The importance of general examination:
- Helps to determine the most body system should be stressed during systems examination.
- With proper history the general examination may be enough to obtain the diagnosis OR a short list of diagnoses.
Components
- General patient condition
- Face
- Fever
- Pallor
- Jaundice
- Cyanosis
- Lymph nodes enlargement
- Hands , Digits & Nails
- Mouth , Oral cavity & Tongue
- Temperature
- Pulse rate
- Blood pressure
- Respiratory rate
- Neck Pulsation
General physical Exam
The clinician is the detective, gathering clues, and the physical assessment of a patient is the investigation itself!
Prepare the scene
- Purpose of General Physical Examination
- Prepare your equipment
- Provide Chaperones
- Prevent Infection
- Preparing the Patient for an Examination
- Position the patient
- Perform the right sequence of examination
Why do we assess patients ? Purpose of General Physical Examination
- Formulate a differential diagnosis
- Diagnose a medical problem
- Assess overall state of health
- Record a baseline values for vital signs
- Standardised approach to obtain a reproducible findings
- Correlate the physical findings with investigation
- Spot diagnosis
- Usually focuses on organ system based on patient’s chief complaint: Remember Signs Vs Symptom
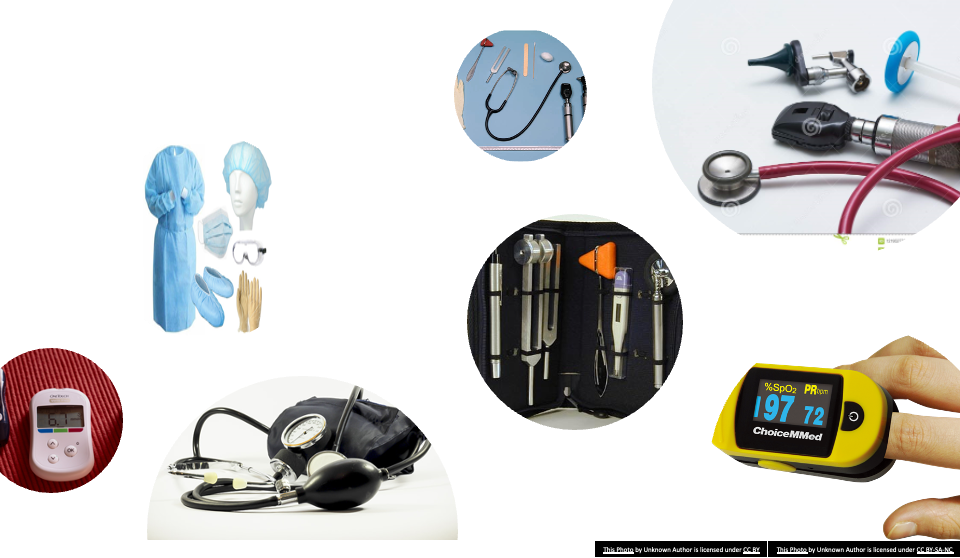
Equipment

Hand hygiene
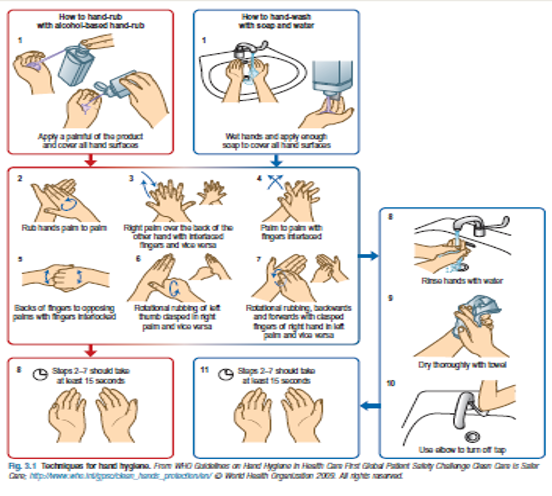
Preparing the Patient for an Examination
Remember WIPER
- Wash hands (before and after)
- Introduce yourself to the patient and seek his or her consent
- Position the patient correctly.
- Expose the patient as needed
- Right side of the bed
Ensure privacy
- Emotional – explain exactly what will occur
- Physical – offer the bathroom; instruct the patient on how to undress.
- Patient comfort is a priority ; coaver with appropriate drape, Keep warm.
Position
Positions facilitate physician’s examination
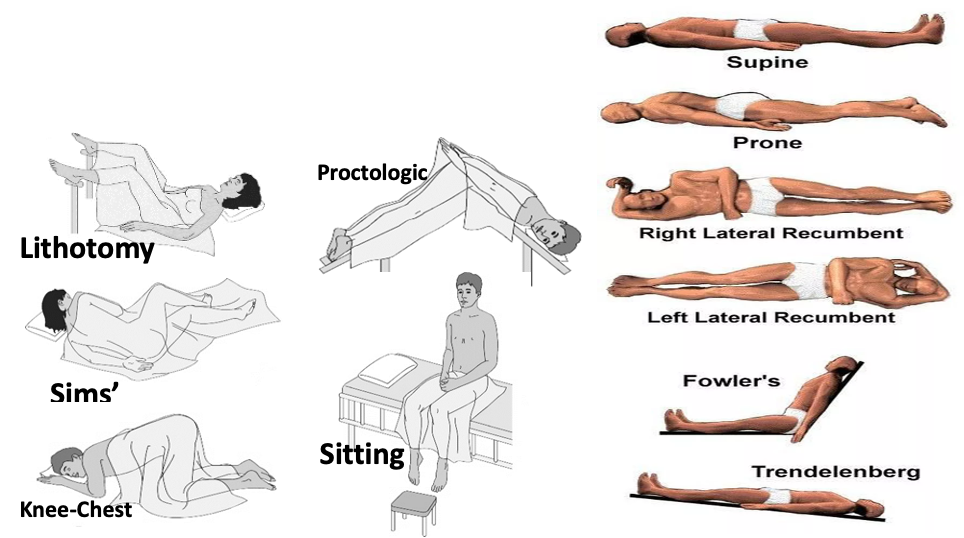
Sequence for performing a physical examination
First, decide how sick the patient seems to be: that is, does he or she look generally ill or well?
First impression:
- Gait and posture
- Facial expression and speech
- Body habitus and nutrition
- Hydration
- Spot diagnoses
Vital signs
- Hands
- Head & Neck, Eyes, ENT
- Lymph-nodes
By measuring X
- Pulse
- Blood pressure
- Temperature
- Respiratory rate
- BMI
- GCS : Glasgow Coma Scale
- They provide important basic physiological information.
The body
- Chest and lungs, heart, breasts
- Abdomen, genitalia, and rectum
- Musculoskeletal and neurological systems
Examination Methods
Inspection
- Visual examination
- Assesses posture, mannerisms, and hygiene
- Size, shape, color, position, symmetry
- Presence of abnormalities
Palpation
- Touch texture, temperature, shape
- Presence of vibration or movements
- Superficial or with additional pressure
Percussion
- Tapping and striking the body to hear sounds or feel vibrations
- Determine location, size, or density of structure or organ.
Auscultation
- Listening to body sounds
- Assess sounds from heart, lungs, and abdominal organs
General appearance
-
Skin – a good indicator of overall health
-
Hair – pattern of growth and texture
-
Head & Face -Abnormal condition of scalp or skin -Puffiness -Abnormal growths
-
Throat; swelling or redness
-
Ears -Outer ear -Symmetry and size -Presence of lesions, redness, or swelling -Inner ear structures -Canals -Eardrums
-
Nose and sinuses -Nasal mucosa -Structures of nose -Palpation to check for tenderness in sinuses
-
Neck -Lymph nodes and major blood vessels -Thyroid: -Inspection -Palpation Percussion -Auscultation
-
Eyes -The presence of disease or abnormalities -Pallor and jaundice -Pupils for light response