anti-glaucoma drug classes:
| Class | Examples | Mechanism | Key AEs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prostaglandin analogs | latanoprost, travoprost, bimatoprost, tafluprost | ↑ Uveoscleral outflow via FP-receptor | Iris pigmentation, eyelash growth, hyperemia |
| β-Blockers | timolol, betaxolol, levobunolol, carteolol | ↓ Aqueous production (↓ cAMP in ciliary body) | Bradycardia, bronchospasm, fatigue |
| α2-Agonists | brimonidine, apraclonidine | ↓ Aqueous prod. + ↑ uveoscleral outflow | Dry mouth, fatigue, ocular allergy |
| Carbonic anhydrase inh. | dorzolamide, brinzolamide (topical) | ↓ HCO3– formation → ↓ aqueous production | Stinging, taste disturbance |
| acetazolamide, methazolamide (oral) | Metabolic acidosis, paresthesias, stones | ||
| Rho-kinase inhibitors | netarsudil | ↑ Trabecular outflow, ↓ episcleral venous pressure | Conjunctival hyperemia, corneal verticillata |
| Miotics (cholinergics) | pilocarpine, carbachol | ↑ Trabecular outflow (ciliary m. contraction) | Miosis, brow ache, myopia in low light |
| Osmotic agents (acute use) | mannitol (IV), glycerol (oral) | ↑ plasma osmolality → ↓ vitreous volume | Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance |
| Fixed combos | Cosopt (dorzolamide+timolol), Simbrinza (brinzolamide+brimonidine) | Dual mechanisms | Combined AEs of components |
Ocular Toxicology


Digitalis
- A cardiac failure drug
- Causes chromatopsia (objects appear yellow) with overdose
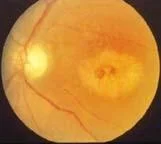
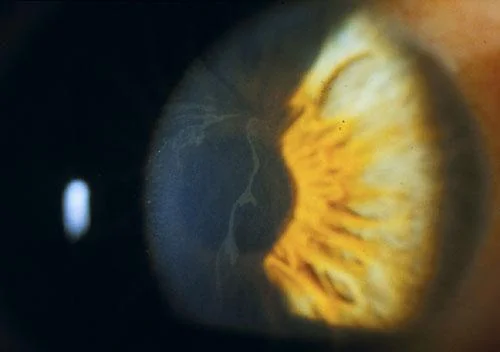
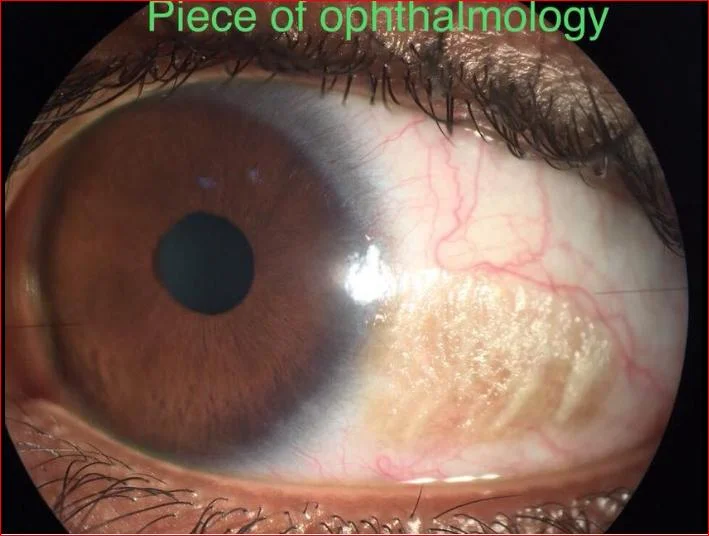
Chloroquines
- E.g. chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine
- Used in malaria, rheumatoid arthritis & SLE
-
Cause vortex keratopathy (corneal verticillata) which is usually asymptomatic but can present with glare and photophobia
-
Also cause retinopathy (bull’s eye maculopathy)
-
Ethambutol
- An anti-TB drug
- Causes a dose-related optic neuropathy
- Usually causes reversible but occasionally permanent visual damage
Other Agents
- Methanol – optic atrophy and blindness
- Contraceptive pills – pseudotumor cerebri (papilledema), and dryness (CL intolerance)
- Hypervitaminosis A – yellow skin and conjunctiva, pseudotumor cerebri (papilledema)
- Hypovitaminosis A – night blindness (nyctalopia), sterile corneal melting (keratomalacia), dry eyes (Xerophthalmia) and bitot’s spots