Marasmus
Definition:
It is a form of undernutrition characterized by failure to gain weight due to inadequate caloric intake.
Incidence:
Commonly in infants between the age of 6 months to 2 years. Z
Etiology
Malnutrition / Chronic diseases
- Dietary errors
- Infection: T.B, pyelonephritis
- Gastroenteritis
- Parasitic infestations: Ascaris, ankylostoma, giardia
- Congenital anomalies: Large V.S.D , renal agenesis, pyloric stenosis (interrupted feedings, tachycardia consuming more calories)
- Metabolic diseases: Galactosemia, Fructose intolerance
- Prematurity
- Some cases of mental retardation
- Low socio-economic status
- Endocrine causes: DM, hyperthyroidism
Assessment of Infant with Marasmus
Failure to thrive loss of weight (weight < 60% of expected) Z
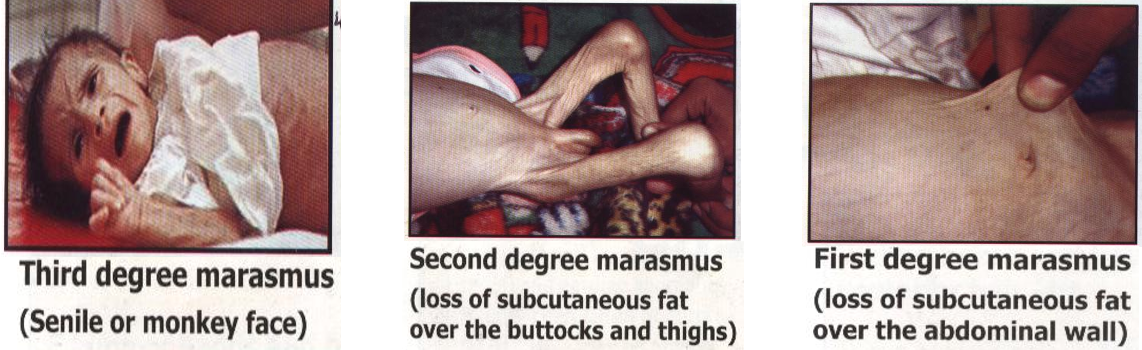
Loss of subcutaneous fat: Z measured at many parts of the body according to the degrees:
- 1st degree: s.c fat in the abdominal wall
- 2nd degree: s.c fat in the abdominal wall and limbs - buttocks, Thighs
- 3rd degree: s.c fat in the abdominal wall, limbs, and senile monkey face
Features Z
- Muscle wasting: thin muscles and prominence of bony surfaces
- G.I.T disturbances: anorexia in advanced cases, hunger, constipation, or diarrhea
- Liability to infection
- Hypovolemia
- Weak feeble pulse, subnormal temperature, pulse rate
- Senile face
- Pallor
Complications of Marasmus
- Intercurrent infection: Bronchopneumonia is the cause of death
- Gastroenteritis
- Hemorrhagic tendency, purpura
- Hypothermia; low subcutanous fat
- Hypoglycemia; low glycogen stores
- Edema; Uncommon pure marasmus (marasmic kwashiorkor)
Investigations for Marasmic Infant
- Blood analysis: W.B.C, Electrolytes, Sugars, ketones, Plasma proteins
- Urine analysis: culture, sugar, ketones, calcium, phosphate, amino acids
- Stool analysis for parasites
- X-ray for chest and heart
- Tuberculin test for T.B.
Prevention
- Proper diet: balanced nutritional diet
- Encourage breastfeeding up to weaning
- Proper weaning
- Proper vaccination: measles, T.B., whooping cough
- Education regarding the cheap sources of balanced diet, family planning
- Proper follow-up of the growth rate
- Early treatment of defects or associated diseases
Treatment
-
A. Proper Dietary Management
- Adequate balanced feeding
- Teaching about nutritional needs, preparation of diet, technique of administration of food
- If there is vomiting or anorexia, give IV fluids or nasogastric tube feeding
- Gradual increase in the amount and concentration of formula (total calories is 120-200 cal/kg/d)
-
B. Treatment of the Cause
-
C. Emergency Treatment for Complications
-
D. Blood Transfusion
-
E. Vitamins and Minerals Supplementation