INVESTIGATIONS TO DO
-
CBC:
- Anemia (Hb. usually around 8g)
- WBCs & platelets high (due to hyperactive bone marrow)
- Reticulocytes are high
-
LFTs: high bilirubin (which type?) - indirect
-
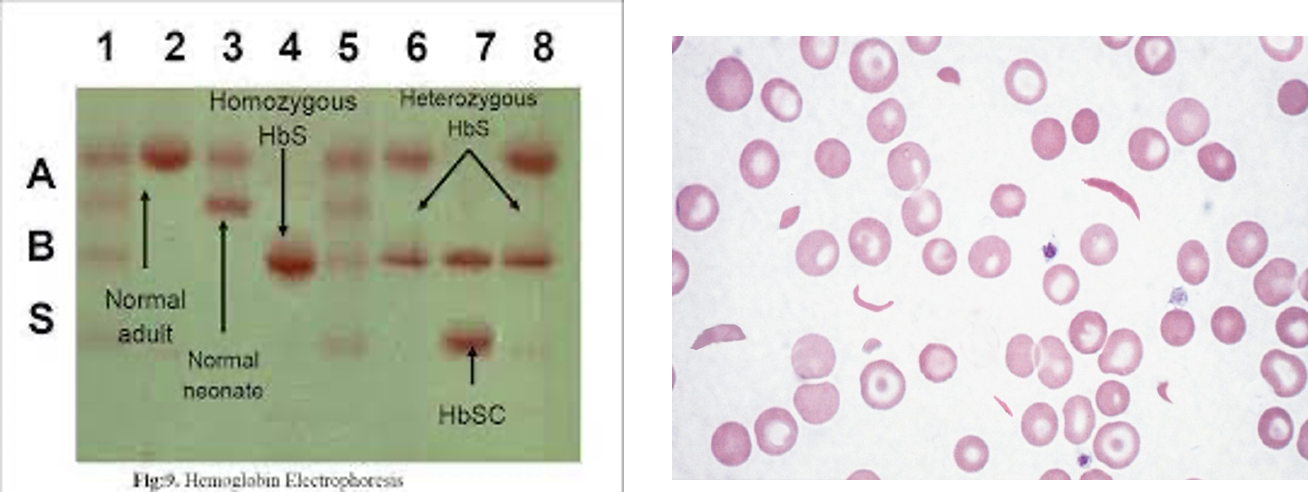
Peripheral smear: shows sickled cells
-
Hb. Electrophoresis: This is confirmatory. It shows:
- 80-90% Hb.S
- Remaining is Hb.F
- No Hb.A (in pure Hb.SS)
-
Solubility test: Patient’s blood mixed with sodium dithionite solution → solution turns turbid (due to sickling)
-
Sickling test: Drop of blood on a slide → add sodium metabisulfite → causes excess sickling (seen under the microscope)
-
Genetic testing: Available but not done routinely for diagnosis.
(Electrophoresis and Peripheral Smear)
 (Image of Solubility Test - Turbid)
(Image of Solubility Test - Turbid)
SCREENING
- Screening for SCD done on all newborns in the U.S. and most countries
- Premarital screening done in K.S.A.
- In utero screening of the fetus can be done (sample of amniotic fluid or placenta → genetic analysis)