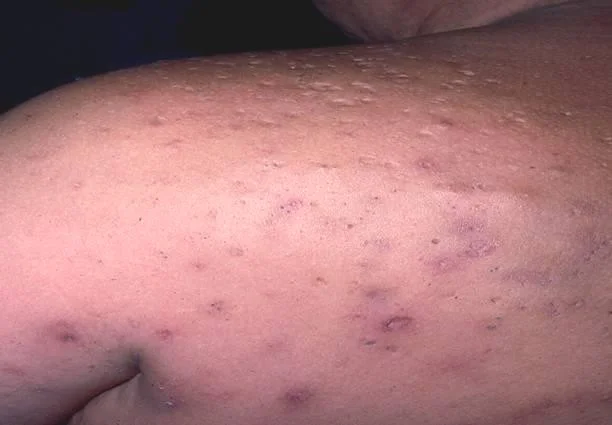 Severe nodulocystic acne with presence of scarring
Severe nodulocystic acne with presence of scarring
- Acne should be treated aggressively to avoid permanent scarring and cysts
- Refer patients with difficult to control acne or the presence of scarring to dermatology
Question 1
- How would you describe Jim’s skin exam? a. Mild comedonal acne without presence of scarring b. Mild inflammatory acne without comedones c. Moderate mixed comedonal and inflammatory acne with presence of scarring d. Moderate mixed comedonal and inflammatory acne without presence of scarring
Question 2
- Which is (are) related to the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris? a. Androgens in the circulation b. Bacteria in the hair follicle c. Follicular plugging d. Sebum secretion e. All of the above
Question 3
- Which of the following agents are effective in treating acne vulgaris? a. Oral antibiotics b. Topical benzoyl peroxide c. Topical retinoid creams d. All of the above
Exercise 2

Non- classic Presentation Scenario
- HPI: Ms. M is a 22-year-old woman who was referred to the dermatology clinic for new onset acne
- PMH: no major illness or hospitalizations, no pregnancies
- Allergies: allergic to penicillin (rash)
- Medications: occasional multivitamin
- Family history: noncontributory
- Social history: lives in the city and attends college
- Health-related behaviors: gained 40 pounds over the past 4 years despite a healthy diet and exercise habits
- ROS: new upper lip and chin hair growth, irregular menstrual cycles since menarche, last period was 4 months ago
Exam Findings
- Moderate comedonal and inflammatory acne of cheeks and jaw line. Also with scattered terminal hairs on the upper lip and lower chin.
- Hair loss noted on frontal and parietal scalp.
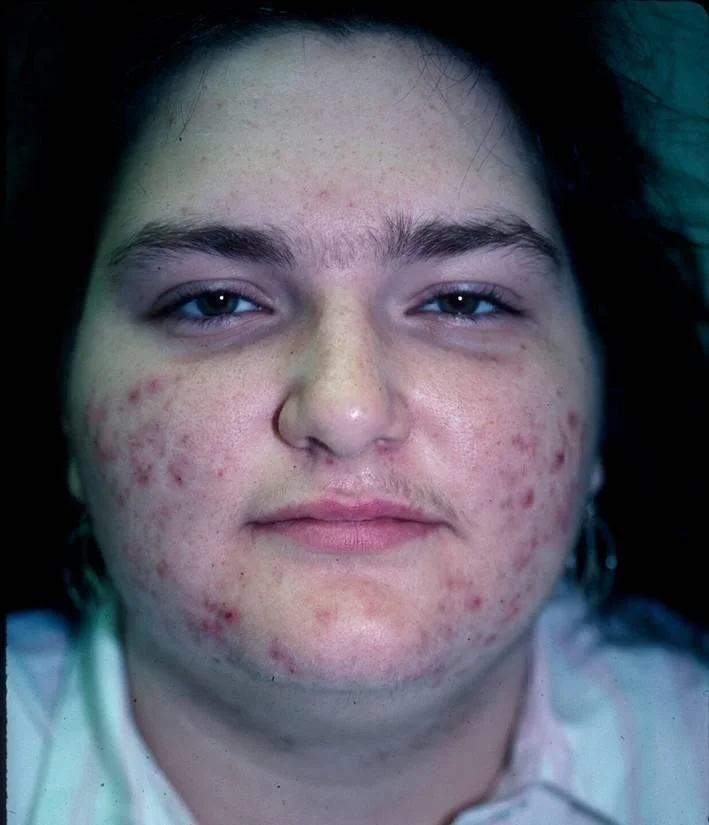
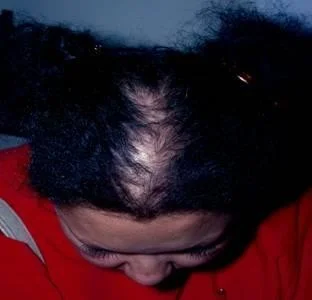
Ms. M was given spironolactone and her acne improved. Why did this medication work?
a. Spironolactone has anti-androgenic effects b. Spironolactone has anti-comedonal activity c. Spironolactone when used appropriately has anti-bacterial activity d. The diuretic effect of spironolactone eliminated sodium resulting in less sebum
Based on the history and exam, what is the most likely diagnosis?
a. Cushing Syndrome b. Gram negative folliculitis c. Polycystic ovarian syndrome d. S. aureus folliculitis
Case Five
Case Five: History
- HPI: Ahmed is an 18-year-old man who presents with four years of bad acne on his face and chest. He has been taking oral minocycline 100 mg BID, topical tretinoin, and a combination of benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin for 18 months without improvement.
- PMH: none
- Allergies: Sulfa (rash)
- Medications: minocycline, tretinoin cream, benzoyl peroxide/clindamycin gel
- Family history: both parents had acne
- Social history: high school senior in three Advanced Placement courses
Case Five: Skin Exam
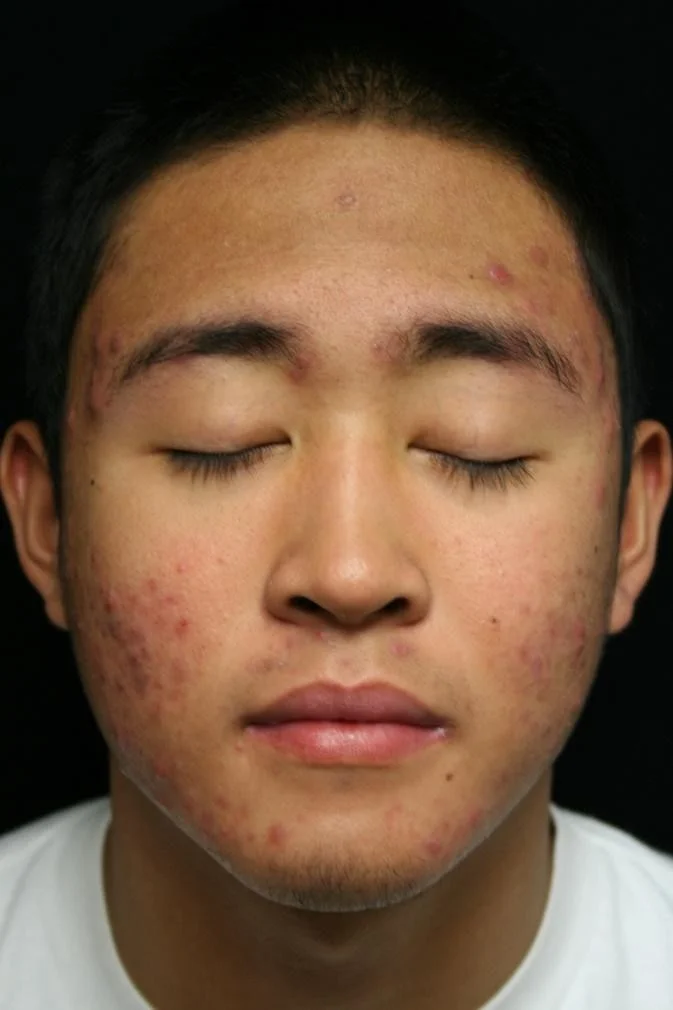
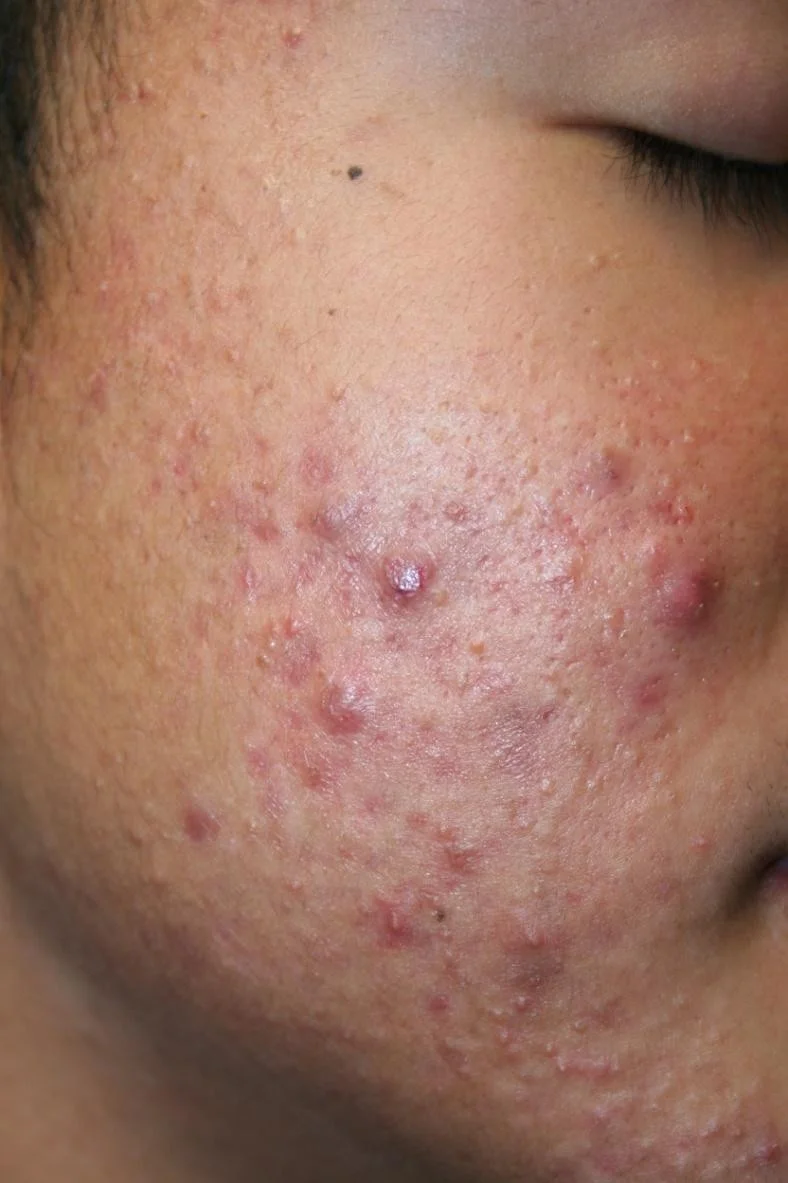
Case Five, Question 1
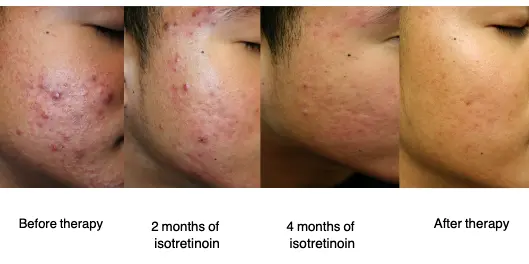
- Ahmed clearly has acne vulgaris. He has nodules and some early scarring. What is the next appropriate therapy? a. Bactrim for gram negative acne (allergic to sulfa medications) b. Change from minocycline to tetracycline (tetracycline is not stronger than minocycline, and poorly tolerated) c. Glycolic acid peels (may help mild acne, but need oral therapy for nodular, scarring acne) d. Isotretinoin
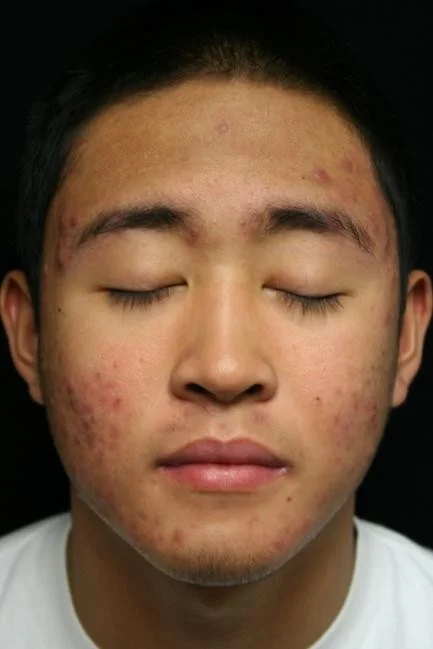
Oral Isotretinoin Indications:
- Severe, recalcitrant nodular cystic acne
- Severe acne refractory to oral antibiotics
- Scarring acne
Isotretinoin side effects
- Teratogenicity / birth defects
- Dry lips, dry eyes
- Nosebleeds
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Myalgias and elevated creatinine kinase
- Other rare side effects
Isotretinoin improves severe, refractory nodular acne