Therapeutics
Investigations to determine thyroid status
1- Tests to establish whether there is thyroid dysfunction
-
TSH (evaluate thyroid and pituitary functions) single best screening
-
Thyroid hormone (free & total ) concentrations in plasma (T3 & T4) (free T3 and T4 provide more reliable) (total T3 and T4 for ttt monitor)
2- Tests to elucidate the cause of the thyroid dysfunction:
-
Thyroid autoantibodies ( Anti-TPO – TSI – TG Abs)
-
Serum thyroglobulin (TG) : response to antithyroid, as tumor marker
-
T3 Resin uptake: measure unsaturated (TBG) in blood = amount of T4
-
calcitonin test: for medullary thyroid cancer in solitary thyroid nodule
-
Biopsy of the thyroid
-
Ultrasonography (sonar) of the thyroid
-
Radioactive iodine uptake scanning of the thyroid
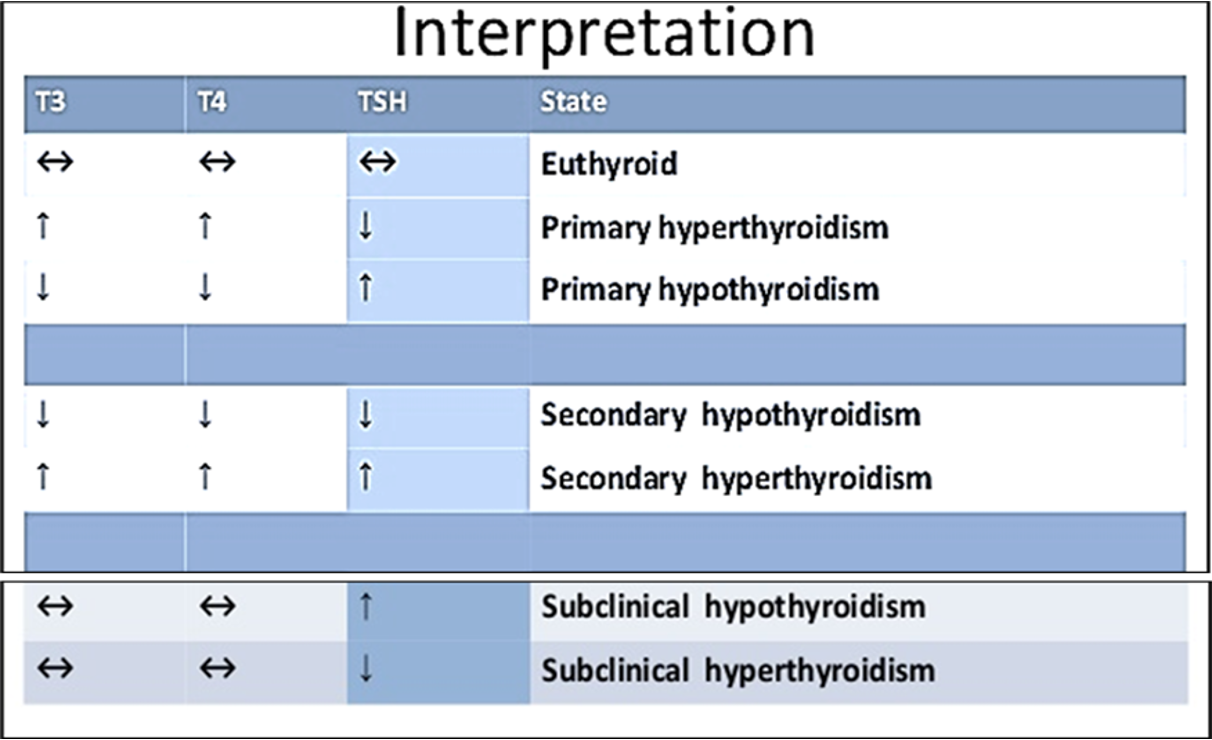
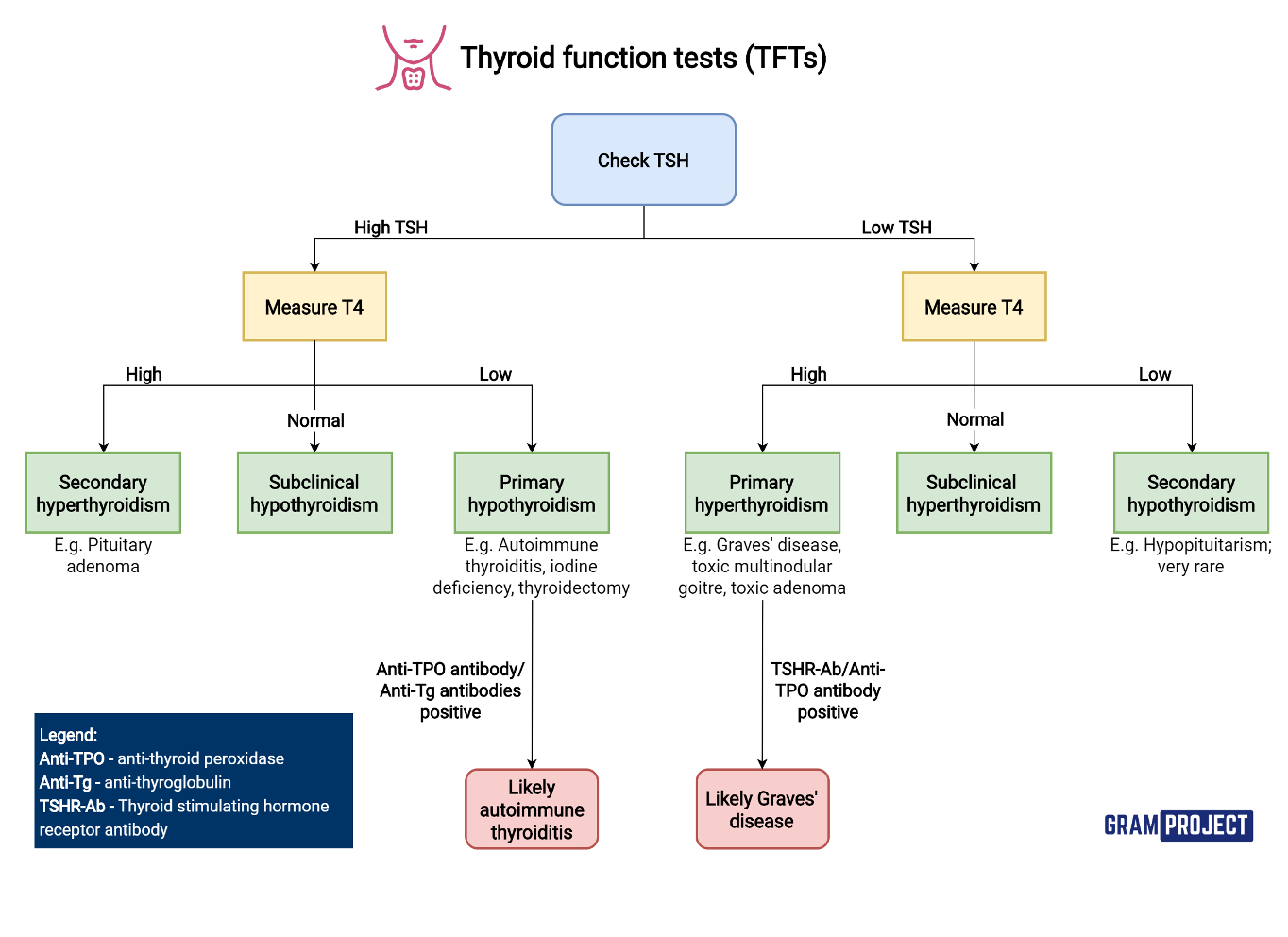
Plasma TSH (Thyrotropin): ++++ 1st to be assessed
TSH concentration in plasma is elevated ↑ in cases of :
-
Primary hypothyroidism: under secretion of thyroid hormones due to causes in thyroid gland
-
Secondary hyperthyroidism: over secretion of thyroid hormones due to hyperfunction of the anterior pituitary that secretes TSH
TSH concentration in plasma is reduced ↓ in cases of :
- Primary hyperthyroidism: over secretion of thyroid hormones due to causes in thyroid
- Secondary hypothyroidism: under secretion of thyroid hormones due to hypofunction of the anterior pituitary
TSH May be misleading in:
-
1st trimester of pregnancy; TSH may be very low (less than 0.1 mU/L) in 3% of cases due to the weak thyrotrophic effects of human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) which is high in this period
-
First 4-6 month of hyperthyroidism treatment; TSH may be still low even T3 & T4 are normal (or even below normal) so, follow up of patients during this period by. TSH is not reliable