Head injury severity
| Severity | GCS |
|---|---|
| Mild | ≥ 13 |
| Moderate | 9- ≤ 12 |
| Severe | ≤ 8 |
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)-
is the leading cause of death in trauma patients- 50% of all traumatic deaths.
Primary injury the anatomic and physiologic disruption that occurs as a direct result of trauma
Secondary injury -extension (sequelae) of the primary injury, result from local swelling, increased ICP, hypoperfusion, hypoxemia, or other factors.
Aim: detection and treatment of primary injury and prevention of secondary injury
management
- Maintain BP >90 mmHg, PaO2 >60 mmHg (75-100mmHg)
- Assess GCS and lateralizing signs- pupil and motor function
- a neurological symptom that suggests an issue with one side of the brain or body
- Pupillary asymmetry >1 mm suggests intracranial injury
- Larger pupil is on the side of the mass lesion
- Extremity weakness- detected by testing motor power
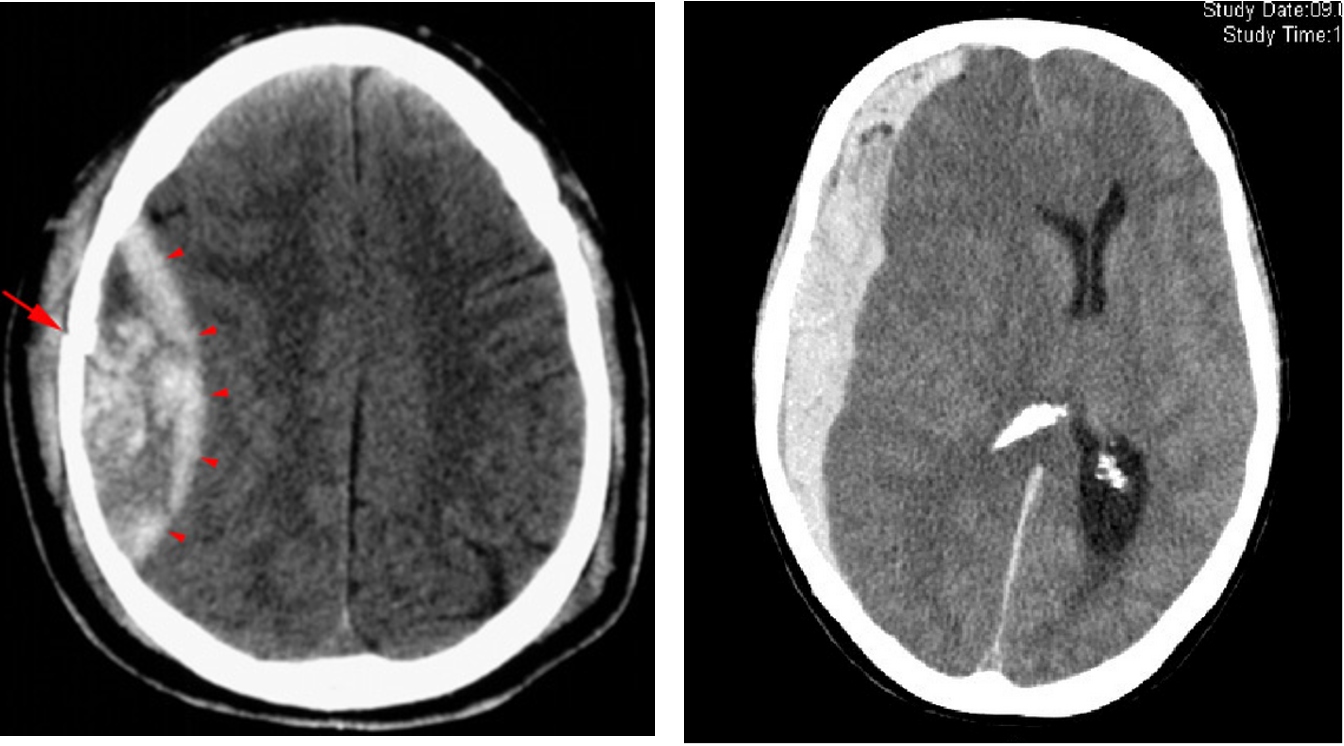
- CT scan head- accurate localization of the lesion
- Epidural or subdural hematoma: Treatment: evacuation
- Intracerebral hematoma & contusion
- Diffuse axonal injury: maintain brain perfusion & prevent rise in ICP.
(Image: Epidural Hematoma & Subdural Hematoma)