Kumr & Clark P: 1079-1091
Internal Medicine
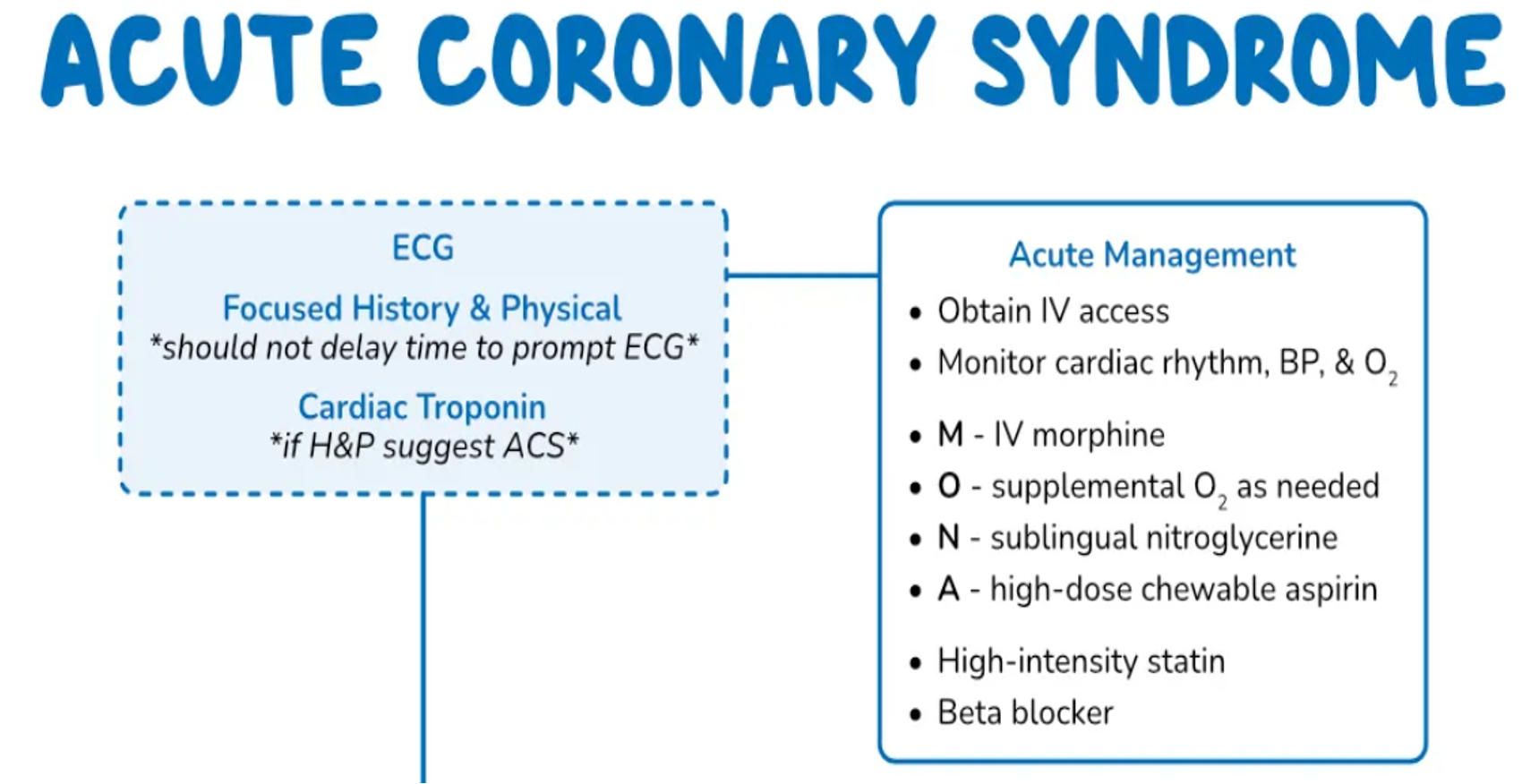
Acute Management
all simultaneously
- Efficient & direct history
- Initiate stabilization interventions
- Plan for further cardiac care
 Remember important Life threatening conditions causing chest pain
Remember important Life threatening conditions causing chest pain
- They
- Can’t
- Misses
Initial Approach
Chest pain suggestive of ischemia
Immediate assessment within 10 Minutes
Initial Labs and Tests
- 12 lead ECG
- Obtain initial cardiac enzymes
- electrolytes, cbc lipids, bun/cr, glucose, coags
- CXR
Emergent care
- History & Physical
- IV access
- Cardiac monitoring
- Oxygen
- Aspirin x
- nitrates & nitrites x
history & Physical
- Establish diagnosis
- Read ECG
- Identify complications
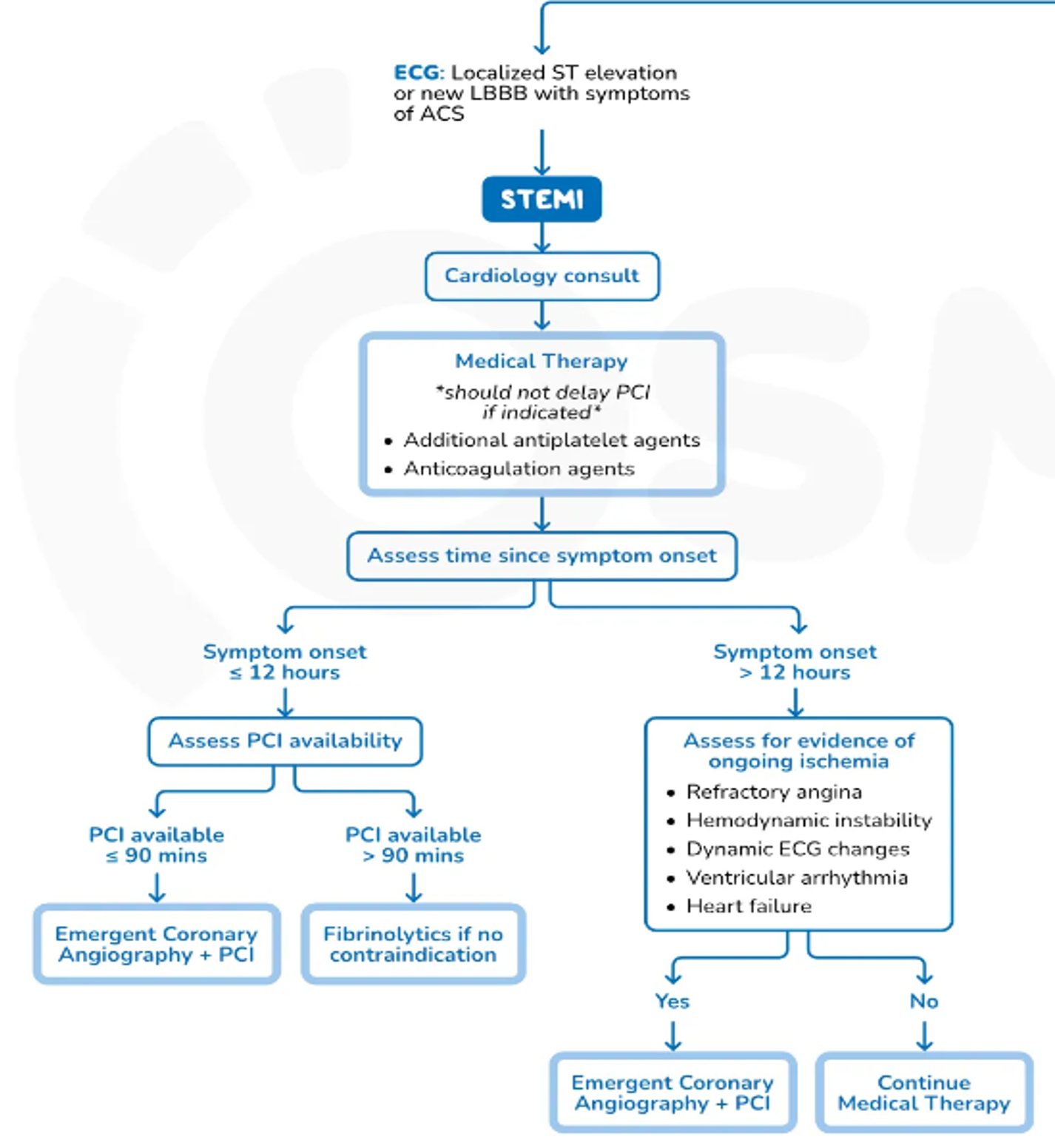
- Assess for reperfusion
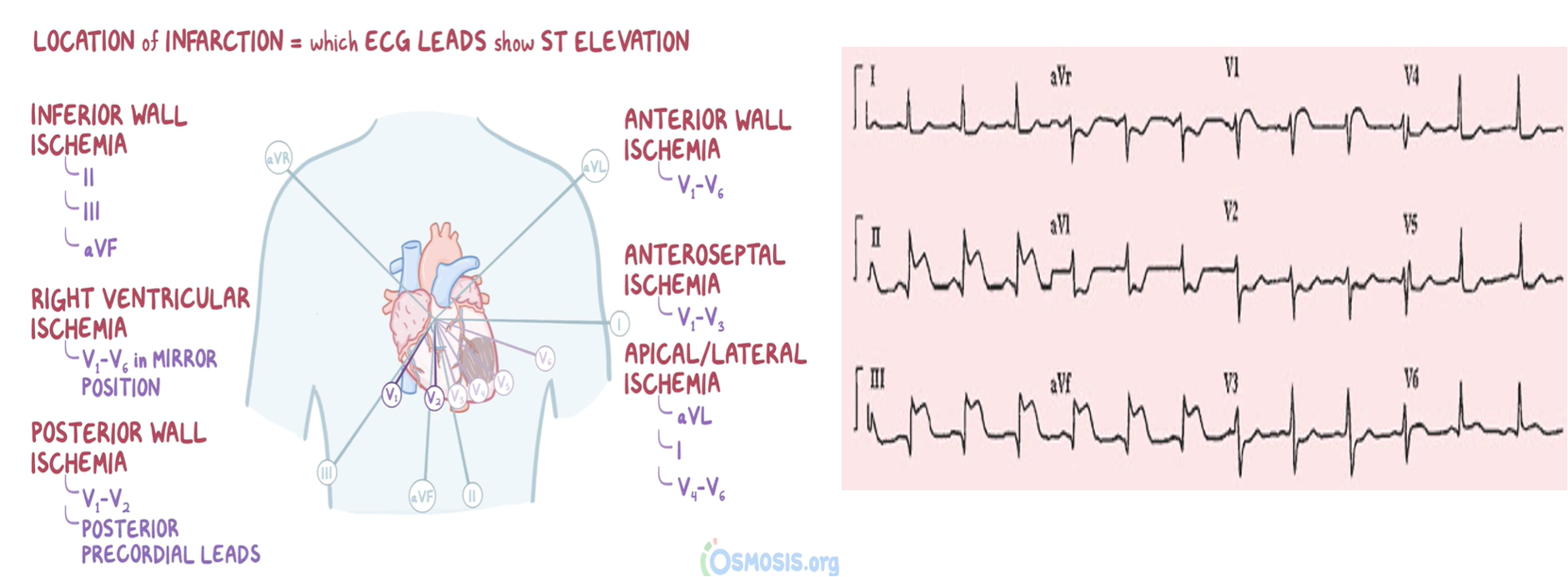
ECG Readings
Coronary Artery
COMMENT ON ECG
- ST ELEVATION IN LEAD II , III, aVF
- INFERIOR MI
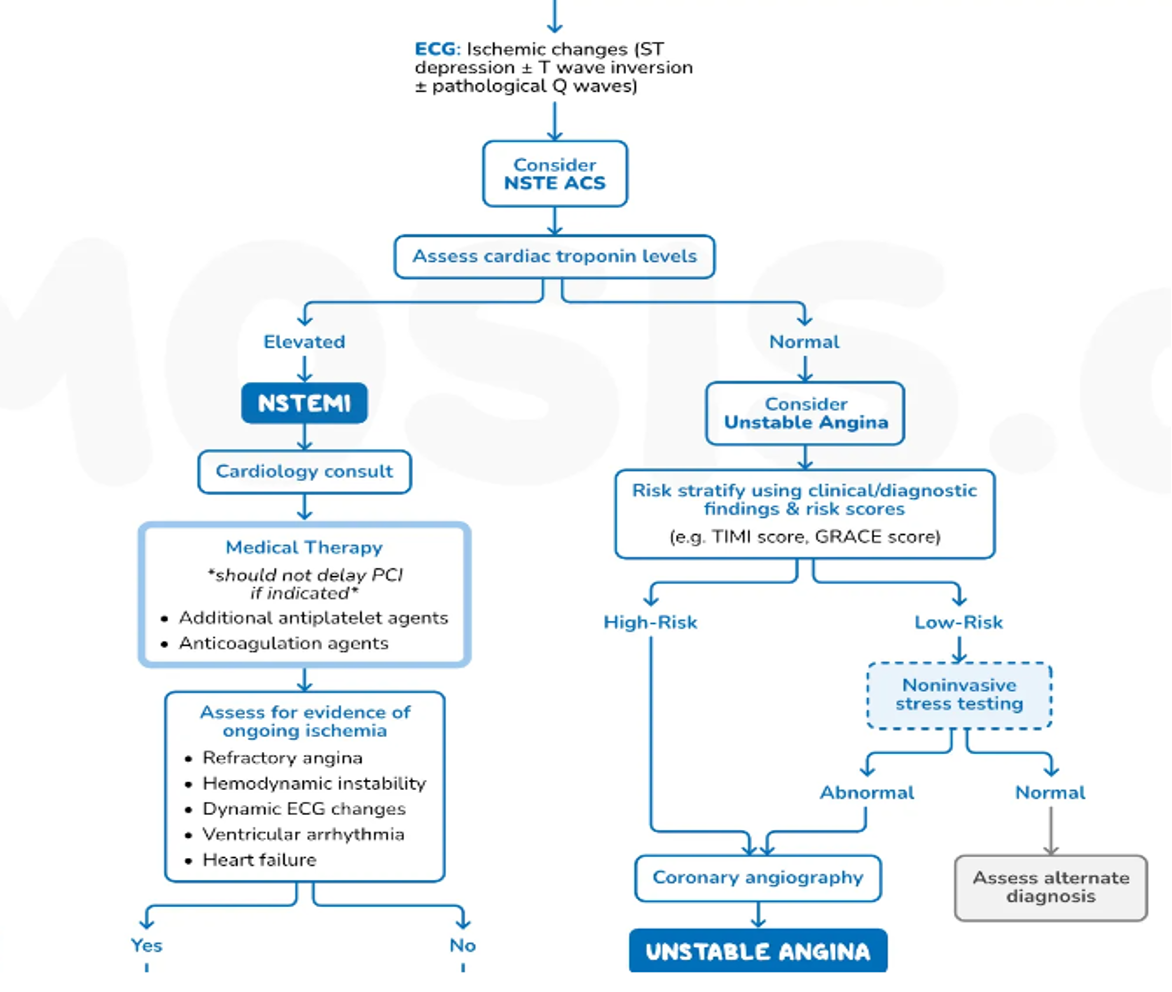
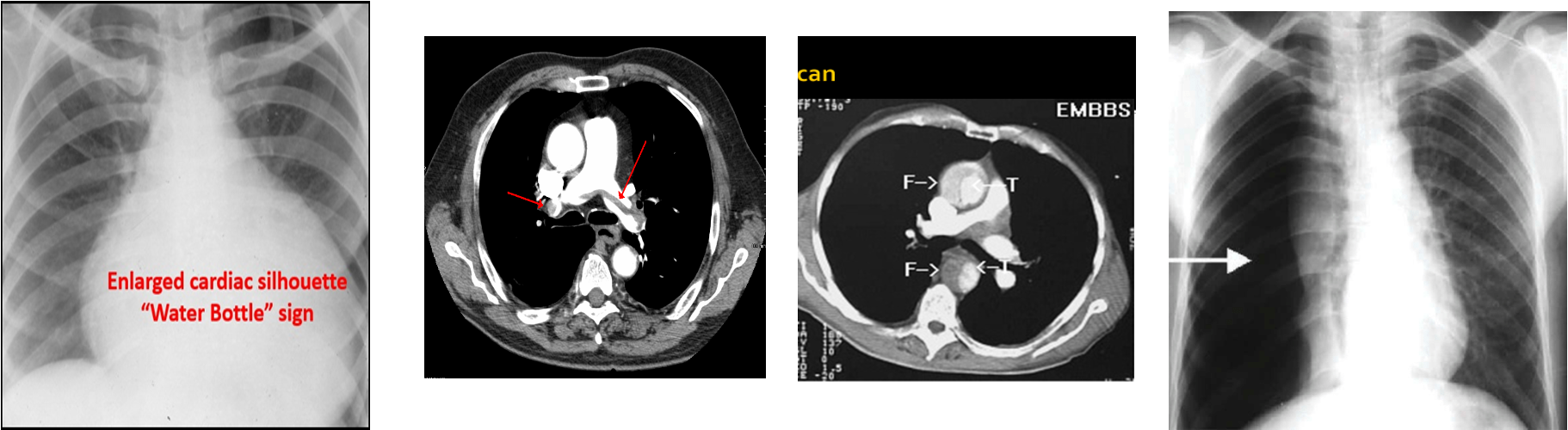
Posterior MI
0.5 mm or 0.05 mV

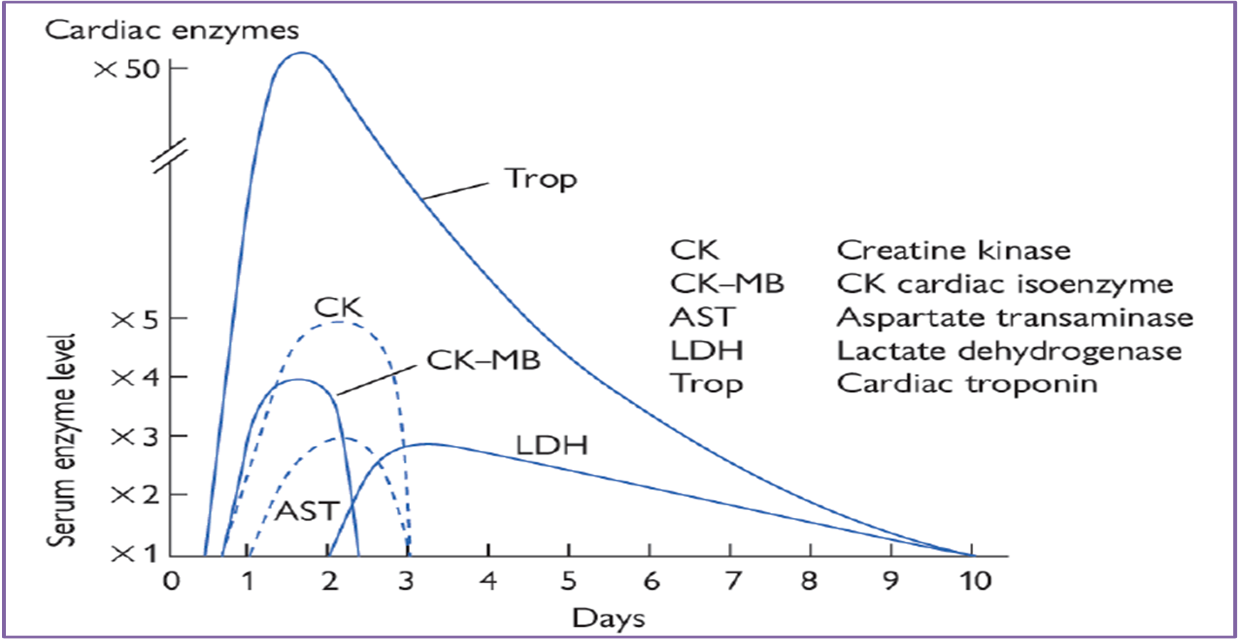
Investigations
-
Troponin T and I: highest sensitivity and specificity for detecting MI; appear within 4 hours; peak at 24 to 48 hours and decline slowly; remain 7 to 10 days
-
Creatine phosphokinase myocardial band (CPK-MB): first measurable at 6 to 10 hours; peaks at 24 hours; baseline by 48 to 72 hours
Acute coronary syndrome classification
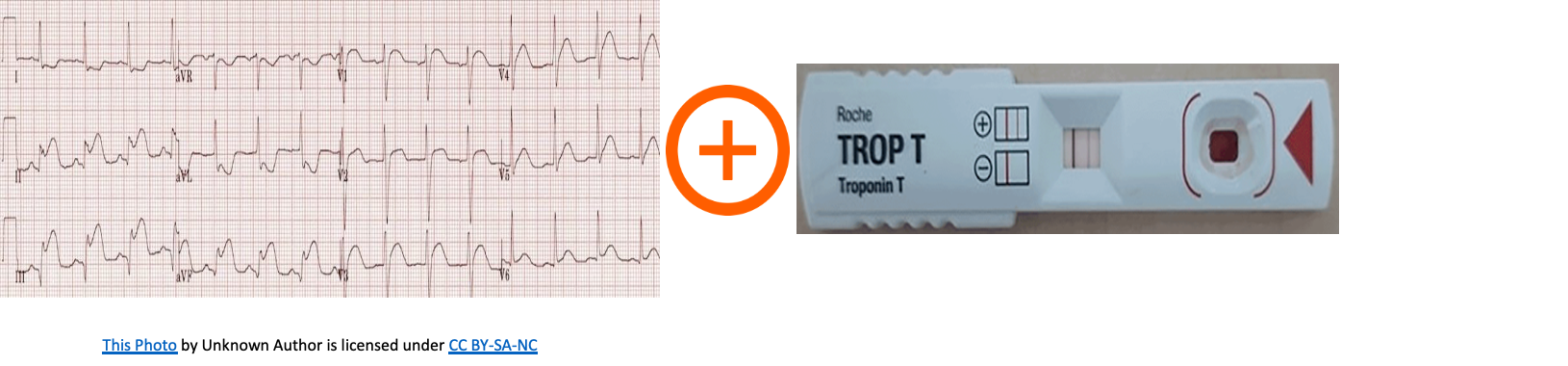

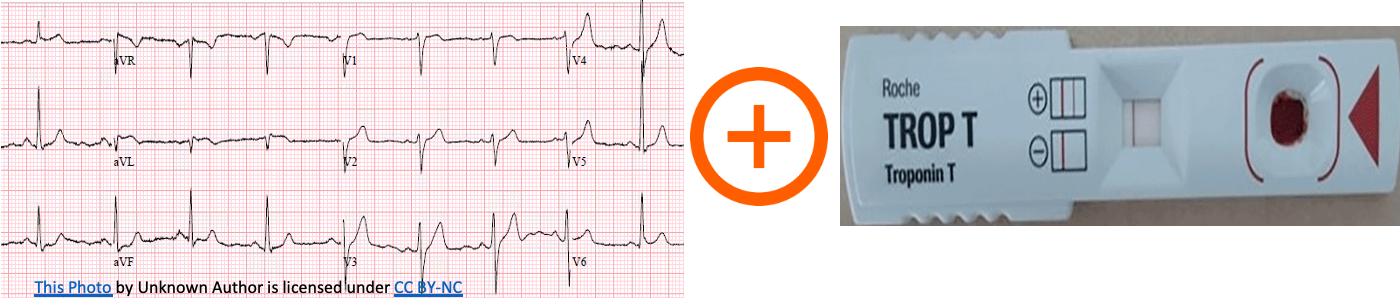
ACS Case scenarios
FM
Symptoms suggestive of ACS
- Pain in upper arms, back or jaw, that lasts longer than 15 minutes
- Pain in combination with nausea, vomiting,
- sweating & breathlessness.
- Pain in combination with dizziness or feeling light-headed
- New onset chest pain, or a sudden deterioration in previously stable angina.