Viral Warts
-
Warts (or verrucae), are benign growths on the skin or mucous membranes that cause cosmetic problems and discomfort.
-
Are seen in all ages but commonly appear in children and teenagers.
-
Viral warts (verruca) are due to infection of the skin and mucus membranes by human papilloma virus (HPV).
-
More than 80 different types of HPV are identified.
-
Have affinity for different tissues of the body as type 36 & 38 for the skin and usually they are benign.
-
While type 16 & 18 have affinity to mucus membranes and can change into cancer
Clinical types of viral warts (Verrucae)
1. Skin Infections:
- i. Common warts (verruca vulgaris),
- ii. Flat warts (verruca plana).
- iii. Plantar or foot warts (verruca plantaris).
2. Mucous membranes infection:
- Ano-genital warts (condyloma acuminata).
Pathogenesis
- Incubation period is 2 - 9 months
- Excessive proliferation of skin growth slowly develops
- More than 50% disappear within 2 years without treatment.
- HPV is passed from person to person by direct or indirect contact, and from one body location to another on the same person
- The virus enters the body through:
- Area of skin that is moist, peeling, or cracked
- Sexually transmitted as in Condyloma acuminita.
Skin viral warts – Clinical features
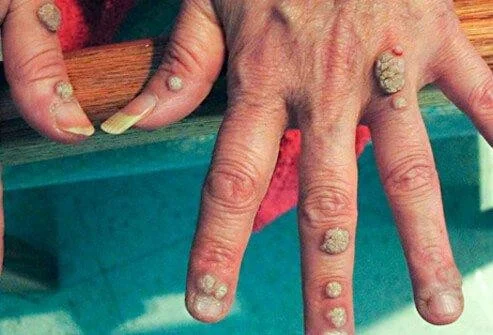
1- Common warts
- Appear most often on tops of fingers and hands
- As rough, thick, papules
- Develop as solitarily or in large numbers
- Small satellite warts may surround the original lesion (because the virus is usually present in a one-cm radius surrounding the wart)
2- Flat warts
- Are small, slightly elevated, flat-topped, pink or tan papules
- Are smoother than the common wart
- They occur primarily on the face, arms, and legs
- A person can have several, even hundreds of them
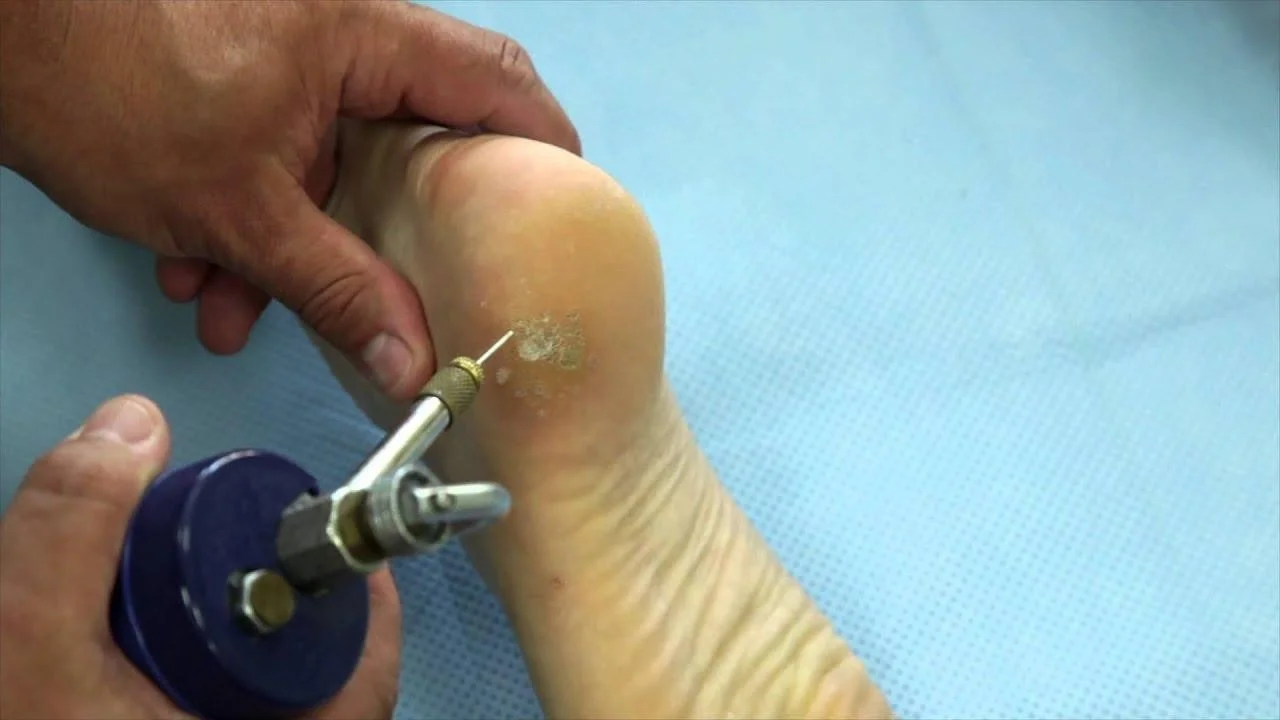
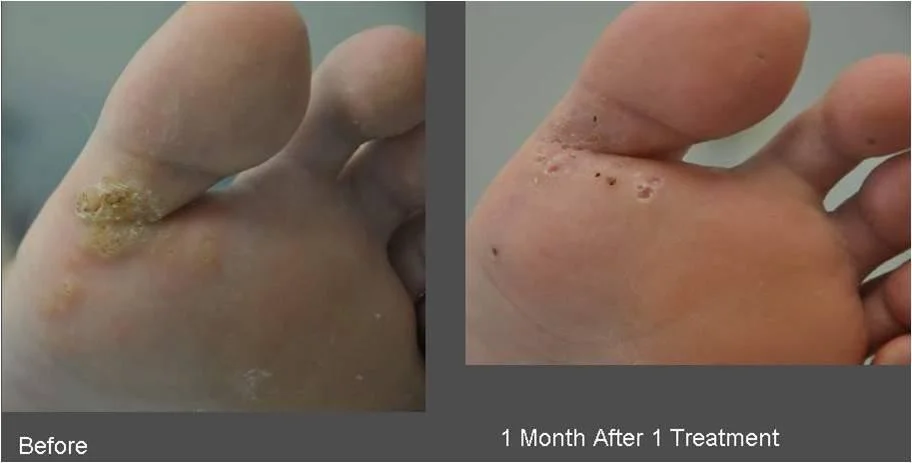
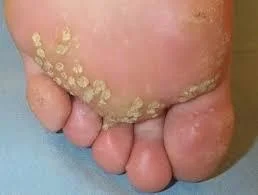
3- Plantar warts
- Occur on the soles of the feet
- Often thick and callused, grow inward,
- Can be painful
Mucosal viral warts - Clinical features
- Ano-genital warts (condyloma acuminata)
- Are gray in color that grow in mucous membranes
- Vary in size from small, shiny papules, to large lesions
- Can extend internally into the vagina and cervix, the rectal area, and inside the urethra
- Are painless, but there can be itching and burning
Diagnosis
- Is clinically
- No specific investigation is done
Treatment
- Common warts, especially in children, have a high rate of spontaneous remission, but without treatment, spread can occur
- Treatment is by physical or chemical destruction of the lesion
1) Physical destruction:
- Curettage: warts are anesthetized and then scraped with a curette
- Cautery: electrical burning of lesions
- Cryotherapy by Liquid nitrogen
- Surgical removal or excision
- LASER is used also for removal of warts
2) Chemicals destruction:
- Podophyllin:
- Used for mucous membranes especially genital warts ,should be used cautiously as it is toxic.
- Salicylic acid in high concentrations
- Silver nitrate in form of pencils
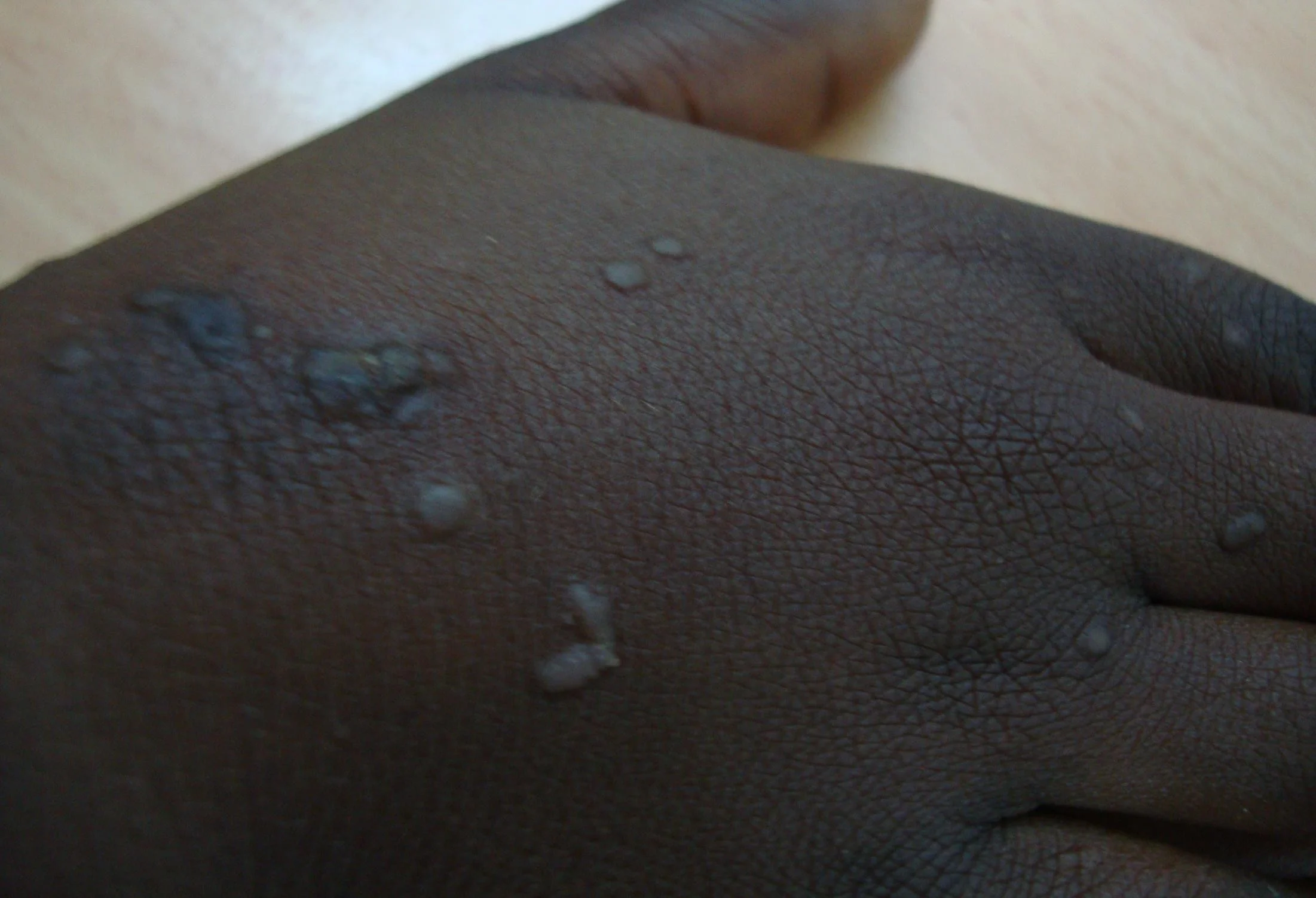
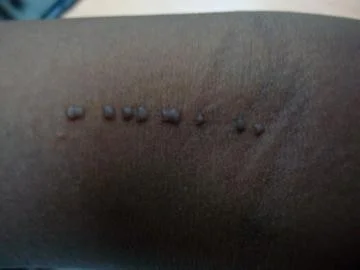 Linear lesion, localized papules
Linear lesion, localized papules


Cryotherpy