EM
Tension-type headache
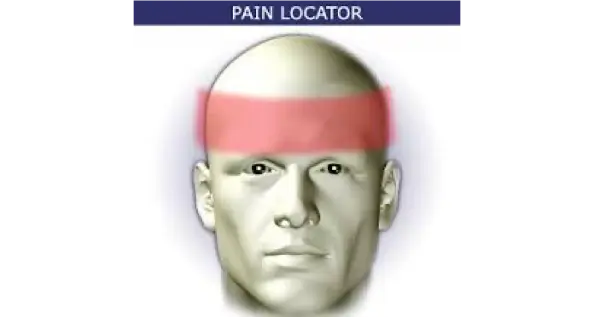
Tension headache is generally a diffuse, mild to moderate pain in your head that’s often described as feeling like a tight band around your head
- Most common type of primary headache
- Women> men
Tension headaches are divided into two main categories — episodic and chronic.
-
Episodic tension-type headaches are defined as tension-type headaches occurring fewer than 15 days a month,
-
chronic tension headaches occur 15 days or more a month for at least 6 months
| Category | Criterion |
|---|---|
| A | At least 10 episodes occurring >1 but <15 days per month for at least 3 months and fulfilling criteria B – D |
| B | Headache lasting from 30 minutes to 7 days |
| C | Headache has at least two of the following characteristics
|
| D | Both of the following
|
| E | Not attributed to another disorder |
Tension pathophysiology
- Tension headaches are caused by muscle contractions in the head and neck regions.
- Various precipitating factors may cause tension-type headaches in susceptible individuals:
- Stress: usually occurs in the afternoon after long stressful work hours or after an exam
- Sleep deprivation
- Uncomfortable stressful position
- Irregular mealtime (hunger)
- Eyestrain
- Other triggers---alcohol, smoking, cold temperature, caffeine, dehydration etc
Treatment
- Reassurance
- Avoiding triggers
- stress management techniques---regular exercise, deep breathing techniques, biofeedback cognitive behavioral therapy.
- Other nonmedicinal approaches--- yoga, massage, heat, ice, acupuncture(chronic tension headache), physiotherapy(for musculoskeletal symptoms)
Drug therapy
- acute management-analgesics acetaminophen, NSAIDS
- prophylaxis—TCAs(amitriptyline), SSRIs,s supplements such as riboflavin
IM
Tension Headache
- Most common type of headache
- It is due to head and neck muscles becoming tense and tight
Clinical Features:
- a. Usually bilateral, in the forehead, neck or generalized
- b. Like a tight band around the head (not throbbing)
- c. No nausea/vomiting
- d. Scalp & forehead tenderness usually MOJOOD
- e. Patient may have sensitivity to light & sounds (like migraine)
- f. No neuro features or aura
Triggering Factors
Mostly same as migraine (lack of sleep, dehydration, loud noise, glaring lights, stress etc)
Acute Treatment:
- a. Take a nap
- b. Eat something/ take fluids
- c. Simple analgesics like Panadol, NSAIDs. Muscle relaxants may be added (Relaxon tabs)
- d. No triptans or other migraine specific drugs
- e. Apply cold or hot packs to the head
Chronic Treatment:
Given if very frequent headaches.
- Antidepressants (amitriptyline)
- Relaxation techniques
Rapid Fire Questions on Tension Headache
- What is the cause of tension headache? tense muscles
- What are the triggering factors? lack of sleep, dehydration, sound light stress
- What is the treatment? Analgesics, Relaxon, Relaxation techniques
- Triptans and ergotamine are very good for this, right or wrong? wrong
- What is the nature of the headache? tightnening band, dull ache
- Any aura or neuro features? no
- Any associated nausea /vomiting? no
FM
Tension-type Headache
- Most common type of primary headache
- More in women than men .
- Mild to moderate in intensity
- Bilateral
- Pressing and tightening (non-pulsating) headache
- Not aggravated by movement such as walking or climbing stairs.
Pain Locator
- Most common type of primary headache
- More in women than men.
- Mild to moderate in intensity
- Bilateral
- Pressing and tightening (non-pulsating) headache
- Not aggravated by movement such as walking or climbing stairs.
Treatment
- OCT pain relieves: Aspirin or ibuprofen.
- Combination therapy: Aspirin or acetaminophen with caffeine or a sedative drug.
- Preventive involves the use of daily prophylactic medications antidepressants (amitriptyline low dose), behavioral therapies and physical therapy.
