Patient is already diagnosed, no history is taken
Start introducing your self, ask if they know about their condition why is it happeneing from their knowledge. instruct how to apply good attachment to avoid most of complication. emphasize and question patient understanding throughout the counseling.
https://geekymedics.com/information-giving-overview/
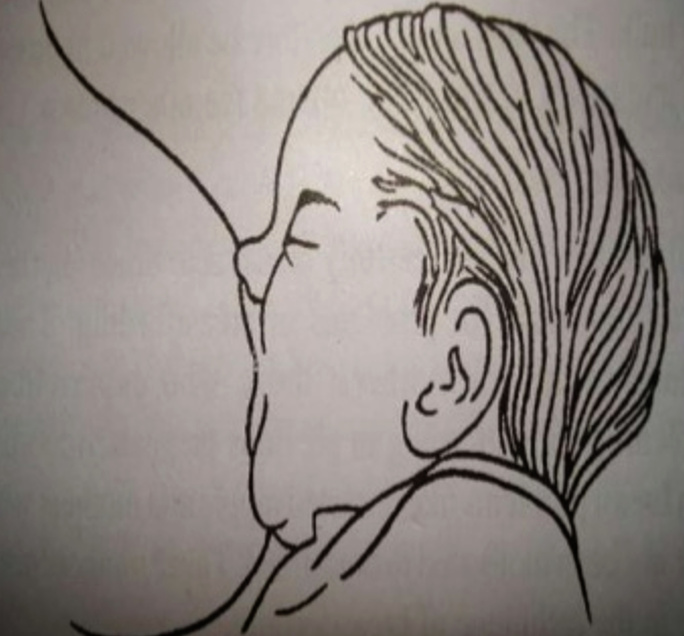
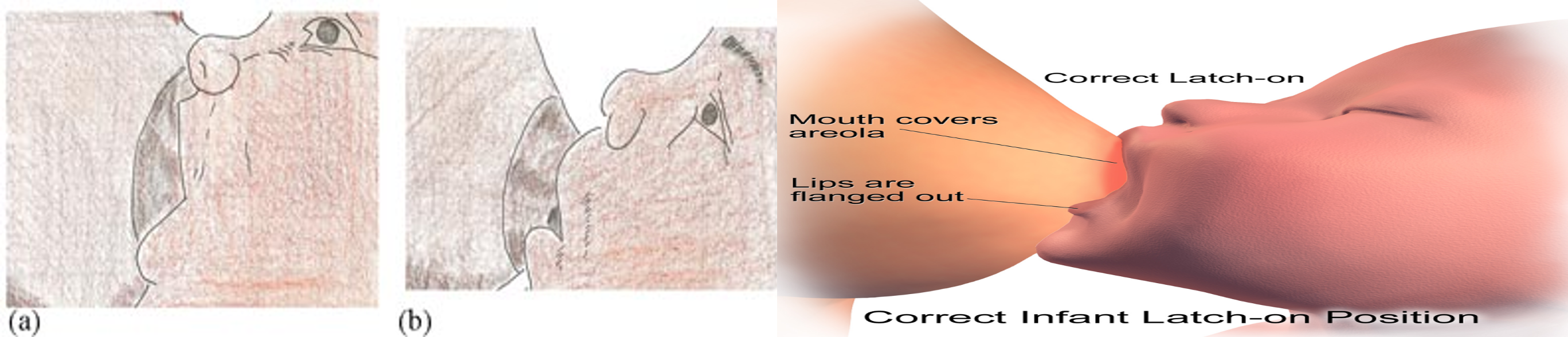
How to achieve good attachment?
4 Criteria of good attachment: Z
- Baby’s chin is touching the breast
- Baby’s mouth is widely open
- Lower lip is turned outwards
- More areola tissue above than below the mouth
- No pain while breast feeding
Pros of breast feeding
For the Baby:
- Optimal Nutrition: Provides complete and easily digestible nutrition.
- Enhanced Immunity: Reduces risk of infections, allergies, and other illnesses.
- Healthy Development: Supports proper physical development, including dental and jaw health, and potentially higher IQ.
- Emotional Well-being: Fosters bonding and emotional security.
- Long-Term Health: Linked to reduced risks of obesity and heart disease.
For the Mother:
- Postpartum Recovery: Helps uterus contract, aiding in faster recovery.
- Natural Contraception: Can delay menstruation.
- Weight Management: Assists in returning to pre-pregnancy weight.
- Reduced Cancer Risk: Lower risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
- Cost-Effective and Convenient: Saves money and time compared to formula feeding.
- Emotional Bonding: Strengthens the mother-child bond and releases calming hormones.
Scenarios
1. Breast Engorgement
Scenario: A mother presents with swollen, painful breasts a few days after delivery.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Ask about the frequency and duration of breastfeeding sessions. Check for signs of engorgement such as firmness, warmth, and tenderness.
- Education: Explain that engorgement is common as milk supply increases. Encourage frequent breastfeeding to relieve engorgement.
- Management: Suggest warm compresses before feeding to help milk flow and cold compresses after feeding to reduce swelling. Advise gentle breast massage and hand expression if needed.
- Follow-up: Schedule a follow-up to ensure the engorgement is resolving and to adjust the plan if necessary.
2. Mastitis
Scenario: A mother reports flu-like symptoms, breast pain, and redness.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Inquire about symptoms, breastfeeding patterns, and any recent changes. Examine the breast for redness and warmth.
- Education: Explain that mastitis is an infection often caused by milk stasis. Stress the importance of continuing to breastfeed or pump to clear the blockage.
- Management: Recommend rest, hydration, and analgesics for pain relief. If symptoms persist, discuss the need for antibiotics.
- Follow-up: Ensure the mother understands the treatment plan and schedule a follow-up to monitor recovery.
3. Breast Abscess
Scenario: A mother has a painful, swollen area on her breast that is not improving with mastitis treatment.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Confirm symptoms and perform a physical examination. Ultrasound may be needed to diagnose an abscess.
- Education: Explain that a breast abscess is a collection of pus that may require drainage.
- Management: Discuss options for drainage, either through needle aspiration or surgical intervention. Continue breastfeeding if possible, or pump to maintain milk supply.
- Follow-up: Arrange for follow-up care to monitor healing and prevent recurrence.
4. Sore or Fissured Nipple
Scenario: A mother complains of nipple pain and visible cracks.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Ask about breastfeeding techniques and observe a feeding session if possible.
- Education: Teach proper latch techniques to prevent further damage. Explain the importance of air-drying nipples and using lanolin or breast milk for healing.
- Management: Suggest temporary use of nipple shields if pain is severe. Encourage frequent, short feedings to reduce stress on nipples.
- Follow-up: Monitor healing progress and adjust breastfeeding techniques as needed.
5. Perceived Insufficiency and Low Breast-Milk Production
Scenario: A mother is concerned that her baby is not getting enough milk.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Evaluate the baby’s weight gain, diaper output, and feeding frequency.
- Education: Reassure the mother about normal feeding patterns and growth indicators. Discuss signs of adequate milk intake.
- Management: Suggest increasing breastfeeding frequency and ensuring effective latch. Consider lactation supplements if appropriate.
- Follow-up: Schedule regular weight checks and provide ongoing support to build confidence.
6. Short-Term Separation Such as Employment Outside the Home
Scenario: A mother is returning to work and worried about maintaining breastfeeding.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Discuss the mother’s work schedule and available facilities for pumping.
- Education: Explain the importance of maintaining milk supply through regular pumping. Discuss storage and handling of expressed milk.
- Management: Help create a pumping schedule that fits the work routine. Suggest introducing a bottle to the baby before returning to work.
- Follow-up: Offer support and resources for balancing work and breastfeeding.
7. Formula Feeding
Scenario: A mother is considering or has decided to formula feed.
Counseling Process:
- Assessment: Understand the reasons for choosing formula feeding and any concerns the mother may have.
- Education: Provide information on safe formula preparation and feeding techniques. Discuss the importance of bonding during feeding times.
- Management: Support the mother’s decision and ensure she has access to resources and information on infant nutrition.
- Follow-up: Offer continued support and address any questions or concerns as they arise.