Introduction to Diagnostic Imaging Modalities
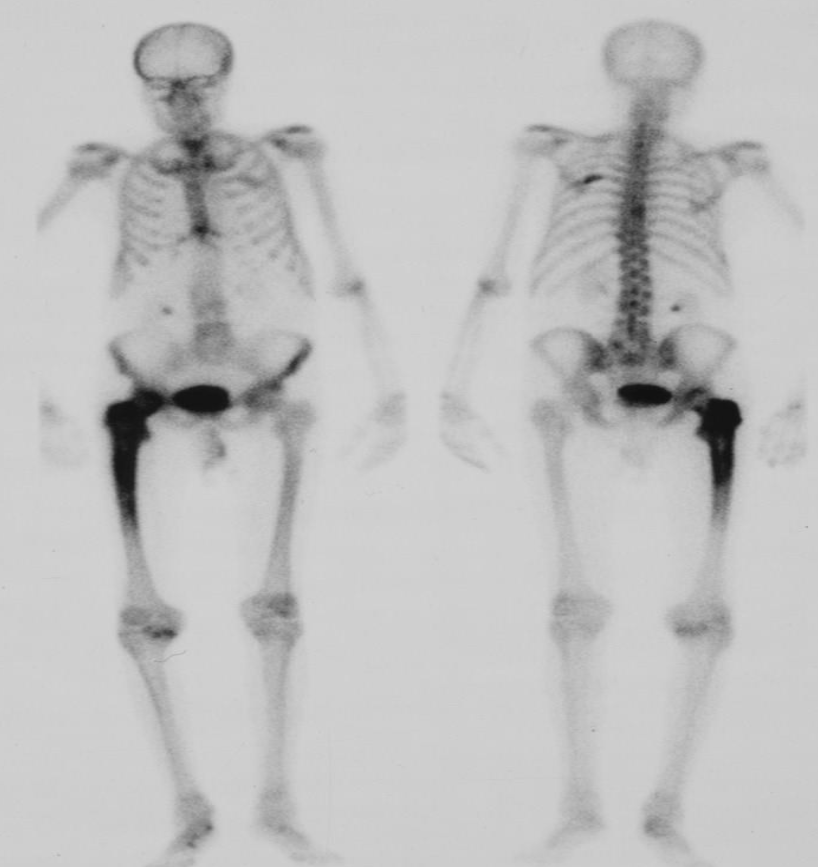
- Radionuclide bone scan.
- 99mTc
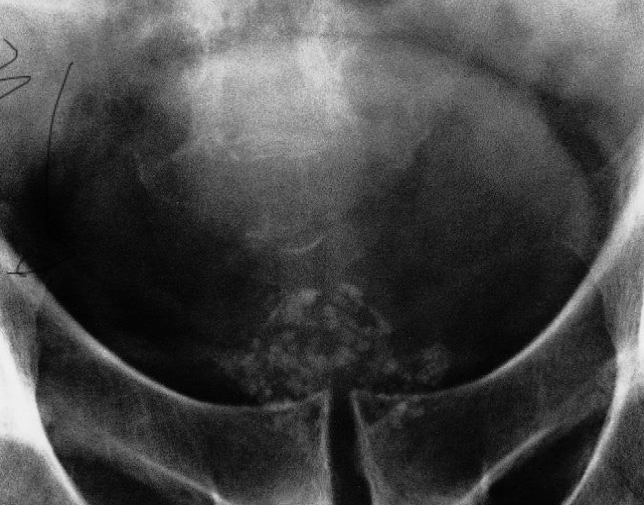
- The increased uptake in the
- femur
- Paget’s disease
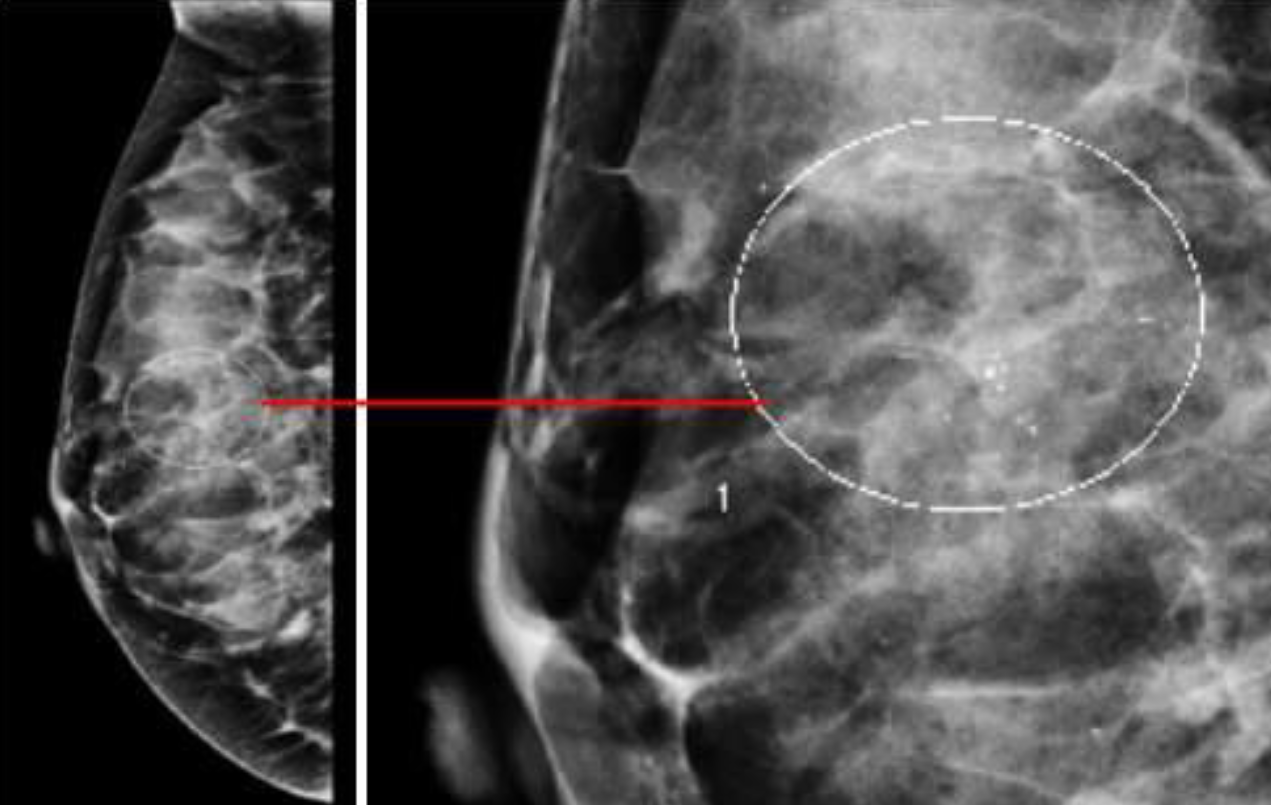 Palpable mass Breast pain and nipple discharge
Palpable mass Breast pain and nipple discharge
Additional views. Such as magnification views are done to detect
microcalcifications
A. Imaging study? Mammography B. What abnormality is demonstrated in the given image. microcalcifications C. What is the most probable diagnosis benign and malignant breast lesions
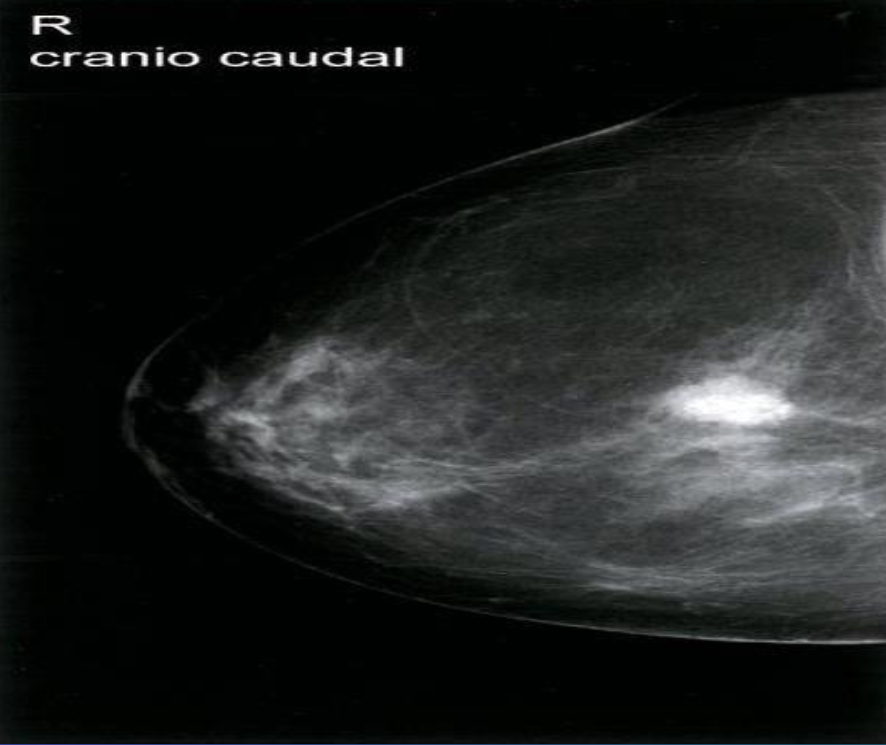 A. Imaging study? Mammography (right breast; craniocaudal view)
B. Describe the lesion shown in the given image.
C. List 2 features of the shown lesion high density and indistinct margins
D. What is the most probable diagnosis; Breast Cancer
A. Imaging study? Mammography (right breast; craniocaudal view)
B. Describe the lesion shown in the given image.
C. List 2 features of the shown lesion high density and indistinct margins
D. What is the most probable diagnosis; Breast Cancer
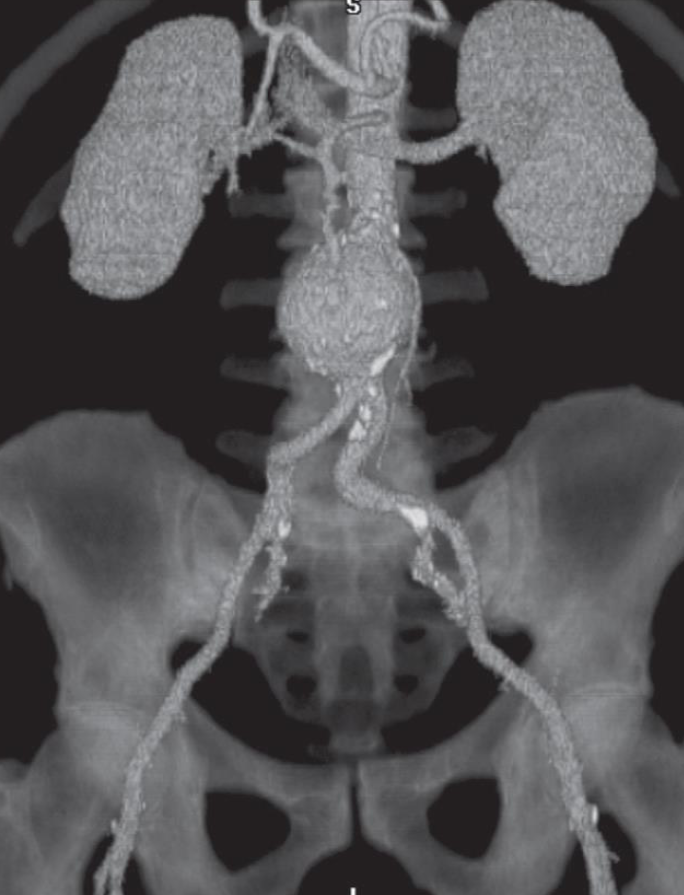 A. Imaging study? CT angiogram (3D)
B. What is the most probable diagnosis; Aortic aneurysm.
A. Imaging study? CT angiogram (3D)
B. What is the most probable diagnosis; Aortic aneurysm.
Contrast media, risk, precaution and management
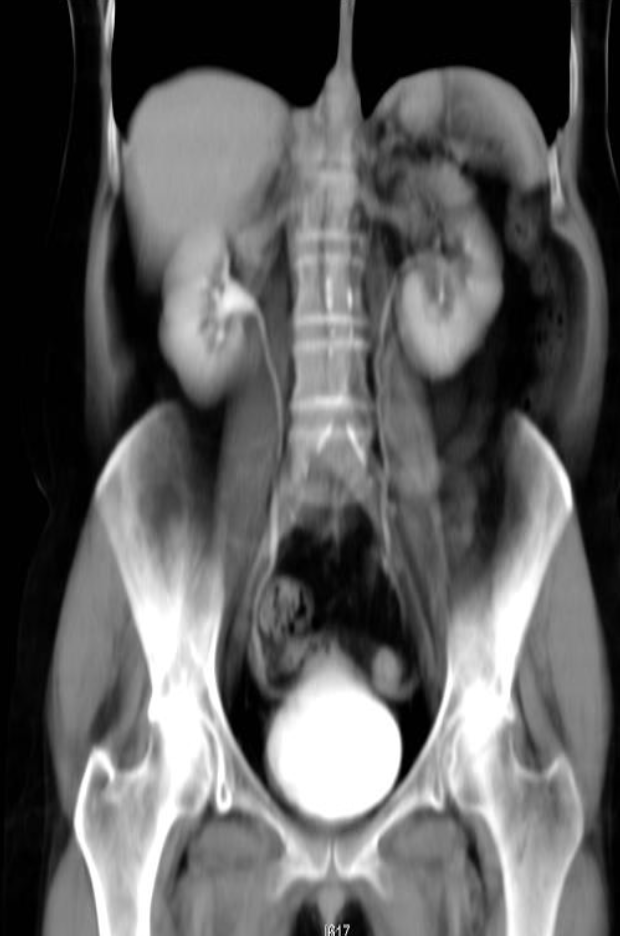 A. Give the name of the imaging examination in the given image. CTU
B. Give the NAMES of the used contrast media for the examination Iodide Contrast Media
A. Give the name of the imaging examination in the given image. CTU
B. Give the NAMES of the used contrast media for the examination Iodide Contrast Media
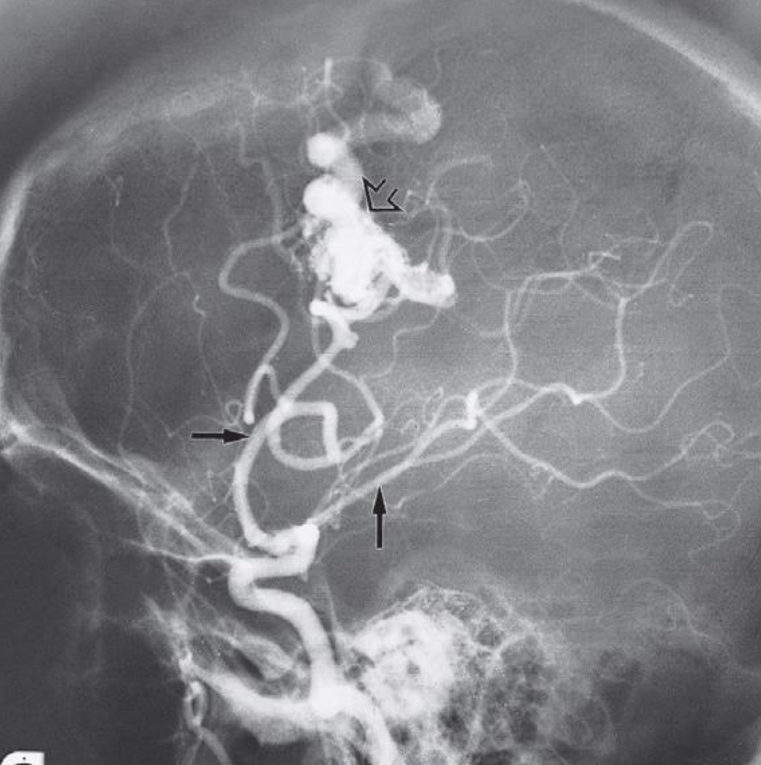 A. Imaging modality or technique or study? Digital Subtraction Angiography
B. Type or name of contrast? Iodine base
A. Imaging modality or technique or study? Digital Subtraction Angiography
B. Type or name of contrast? Iodine base
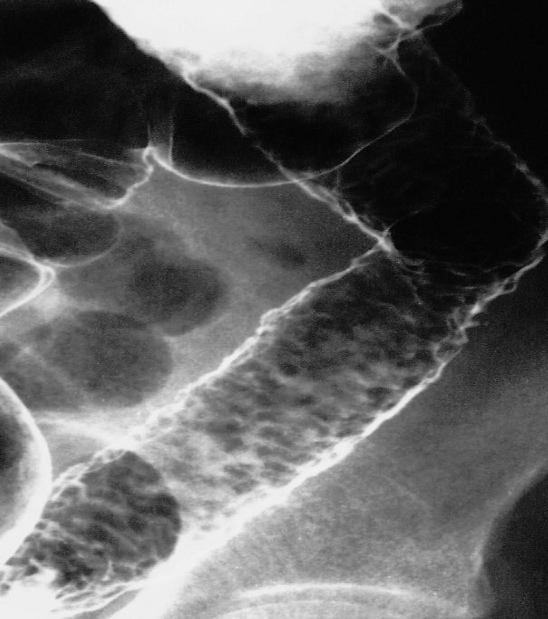
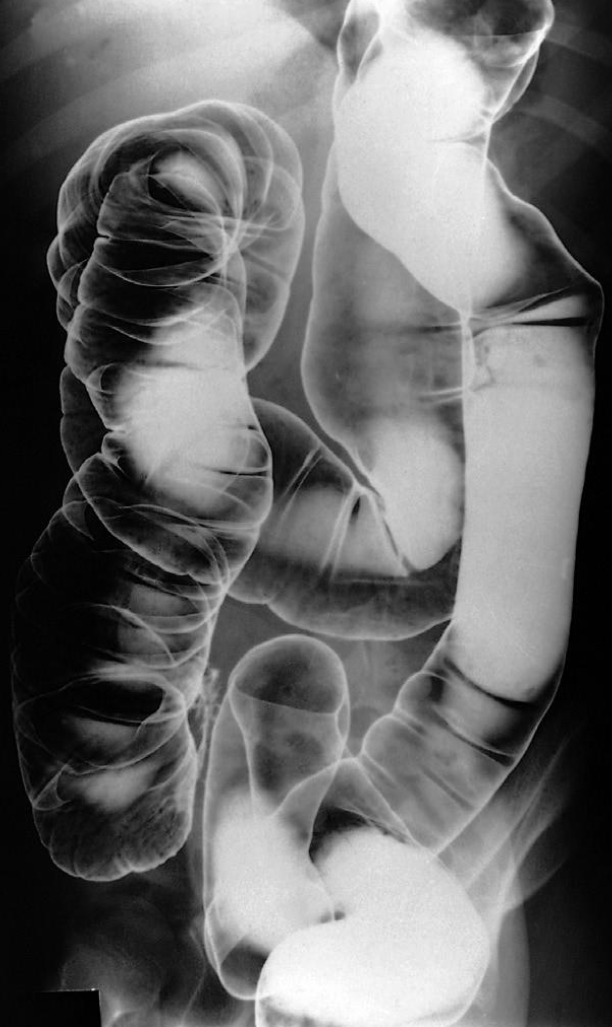 A. Give the name of the imaging examination in the given image. Enema double contrast
B. Give the NAMES of the used contrast media for the examination Barium & air (+ve Vs –ve)
A. Give the name of the imaging examination in the given image. Enema double contrast
B. Give the NAMES of the used contrast media for the examination Barium & air (+ve Vs –ve)
RESPIRATORY AND CARDIOVASCULAR RADIOPLOGY
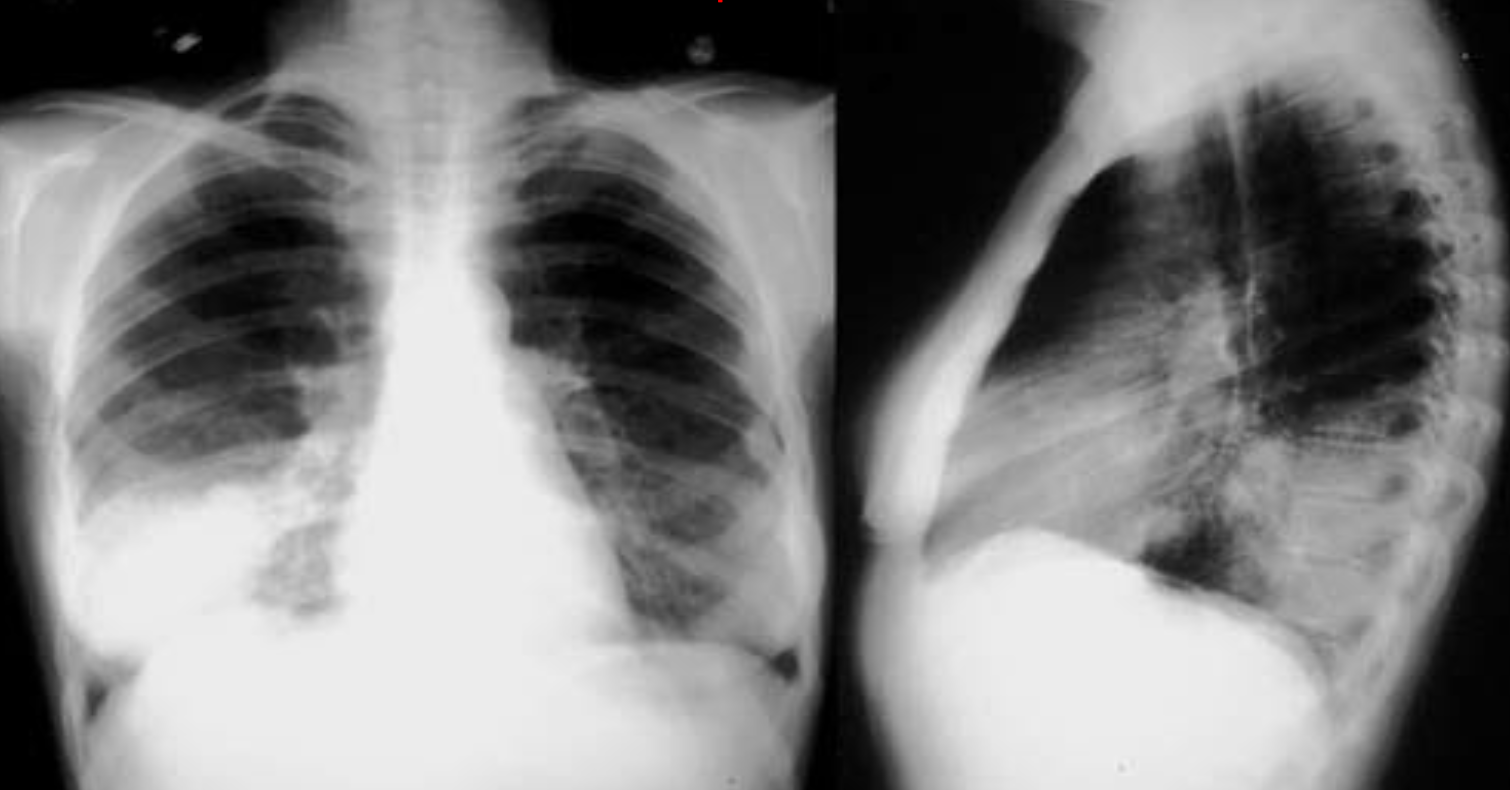 A. What is the most likely diagnosis in the given images; RT lower lobe pneumonia
B. Which lobe of the lung affected by this disease in the given image. Lower lobe, reverse change of opacity from spine
A. What is the most likely diagnosis in the given images; RT lower lobe pneumonia
B. Which lobe of the lung affected by this disease in the given image. Lower lobe, reverse change of opacity from spine
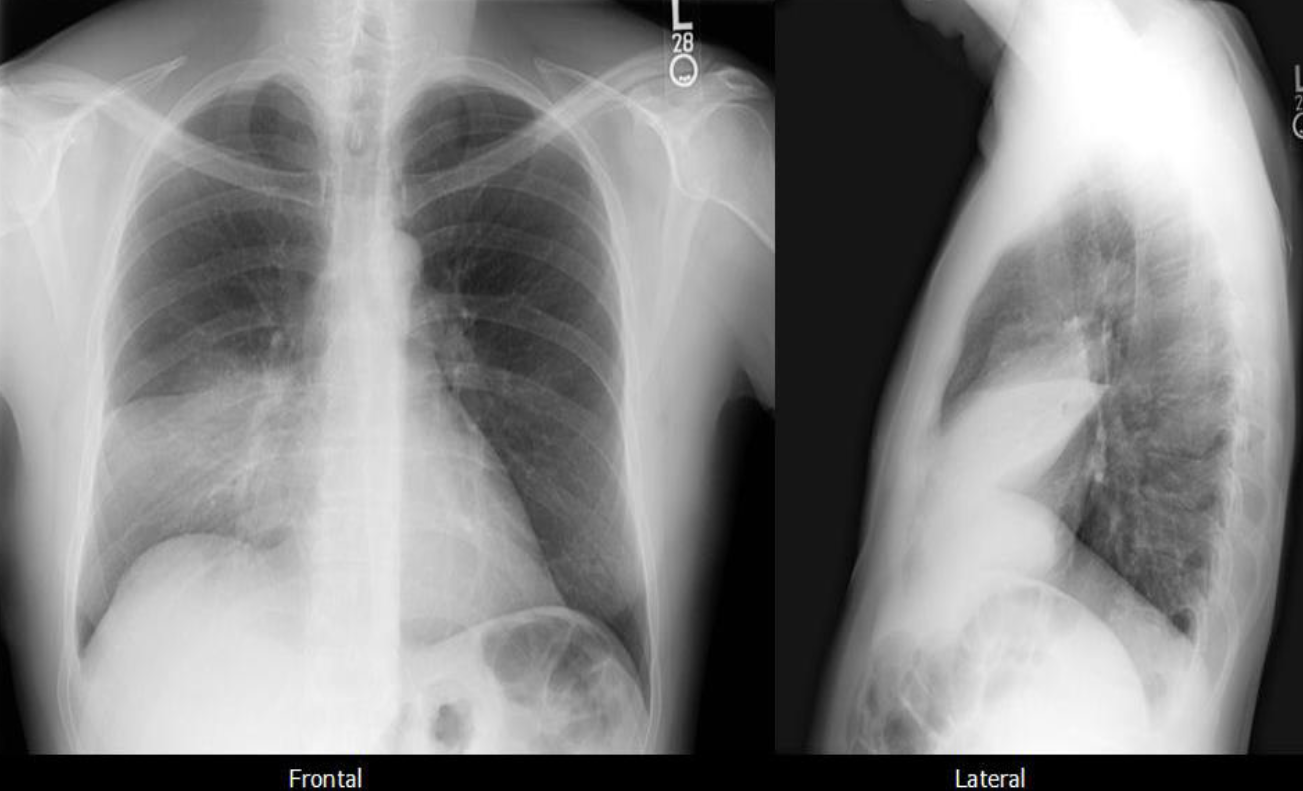 A. What is the most likely diagnosis in the given images
pneumonia ex… due fever cough and the imaging
A. What is the most likely diagnosis in the given images
pneumonia ex… due fever cough and the imaging
B. Which lobe of the lung affected by this disease in the given image. Right middle Lobe Lesion, due obliteration of diaphragm - and lateral of horizontal fissure opaque
 Pneumonia most common due to no deviations of midline - could be truama, ectopy, etc… so follow through with case given for diagnosis
Pneumonia most common due to no deviations of midline - could be truama, ectopy, etc… so follow through with case given for diagnosis
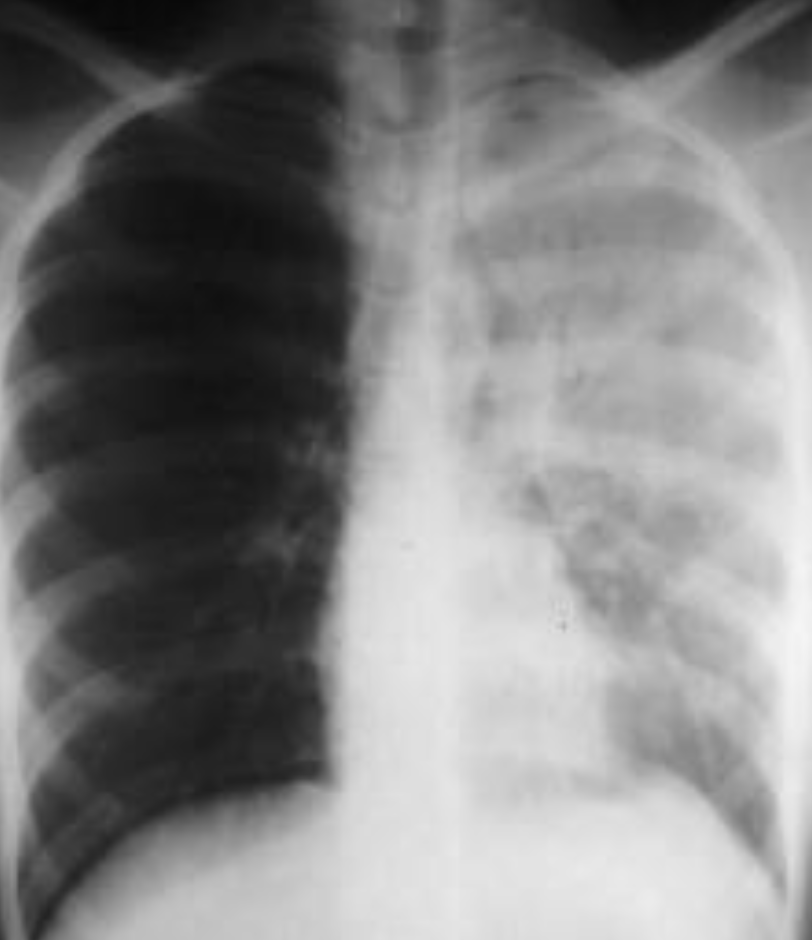
- The left hemithorax is opaque
- There is no shift of the heart or trachea
- The opacified hemithorax contains air bronchogram
- No loss of lung volume
 Female patient presents with chest pain and fever
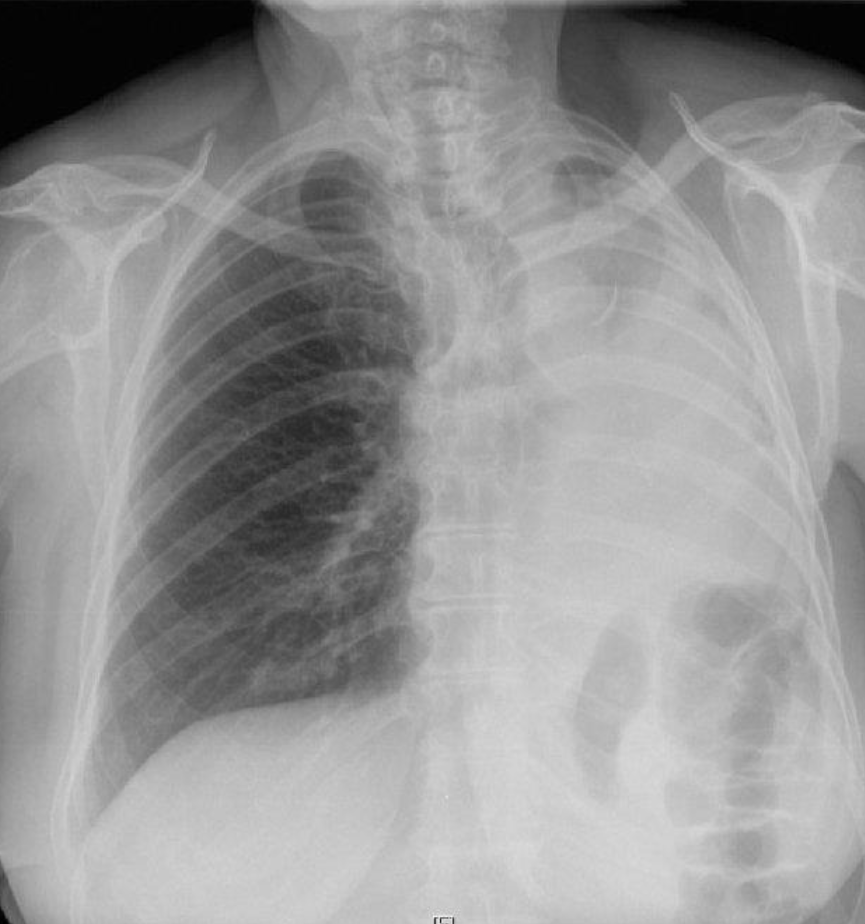
Female patient presents with chest pain and fever
- Modality ? Plain X-ray
- Findings ? Ipsilateral shifting of trachea and heart to the abnormal side - hemithorax
- Diagnosis? Pneumonia Collapse
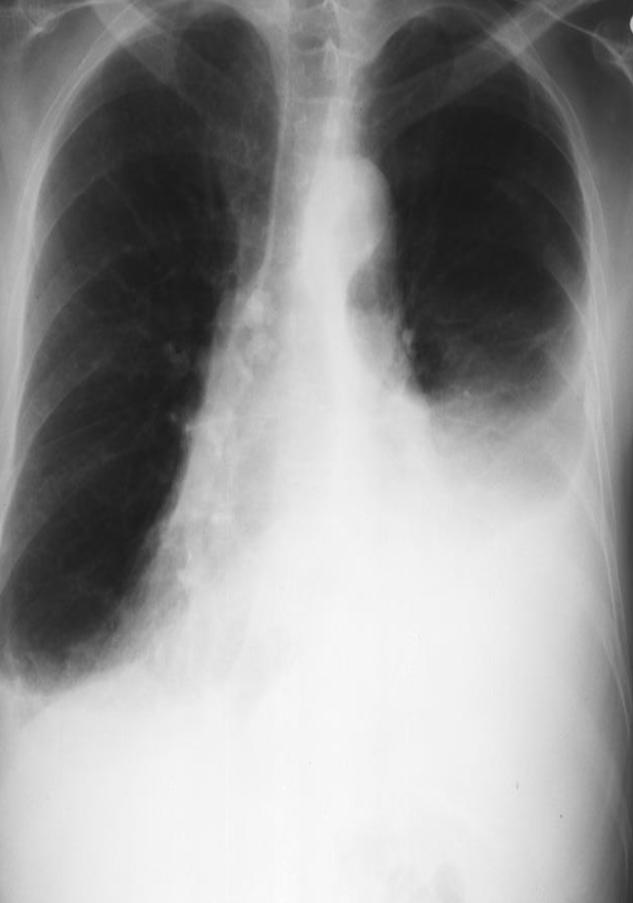 Meniscus sign
Meniscus sign
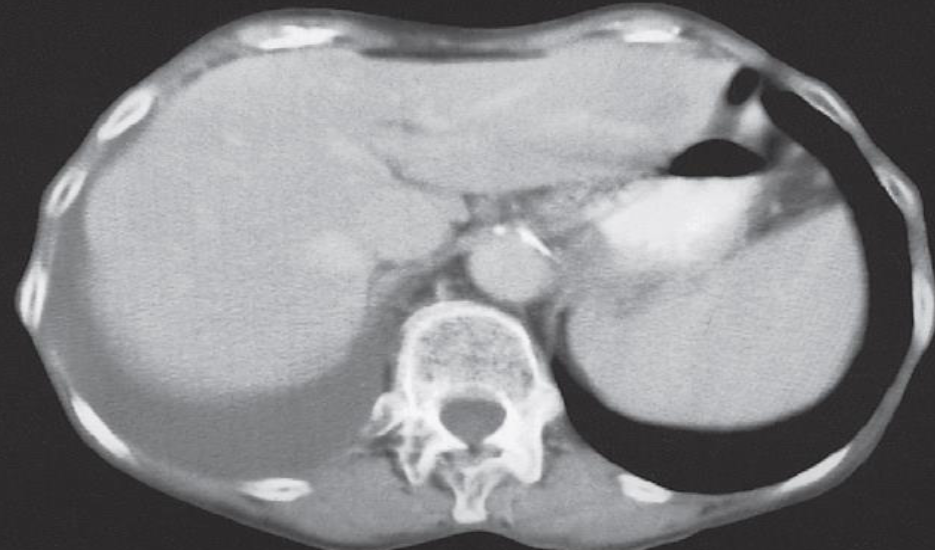 A. Imaging examination CT, X-RAY
B. Sign (Image 2) Meniscus Sign, Dullness on percussion
C. Diagnosis Pleural Effusion
A. Imaging examination CT, X-RAY
B. Sign (Image 2) Meniscus Sign, Dullness on percussion
C. Diagnosis Pleural Effusion
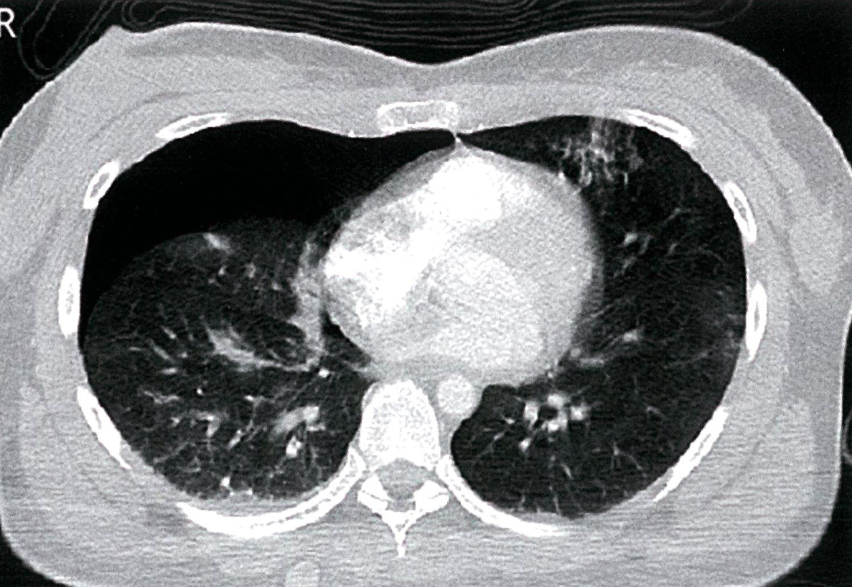
- Right anterior pneumothorax
- CT thorax (axial view; lung window)
Y
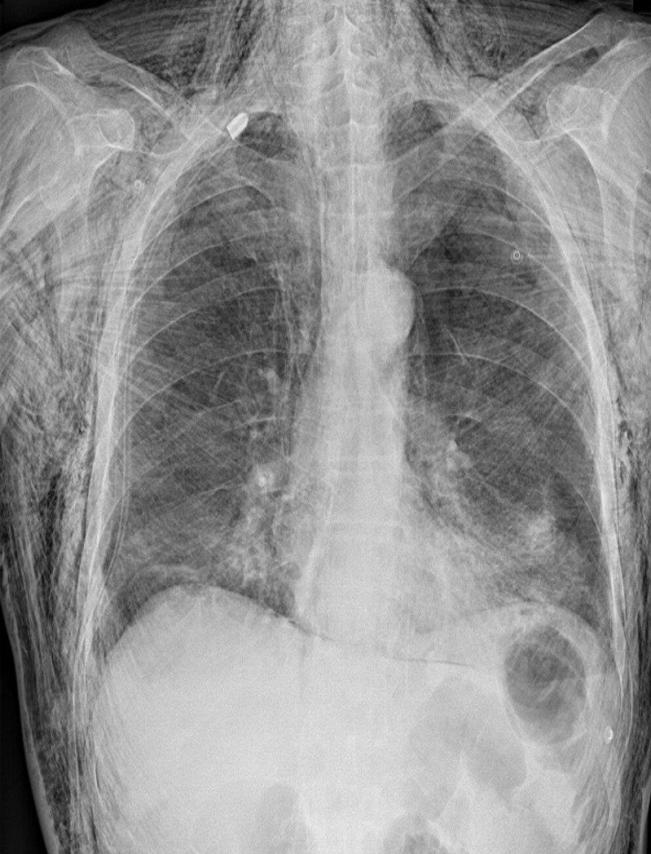 Traumatic subcutaneous emphysema
X-ray chest (PA view)
Traumatic subcutaneous emphysema
X-ray chest (PA view)
- Extensive subcutaneous emphysema is seen
- as linear lucencies throughout the soft tissues
- of the thorax, neck, and upper abdomen
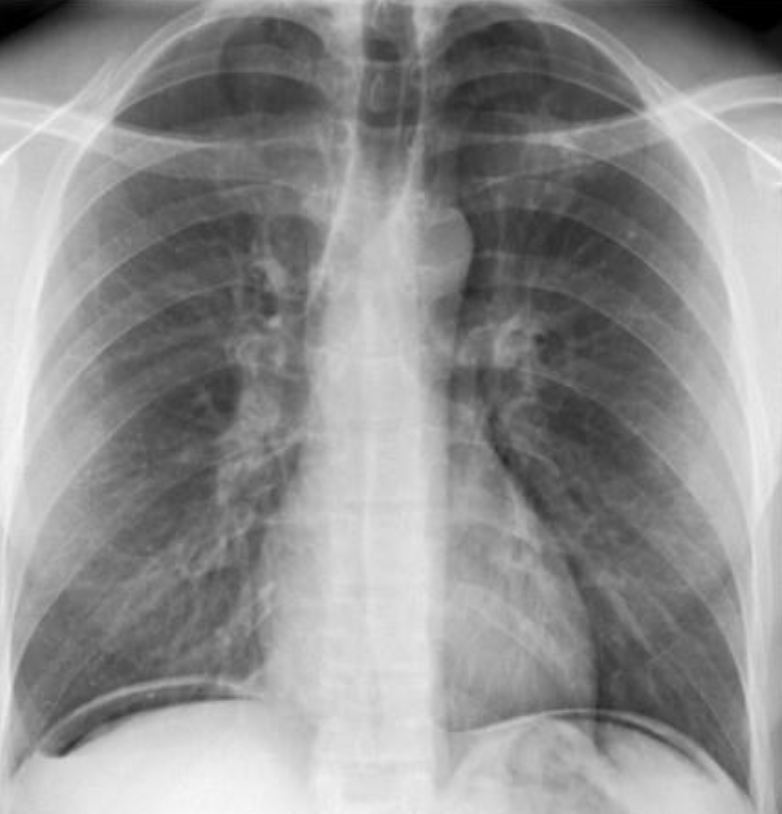
- Free air under the domes of diaphragm - Bilateral
- in pneumoperitoneum.
- It occur in perforation of bowel
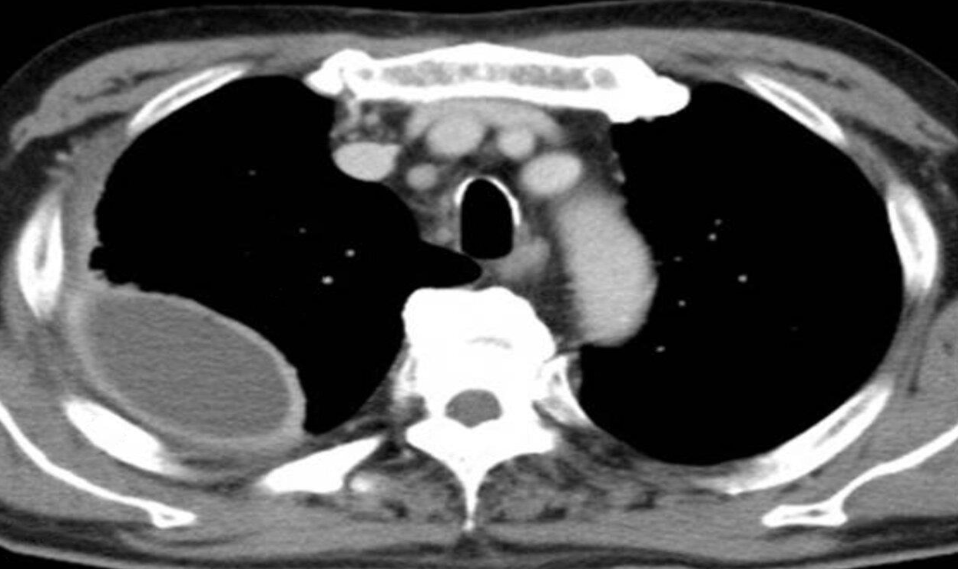 T scans show right-sided pleural fluid collections (PC). Each collection has a lenticular (biconvex) shape and is accompanied
by thickening of the adjacent parietal (red line) and visceral pleurae (green line).
T scans show right-sided pleural fluid collections (PC). Each collection has a lenticular (biconvex) shape and is accompanied
by thickening of the adjacent parietal (red line) and visceral pleurae (green line).
A. Imaging examination CT - Contrast; axial plane, mediastinal window)
B. What is the name of Sign & what does it usually mean? split-pleura sign
C. Diagnosis empyema
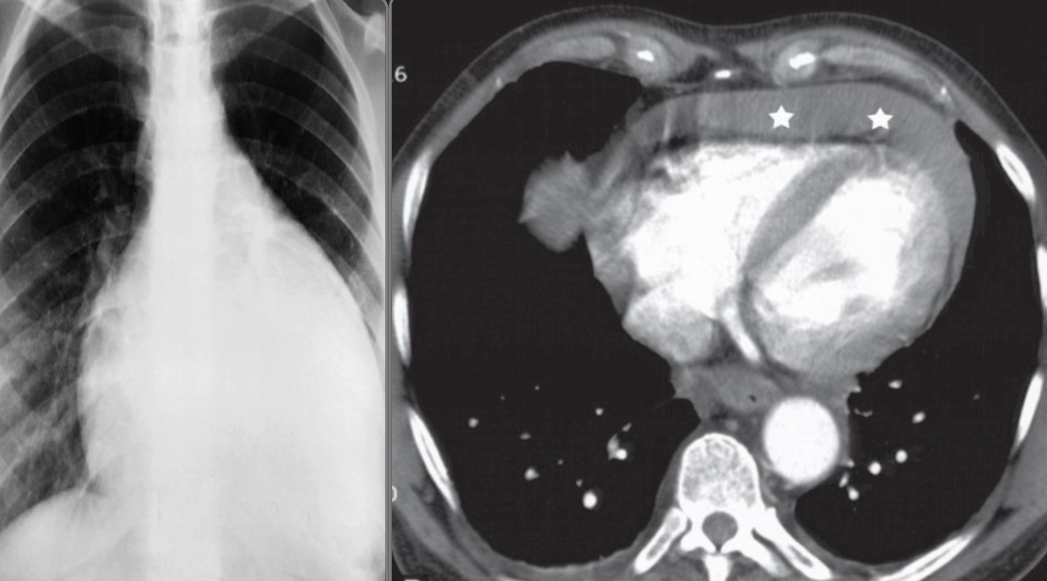 A. Imaging modality Plain X-ray / CT
B. Findings or description Cardiomegaly, globular shape, fluid collection around heart
C. What is the most likely diagnosis ? Pericardial effusion
A. Imaging modality Plain X-ray / CT
B. Findings or description Cardiomegaly, globular shape, fluid collection around heart
C. What is the most likely diagnosis ? Pericardial effusion
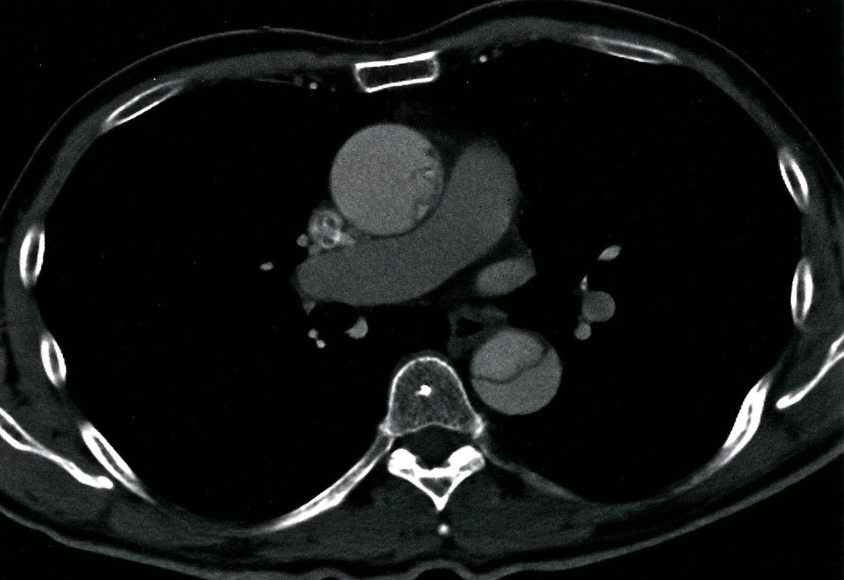
- CT thorax (with contrast; axial view)
- A mucosal flap can be seen dividing the lumen of the ascending and descending aorta.
- This radiological appearance confirms an aortic dissection.
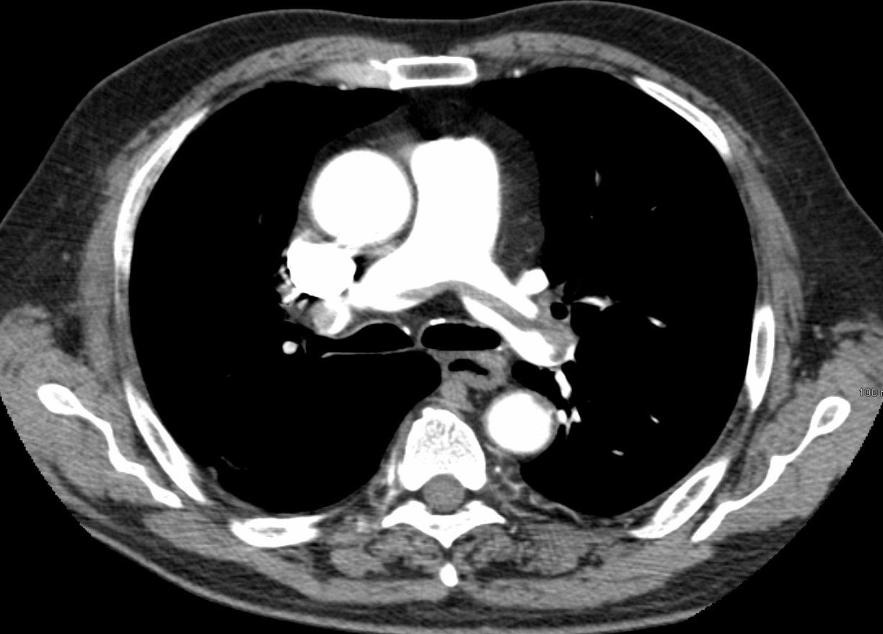
- CT chest (with contrast; axial plane)
- some contrast has lucent area with hypodense, due filling defect
- Pulmonary embolism.
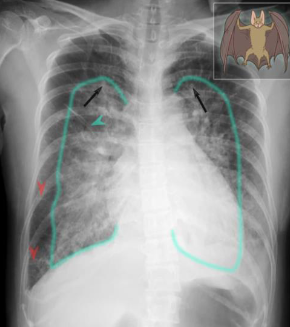
- Imaging examination X-ray chest (PA view)
- Findings or description
- The cardiac silhouette is enlarged
- upper lobe vessels are prominent
- Bilateral perihilar opacity batwing, or butterfly appearance.
- Thickened interlobular septae (Kerley lines)
- Diagnosis Pulmonary edema
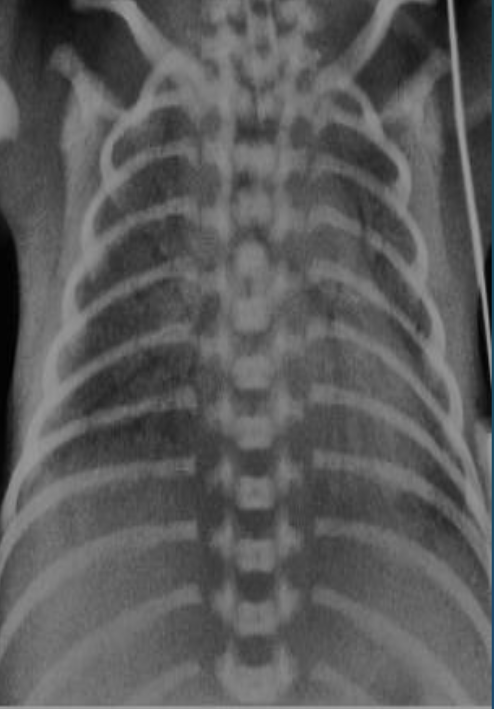
Imaging examination X-ray chest (frontal view) of a premature infant
Findings or description - General granular opacity of the lungs Note the uniformity of distribution of the changes in the lungs - The vessels, the heart borders and the diaphragm outlines are indistinct - Air bronchograms are visible.
Diagnosis Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline membrane disease).
RADIOLOGY OF GI TRACT & BILIARY SYSTEM
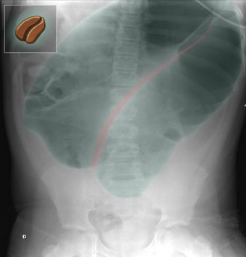
 A. Imaging examination
X-ray abdomen (AP view)
A. Imaging examination
X-ray abdomen (AP view)
What is the name of Sign & what does it usually mean? Markedly dilated bowel . The configuration, including the double wall thickness of the two apposed bowel loops, resembles a bean “coffee bean sign”.
Diagnosis Sigmoid volvulus
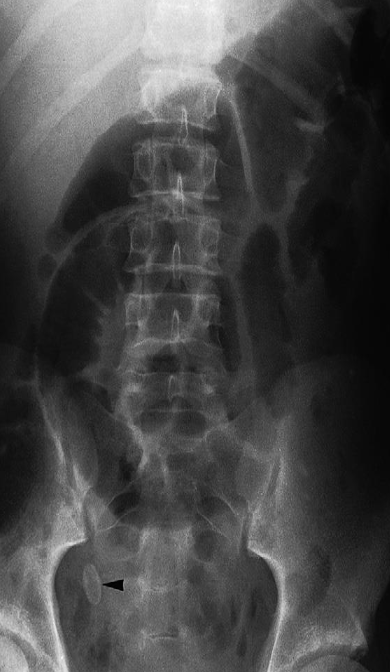
Imaging examination Plain X-ray
Findings or description The oval calcified shadow (arrowhead) is a faecolith in the appendix.
Sign Note the dilated loops of small bowel in the centre of the abdomen due to peritonitis – the so-called sentinel loops
Diagnosis Appendicolith

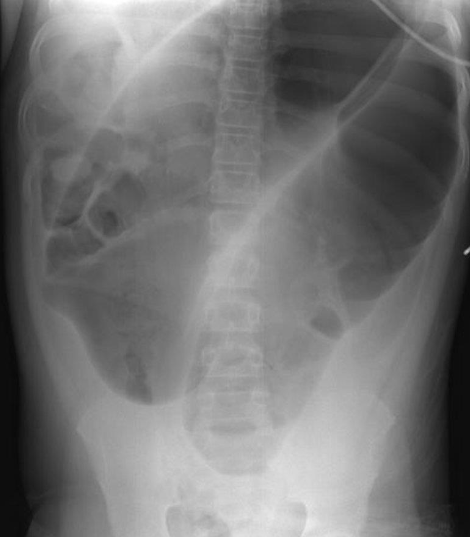
A. Imaging examination
- Findings or description
- Diagnosis
Barium swallow Pharyngeal pouch (Zenker’s diverticulum). The pouch lies behind the oesophagus, which is displaced forward
Y 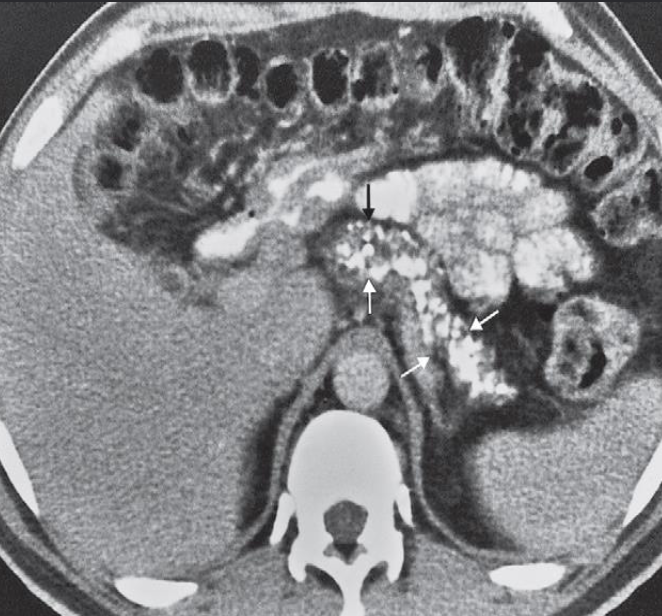 A. Describe the abnormality marked by arrows in the given image.
A. Describe the abnormality marked by arrows in the given image.
- CT scan showing numerous
- small areas of calcification
- within the pancreas (arrows).
B. What is the most probable diagnosis in the given image. Chronic pancreatitis
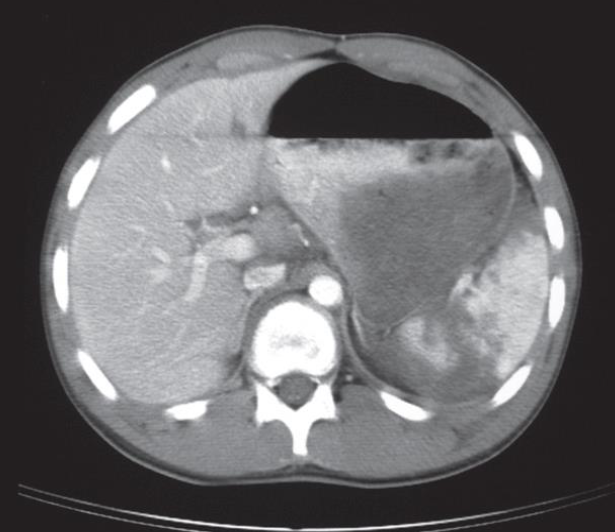 A. Give the name of the used imaging modality .
CT
A. Give the name of the used imaging modality .
CT
B. What abnormality is demonstrated in the given image? Ruptured spleen- The spleen is shattered with low density blood adjacent to the fragments.
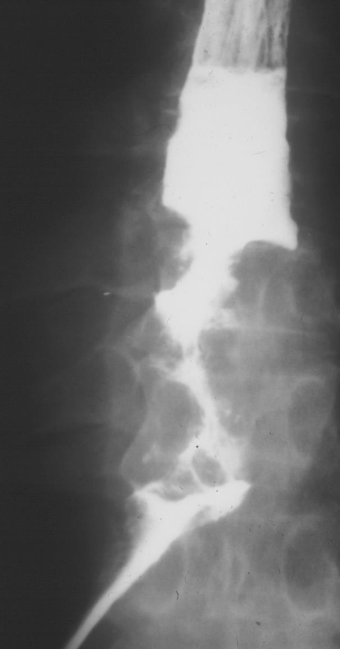 Dysphagia presentation
Oesophageal carcinoma
BARIUM SWALLOW
There is an irregular stricture
with shouldering at the upper
end.
Dysphagia presentation
Oesophageal carcinoma
BARIUM SWALLOW
There is an irregular stricture
with shouldering at the upper
end.
- CROHN’S DISEASE
- Cobble stone appearances
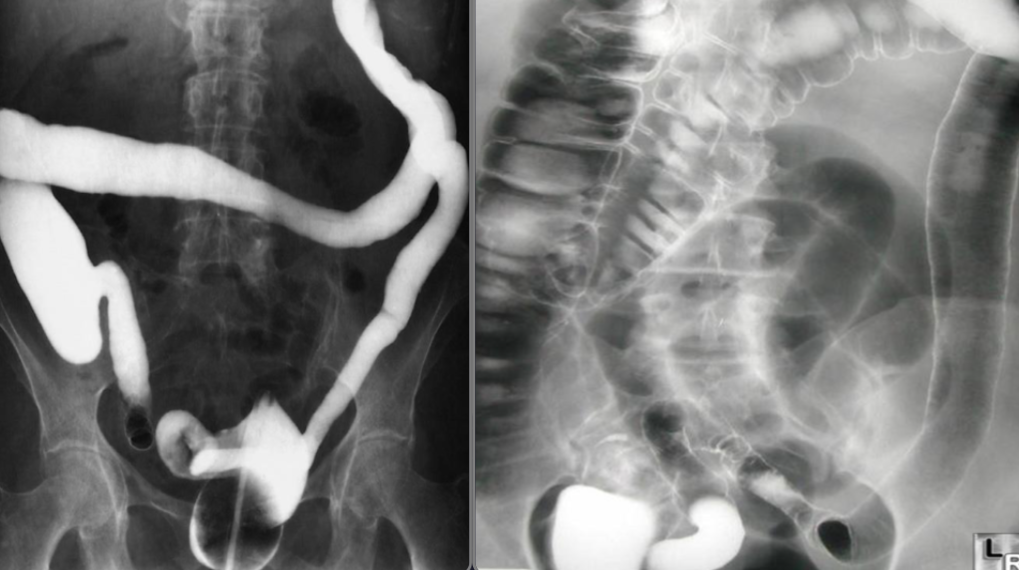 Ulcerative colitis
Single & Double (rt) contrast barium enema
Ulcerative colitis
Single & Double (rt) contrast barium enema
- The haustra are lost and the colon becomes narrowed and shortened, coming to resemble a rigid tube.
- Narrowing and shortening of colon Feature less colon give lead pipe appearances
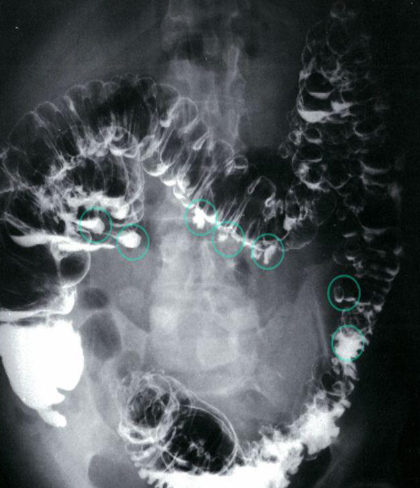 Abdominal pain and diarrhea
Abdominal pain and diarrhea
Imaging examination Diverticulosis - Double-contrast barium enema of the colon
Findings or description Multiple diverticula in the colon can be seen (examples circled in green).
Diagnosis Diverticulosis
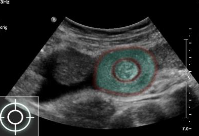 Target sign in intussusception
Ultrasound abdomen (bowel; transverse plane)
Target sign in intussusception
Ultrasound abdomen (bowel; transverse plane)
-
Concentric alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic rings are visible.. Together the alternating
-
layers produce a target-like appearance (target sign)
Y 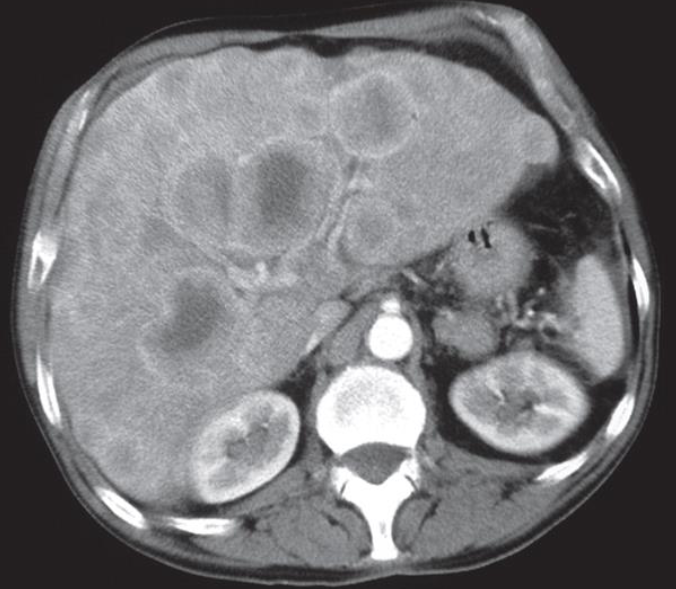 The patient had carcinoma of the bronchus.
The patient had carcinoma of the bronchus.
CT scan of liver metastases. There are a large number of low density lesions in both lobes of the liver, which show enhancement around their edges.
LIVER METASTASIS
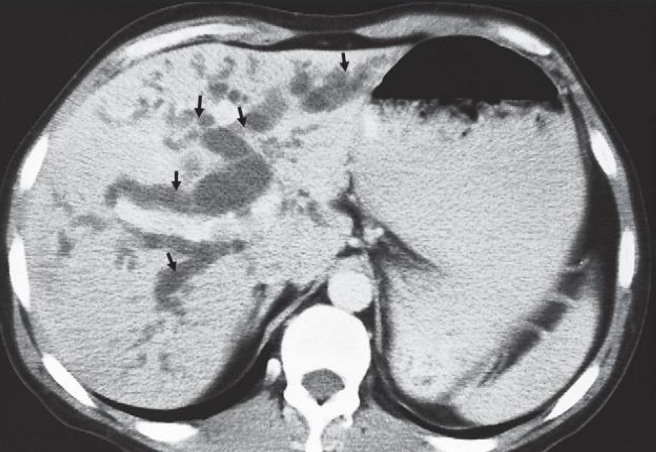 Imaging examination CT scan
Findings or description showing dilated intrahepatic ducts (arrows) in the liver
Diagnosis Dilated biliary ducts
Imaging examination CT scan
Findings or description showing dilated intrahepatic ducts (arrows) in the liver
Diagnosis Dilated biliary ducts
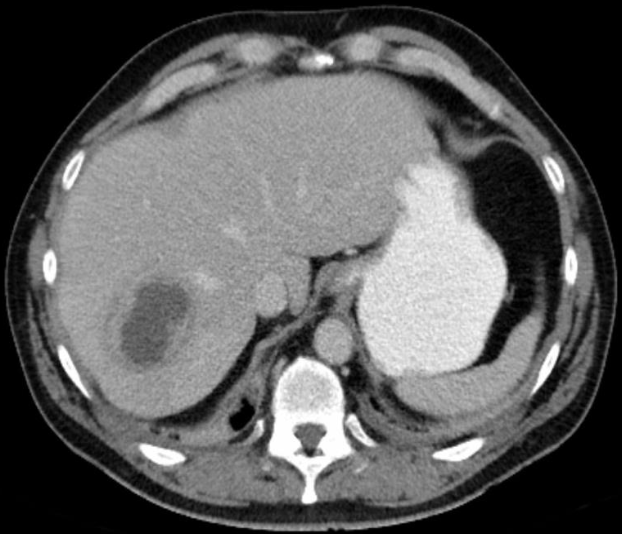
LIVER ABSCESS
Y
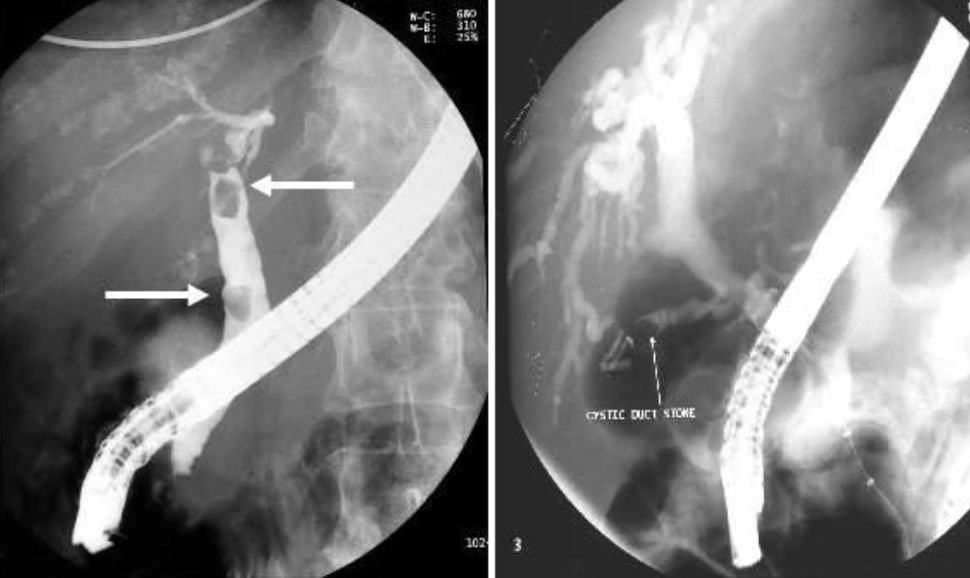 Stone in CBD ERCP study
Stone in CBD ERCP study
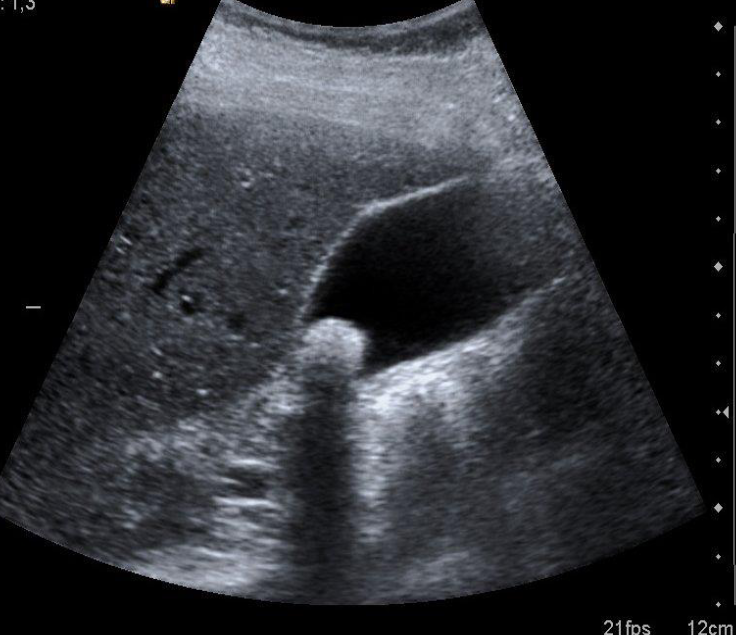 Acute abdomen presentation
Diagnosis of Cholelithiasis
Hyperechoic shadow from stone - wall is normal
Acute abdomen presentation
Diagnosis of Cholelithiasis
Hyperechoic shadow from stone - wall is normal
Y
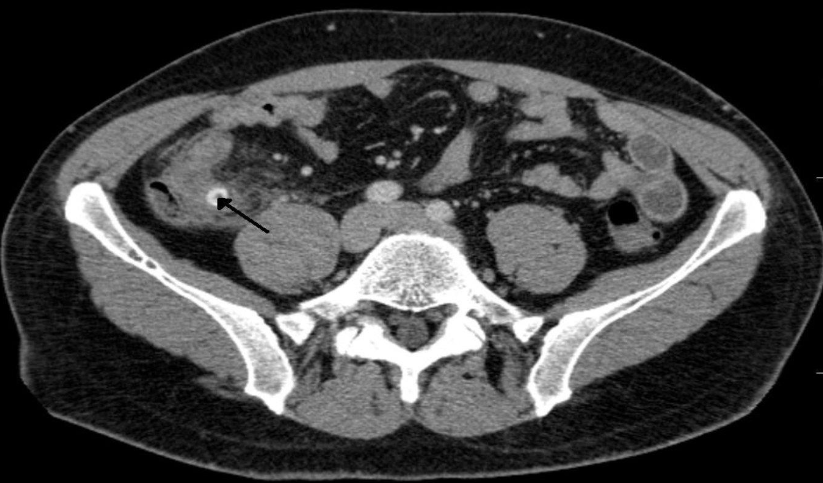 Perforated appendicitis due to fecalith
CT abdomen (IV contrast; axial section)
There is distension of the appendix (. A well-defined, round, hyperdense lesion (black arrow), characteristic of an appendiceal fecalith. A small
pocket of extraluminal air (red overlay)
Perforated appendicitis due to fecalith
CT abdomen (IV contrast; axial section)
There is distension of the appendix (. A well-defined, round, hyperdense lesion (black arrow), characteristic of an appendiceal fecalith. A small
pocket of extraluminal air (red overlay)
RADIOLOGY OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
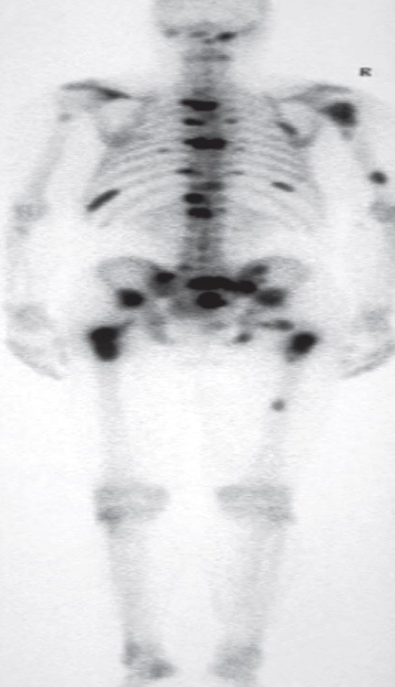 A. Give the name of the used imaging modality
SCINTIGRAPHY /RADIONUCLIDE BONE SCAN
B. What is the most probable diagnosis ? Metastasis
C. Describe the abnormality. Multiple areas of increased uptake
A. Give the name of the used imaging modality
SCINTIGRAPHY /RADIONUCLIDE BONE SCAN
B. What is the most probable diagnosis ? Metastasis
C. Describe the abnormality. Multiple areas of increased uptake
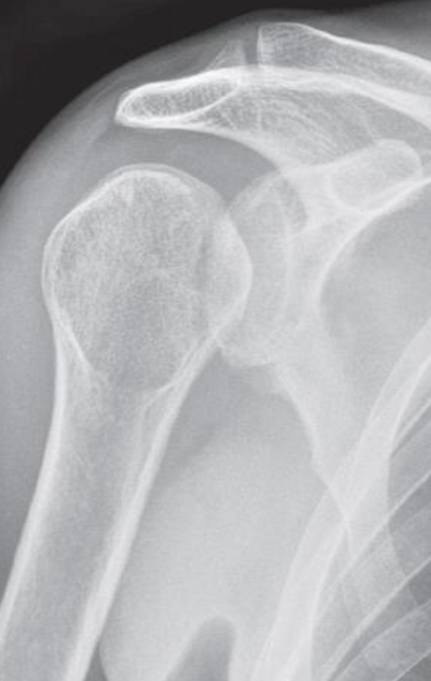
- Plain X-ray
- Electric shock or epileptic seizure
- ‘lightbulb’ appearance of the humeral head.
- Posterior dislocation of the shoulder
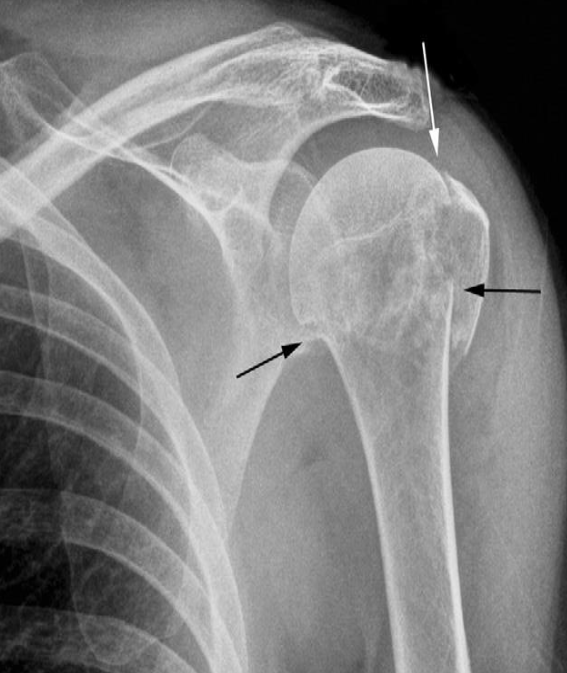 Fracture of the neck of the humerus (black arrows)
The greater tuberosity is also fractured (white arrow)
Fracture of the neck of the humerus (black arrows)
The greater tuberosity is also fractured (white arrow)
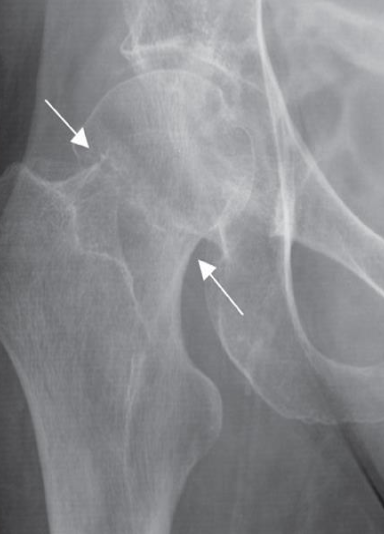 Impacted femoral neck
fracture (arrows) causing only a
sclerotic line and disruption of
the trabecular architecture.
Impacted femoral neck
fracture (arrows) causing only a
sclerotic line and disruption of
the trabecular architecture.
 Intertrochanteric fracture
(arrows) between the greater
and lesser trochanters
Intertrochanteric fracture
(arrows) between the greater
and lesser trochanters
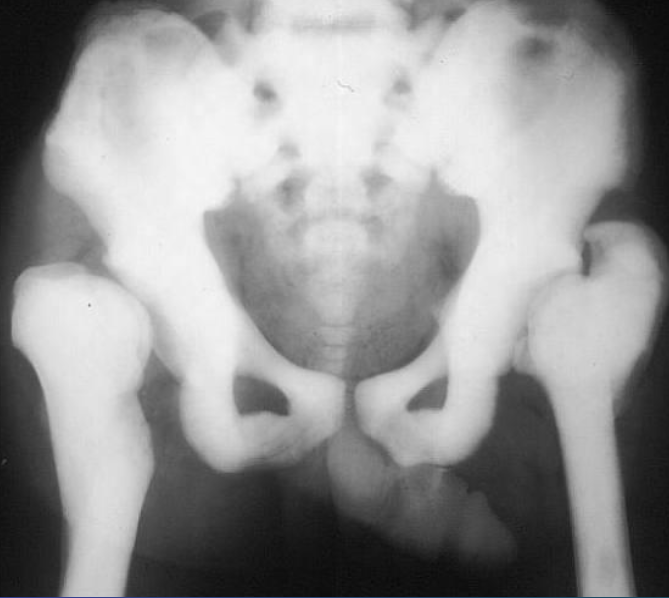
 Pelvic ring fracture
X-ray pelvis (AP view)
Bilateral pubic ramus fractures are also present.
Pelvic ring fracture
X-ray pelvis (AP view)
Bilateral pubic ramus fractures are also present.
 Spiculated (sunray) periosteal reaction in a case of
osteogenic sarcoma (arrows)
Spiculated (sunray) periosteal reaction in a case of
osteogenic sarcoma (arrows)
 ‘Onion skin’ periosteal reaction in a
case of Ewing’s sarcoma (arrows). Here
the periosteal new bone consists of
several distinct layers.
‘Onion skin’ periosteal reaction in a
case of Ewing’s sarcoma (arrows). Here
the periosteal new bone consists of
several distinct layers.
Y
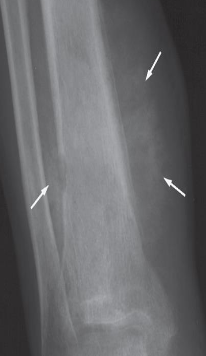
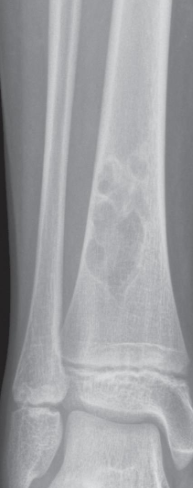 Describe the lesion A well-defined sclerotic edge can be seen
Describe the lesion A well-defined sclerotic edge can be seen
indicating a benign lesion.
Diagnosis a fibrous cortical defect
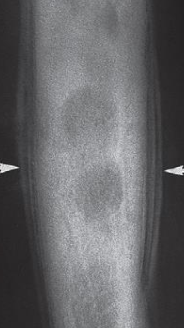
Y 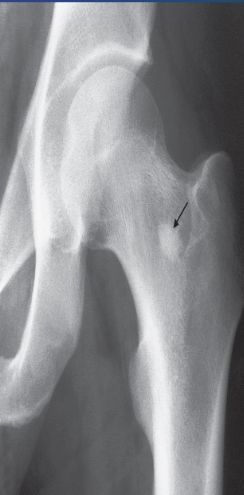 Describe the lesion well-defined area of compact bone in the neck of the femur (arrow
Diagnosis This common finding is without significance.
Describe the lesion well-defined area of compact bone in the neck of the femur (arrow
Diagnosis This common finding is without significance.
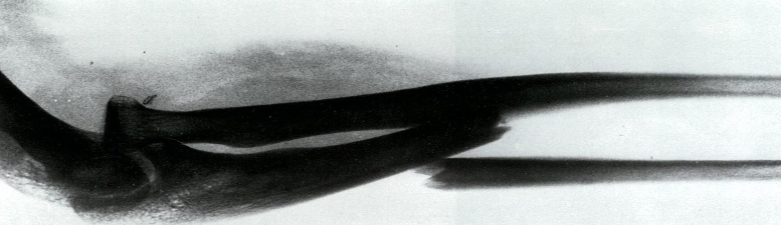
- Monteggia fracture-dislocation
- X-ray of the elbow (lateral view)
- Fracture of the proximal ulna with anterior dislocation of the head of the radius.
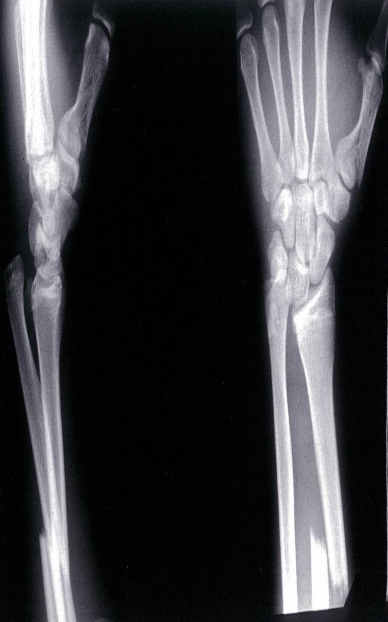
- Galeazzi fracture and fracture of the first metacarpal bone
- X-ray of the distal lower arm (left, lateral view; right, PA view)
- A distal third radius fracture and distal ulnar head dislocation can be seen; this fracture pattern is referred to as a Galeazzi fracture. Fracture of the first metacarpal bone
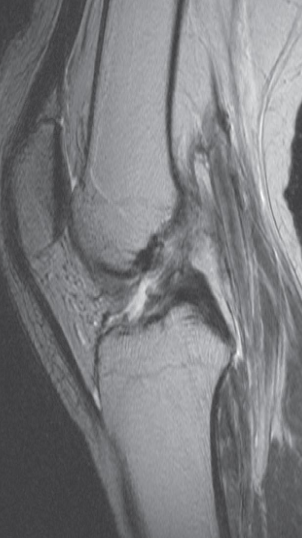 Imaging modality? MRI scan
Finding with a tear the anterior
Diagnosis Cruciate ligament (disrupted)
Imaging modality? MRI scan
Finding with a tear the anterior
Diagnosis Cruciate ligament (disrupted)
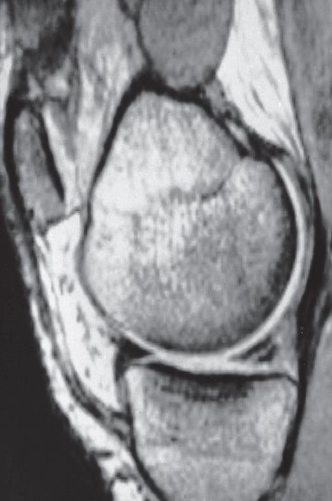 Imaging modality? Sagittal MRI through the medial part of the knee
joint
Finding tear in the posterior horn of the medial meniscus . The anterior horn appears normal.
Diagnosis the medial meniscus Tear
Imaging modality? Sagittal MRI through the medial part of the knee
joint
Finding tear in the posterior horn of the medial meniscus . The anterior horn appears normal.
Diagnosis the medial meniscus Tear
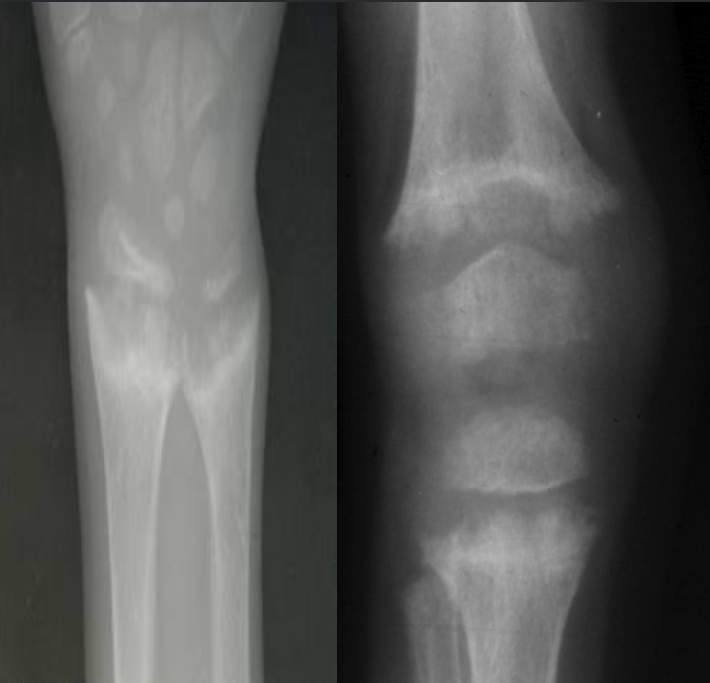 A. Give ONE radiological sign for an abnormal
wrist/knee.
A. Give ONE radiological sign for an abnormal
wrist/knee.
B. What is the most likely diagnosis in the given image? Rickets
- Growth plate is widened
- Metaphysical margin is cupped and irregular
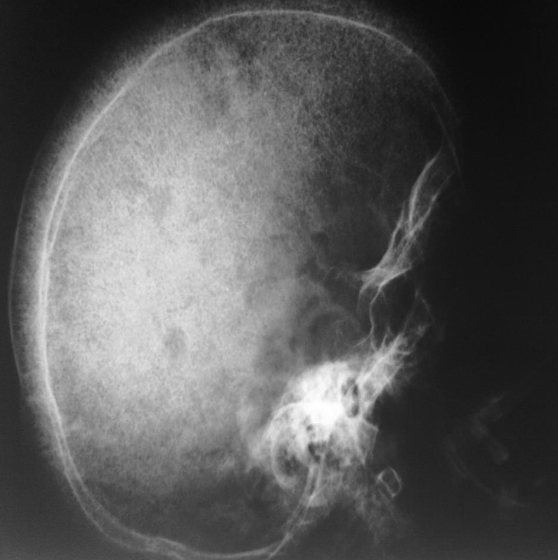
- Thalassemia
- Skull x-ray
- Hair on end appearance
 Osteopetrosis
Generalized increase in bone density
Osteopetrosis
Generalized increase in bone density
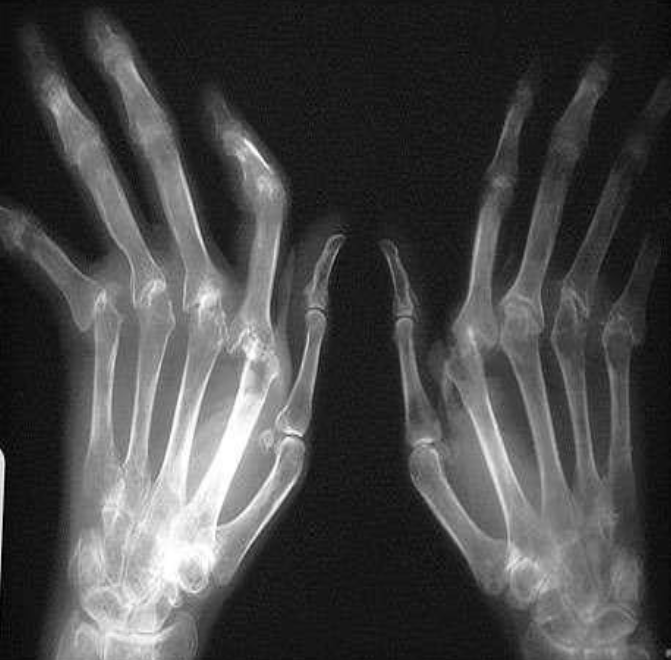
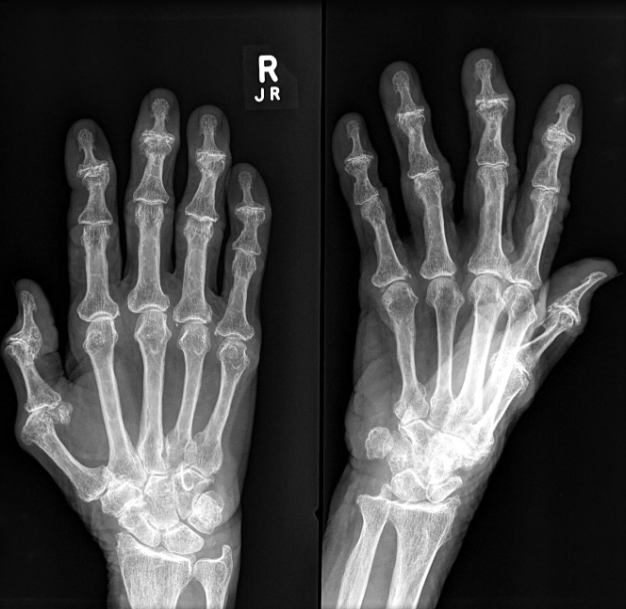
Rheumatoid Arthritis Radiological sign:.
- Around joint, periarticular osteopenia/osteoporosis
- Changes more to the proximal joints than distal
- Swan neck and Boutonnière deformity and extensive erosive
 Rugger jersey spine’ (renal osteodystrophy
Rugger jersey spine’ (renal osteodystrophy
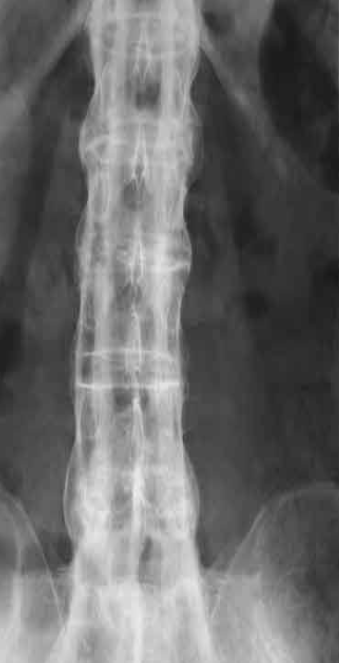 Bamboo spine | Ankylosing spondylitis
Bamboo spine | Ankylosing spondylitis
A. Give the name of the used imaging modality. B. What name is given to this appearance of the spine?
Y
 Osteoarthritis - 60-Year-old patient with pain in the
hands.
Osteoarthritis - 60-Year-old patient with pain in the
hands.
- Distal: osteosclerosis
- Osteophytes (Osteospike)
- Reduction of the joint space, sclerotic changes
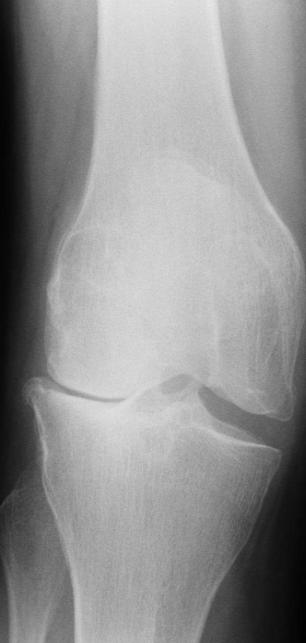 Imaging modality Lateral compartment osteoarthritis of the knee X-ray right knee (AP view)
Findings Osteophytes - bone spurs // Subchondral Sclerosis
Diagnosis Osteoarthritis
Imaging modality Lateral compartment osteoarthritis of the knee X-ray right knee (AP view)
Findings Osteophytes - bone spurs // Subchondral Sclerosis
Diagnosis Osteoarthritis
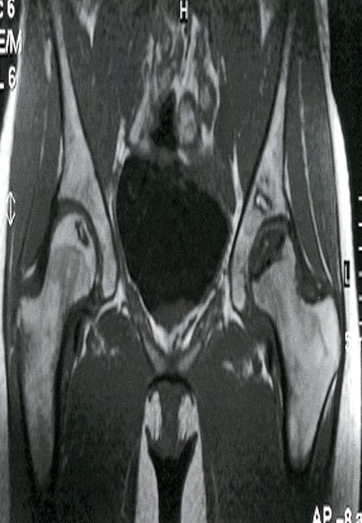 Bilateral osteonecrosis of the femoral head
MRI hips (T1 weighted; coronal view) of a 32-year-old
woman with groin pain
There is a well-defined crescent-shaped area of intermediate
to low signal within the subchondral marrow of the left
femoral head . On the right side, there is a slightly smaller
area of abnormal oval-shaped signal within the epiphysis of
the right femoral head.
Bilateral osteonecrosis of the femoral head
MRI hips (T1 weighted; coronal view) of a 32-year-old
woman with groin pain
There is a well-defined crescent-shaped area of intermediate
to low signal within the subchondral marrow of the left
femoral head . On the right side, there is a slightly smaller
area of abnormal oval-shaped signal within the epiphysis of
the right femoral head.
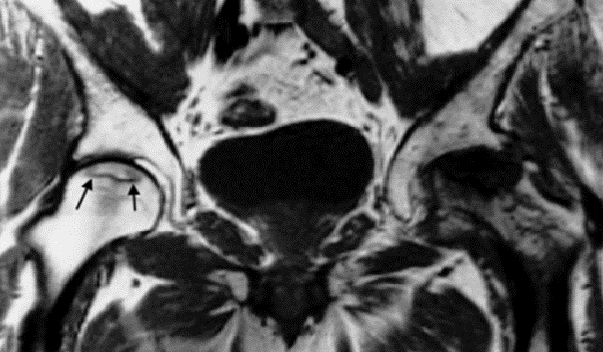 Coronal MRI scan showing avascular necrosis of
both femoral heads. The changes on the left are
very severe and advanced. The changes in the right
hip are relatively early and show a rim of low
signal demarcating the ischemic area (arrows)
Coronal MRI scan showing avascular necrosis of
both femoral heads. The changes on the left are
very severe and advanced. The changes in the right
hip are relatively early and show a rim of low
signal demarcating the ischemic area (arrows)
Y
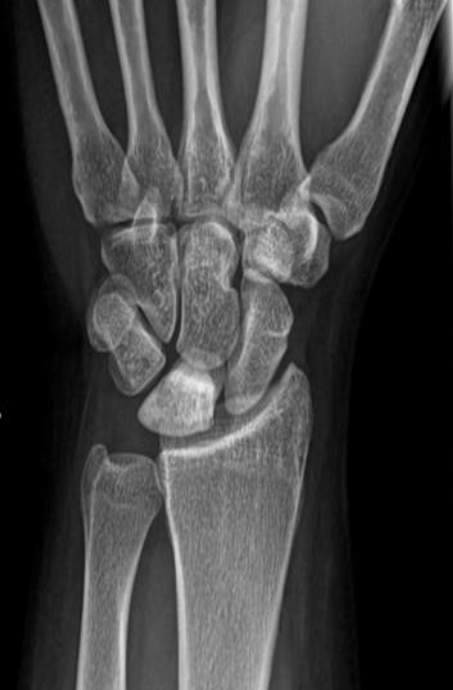 Plain x-ray
Avascular necrosis of lunate
Plain x-ray
Avascular necrosis of lunate
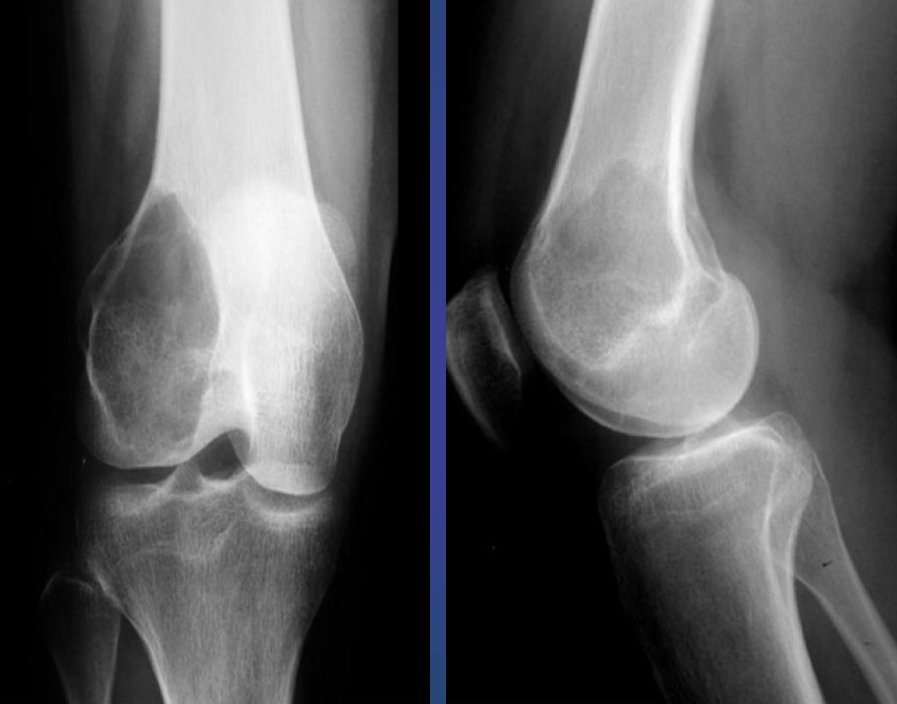 Giant cell Tumor.
Giant cell Tumor.
- Growth plate is closed
- Expansile lytic lesion,
- Eccentric in the metaphysis
Y
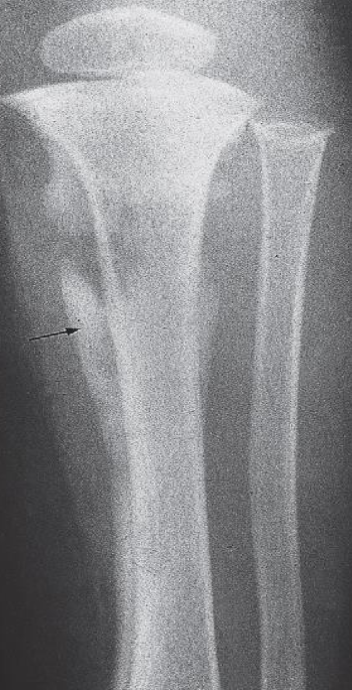 Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
- Destruction of the upper end of the tibia
- Periosteal reaction along the tibia.
Imaging of Urinary system
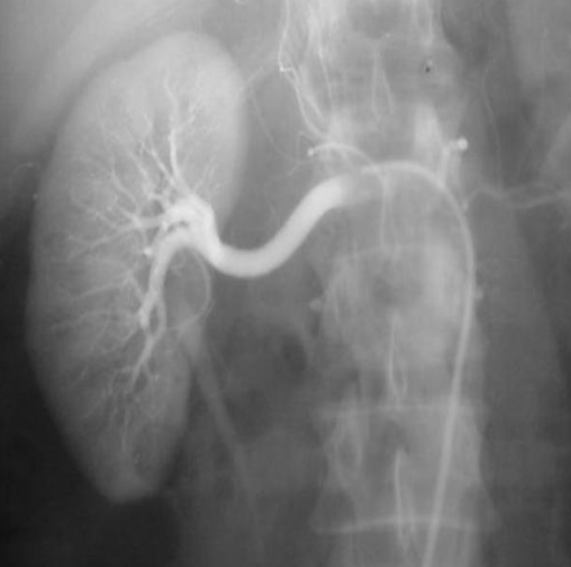 Renal arteriogram
Anatomy ?
Renal arteriogram
Anatomy ?
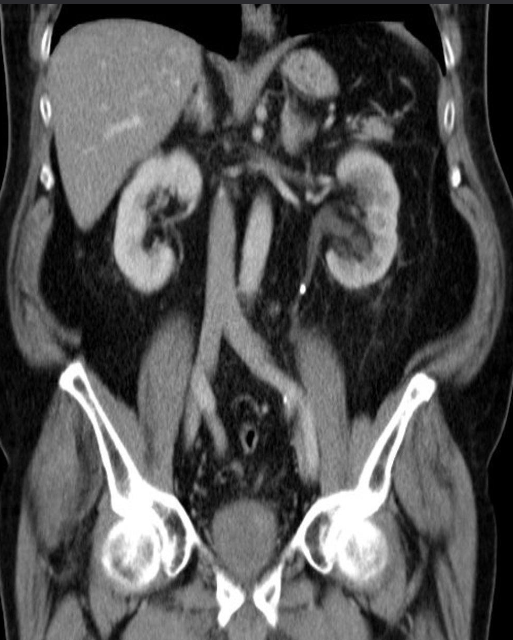 Abdominal CT with IV contrast , coronal section
Hyperdense calculi located in the proximal third of the left ureter. As a result, the proximal ureter and the renal pelvis are dilated.
Abdominal CT with IV contrast , coronal section
Hyperdense calculi located in the proximal third of the left ureter. As a result, the proximal ureter and the renal pelvis are dilated.
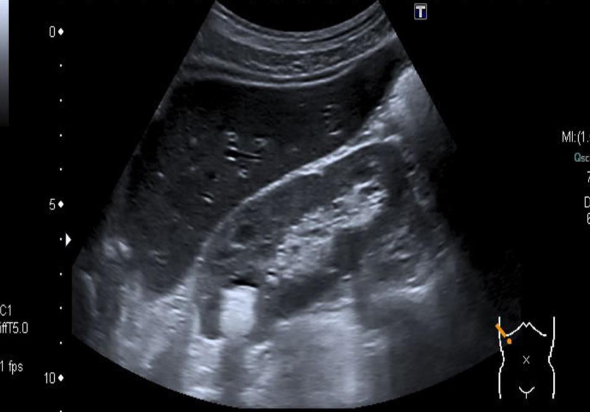 US- There is a round, hyperechoic lesion at the upper pole of the kidney in the renal parenchyma, which shows a dorsal acoustic shadow and is most likely a kidney stone.
US- There is a round, hyperechoic lesion at the upper pole of the kidney in the renal parenchyma, which shows a dorsal acoustic shadow and is most likely a kidney stone.
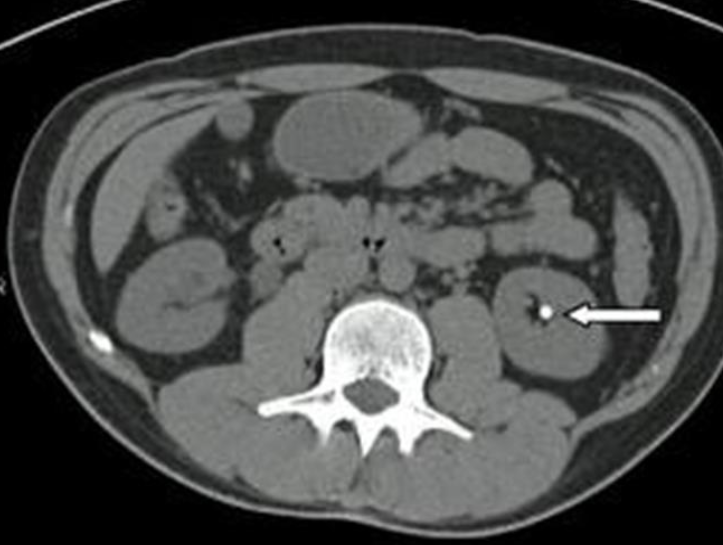 B. Identify the abnormality marked by arrow in the given image? Kidney stone
B. Identify the abnormality marked by arrow in the given image? Kidney stone
A. Give the name of the imaging examination in the given image. CT without contrast
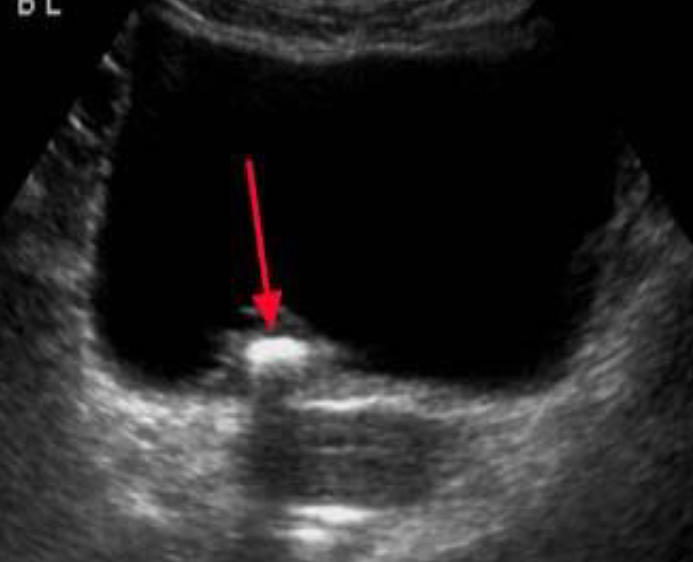 Ultrasound - Bladder calculus
Ultrasound - Bladder calculus
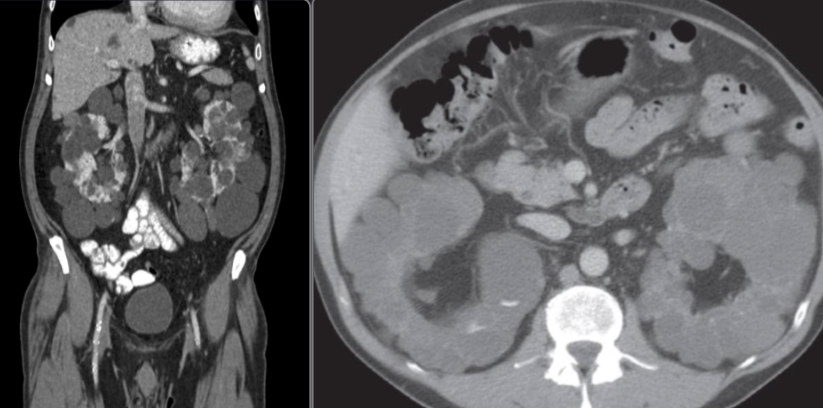 Polycystic kidneys disease
Polycystic kidneys disease
CT abdomen (with contrast; coronal plane) Both kidneys are markedly enlarged and feature multiple round-to-ovoid, hypodense lesions of various sizes compatible with cysts. Some smaller cysts are present in the liver.
The CT features are consistent with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
2nd img Polycystic kidneys disease CT scan, taken after intravenous contrast enhancement, showing that both kidneys are greatly enlarged and almost entirely replaced by cysts of variable size.
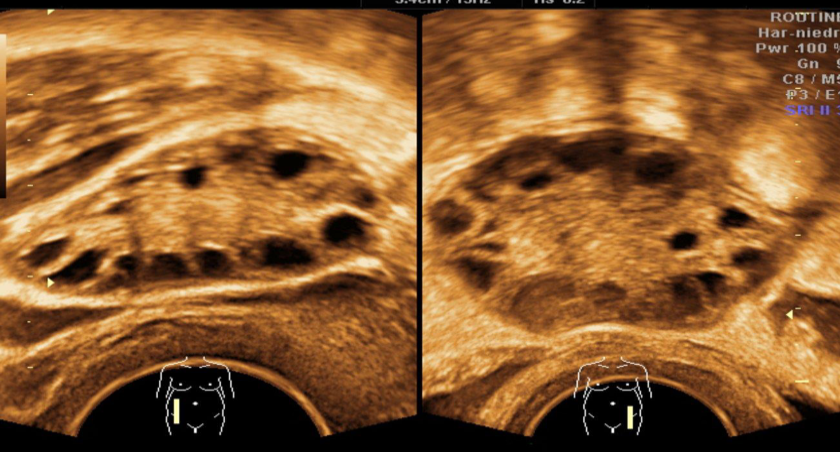
A. Imaging study Transvaginal ultrasound of the right and left ovary: B. Describe the abnormality both ovaries contain multiple anechoic cysts. There is a relative increase of stromal tissue and capsule thickness with increased ovarian size C. What is the most likely diagnosis polycystic ovary syndrome.
Y
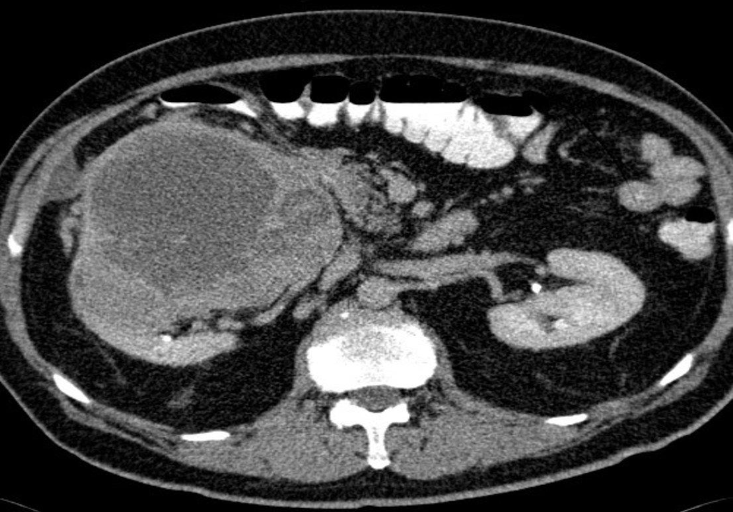 Axial CT of the abdomen after oral and IV contrast medium administration
A large, relatively sharply demarcated tumor can be
seen in the right kidney. This finding is characteristic of
Renal Cell carcinoma.
Axial CT of the abdomen after oral and IV contrast medium administration
A large, relatively sharply demarcated tumor can be
seen in the right kidney. This finding is characteristic of
Renal Cell carcinoma.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM IMAGING # Y
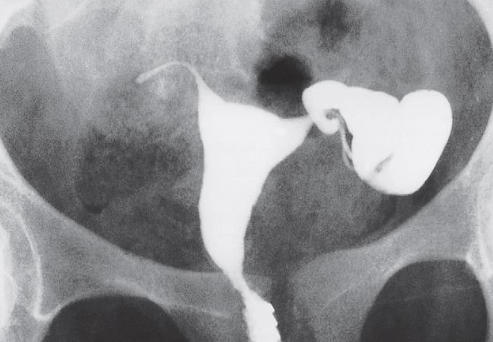 HSG – Unilateral Hydrosalpinx
HSG – Unilateral Hydrosalpinx
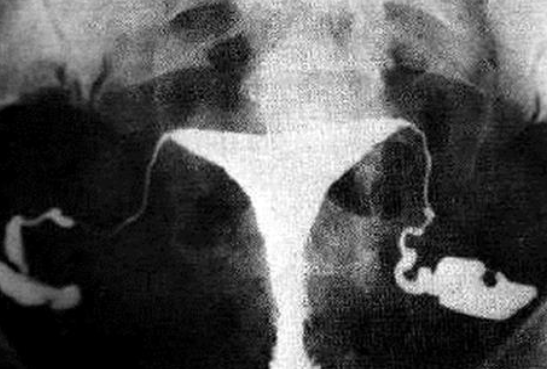 HSG – Bilateral Hydrosalpinx
HSG – Bilateral Hydrosalpinx
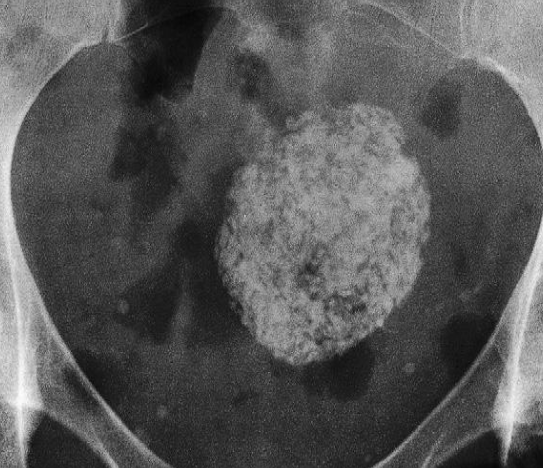 Calcified Uterine Leiomyoma
Plain radiograph:
Calcified Uterine Leiomyoma
Plain radiograph:
- Calcification in a large uterine fibroid
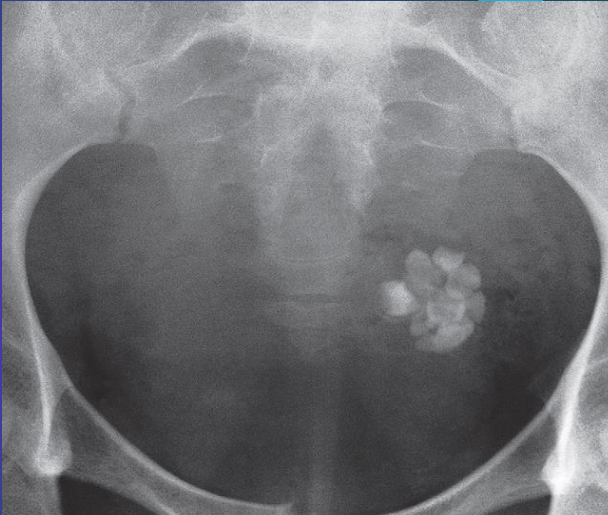 Dermoid cyst.
Plain film of showing well-developed teeth within the cyst.
Dermoid cyst.
Plain film of showing well-developed teeth within the cyst.
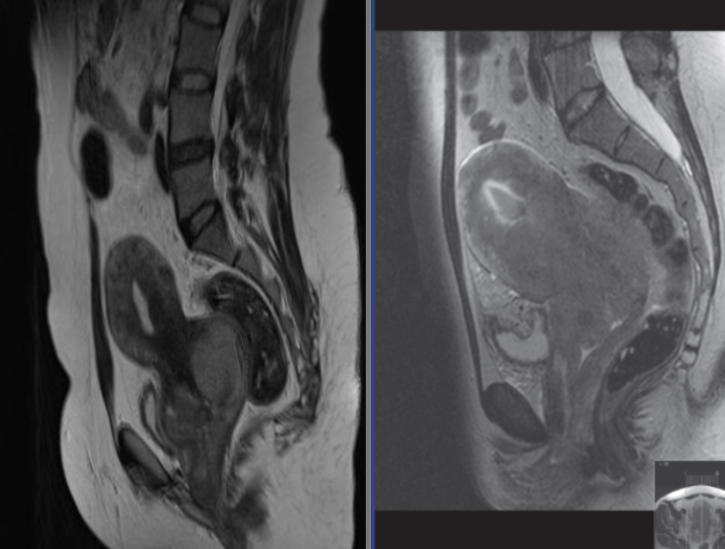 Two different cases. T2 weighted sagittal MRI showing carcinoma of
cervix
Two different cases. T2 weighted sagittal MRI showing carcinoma of
cervix
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM IMAGING
 Scrotal US - A hydrocoele is demonstrated surrounding an otherwise normal testis .
Scrotal US - A hydrocoele is demonstrated surrounding an otherwise normal testis .
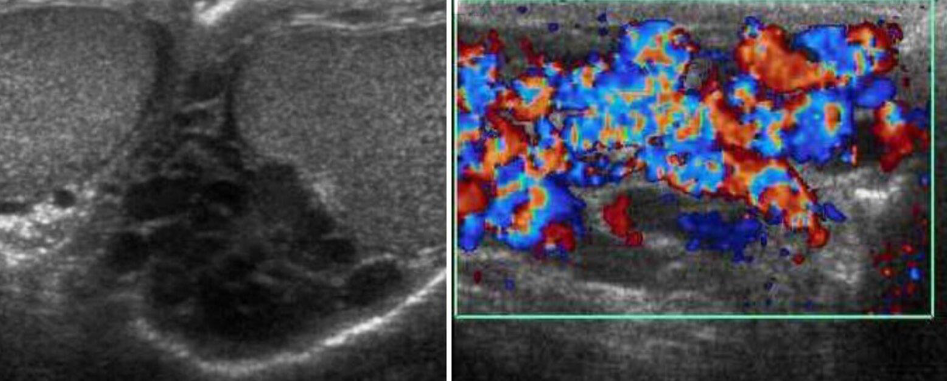 A man presents with testicular atrophy and infertility
A man presents with testicular atrophy and infertility
Ultrasound of the scrotum Dilated pampiniform veins can be seen within the left scrotum. Doppler sonography (image b) shows the venous reflux. These findings are characteristic of varicocele.
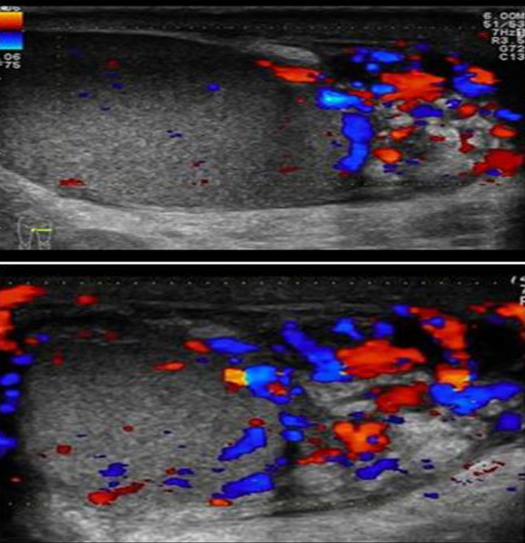 Patient presented with scrotal pain
and swelling - Ranges from mild tenderness to a severe febrile process with acute unilateral scrotal pain. -
Patient presented with scrotal pain
and swelling - Ranges from mild tenderness to a severe febrile process with acute unilateral scrotal pain. -
A. Give the name of imaging examination. Color Doppler ultrasound
B. Describe the abnormality imaging shows Reactive hydrocele and scrotal wall thickening , edematous epididymis and shows increase vascularity on Doppler
C. What is the most probable diagnosis in the ? Epididymitis
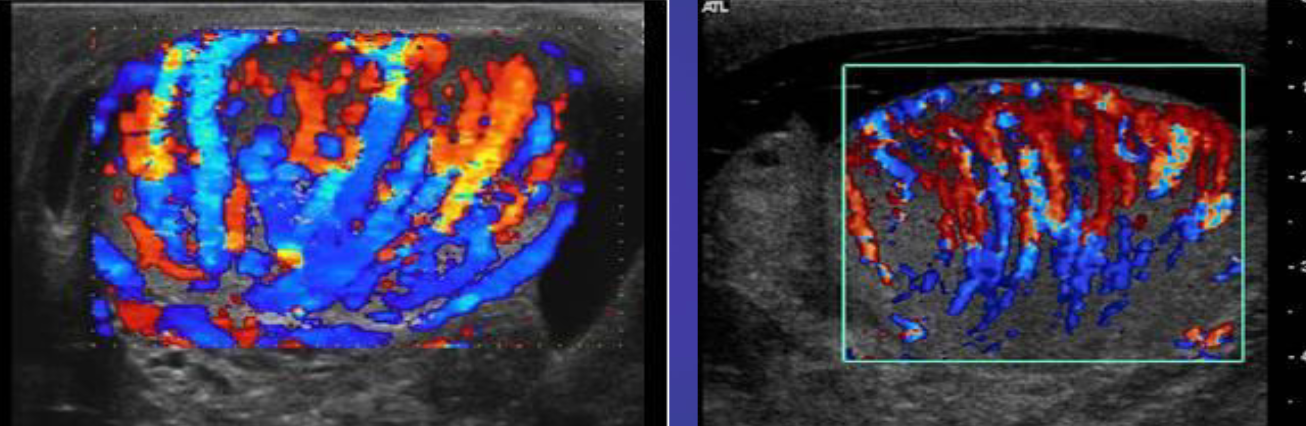 A. Give the name of imaging examination.
*Color Doppler ultrasound is the gold standard investigation.
A. Give the name of imaging examination.
*Color Doppler ultrasound is the gold standard investigation.
B. Describe the abnormality
- Hypoechogenicity: Focal or diffuse
- Hypervascularity: Focal or diffuse
- Swelling - Scrotal wall thickening + Scrotal pain and swelling
C. What is the most probable diagnosis in the ? Orchitis
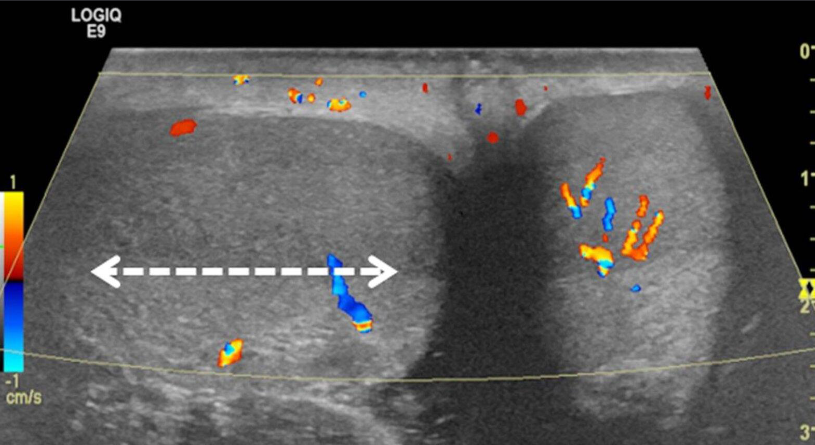 A. Give the name of imaging examination.
Color Doppler ultrasound of both testes (transverse plane) of a 14-year-old boy
A. Give the name of imaging examination.
Color Doppler ultrasound of both testes (transverse plane) of a 14-year-old boy
B. Describe the abnormality woke up with acute right scrotal pain - The right testis shows intratesticular flow slightly reduced compared to the left testis
C. What is the most probable diagnosis ? These findings are consistent with testicular torsion
- Prostatic calcification
- symmetrical about the midline, are seen just inferior to the bladder
Skull & Brain Imaging
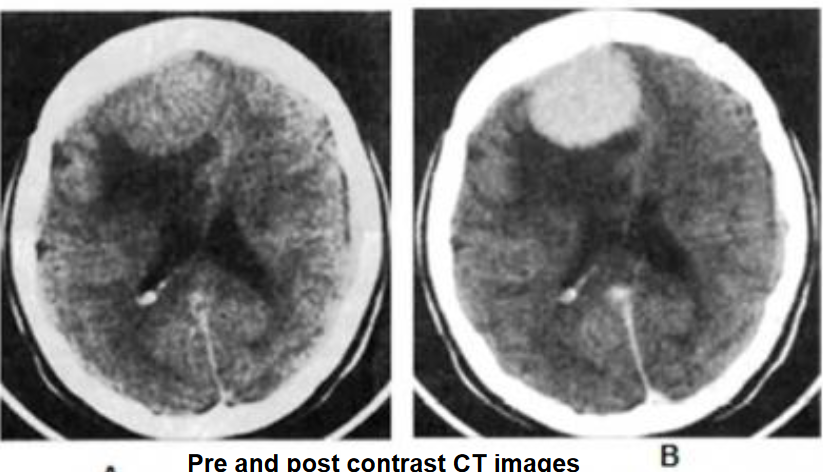
 A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion
A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion
- Contrast CT*
B. Give ONE cause for the pattern of contrast enhancement shown Enhanced lesion: Lesion which shows contrast uptake
- Homogenous
- Ring
- Serpigenous [AVM]
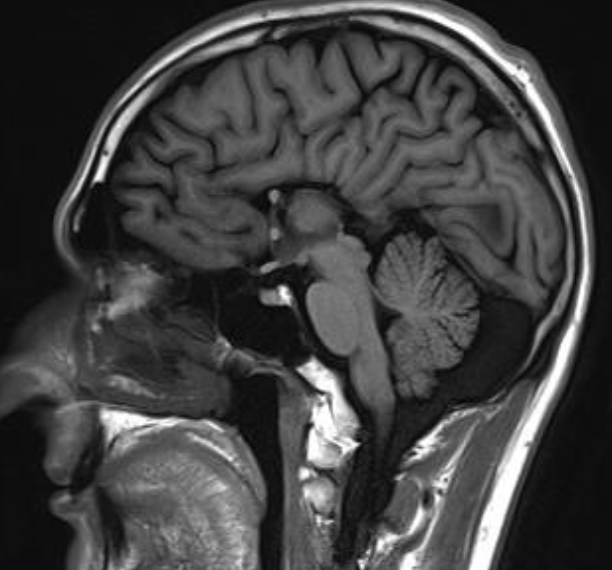 Agenesis of corpus callosum
Sagittal T1 MRI brain
Agenesis of corpus callosum
Sagittal T1 MRI brain
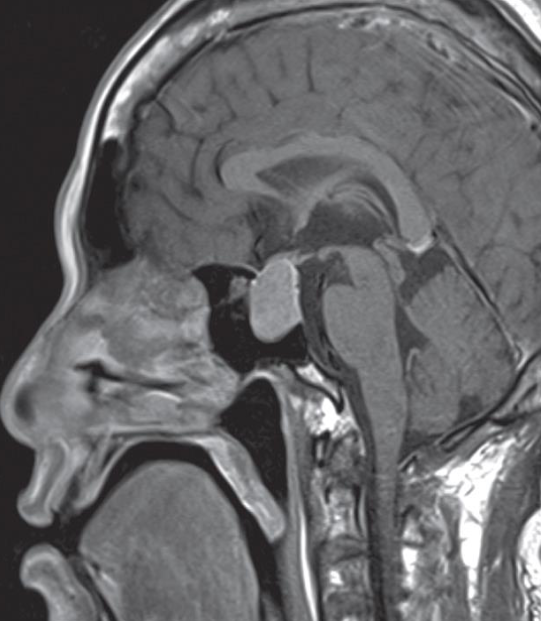 Pituitary macroadenoma
Sagittal T1 post contrast MRI showing a macroadenoma
Pituitary macroadenoma
Sagittal T1 post contrast MRI showing a macroadenoma
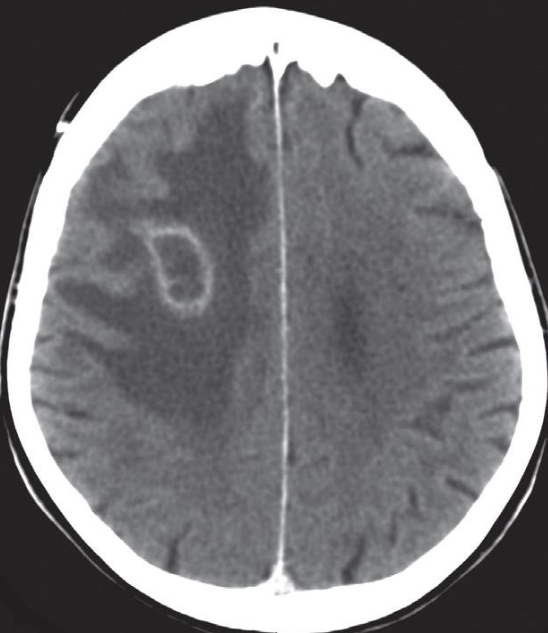
 Meningioma- - contrast enhanced CT
Findings
Meningioma- - contrast enhanced CT
Findings
- Hyperdense well-demarcated oval extra-axial mass
- Calcifications
- Associated with perifocal edema.
- The lesion shows homogeneous enhancement on the
 Axial T1 post contrast MRI - Meningioma MR
Axial T1 post contrast MRI - Meningioma MR
- Dural based
- Homogenous enhancement [Gd- DTPA] [Dural tail]
A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image. oval mass in the left parietal region, with well-defined borders, appears hypointense to grey matter on the T1 & hyperintense on T2-weighted image.
B. Give ONE cause for the pattern of contrast enhancement shown in the given image Meningioma
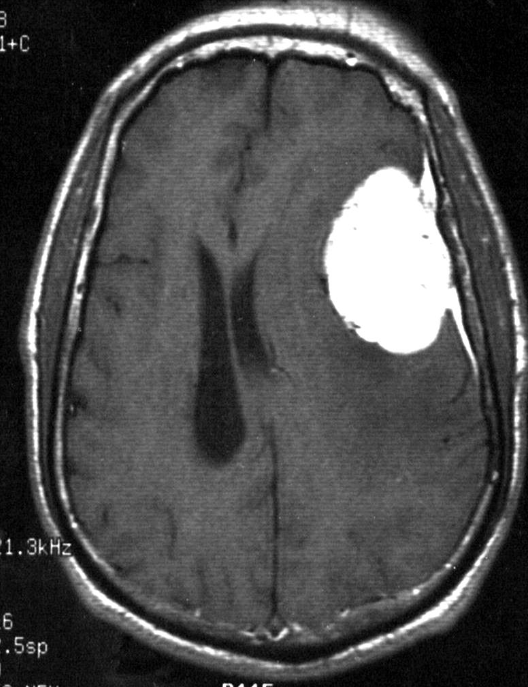
 A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image
. (a) Post contrast CT scan showing a right frontal low density ring-enhancing lesion with surrounding vasogenic oedema
A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image
. (a) Post contrast CT scan showing a right frontal low density ring-enhancing lesion with surrounding vasogenic oedema
B. Give ONE cause for the pattern of contrast enhancement shown in the given image Cerebral abscess
 A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image
A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image
- Axial T1 MRI post contrast.
- Multiple ring enhancing lesions
B. Give ONE cause for the pattern of contrast enhancement shown in the given image Tuberculomas ++ Chronic cough / Pulmonary TB
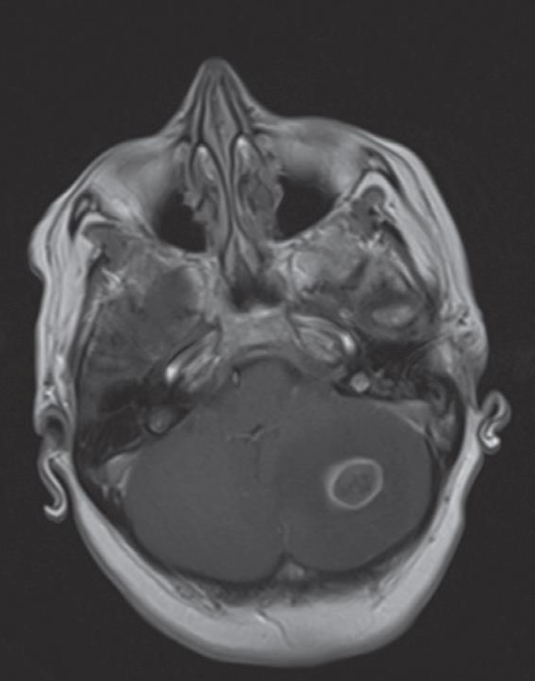 A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image
A. Give the name of the pattern of contrast enhancement of the lesion in the given image
- Enhanced axial T1 weighted MRI scan
- ring-enhancing cerebellar metastasis
B. Give ONE cause for the pattern of contrast enhancement shown in the given image Metastatic brain tumors
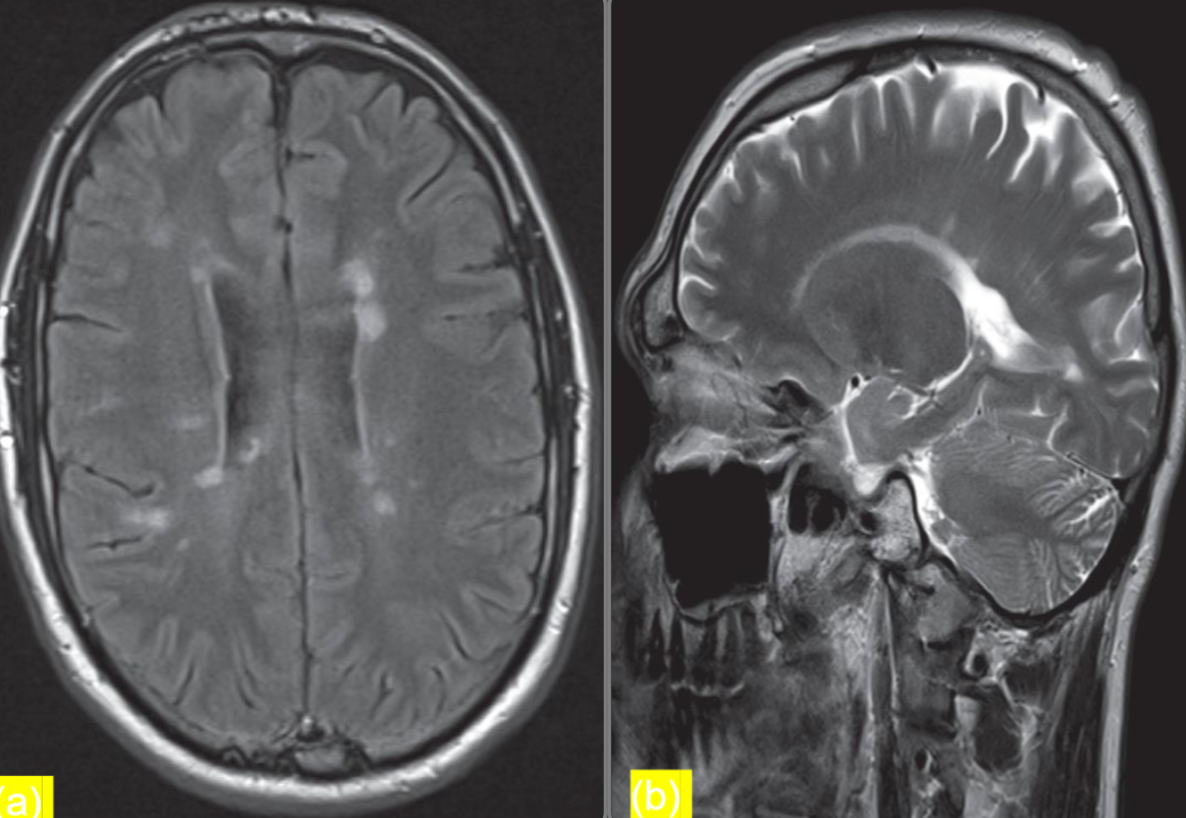 Patients presents with optic neuritis
Patients presents with optic neuritis
(a) Axial FLAIR sequence at the level of the lateral ventricles
- shows periventricular areas of linear and ovoid hyperintense
- signal orientated perpendicular to the body of the right lateral ventricle. This feature is known as Dawson fingers and is
- strongly associated with multiple sclerosis.
(b) Parasagittal T2-weighted MRI
- shows plaques of demyelination as high signal in the white matter, particularly along the
- margins of the lateral ventricles
Modality MRI Findings Plaques of demyelination, dawson fingers Diagnosis multiple sclerosis
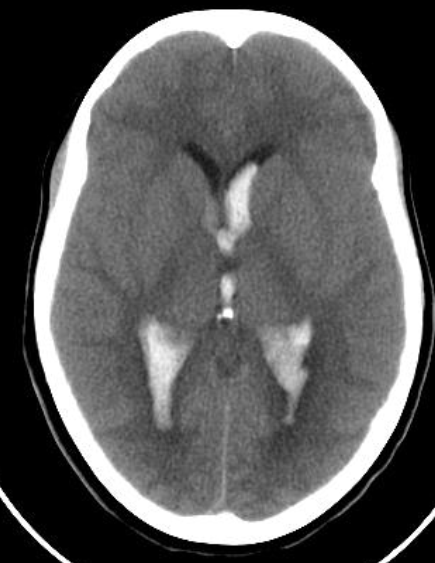
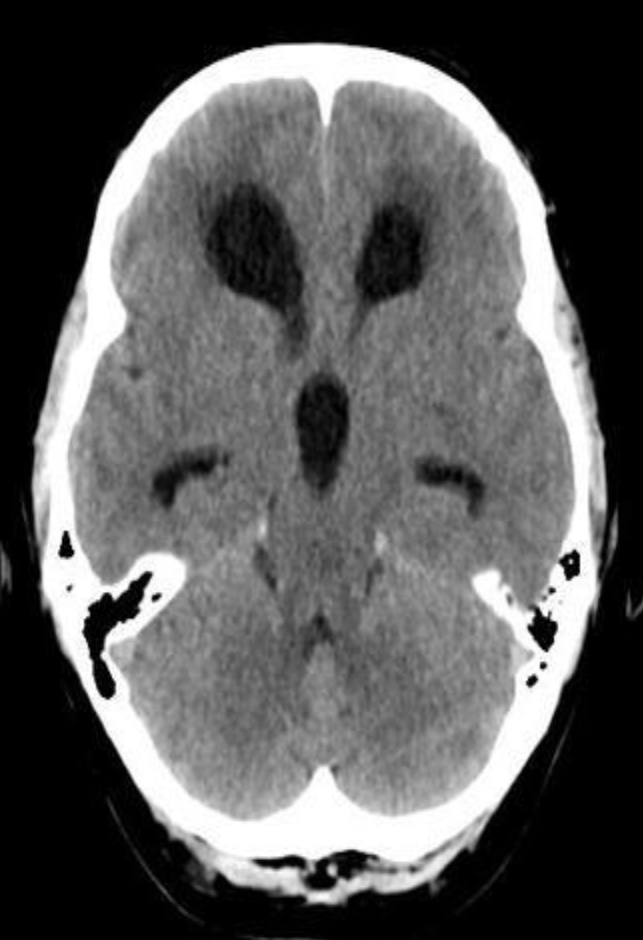 CT brain - Hydrocephalus
CT brain - Hydrocephalus
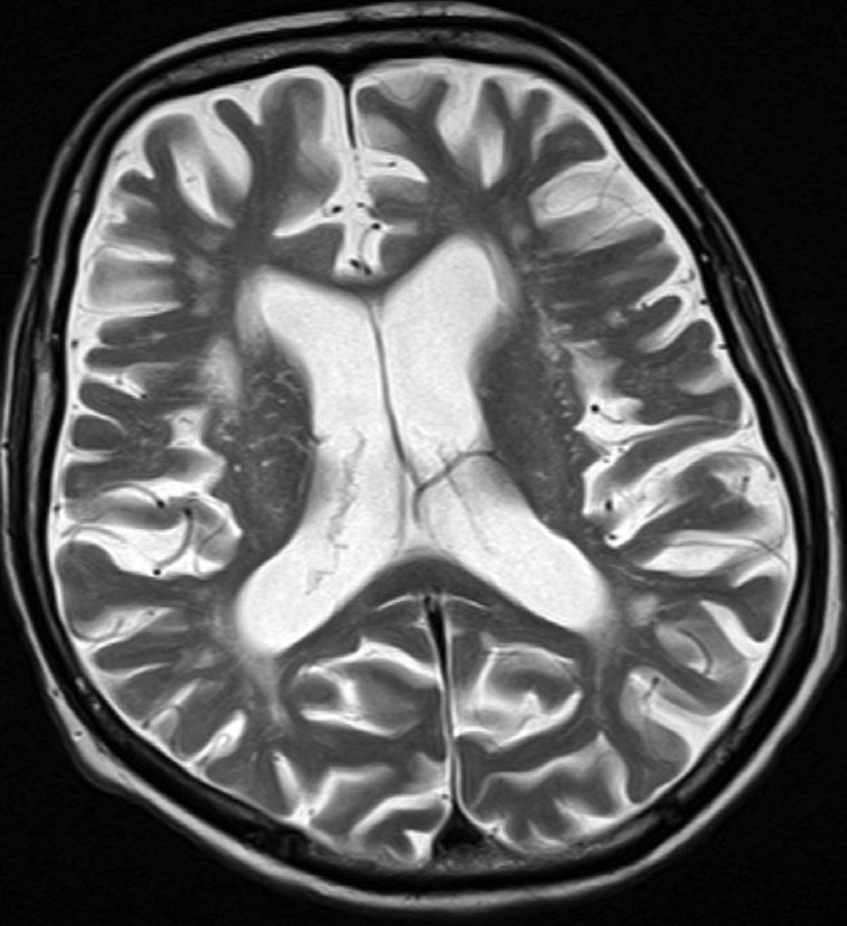 Axial T2-weighted MRI - Cerebral atrophy
showing prominence of the ventricles and generalized widening of
the cerebral sulci in keeping with age-related atrophy.
Axial T2-weighted MRI - Cerebral atrophy
showing prominence of the ventricles and generalized widening of
the cerebral sulci in keeping with age-related atrophy.
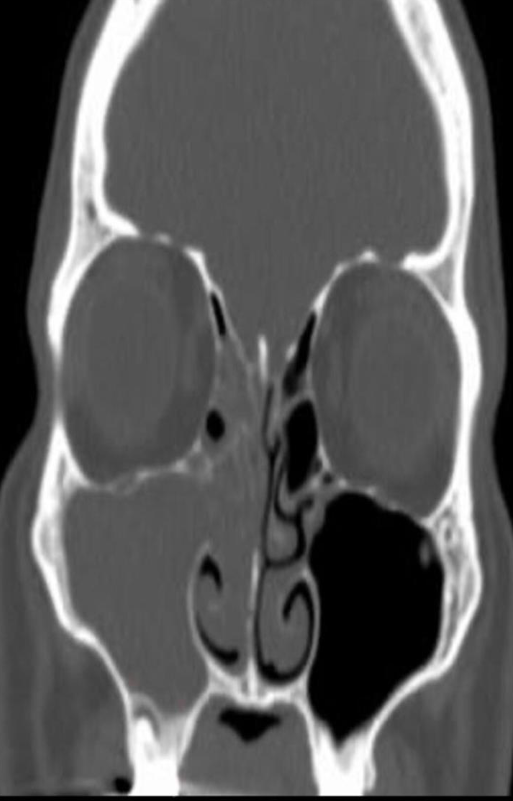
Modality CT paranasal sinuses (coronal plane)
Findings right maxillary sinus is completely opacified. Extensive soft tissue density material is also present in the ipsilateral nasal cavity and the right ethmoid sinus is nearly completely opacified.
Diagnosis acute sinusitis
Imaging of the spine and spinal cord
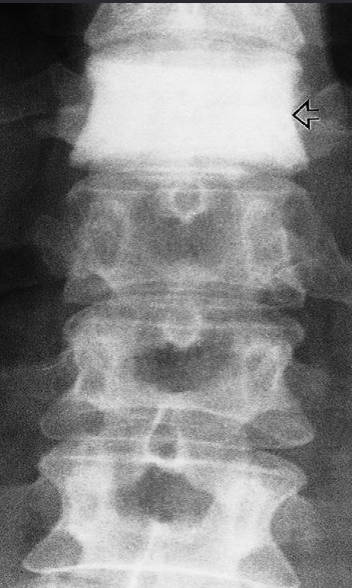 A. ONE radiological manifestation for marked abnormality.
Dense vertebra
B. Identify the most likely cause of the abnormal vertebrae shown
(arrow) due to metastases of carcinoma of the breast
A. ONE radiological manifestation for marked abnormality.
Dense vertebra
B. Identify the most likely cause of the abnormal vertebrae shown
(arrow) due to metastases of carcinoma of the breast
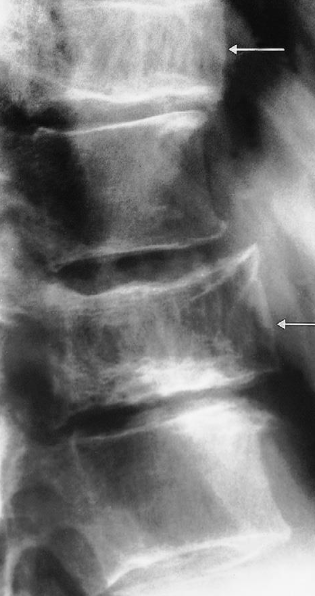 A. ONE radiological manifestation for marked abnormality.
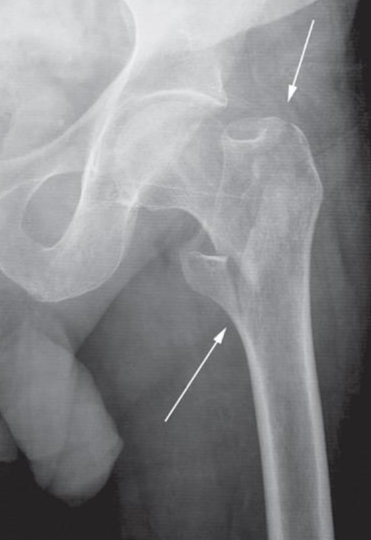
Increased density and coarse trabeculae in the wider than the normal vertebral bodies (arrows)
A. ONE radiological manifestation for marked abnormality.
Increased density and coarse trabeculae in the wider than the normal vertebral bodies (arrows)
B. Identify the most likely cause of the abnormal vertebrae shown Paget’s disease
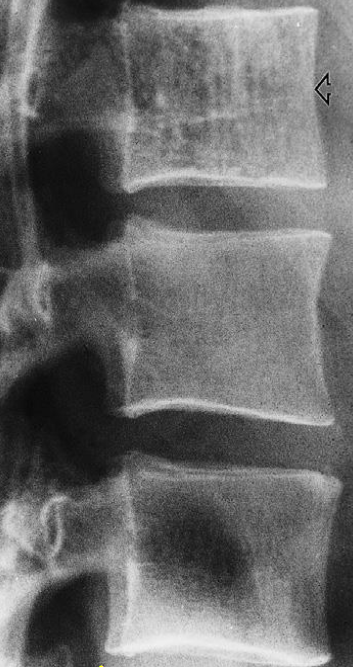 A. ONE radiological manifestation for marked abnormality.
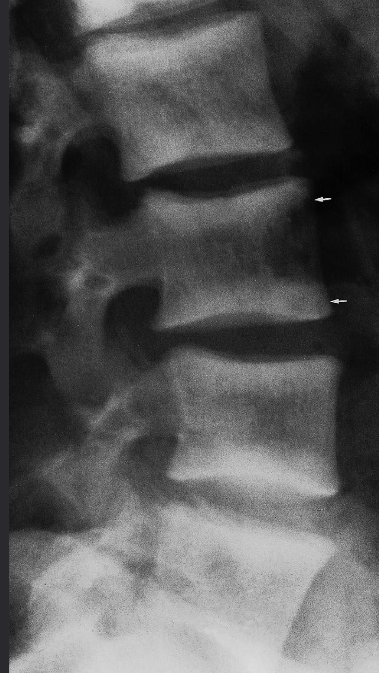
Vertical striations are present in this normal-sized vertebra
A. ONE radiological manifestation for marked abnormality.
Vertical striations are present in this normal-sized vertebra
B. Identify the most likely cause of the abnormal vertebrae shown Haemangioma
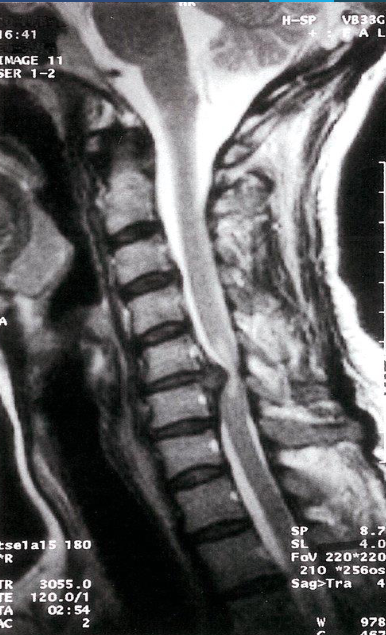 Cervical disk herniation
MRI cervical spine (T2-weighted; sagittal plane) of a
patient with symptoms of cervical myelopathy
A herniated disk at C5–6 effaces the dural sac and compresses the spinal cord. Hyperintense compression-induced edema is seen within the cord
Cervical disk herniation
MRI cervical spine (T2-weighted; sagittal plane) of a
patient with symptoms of cervical myelopathy
A herniated disk at C5–6 effaces the dural sac and compresses the spinal cord. Hyperintense compression-induced edema is seen within the cord
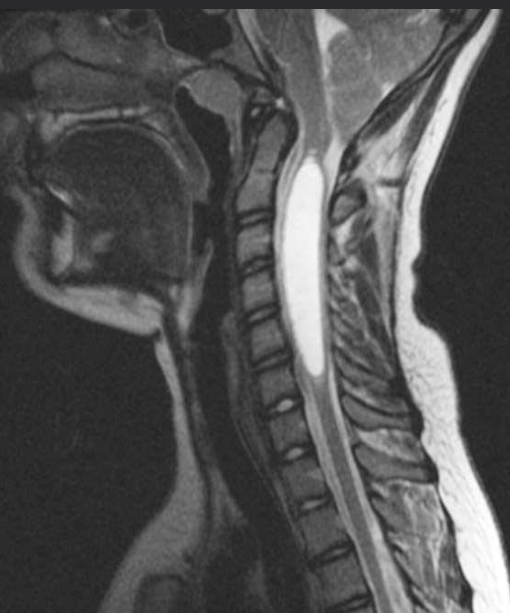 Sagittal T2 MR - Syringomyelia
Sagittal T2 MR - Syringomyelia
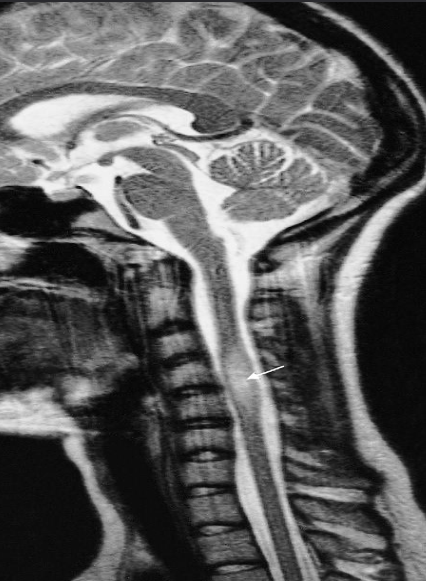 young adult women with optic neuritis
T2 -weighted MRI showing a plaque of demyelination (arrow) in a patient with multiple sclerosis
young adult women with optic neuritis
T2 -weighted MRI showing a plaque of demyelination (arrow) in a patient with multiple sclerosis
Y
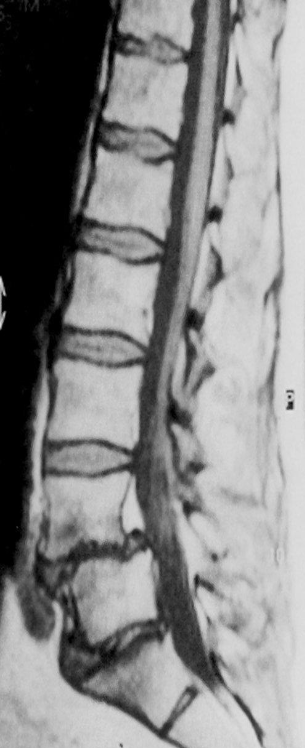 Modality MRI lumbar spine (sagittal plane)
Findings anterolisthesis of the L4 vertebral body
Diagnosis Spondylolisthesis
Modality MRI lumbar spine (sagittal plane)
Findings anterolisthesis of the L4 vertebral body
Diagnosis Spondylolisthesis
Y
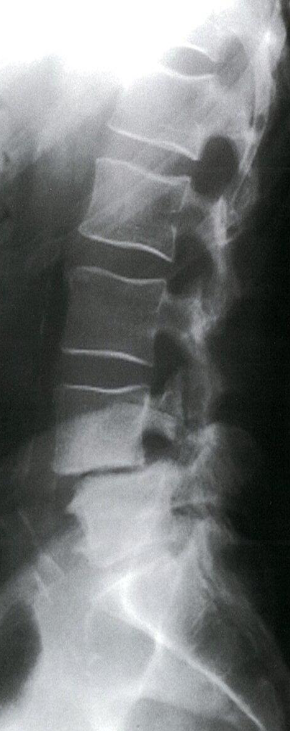 Modality X-ray lumbar spine (lateral view)
Modality X-ray lumbar spine (lateral view)
Findings Anterior displacement of L4 on L5 is visible. In addition, there is degenerative disk disease with narrowing of the L4–L5 disk space.
Diagnosis Disc Space Narrowing e.g. degenerative disc disease; Associated with endplate sclerosis and osteophytes
CT Brain IN EMERGENCY
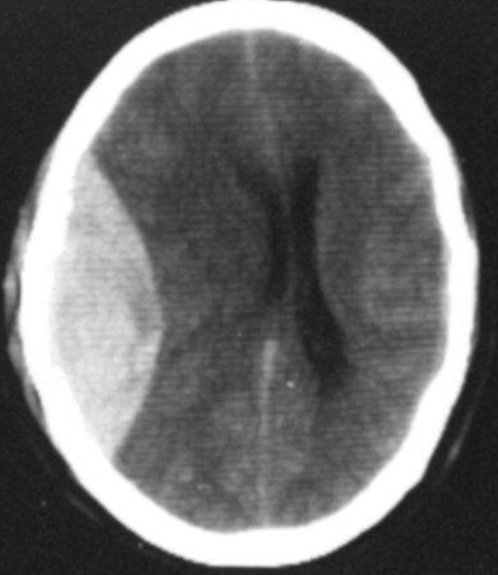 Epidural hematoma
Epidural hematoma
- Convex inner margin (lens-shaped)
- High density area
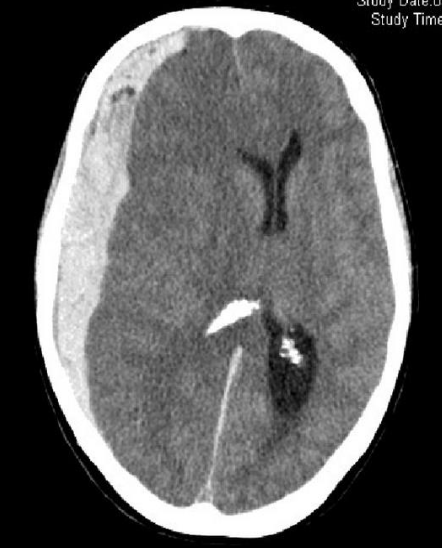 CT brain - Acute subdural hemorrhage
CT brain - Acute subdural hemorrhage
- crescent shape
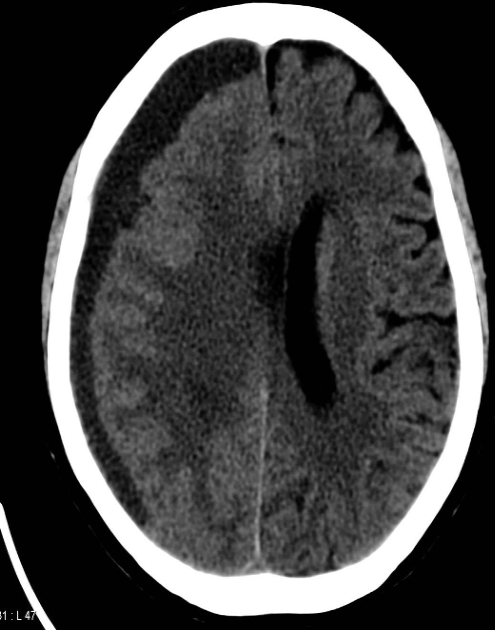 CT brain - Chronic subdural hemorrhage
CT brain - Chronic subdural hemorrhage
- Concave
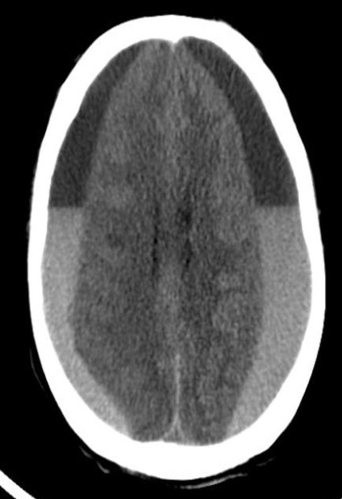 CT brain - Acute on chronic subdural hematoma
CT brain - Acute on chronic subdural hematoma
- Inner margins are concave
 A. Imaging study. *CT head *(without contrast; axial plane)
A. Imaging study. *CT head *(without contrast; axial plane)
B. What is the most likely diagnosis? Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Multiple areas of high attenuation in the basal cisterns, Sylvian fissures, and sulci are
- characteristic of extensive subarachnoid hemorrhage.
 Intra ventricular hemorrhage
Intra ventricular hemorrhage
- Anterior/Posterior Horns hemorrhages
- 3rd ventricles
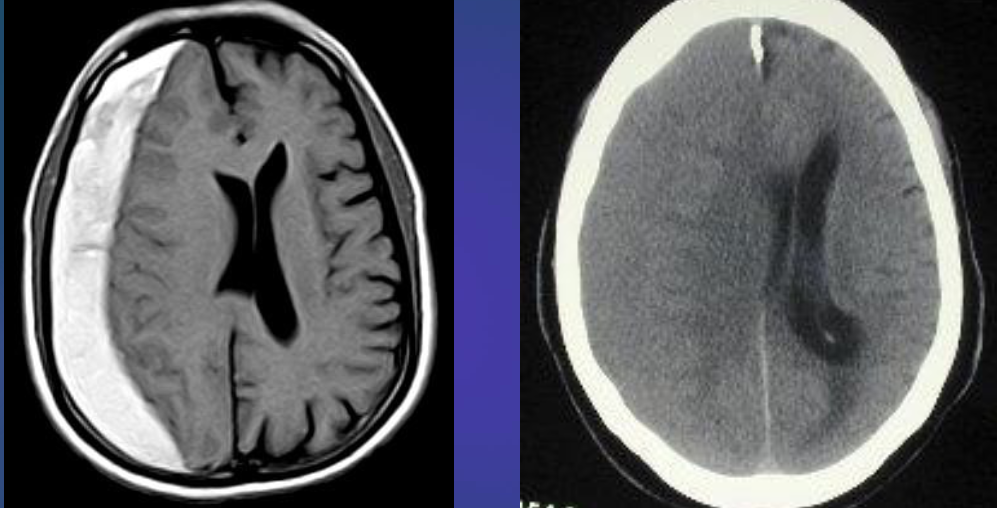 Subacute subdural hematoma
Subacute subdural hematoma
- Shifting + Isodensity ~~ SOL
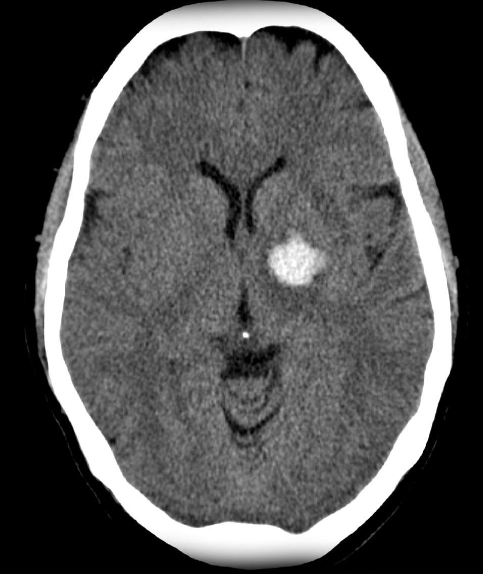 Intracerebral hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage
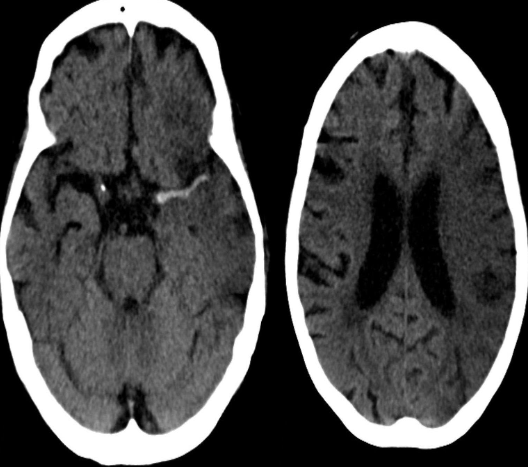 Infarction appear hypodense on CT without contrast
Infarction appear hypodense on CT without contrast
Sign? Hyperdense sign in stroke; LT Middle cerebral artery hyperintense
Y
 Dense basilar artery and middle cerebral arteries on CT
Thrombus in vessel is hyperdense relative to flowing blood
Dense basilar artery and middle cerebral arteries on CT
Thrombus in vessel is hyperdense relative to flowing blood
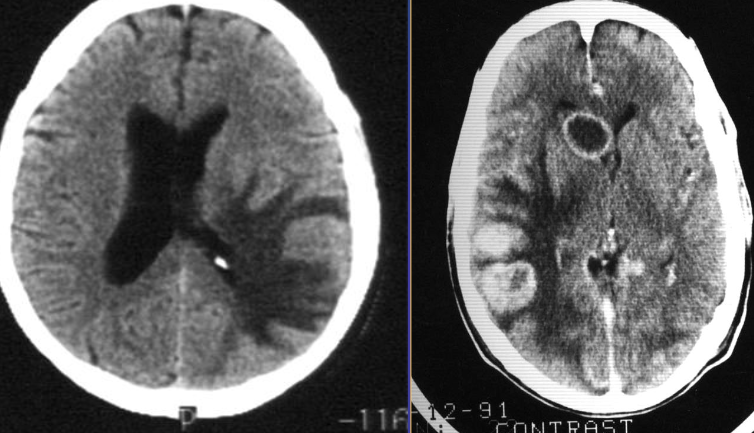 Vasogenic edema - causes may include MS, Abscess, Myoma. SOL’s
Vasogenic edema - causes may include MS, Abscess, Myoma. SOL’s
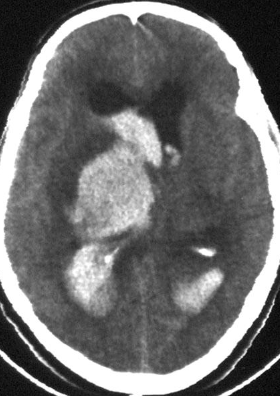 Cytotoxic edema - causes could be hemorrhage or infarction
Cytotoxic edema - causes could be hemorrhage or infarction
Thyroid and parathyroid Imaging Y
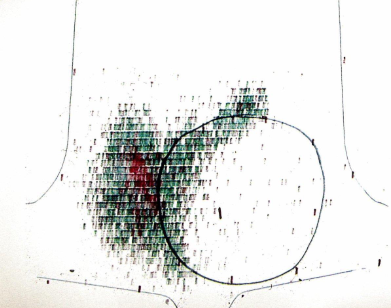 Cold nodule on thyroid scintigraphy
A large cold nodule (black circle) is
visible within the left thyroid lobe as an
area of decreased radiotracer uptake
Cold nodule on thyroid scintigraphy
A large cold nodule (black circle) is
visible within the left thyroid lobe as an
area of decreased radiotracer uptake
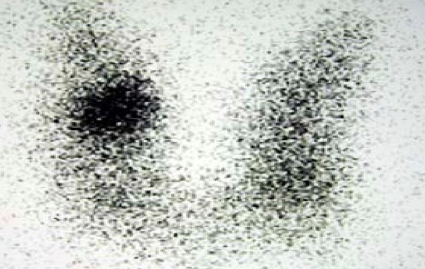
- Thyroid scan hot nodule
- Nuclear medicine thyroid scintigraphy (Tc-99m pertechnetate)
The rounded area in the right thyroid lobe represents a so-called hot thyroid nodule, which shows increased radioisotope uptake compared to the rest of the thyroid gland.
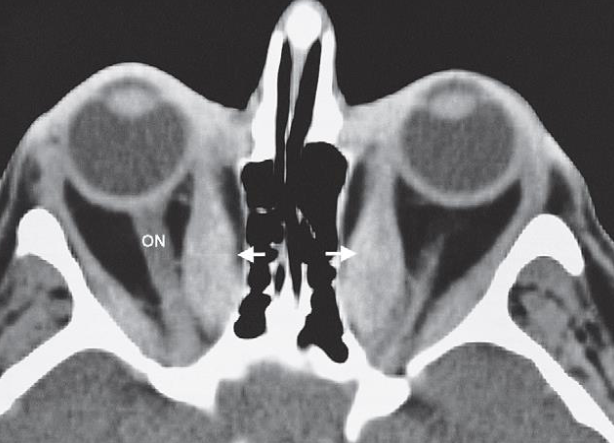
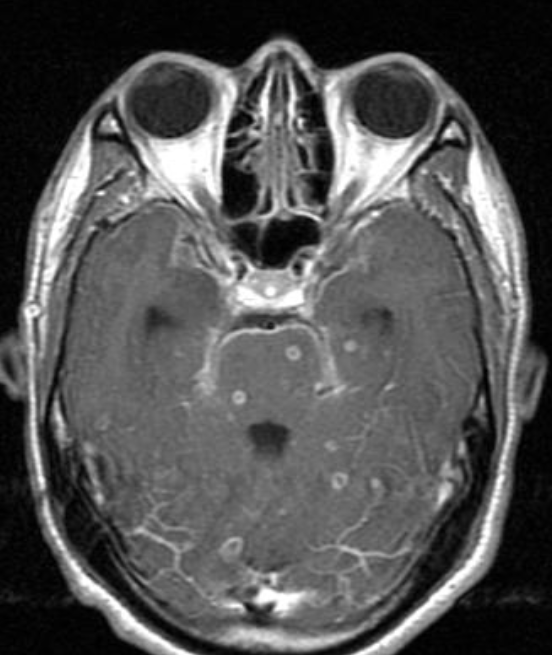
- Thyroid eye disease.
- CT scan through the orbits
- showing enlargement of the extraocular muscles, particularly the medial rectus (arrows).
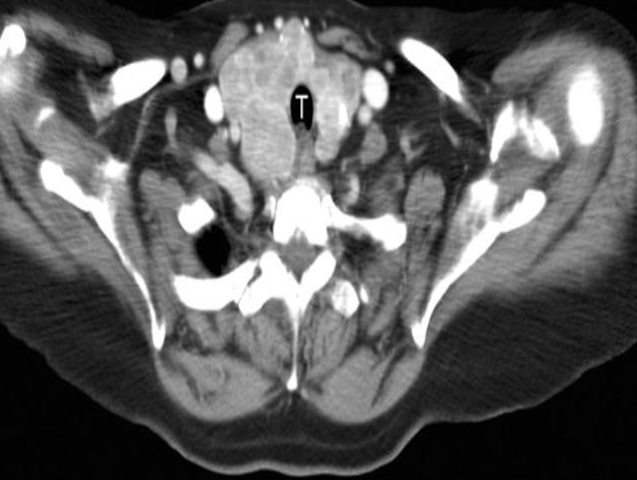 Patient presented with anterior neck swelling
Patient presented with anterior neck swelling
CT Multinodular goitre The enlarged thyroid enhances avidly after intravenous contrast showing many nodules of varying size.
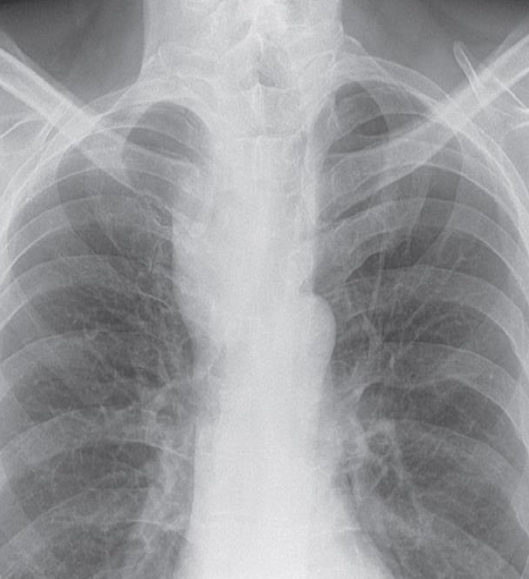 Retrosternal goitre.
XR showing a large, right- sided, superior mediastinal mass displacing the trachea
Retrosternal goitre.
XR showing a large, right- sided, superior mediastinal mass displacing the trachea