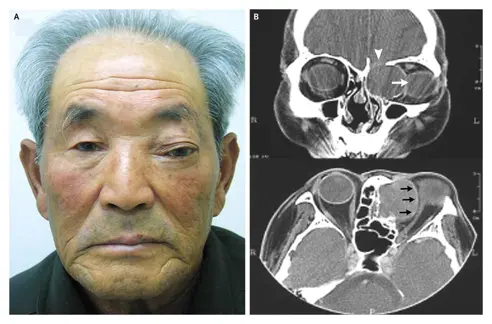
Orbit
Objectives
- Recognize different causes of proptosis e.g., Chronic Thyroid eye diseases (the commonest cause of unilateral or bilateral proptosis in adults).
- Recognize the most common causes of orbital and periorbital tumors.
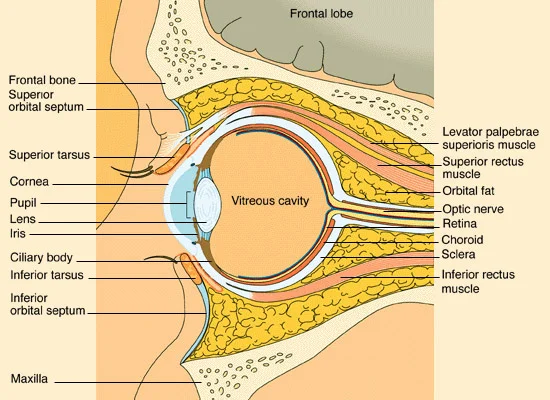
Anatomical Diagram of the Eye
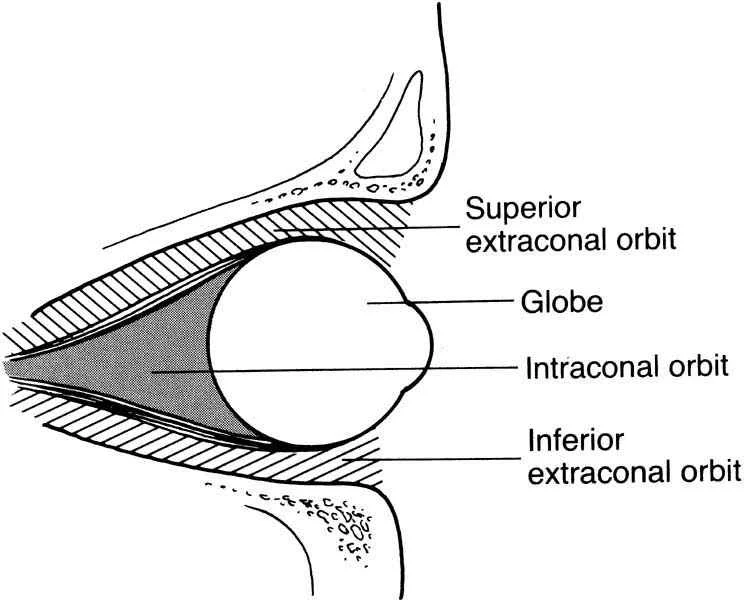
Orbital Compartments
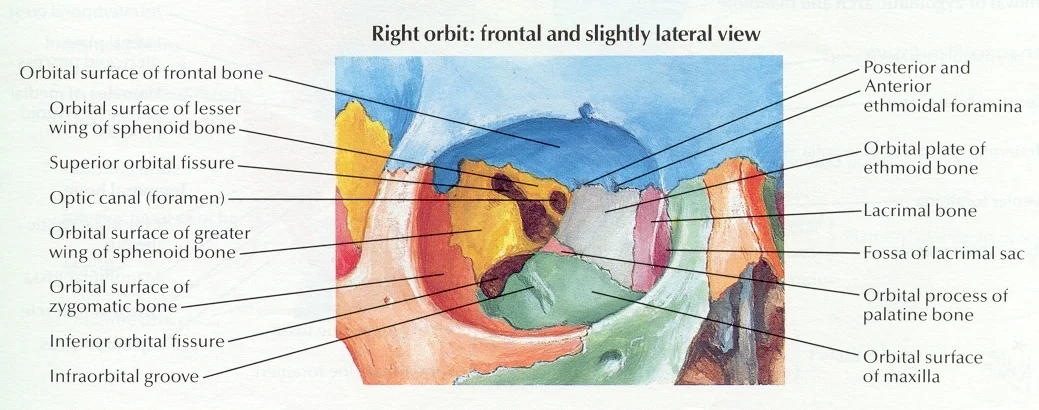
Anatomy
Sinuses
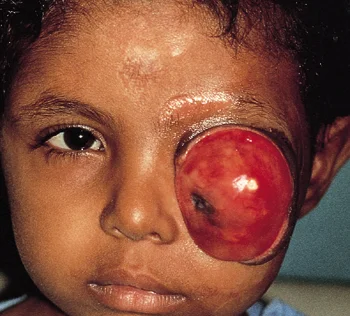
Secondary Malignancies
- Local primary
- eye, eyelid, sinuses
- Metastasis
- Children:
- Neuroblastoma
- ALL (Leukemia)
- AML (Chloroma)
- Adults:
- Breast
- Lung
- Prostate
- Children:
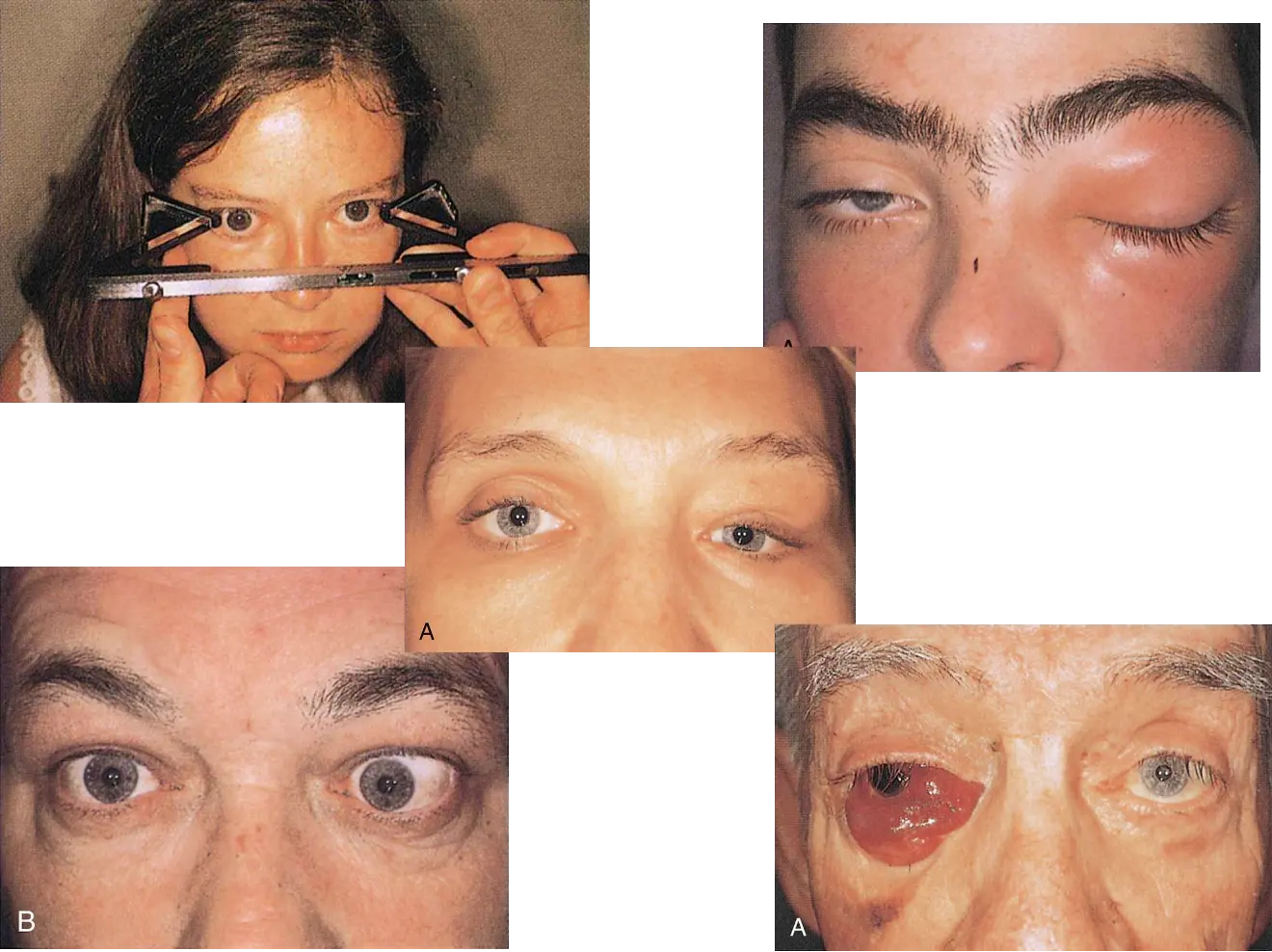
Evaluation
- 7 P’s
- Pain
- Proptosis
- Progression
- Palpation
- Pulsation
- Periorbital changes
- Past medical history
Proptosis
- Infection
- Inflammation
- Congenital
- Vascular
- Neural
- Mesenchymal
- Lymphoid
- Secondary
- Lacrimal gland
Congenital
- Dermoid cysts
- Most common orbital tumors in kids
- Usually presents at a suture junction
- Surgical: Total complete excision keeping the cyst wall intact
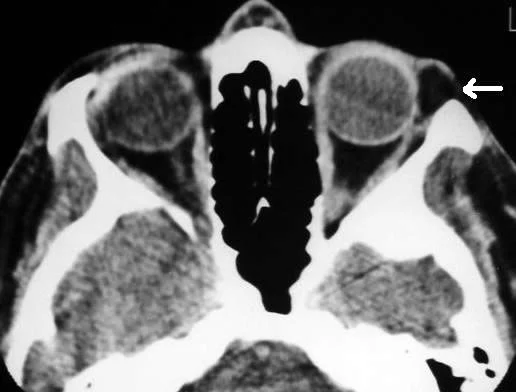
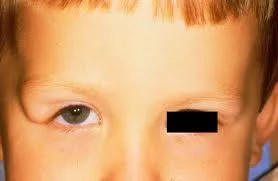
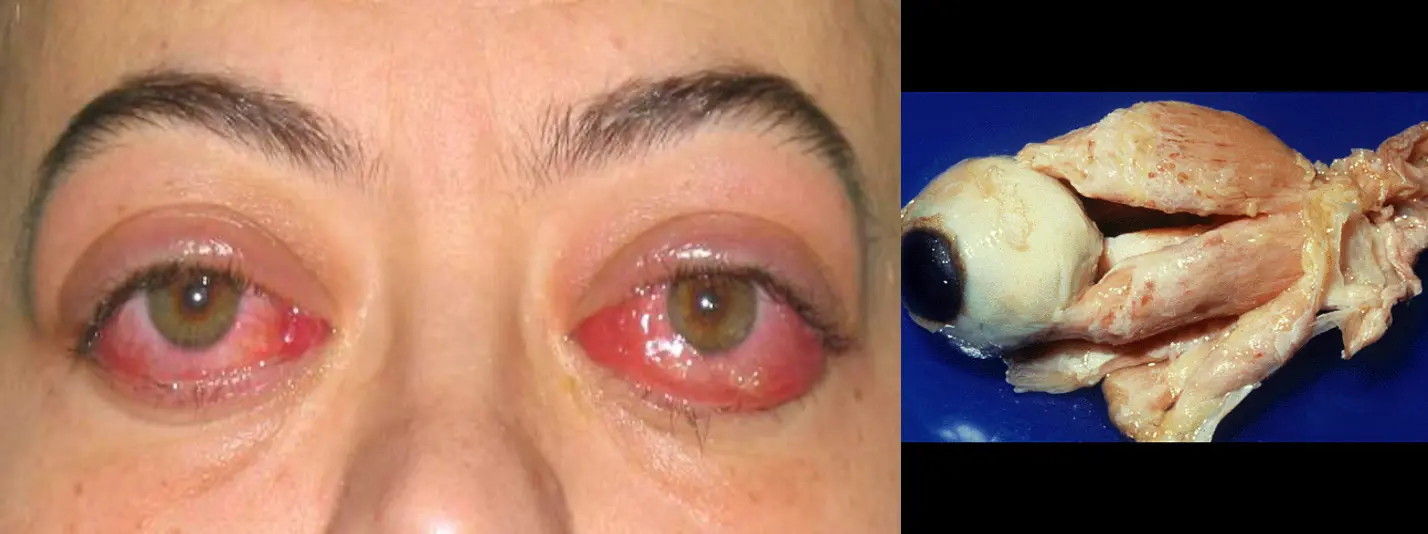
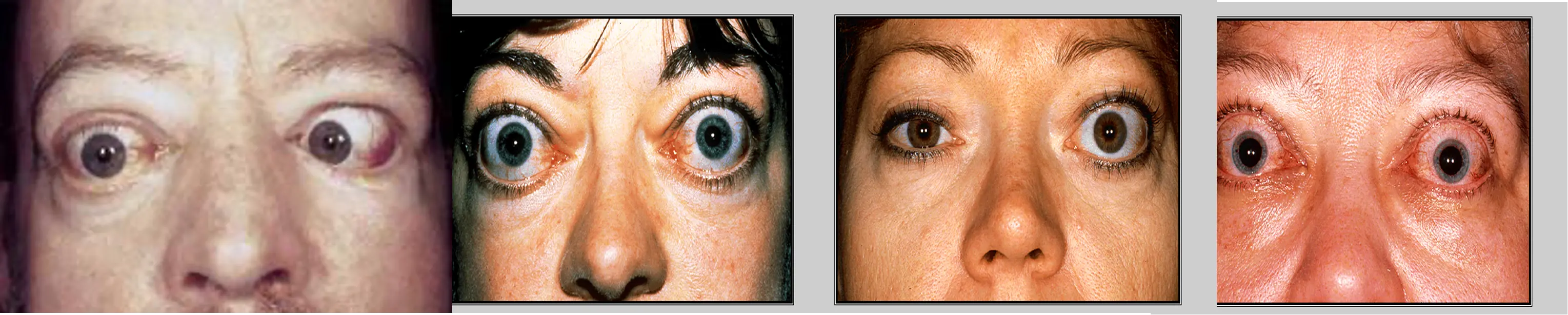
Thyroid Eye Disease
-
Pleomorphic cellular infiltration of EOM>enlargement >degeneration>fibrosis>restrictive myopathy>diplopia.
-
Infiltration of the orbital fat with chronic inflammatory cells with the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans and water retention>↑orbital content.
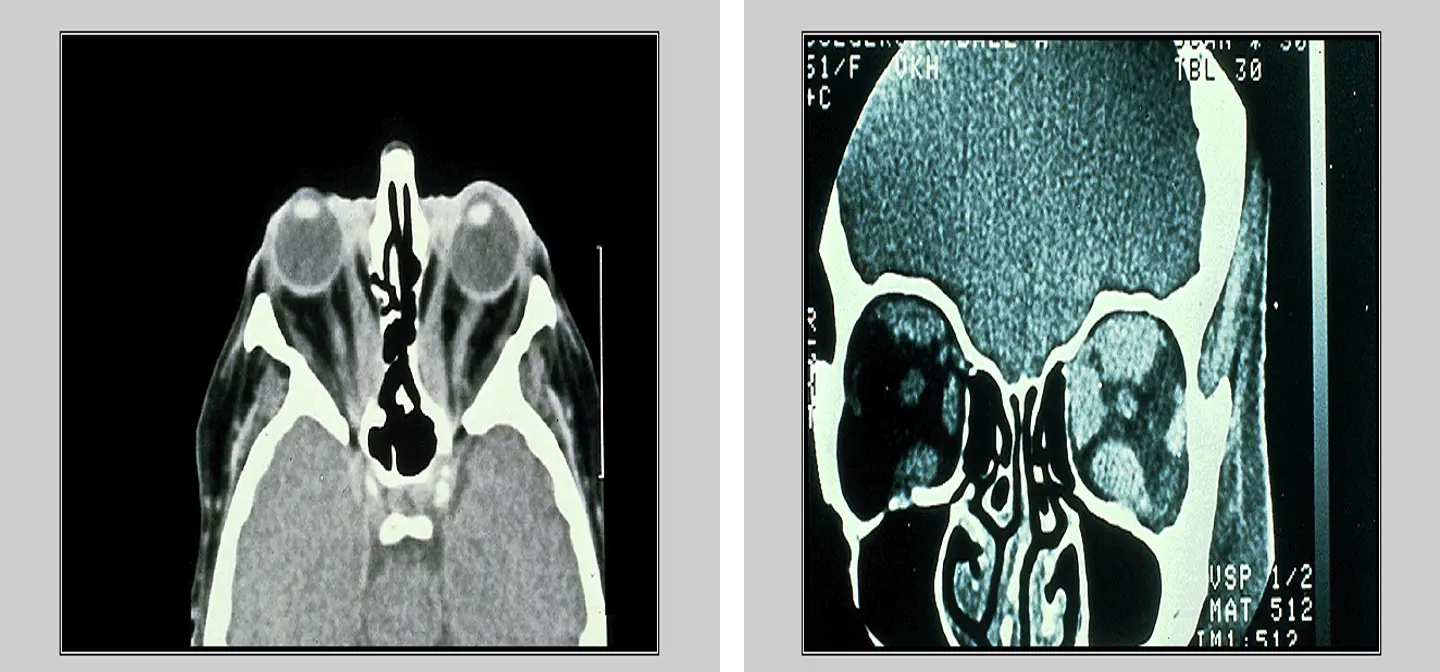
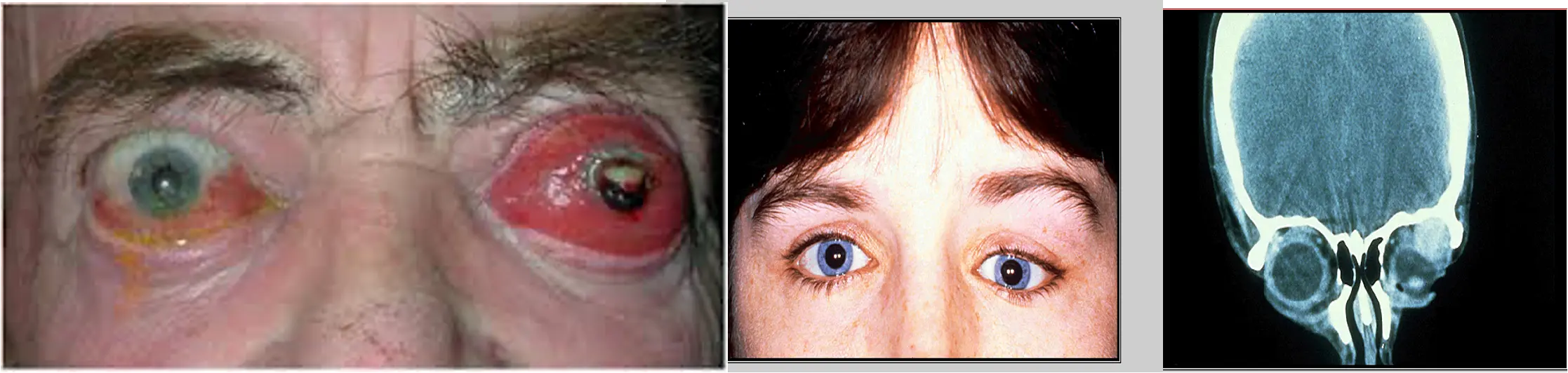
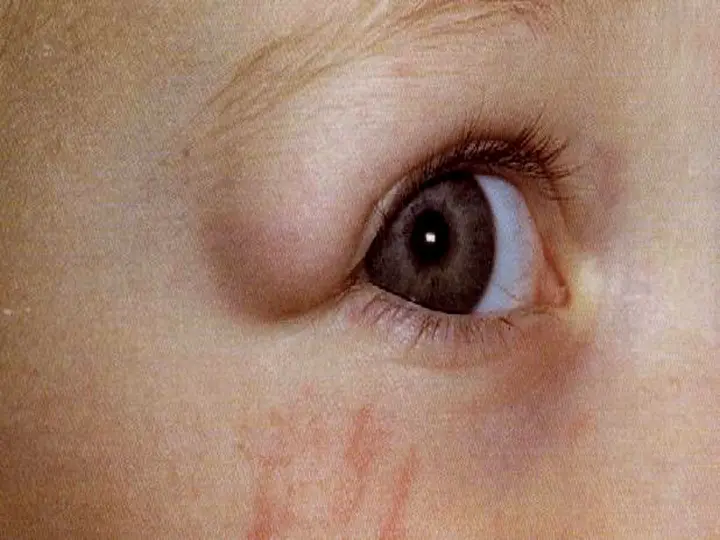
Frontal sinus mucocele

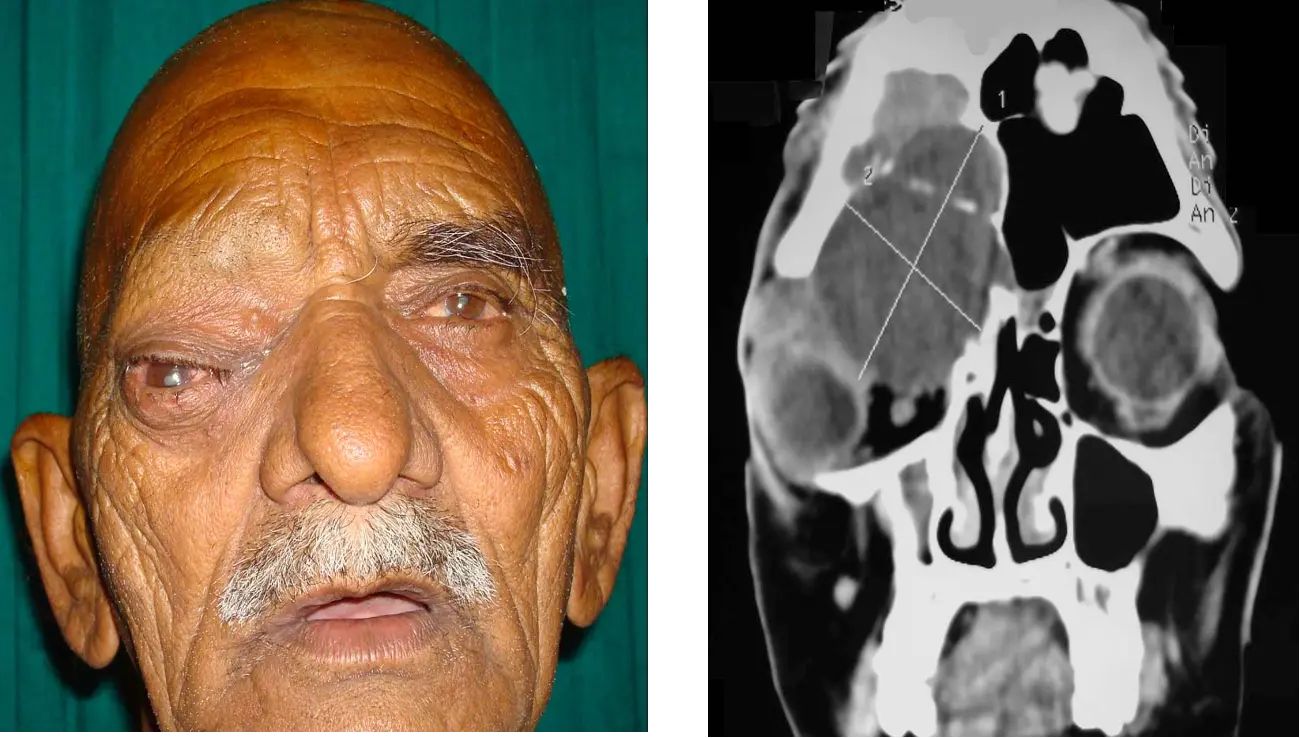
Ethmoidal sinus mucocele: