Right vs left
if macula is left sided from disc its left eye
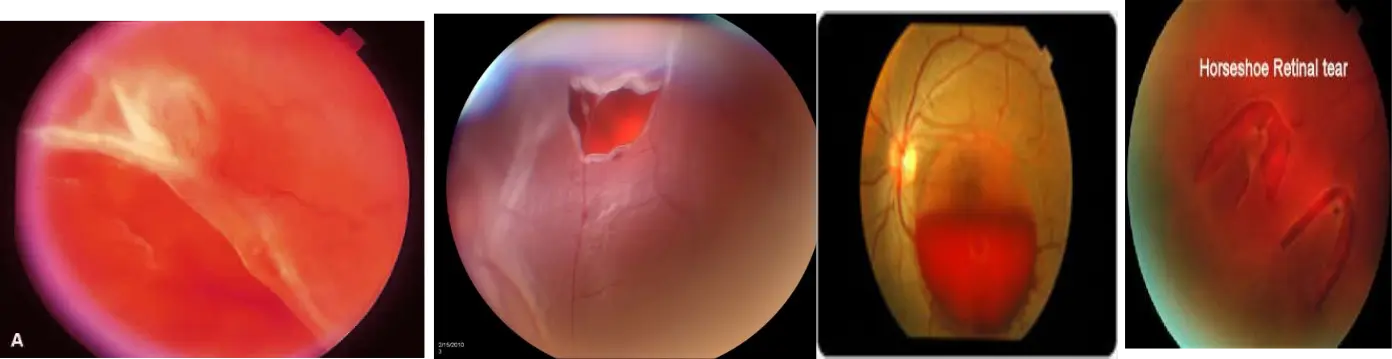
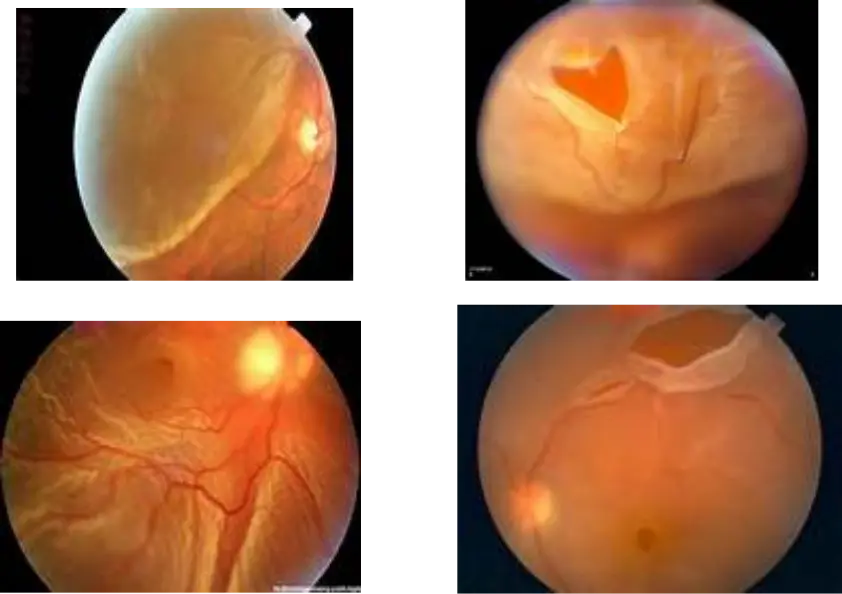
Retinal Detachment
Common presentation: Sudden, painless vision loss
Treatment:
- Close the tears: by photocoagulation, condensation, electric coagulation
- If total: Surgery:, Scleral buckling: Virectomy and Retinopexy
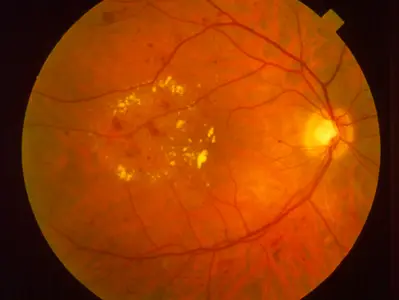
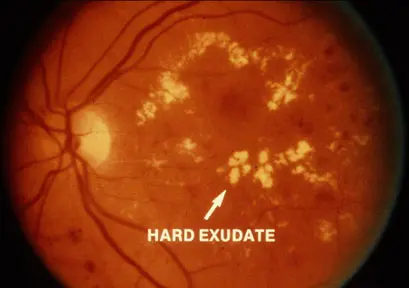
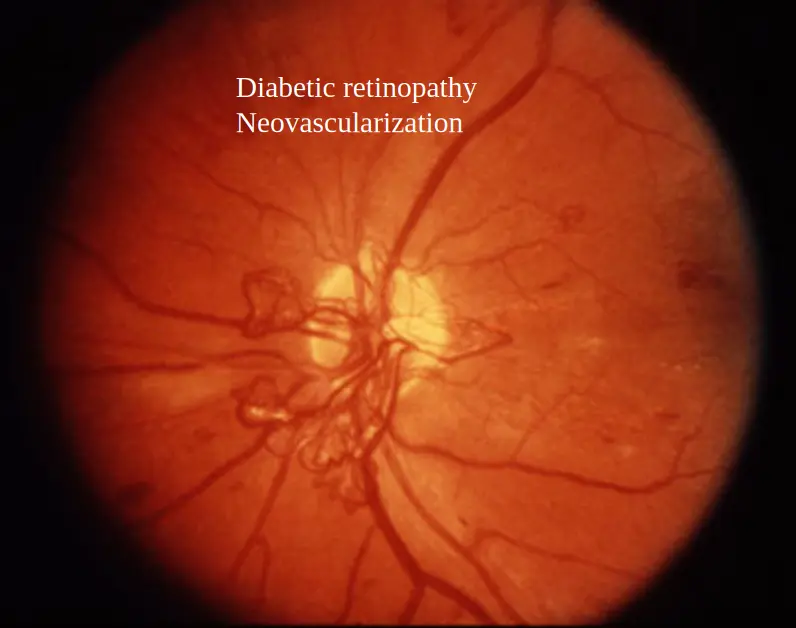
Diabetic retinopathy
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy: If there are exudates and hemorrhages only, with no abnormal vessels, it is
Presentation:
- gradual painless vision loss
First Pathological changes:
- Microaneurysm
Treatment:
- Argon laser grid pattern
- intravitreal injection
- surgery
 Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
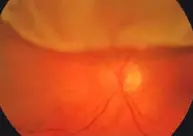
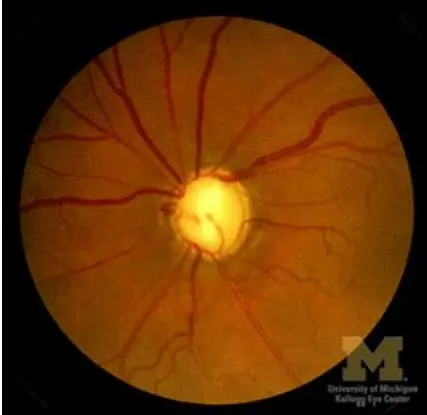
Describe the optic Disc
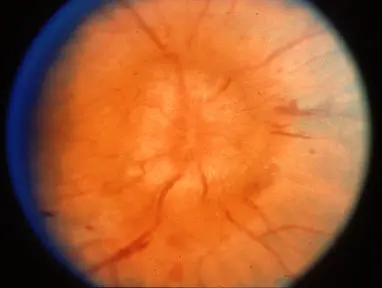
Optic disc swelling
optic neuritis - unilateral swelling, acute loss of vision
Describe the veins Y
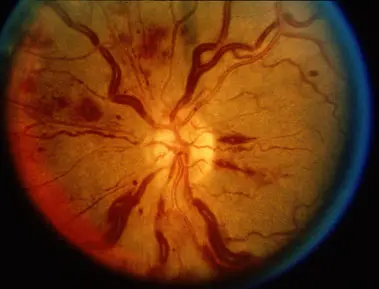
Diabetic retinopathy
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Exudates
- Microaneurysms
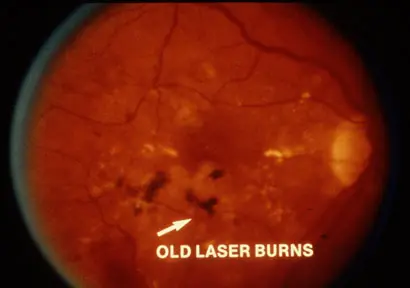
Pattern of Laser?:
Argon laser PRP (Panretinal Photocoagulation)
Indicated for:
- PDR (Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy)
- Ischemic central retinal vein occlusion
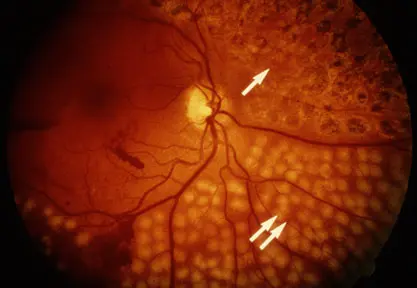
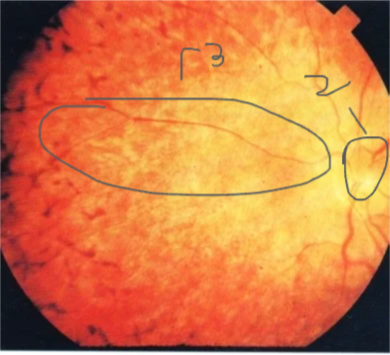
Retinal Photo of diabetic patient
 New neovascularization = PDR
New neovascularization = PDR
Treatment:
- PRP
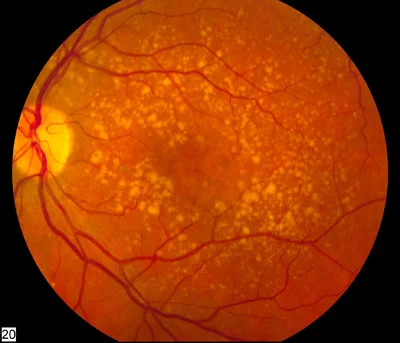
Retinitis Pigmentosa or Pigmentary retinopathy
- Pigmentation in periphery
Symptoms:
- Night blidness, Tunnel vision
- Gradual painless vision loss
- Photopsia
Fundus - three findings
- Optic disc wax color,
- Bone spicule pigment deposition
- *Attenuation or narrowing blood vessels
Treatment:
- Genetic counseling
- Avoiding sunlight and UV
- Vasodilator, Vitamins
- Supplement of taurine
- Low vision aids
- Grid laser coagulation is used with caution for CME
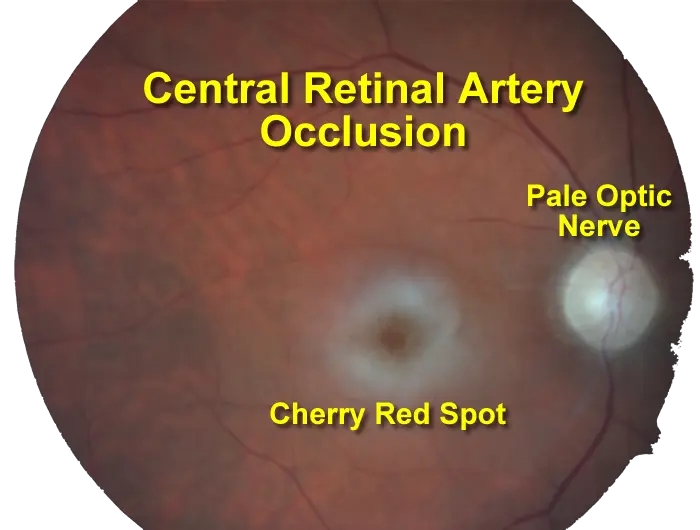
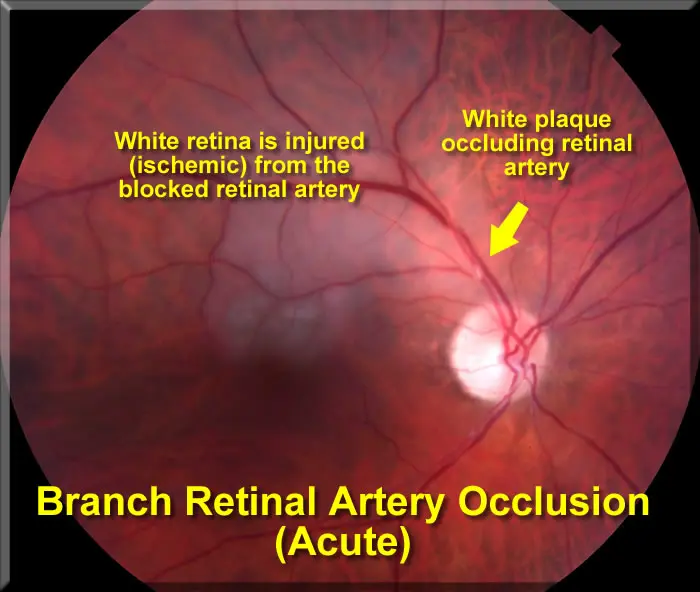
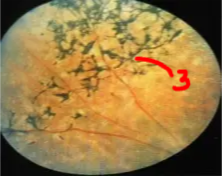
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
Symptom
- Gradual painless vision loss
Copmlications
- macular edema
- changes to ischemic type
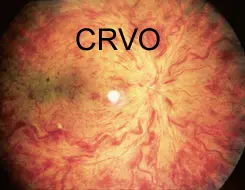 CRVO
CRVO
Central retinal artery Occlusion (Cherry red spots)
Sign:
- Cherry red spots
Presentation:
- Acute painless visual loss
Resuscitation of retina from 1-4 hours
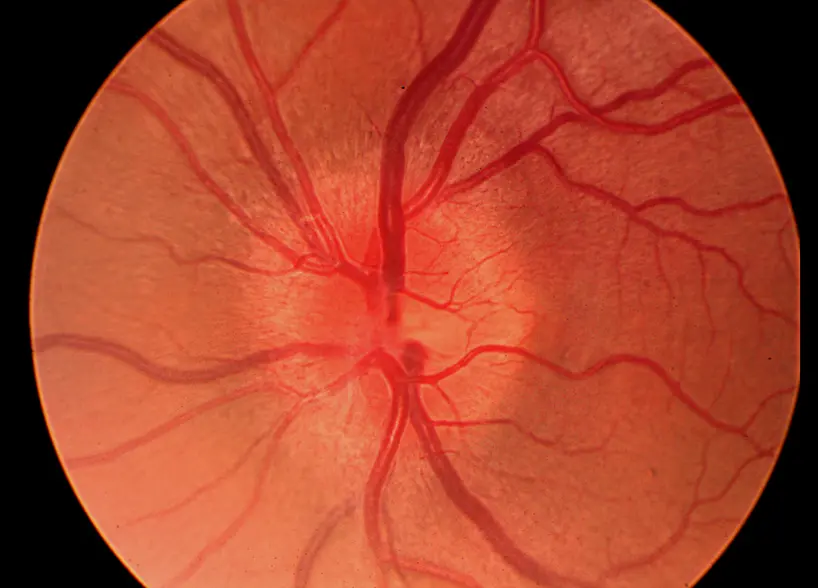
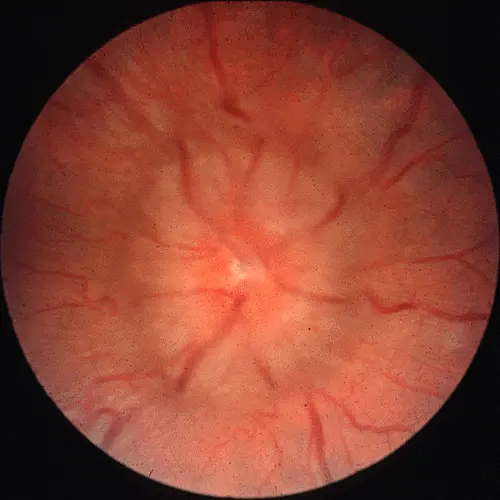
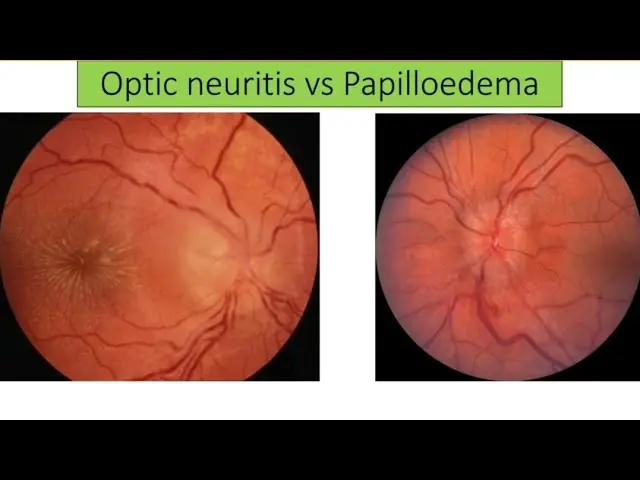
Optic Disc Swelling
-
Optic Disc Swelling: Needs diagnosis based on cause.
-
Differentiating Causes: Check if Unilateral or Bilateral & check Vision.
-
If Bilateral Swelling + Normal Vision (Early):
- Likely Papilledema (due to ↑ Intracranial Pressure).
- Usually no pain with eye movement.
- Look for headache, nausea. Needs neuro-imaging.
-
If Unilateral Swelling (or Normal Disc) + Acute Vision Loss + Pain with Eye Movement:
- Likely Optic Neuritis (Inflammation).
- Vision affected early and significantly. Color vision often poor.
- Needs investigation (e.g., MRI) for causes like MS.
-
Difference:
- Papilledema = Pressure problem, typically bilateral, vision okay initially.
- Optic Neuritis = Inflammation problem, typically unilateral, vision poor early, often painful eye movement.
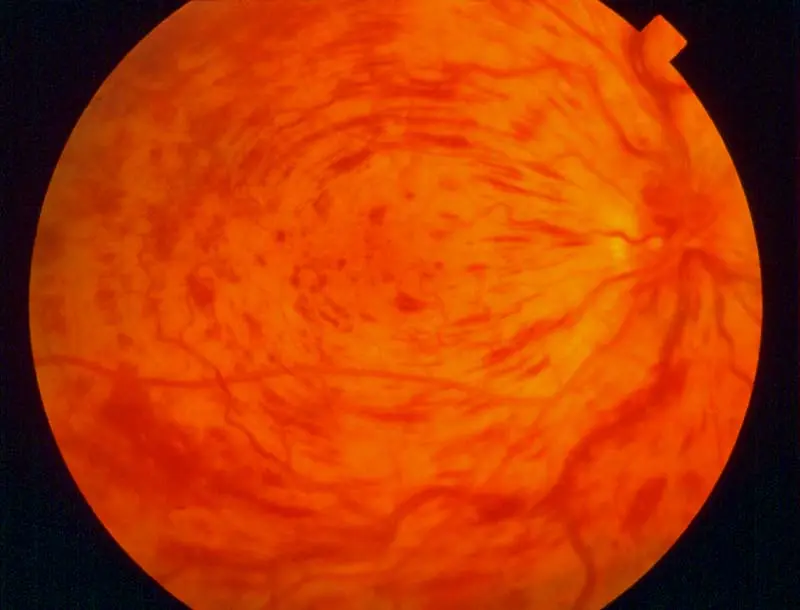
Central retinal vein occlusion
all of the following are a complication of this case EXCEPT ?
- A) ischemia
- B) Macular edema
- C) Neovascular glaucoma
- D) cataract
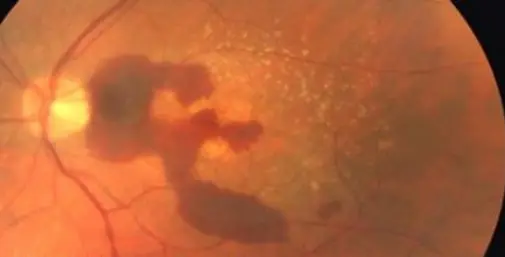
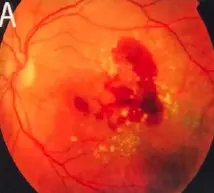
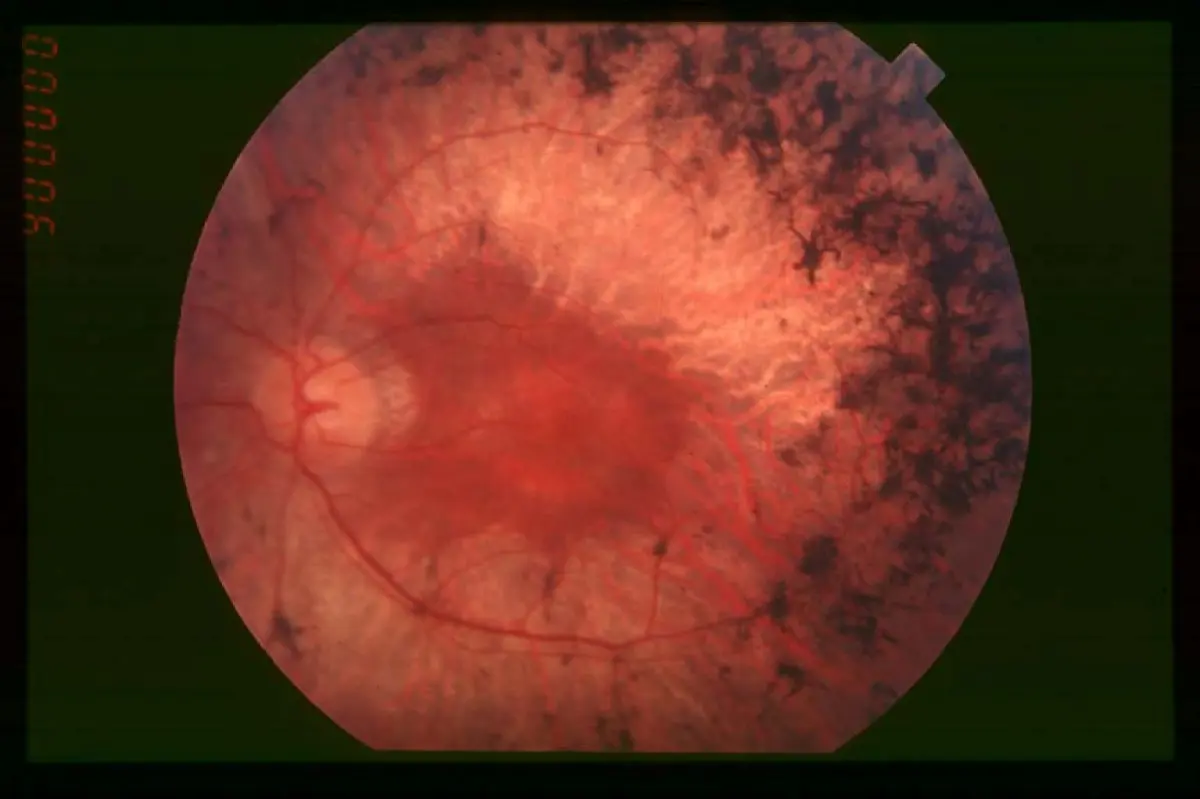
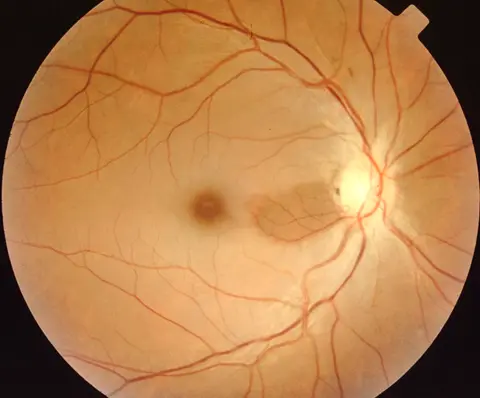
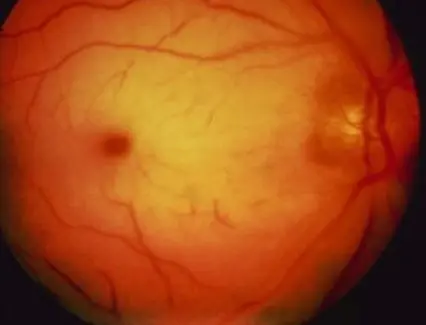
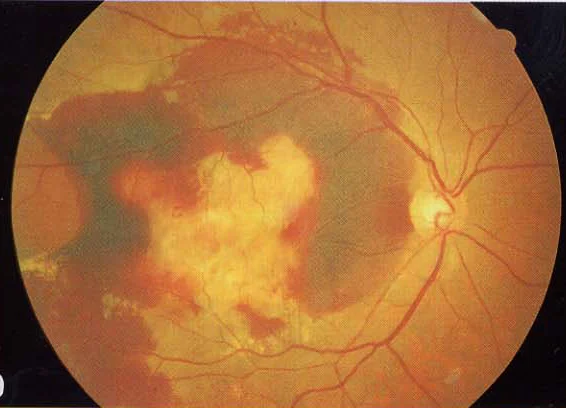
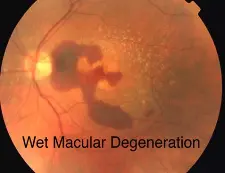
Wet macular age related degeneration
Male nondiabetic patient aged 75 years old presented by this picture in the left eye
What is treatment in this condition? Intravitreal injection of AVGF
-
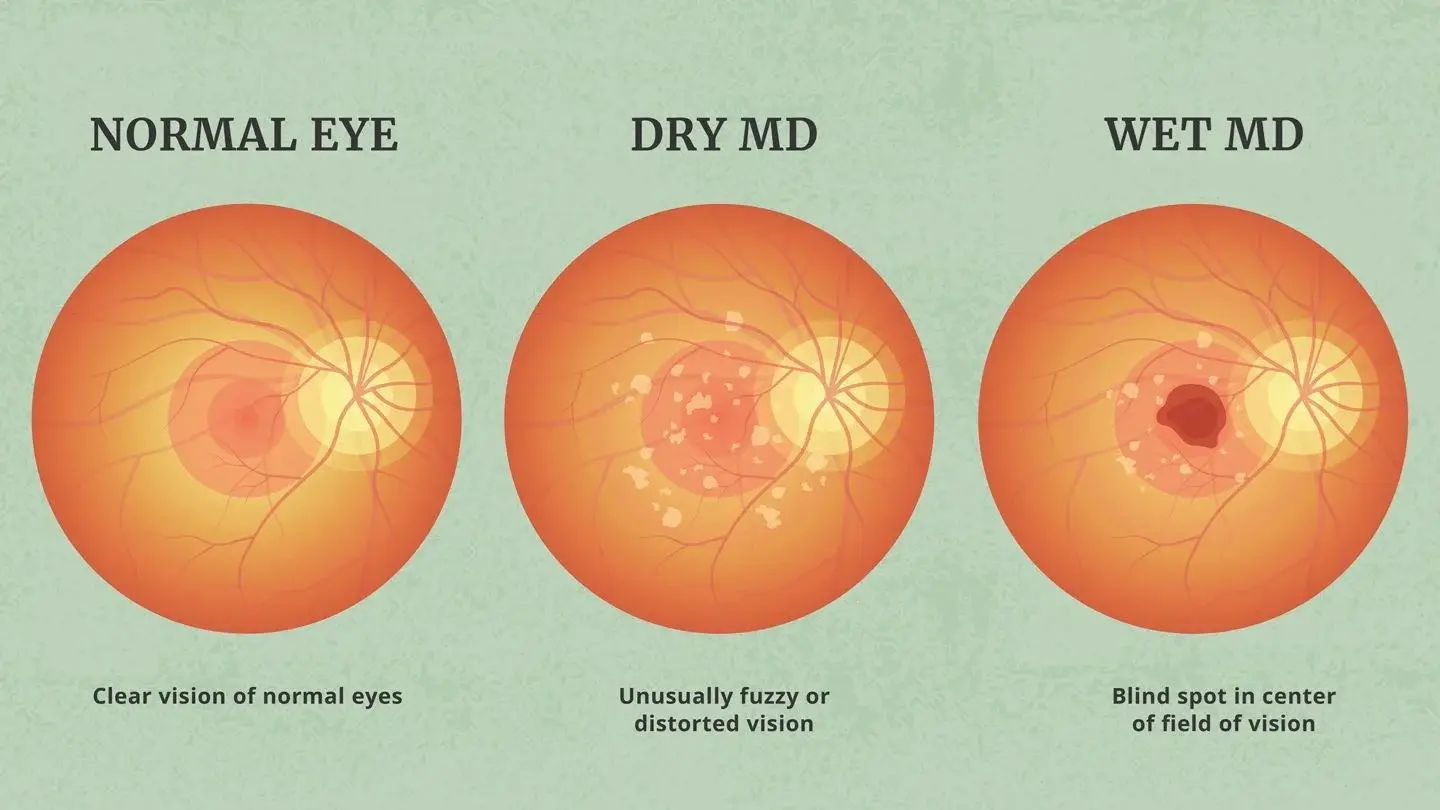
Fundus:
- Dry: drusen, RPE change
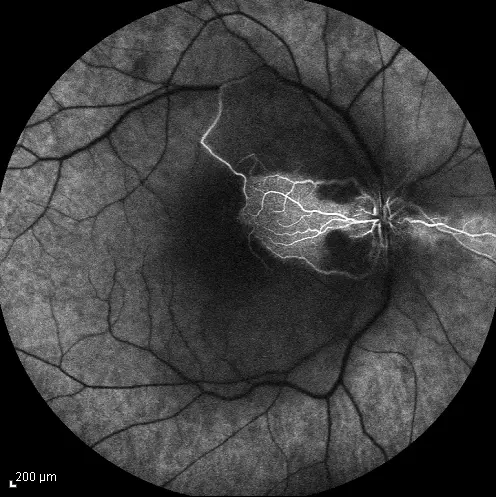
- Wet: gray-yellow CNV under retina of posterior pole, associated with dark red subretinal hemorrhage, which covers CNV sometimes
-
FFA: CNV leakage, bleeding
-
Nonexudate:
- Drusen
- RPE atrophy
- Degeneration of photoreceptor
- Choroid capillary atrophy
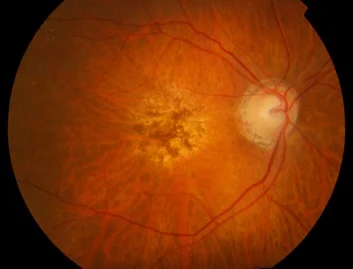
- Exudate:
- Drusen
- Damage of Bruch’s membrane
- CNV - corroidal new vessels
- Disciform scar formation under macula, bleeding and leakage of CNV
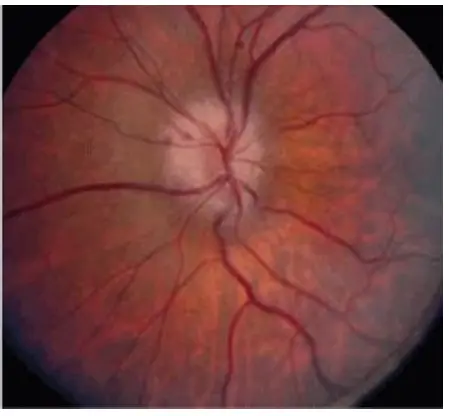
Optic neuritis
What is correct about this condition? Direct Pupil response is affected
Progressive optic neuropathy
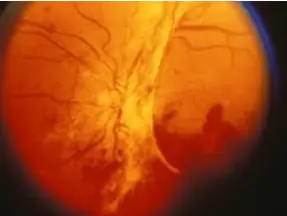 treatment? Laser and intravitreal injection.
treatment? Laser and intravitreal injection.
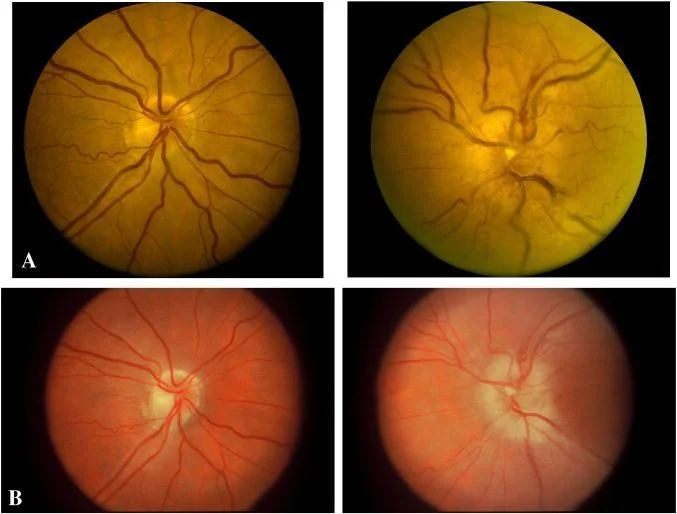
AAION: Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Mean age of onset: 70 years
- Headache is the most common symptom.
- Rheumatic myalgia (poly myalgia rheumatica)
- Scalp tenderness
- Jaw claudication
- Malaise, anorexia, weight loss, low-grade fever
- Severe visual loss, developing over hours to days.
- Pallid disc edema (chalky white appearance of the disc)
- Disc of fellow eye: normal