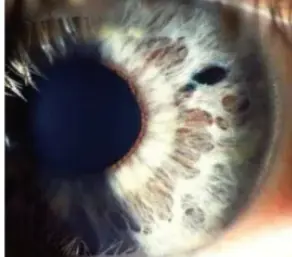
Narrow Angle Glaucoma
- Elevated Pressure
- Damaged Optic Nerve
- Trabecular Meshwork with blocked drainage
- Blocked Fluid Flow
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Definition: ACG
It is defined as an optic neuropathy which occurs as a result of high intraocular pressure due to narrow or closed angles.
Angle-Closure Glaucoma: High-Risk Groups
-
Elderly
-
Hyperopic patients
-
Positive family history of angle closure
-
Females
-
Age: after 40 yrs
-
Gender: Female:Male::4:1
-
Race
- prevalence higher in South-East Asians, Chinese & Eskimos
-
Family history
- first-degree relatives are at increased risk (≈ 3.5 times)
-
Hypermetropes
Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma is an Emergency
Precipitating Factors
- Dim illumination
- Emotional Stress
- Trauma/illness
- Intense concentration
- Pharmacological pupil dilatation
Clinical Picture
Onset: 50+ years of age
Symptoms
- Severe eye/headache pain
- Blurred vision
- Red eye
- Nausea and vomiting
- Halos around lights
- Intermittent eye ache at night
Signs
- Red, teary eye
- Corneal edema
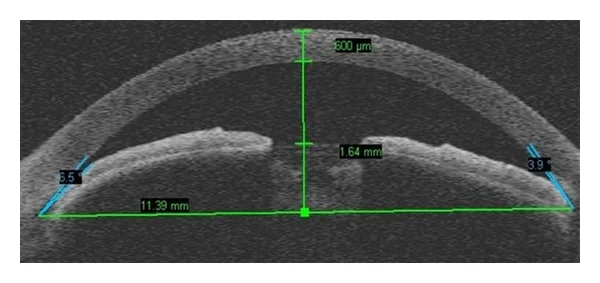
- Closed angle
- Shallow AC
- Mid-dilated, fixed pupil
- Iris atrophy
- AC inflammation
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Red eye.
- Hazy cornea.
- Mid-dilated non-reactive pupil.
Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma
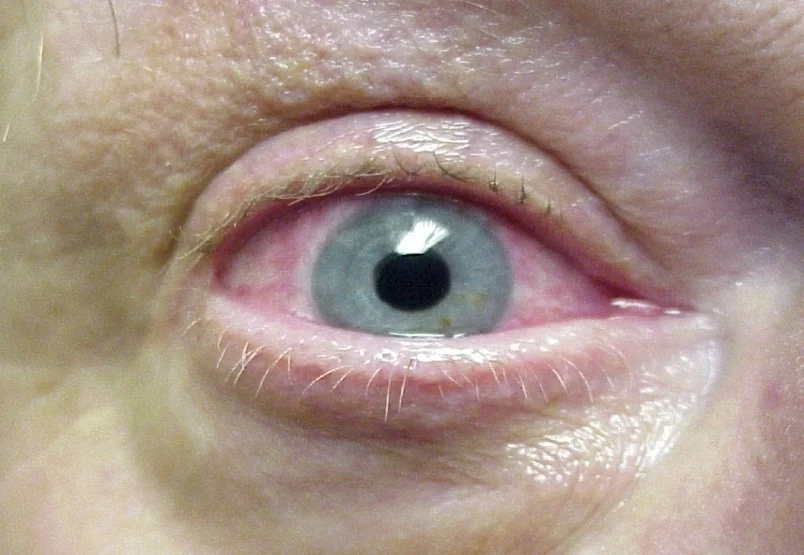
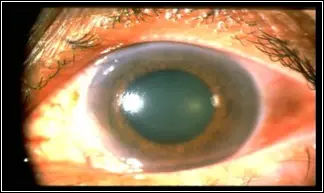
Symptoms and Diagnosis
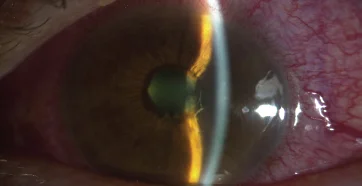
- Closed angles on gonioscopy
- High IOP over 60 or 70 mm Hg
- Cellular reaction in anterior chamber
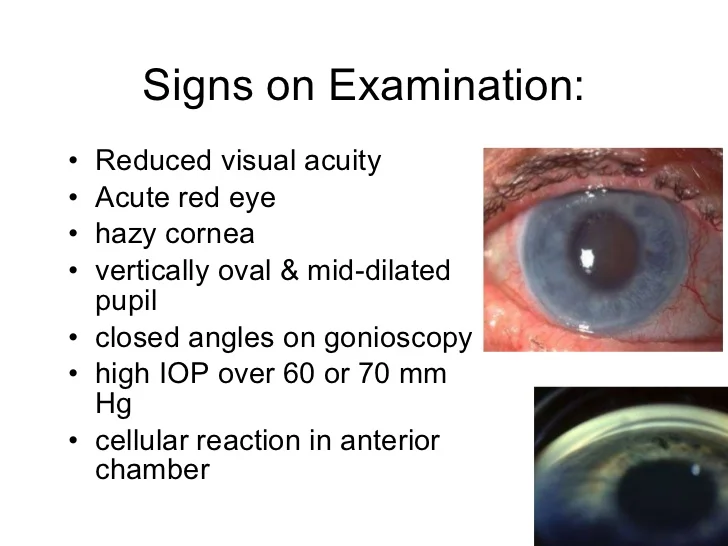
Treatment
-
Principle of therapy is to bring down the IOP as quickly as possible
-
Admit the patient
-
Counsel the patient to make her anxiety-free as far as possible
-
Give IOP lowering drugs
-
Reduce inflammation
-
LASER therapy
-
Beta-blockers
-
Miotics
-
Steroid Eye drops
-
IV Acetazolamide (Inj Diamox, 500mg IV) followed by (250 mg tablet TID)
-
If IOP is still more than 50mmHg
- Hyperosmotic agents:
- Mannitol 20%
- 1-2 gm/kg given I/V within 30-45 minutes
- Oral Glycerol 50%----1-1.5 gm/kg
- Mannitol 20%
- Raise serum osmotic pressure and withdraw fluid from the eye, especially from vitreous
- Vitreous dehydration allows the lens to fall back deepening the AC
- Hyperosmotic agents:
Fellow Eye?
- Fellow eye should be treated with Pilocarpine eye drops 1 drop QID
- To be followed by prophylactic LASER Peripheral Iridotomy