IM
INVESTIGATIONS
Urine analysis Urine C/S Imaging
- Urinalysis : Take a clean, midstream, freshly voided sample (or catheter sample)
- Bacteria: ~ In females, 105 /ml of urine diagnostic of ~ In males, 102 /ml of urine UTI
- Nitrite: positive (produced by bacteria)
- WBCs : more than 8-10/ high power field
- Leucocyte Esterase: positive (an enzyme produced by WBCs)
- RBCs : may be present or absent
-
DIPSTICK TEST ( a quick test but not ideal)
-
Urine C/S
- Not recommended in every case
- Result takes 48-72 hrs
- Recommended in :
- pregnancy
- DM
- recurrent UTI
- Failure to respond to Rx
-
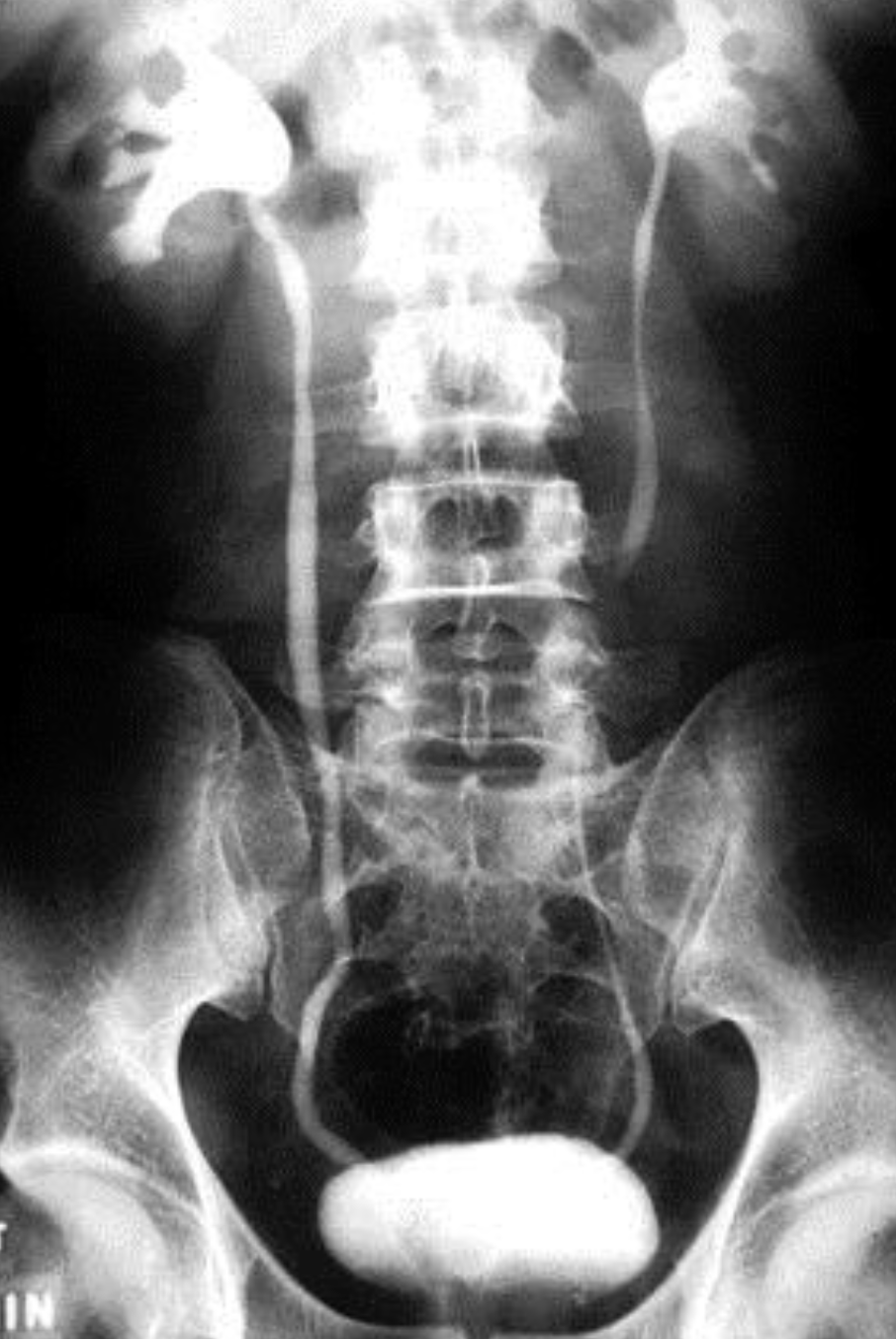
IMAGING: i.v.Pyelogram, u/s, CT (with contrast)
-
Not done routinely
-
Done in the following : a) Recurrent UTI : To find out any abnormality in the urinary tract eg stone, BPH, diverticulum
b) In children (UTI is very rare in children, so if the have it, should rule out any structural abnormality)
i.v. pyelogram (I.V.P)
FM
Investigations
Laboratory
- Dipstick urinalysis
- Microscopic urinalysis (clean catch midstream specimen).
- Urine Culture
Urine Dipstick
- Perform a urine dipstick test as the first diagnostic test in women aged under 65 years with urinary tract symptoms where they have:
- Only 1 of the 3 key signs or symptoms (dysuria, nocturia, or cloudy-looking urine), OR
- None of the 3 key signs or symptoms but other severe symptoms of urgency, frequency, visible hematuria, or suprapubic tenderness.
Laboratory Findings
- Dipstick urinalysis
- Positive leukocyte esterase. Can detect bacteria equivalent to 100,000 colony-forming units/ml
- Positive Nitrites.
- Positive RBCs.
Work Up (Urine Dipstick)
-
Presence of leukocyte esterase
(an enzyme released by leukocytes, reflecting pyuria) -
Nitrite
(reflecting the presence of Enterobacteriaceae which convert urinary nitrate to nitrite) -
Positive for RBCs
Microscopic Urinalysis
-
Microscopic urinalysis (clean catch midstream specimen).
- Look for pyuria, bacteriuria, and leukocyte casts.
- Hematuria and proteinuria may be present.
-
Urine culture recommended in complicated and upper UTI.
Urine Culture
- Should always be performed in:
- Men
- Suspected upper UTI
- With complicating factors:
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes.
It’s not required for symptomatic lower UTI in non-pregnant women.

Indications for Culture
- Has none of the 3 key diagnostic symptoms but has other urinary symptoms, and the urine has positive leukocytes and negative nitrites.
- Is pregnant.
- Is aged over 65 years and is symptomatic and is being started on antibiotics for a UTI.
- Has suspected sepsis or pyelonephritis.
- Has persistent symptoms or antibiotic treatment has failed.
- Has recurrent UTIs (2 in 6 months or 3 in 12 months).
- Has a urinary catheter and will receive antibiotics for a UTI.
- Has a risk of antimicrobial resistance.
Criteria for Diagnosis
- 3 key signs or symptoms (dysuria, nocturia, or cloudy-looking urine).
- Only 1 of the 3 key signs or symptoms plus positive nitrites and leukocyte esterase in urine dipstick.
- Only 1 of the 3 key signs or symptoms plus pus cells in microscopic urine analysis.
- Symptoms plus growth in urine culture.
Blood Culture
- Only indicated in ill patients and if urosepsis is suspected.

Role of Imaging
-
In complicated UTI
-
Renal stones or obstruction
-
Hydronephrosis or abscess
-
Poor bladder emptying
-
Illness despite 3 days of treatment
-
Urinary tract congenital anomalies
-
Visualization for biopsy
-
Plain x-ray
-
Ultrasonography
-
CT
-
Intravenous pyelography (IVP)
-
Micturating cystourethrography
-
Cystoscopy
