Papilledema
Definition
- Bilateral optic disc swelling due to increased intracranial pressure.
Causes:
-
Intracranial tumors.
-
Hydrocephalus.
-
Pseudotumor cerebri: Often occurs in young, overweight females.
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Severe headache, may have preretinal hemorrhages (i.e., Terson syndrome).
-
Arteriovenous malformation.
-
Brain abscess: Often associated with fever.
-
Meningitis: Fever, stiff neck, headache
-
Encephalitis: Often produces mental status abnormalities.
-
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Symptoms
- Episodes of transient, often bilateral visual loss (lasting seconds), related to change in position (altering intracranial pressure)
- Headache
- Double vision
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Signs
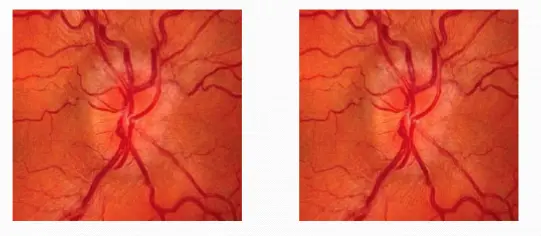
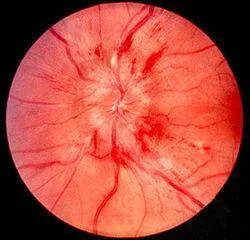
- Bilaterally swollen, hyperemic discs
- Papillary or peripapillary retinal hemorrhages
- Dilated, tortuous retinal veins;
 Signs
Signs
- Normal pupillary response and color vision;
- Enlarged physiologic blind spot by formal visual field testing.
Treatment
- Treatment should be directed at the underlying cause of the increased intracranial pressure.